数据治理篇-离线硬盘整理
@ 20240723 & lth
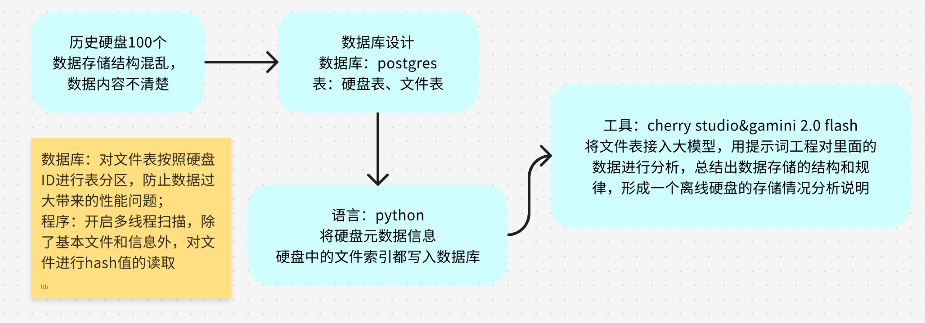
目标:对历史混乱存储结构的二维数据机械硬盘,开展数据索引&元数据属性的解析
技术栈:python、multiprocessing、ThreadPoolExecutor、postgres、cherry stutio、gamini 2.0
逻辑:
1、数据库表结构设计,索引创建,按照硬盘ID自动表分区(表数据超过1亿);
2、遍历硬盘下的所有文件,建立索引;
3、数据分类:正射TIF、矢量SHP、ArcGIS切片包、航拍原片.jpg、POS.txt、航线.kmz&kml
4、元数据处理:待调研硬盘里面的存储逻辑和具体数据结构
索引 --> 可以理解为目录
表分区
父表(ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned):就是整个图书馆的“总目录”或“图书管理员”。您总是向它下达指令。
分区键(disk_id):就是书柜上的“标签”(作者名)。
子分区(ew_disk_index_desc_d1等):就是那些分好类的、独立的小书柜。
分区裁剪:就是图书管理员根据您要找的作者,直接带您去对应书柜的这个智能行为。
所以,表分区就是把一张大到难以管理的表,预先按照某个规则(比如按硬盘ID),切分成很多张易于管理的小表。当您查询时,数据库会自动帮您选择正确的小表进行操作,从而极大地提升效率。
硬盘处理
读取硬盘中所有文件并写入数据库,找寻数据存储中存在的客观规律
1. 数据库结构设计
表结构
硬盘表
CREATE TABLE disks (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, -- 硬盘唯一ID,自增
disk_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL UNIQUE, -- 硬盘驱动器的卷标或自定义名称,必须唯一
disk_sn VARCHAR(100) UNIQUE, -- 硬盘的物理序列号,理论上也应唯一
capacity_gb float4, -- 硬盘容量 (TB)
used_capacity_gb float4, -- 已使用容量 (TB)
storage_location VARCHAR(255), -- 物理存放位置,如 "A栋3楼数据柜-05号"
status VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT 'In_Use', -- 硬盘状态,如 'In_Use', 'Archived', 'Retired'
disk_password VARCHAR(255), -- 硬盘密码(如有加密需求)
remark TEXT, -- 备注
added_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT NOW() -- 硬盘信息录入时间
);
-- 表注释
COMMENT ON TABLE disks IS '硬盘表';
-- 字段注释
COMMENT ON COLUMN disks.id IS '主键';
COMMENT ON COLUMN disks.disk_name IS '硬盘名称';
COMMENT ON COLUMN disks.disk_sn IS '硬盘序列号(SN)';
COMMENT ON COLUMN disks.capacity_gb IS '标准容量(TB)';
COMMENT ON COLUMN disks.used_capacity_gb IS '已使用容量(TB)';
COMMENT ON COLUMN disks.storage_location IS '存储位置';
COMMENT ON COLUMN disks.status IS '硬盘状态';
COMMENT ON COLUMN disks.disk_password IS '硬盘密码(如有加密)';
COMMENT ON COLUMN disks.remark IS '备注';
COMMENT ON COLUMN disks.added_at IS '录入时间';
文件表
CREATE TABLE ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned (
id BIGINT NOT NULL, -- 不再是BIGSERIAL,因为序列在分区表上行为不同
disk_id INTEGER NOT NULL, -- 作为分区键,不能是NULL
file_path TEXT NOT NULL,
parent_dir TEXT NOT NULL,
file_name TEXT NOT NULL,
file_ext VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
file_size_mb float(8),
file_hash VARCHAR(255),
asset_geometry GEOMETRY(GEOMETRY, 4490),
source_crs VARCHAR(100),
metadata_details JSONB,
capture_time TIMESTAMPTZ,
file_modified_time TIMESTAMPTZ,
indexed_at TIMESTAMPTZ DEFAULT NOW(),
remark TEXT,
-- 关键改动:主键必须包含分区键(disk_id)
PRIMARY KEY (disk_id, id),
-- 关键改动:唯一约束也必须包含分区键(disk_id)
CONSTRAINT ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned_file_path_key UNIQUE (disk_id, file_path)
) PARTITION BY LIST (disk_id); -- 定义为LIST分区,分区键为 disk_id
-- 字段注释
-- 表注释
COMMENT ON TABLE ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned IS '全景/二维数据硬盘文件索引表(按disk_id分区)';
-- 字段注释
COMMENT ON COLUMN ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned.id IS '主键,自增';
COMMENT ON COLUMN ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned.disk_id IS '关联硬盘ID';
COMMENT ON COLUMN ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned.file_path IS '文件绝对路径,唯一标识';
COMMENT ON COLUMN ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned.parent_dir IS '文件父目录路径';
COMMENT ON COLUMN ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned.file_name IS '文件名(含后缀)';
COMMENT ON COLUMN ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned.file_ext IS '文件扩展名(小写)';
COMMENT ON COLUMN ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned.file_size_mb IS '文件大小(MB)';
COMMENT ON COLUMN ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned.file_hash IS '文件SHA256哈希值';
COMMENT ON COLUMN ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned.asset_geometry IS '空间几何(点/线/面),WGS84坐标系';
COMMENT ON COLUMN ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned.source_crs IS '原始坐标系';
COMMENT ON COLUMN ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned.metadata_details IS '详细元数据(JSONB)';
COMMENT ON COLUMN ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned.capture_time IS '拍摄/生成时间';
COMMENT ON COLUMN ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned.file_modified_time IS '文件最后修改时间';
COMMENT ON COLUMN ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned.indexed_at IS '数据入库时间';
COMMENT ON COLUMN ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned.remark IS '备注';
手动表分区
CREATE TABLE ew_disk_index_desc_d1 PARTITION OF ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned
FOR VALUES IN (1);
-- 为 disk_id = 2 创建分区
CREATE TABLE ew_disk_index_desc_d2 PARTITION OF ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned
FOR VALUES IN (2);
-- (可选,但强烈推荐) 创建一个默认分区
-- 用于接收任何不属于上述任何一个disk_id的数据,防止插入错误
CREATE TABLE ew_disk_index_desc_default PARTITION OF ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned
DEFAULT;
文件表索引
索引的作用可以抽象理解为书籍目录,但是索引也会给写入更新删除等操作的性能带来压力;
这些操作同时会额外开销去维护索引,经常用于查询条件 (WHERE)、排序 (ORDER BY) 或关联 (JOIN) 的列创建索引
索引分类:
1、B-tree(默认)等值查询、范围查询、排序、模糊匹配(前缀)
2、GIN 全文搜索、JSON/JSONB、数组、复合值(如hstore)
3、GiST 几何数据、全文搜索(与GIN互补)、相似度搜索(如pg_trgm)
4、SP-GiST 空间分区数据(如IP地址、电话号前缀树)
5、BRIN 超大型表(TB级),按物理顺序存储的数据(如时间序列)
-- 1. 主键和唯一索引 (已在CREATE TABLE中通过PRIMARY KEY和UNIQUE约束自动创建)
-- 2. 空间索引 (GIST)
CREATE INDEX idx_assets_asset_geometry_p ON ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned USING GIST (asset_geometry);
-- 3. 数据类型索引 (B-tree)
CREATE INDEX idx_assets_file_ext_p ON ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned (file_ext);
-- 4. 元数据索引 (GIN)
CREATE INDEX idx_assets_metadata_details_p ON ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned USING GIN (metadata_details);
-- 5. 父目录索引 (B-tree)
CREATE INDEX idx_assets_parent_dir_p ON ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned (parent_dir text_pattern_ops);
-- 6. 文件名索引 (B-tree)
CREATE INDEX idx_assets_file_name_p ON ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned (file_name text_pattern_ops);
-- 7. 文件哈希值索引 (B-tree)
CREATE INDEX idx_assets_file_hash_p ON ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned (file_hash);
-- 8. 拍摄时间索引 (B-tree)
CREATE INDEX idx_assets_capture_time_p ON ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned (capture_time);
-- 9. 硬盘ID索引 (B-tree)
-- 这个索引现在不是必须的了,因为disk_id是分区键。
-- 当查询条件中包含 WHERE disk_id = ... 时,PostgreSQL会自动进行“分区裁剪”,只扫描对应的子表,其效率远高于索引扫描。
-- 因此,您可以省略这个索引。
-- CREATE INDEX idx_ew_disk_index_desc_disk_id_p ON ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned (disk_id); -- 已不再需要
设置ID自增
-- 1. 创建全局序列
CREATE SEQUENCE ds.ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned_id_seq AS BIGINT;
-- 2. 将序列设置为 id 列的默认值
ALTER TABLE ds.ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned
ALTER COLUMN id SET DEFAULT nextval('ds.ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned_id_seq'::regclass);
-- 3. (推荐) 关联序列所有权
ALTER SEQUENCE ds.ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned_id_seq
OWNED BY ds.ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned.id;
自动表分区
当前分区查询
SELECT
parent.relname AS parent_table,
child.relname AS partition_name,
-- 这个函数从系统目录中获取分区的定义表达式
pg_get_expr(child.relpartbound, child.oid, true) AS partition_expression
FROM
pg_catalog.pg_inherits AS inh -- 使用完全限定名称
JOIN
pg_catalog.pg_class AS parent ON inh.inhparent = parent.oid -- 使用完全限定名称
JOIN
pg_catalog.pg_class AS child ON inh.inhrelid = child.oid -- 使用完全限定名称
WHERE
parent.relname = 'ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned' -- 指定您的父表名称
-- 如果您的表不在public模式,您需要在这里指定schema,例如:
-- AND parent.relnamespace = (SELECT oid FROM pg_catalog.pg_namespace WHERE nspname = 'your_schema_name')
;
函数与触发器
-- 步骤 1: 创建插入分区函数
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION fn_create_disk_partition_if_not_exists()
RETURNS TRIGGER AS $$
DECLARE
v_partition_name TEXT;
BEGIN
v_partition_name := 'ew_disk_index_desc_d' || NEW.disk_id;
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM pg_class WHERE relname = v_partition_name) THEN
BEGIN
EXECUTE format(
'CREATE TABLE %I PARTITION OF ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned FOR VALUES IN (%L)',
v_partition_name,
NEW.disk_id
);
RAISE NOTICE 'Partition % created automatically.', v_partition_name;
EXCEPTION
WHEN duplicate_table THEN
RAISE NOTICE 'Partition % was created concurrently.', v_partition_name;
END;
END IF;
RETURN NEW;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
-- 步骤 2: 创建触发器
DROP TRIGGER IF EXISTS trg_create_disk_partition ON ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned;
CREATE TRIGGER trg_create_disk_partition
BEFORE INSERT ON ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned
FOR EACH ROW
EXECUTE FUNCTION fn_create_disk_partition_if_not_exists();
-- 步骤 3: 验证
SELECT '自动化分区函数和触发器已成功部署!' AS deployment_status;
特定表函数查询
SELECT
trigger_name, -- 触发器名称
event_object_table, -- 触发器所在的表
event_manipulation, -- 触发事件 (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE)
action_timing, -- 触发时机 (BEFORE, AFTER)
action_statement -- 执行的动作
FROM
information_schema.triggers
WHERE
event_object_table = 'ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned' -- 精确查找你的表
ORDER BY
trigger_name;
2. 读取硬盘写入数据库
读取PG数据库
import psycopg2
from psycopg2.extras import RealDictCursor
from typing import Optional, Dict, Any
class PostgresDB:
def __init__(self, dbname: str, user: str, password: str, host: str, port: str):
"""初始化数据库连接参数"""
self.db_params = {
"dbname": dbname,
"user": user,
"password": password,
"host": host,
"port": port
}
self.conn = None
self.cur = None
def connect(self) -> None:
"""建立数据库连接"""
try:
self.conn = psycopg2.connect(**self.db_params)
self.cur = self.conn.cursor(cursor_factory=RealDictCursor)
print("数据库连接成功!")
except Exception as e:
print(f"数据库连接失败: {e}")
raise
def disconnect(self) -> None:
"""关闭数据库连接"""
if self.cur:
self.cur.close()
if self.conn:
self.conn.close()
print("数据库连接已关闭")
def check_connection(self) -> bool:
"""检查数据库连接是否有效,如果无效则重新连接"""
if self.conn is None or self.conn.closed:
try:
self.connect()
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"重新连接数据库失败: {e}")
return False
# 测试连接是否真的有效
try:
self.cur.execute("SELECT 1")
return True
except Exception:
try:
self.connect()
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"重新连接数据库失败: {e}")
return False
def execute(self, query: str, params: Optional[tuple] = None) -> None:
"""执行SQL语句"""
retry_count = 0
max_retries = 3
while retry_count < max_retries:
try:
if not self.check_connection():
print("数据库连接无效,无法执行查询")
raise Exception("数据库连接无效")
self.cur.execute(query, params)
self.conn.commit()
return
except psycopg2.OperationalError as e:
retry_count += 1
if retry_count < max_retries:
print(f"数据库连接错误,尝试重连 ({retry_count}/{max_retries}): {e}")
try:
self.connect()
except Exception:
pass
else:
self.conn.rollback()
print(f"SQL执行失败,已达到最大重试次数: {e}")
raise
except Exception as e:
self.conn.rollback()
print(f"SQL执行失败: {e}")
raise
def execute_many(self, query: str, params_list: list) -> None:
"""执行批量插入"""
if not params_list:
return
retry_count = 0
max_retries = 3
while retry_count < max_retries:
try:
if not self.check_connection():
print("数据库连接无效,无法执行批量查询")
raise Exception("数据库连接无效")
self.cur.executemany(query, params_list)
self.conn.commit()
return
except psycopg2.OperationalError as e:
retry_count += 1
if retry_count < max_retries:
print(f"数据库连接错误,尝试重连 ({retry_count}/{max_retries}): {e}")
try:
self.connect()
except Exception:
pass
else:
self.conn.rollback()
print(f"批量SQL执行失败,已达到最大重试次数: {e}")
raise
except Exception as e:
self.conn.rollback()
print(f"批量执行SQL失败: {e}")
raise
def fetchall(self) -> list:
"""获取所有查询结果"""
return self.cur.fetchall()
def fetchone(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""获取单条查询结果"""
return self.cur.fetchone()
def __enter__(self):
"""上下文管理器入口"""
self.connect()
return self
def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):
"""上下文管理器出口"""
self.disconnect()
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 数据库配置
DB_CONFIG = {
"dbname": "dc",
"user": "postgres",
"password": "123456",
"host": "172.00.00.100",
"port": "5432"
}
# 使用上下文管理器方式(推荐)无需手动关闭,自动处理
with PostgresDB(**DB_CONFIG) as db:
# 执行查询示例
db.execute("SELECT version();")
result = db.fetchone()
print(f"PostgreSQL版本: {result['version']}")
硬盘信息索引
from dataclasses import dataclass
from datetime import datetime
from typing import Optional
import os
@dataclass
class DiskInfo:
"""硬盘信息数据类"""
disk_name: str # 硬盘名称
disk_sn: str # 硬盘序列号
capacity_tb: float # 总容量(TB)
used_capacity_tb: float # 已使用容量(TB)
storage_location: str # 存储位置
status: str # 硬盘状态
disk_password: Optional[str] # 硬盘密码
disk_path: str # 硬盘挂载路径
remark: Optional[str] = None # 备注
class DiskManager:
def __init__(self, db):
"""初始化硬盘管理器
Args:
db: PostgresDB实例
"""
self.db = db
def _validate_disk_info(self, disk_info: DiskInfo) -> None:
"""验证硬盘信息的有效性"""
if not os.path.exists(disk_info.disk_path):
raise ValueError(f"硬盘路径不存在: {disk_info.disk_path}")
if disk_info.capacity_tb <= 0:
raise ValueError("硬盘容量必须大于0")
if disk_info.used_capacity_tb < 0:
raise ValueError("已使用容量不能为负")
if disk_info.used_capacity_tb > disk_info.capacity_tb:
raise ValueError("已使用容量不能大于总容量")
def add_disk(self, disk_info: DiskInfo) -> int:
"""添加硬盘信息到数据库
Args:
disk_info: DiskInfo实例
Returns:
int: 插入记录的ID
"""
# 验证硬盘信息
self._validate_disk_info(disk_info)
# SQL插入语句
insert_sql = """
INSERT INTO ds.disks (
disk_name, disk_sn, capacity_tb, used_capacity_tb,
storage_location, status, disk_password, remark
) VALUES (
%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s
) RETURNING id;
"""
# 执行插入
try:
self.db.execute(insert_sql, (
disk_info.disk_name,
disk_info.disk_sn,
disk_info.capacity_tb,
disk_info.used_capacity_tb,
disk_info.storage_location,
disk_info.status,
disk_info.disk_password,
disk_info.remark
))
result = self.db.fetchone()
print(f"成功添加硬盘记录,ID: {result['id']}")
return result['id']
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(f"添加硬盘记录失败: {str(e)}")
文件信息索引
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
import concurrent.futures
import threading
from queue import Queue
import multiprocessing
import os
import hashlib
from datetime import datetime
from typing import Optional, Generator
from dataclasses import dataclass
import json
from pg_tools import PostgresDB
from diskinfo_tools import DiskManager,DiskInfo
@dataclass
class FileInfo:
"""文件信息数据类"""
disk_id: int
file_path: str
parent_dir: str
file_name: str
file_ext: str
file_size_bytes: float
file_hash: Optional[str]
file_modified_time: datetime
capture_time: Optional[datetime] = None
remark: Optional[str] = None
class FileIndexer:
def __init__(self, db, disk_id: int, root_path: str, max_workers: int = multiprocessing.cpu_count()):
"""初始化文件索引器"""
self.db = db
self.disk_id = disk_id
self.root_path = root_path
# 使用Queue来存储处理好的FileInfo对象
self.file_queue = Queue()
# 获取CPU核心数,用于设置线程数
self.max_workers = max_workers
# 用于追踪处理进度
self.processed_files = 0
self.total_files = 0
self.lock = threading.Lock()
def calculate_file_hash(self, file_path: str, chunk_size: int = 8192, max_size: int = 10 * 1024 * 1024) -> str:
"""计算文件的SHA256哈希值
对于大文件,只计算前10MB的哈希值以提高性能
"""
try:
file_size = os.path.getsize(file_path)
sha256_hash = hashlib.sha256()
with open(file_path, "rb") as f:
# 对于大文件,只读取前max_size字节
if file_size > max_size:
bytes_to_read = max_size
while bytes_to_read > 0:
read_size = min(chunk_size, bytes_to_read)
byte_block = f.read(read_size)
if not byte_block:
break
sha256_hash.update(byte_block)
bytes_to_read -= len(byte_block)
# 添加文件大小信息到哈希中,以区分不同大小但前10MB相同的文件
sha256_hash.update(str(file_size).encode())
else:
# 小文件完整计算哈希
for byte_block in iter(lambda: f.read(chunk_size), b""):
sha256_hash.update(byte_block)
return sha256_hash.hexdigest()
except Exception as e:
print(f"计算文件哈希时出错 {file_path}: {str(e)}")
return "error_hash_" + str(hash(file_path))
def process_file(self, file_info: tuple) -> Optional[FileInfo]:
"""处理单个文件的信息
Args:
file_info: (root, file_name)的元组
"""
root, file_name = file_info
file_path = os.path.join(root, file_name)
try:
# 获取文件基本信息
file_stat = os.stat(file_path)
file_size_mb = file_stat.st_size / (1024 * 1024)
file_modified_time = datetime.fromtimestamp(file_stat.st_mtime)
capture_time = datetime.fromtimestamp(file_stat.st_ctime)
# 计算文件哈希值
file_hash = self.calculate_file_hash(file_path)
# file_hash = 0
return FileInfo(
disk_id=self.disk_id,
file_path=file_path,
parent_dir=root,
file_name=file_name,
file_ext=os.path.splitext(file_name)[1].lower().lstrip('.'),
file_size_bytes=file_size_mb,
file_hash=file_hash,
file_modified_time=file_modified_time,
capture_time=capture_time
)
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理文件 {file_path} 时出错: {str(e)}")
return None
def update_progress(self):
"""更新和显示进度"""
with self.lock:
self.processed_files += 1
if self.processed_files % 100 == 0:
progress = (self.processed_files / self.total_files) * 100
print(f"进度: {progress:.2f}% ({self.processed_files}/{self.total_files})")
def scan_files(self) -> Generator[FileInfo, None, None]:
"""使用线程池并行处理文件"""
# 首先收集所有文件信息
all_files = []
for root, _, files in os.walk(self.root_path):
for file_name in files:
all_files.append((root, file_name))
self.total_files = len(all_files)
print(f"发现总文件数: {self.total_files}")
# 使用线程池并行处理文件
with ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=self.max_workers) as executor:
# 提交所有任务
future_to_file = {
executor.submit(self.process_file, file_info): file_info
for file_info in all_files
}
# 获取结果
for future in concurrent.futures.as_completed(future_to_file):
try:
file_info = future.result()
if file_info:
self.update_progress()
yield file_info
except Exception as e:
print(f"处理文件时发生错误: {str(e)}")
def index_files(self) -> None:
"""将文件信息写入数据库"""
insert_sql = """
INSERT INTO ds.ew_disk_index_desc_partitioned (
disk_id, file_path, parent_dir, file_name, file_ext,
file_size_bytes, file_hash, file_modified_time, capture_time
) VALUES (
%s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s, %s
) ON CONFLICT (file_path, disk_id) DO NOTHING;
"""
start_time = datetime.now()
total_files = 0
# 使用批量插入来提高数据库写入性能
batch_size = 1000
batch = []
for file_info in self.scan_files():
try:
batch.append((
file_info.disk_id,
file_info.file_path,
file_info.parent_dir,
file_info.file_name,
file_info.file_ext,
file_info.file_size_bytes,
file_info.file_hash,
file_info.file_modified_time,
file_info.capture_time
))
# 当批次达到指定大小时执行批量插入
if len(batch) >= batch_size:
self.db.execute_many(insert_sql, batch)
total_files += len(batch)
batch = []
print(f"已索引 {total_files} 个文件...")
except Exception as e:
print(f"写入文件 {file_info.file_path} 时出错: {str(e)}")
# 处理剩余的批次
if batch:
self.db.execute_many(insert_sql, batch)
total_files += len(batch)
end_time = datetime.now()
duration = (end_time - start_time).total_seconds()
print(f"索引完成,共处理 {total_files} 个文件")
print(f"总耗时: {duration:.2f} 秒")
print(f"平均速度: {total_files/duration:.2f} 文件/秒")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# C:\Users\Admin\Desktop\process_qj_disk\disk\python.exe C:\Users\Admin\Desktop\ew_disk\disk_files_tools.py
# 数据库配置
DB_CONFIG = {
"dbname": "",
"user": "",
"password": "",
"host": "",
"port": ""
}
# 硬盘信息
disk_info = DiskInfo(
disk_name="", # 硬盘名称
disk_sn="", # 硬盘序列号
capacity_tb=, # 总容量(TB)
used_capacity_tb=, # 已使用容量(TB)
storage_location="", # 存储位置
status="", # 硬盘状态
disk_password=None, # 硬盘密码(如果有)
disk_path="", # 硬盘挂载路径
remark="" # 备注
)
try:
with PostgresDB(**DB_CONFIG) as db:
# 1. 先添加硬盘信息
# disk_manager = DiskManager(db)
# disk_id = disk_manager.add_disk(disk_info)
disk_id = 2
print(f"硬盘信息已添加,ID: {disk_id}")
# 2. 开始文件索引
indexer = FileIndexer(db, disk_id, disk_info.disk_path, 1)
indexer.index_files()
except Exception as e:
print(f"程序执行出错: {str(e)}")



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号