栅格篇 - 栅格转矢量
@ 20240723 & lth
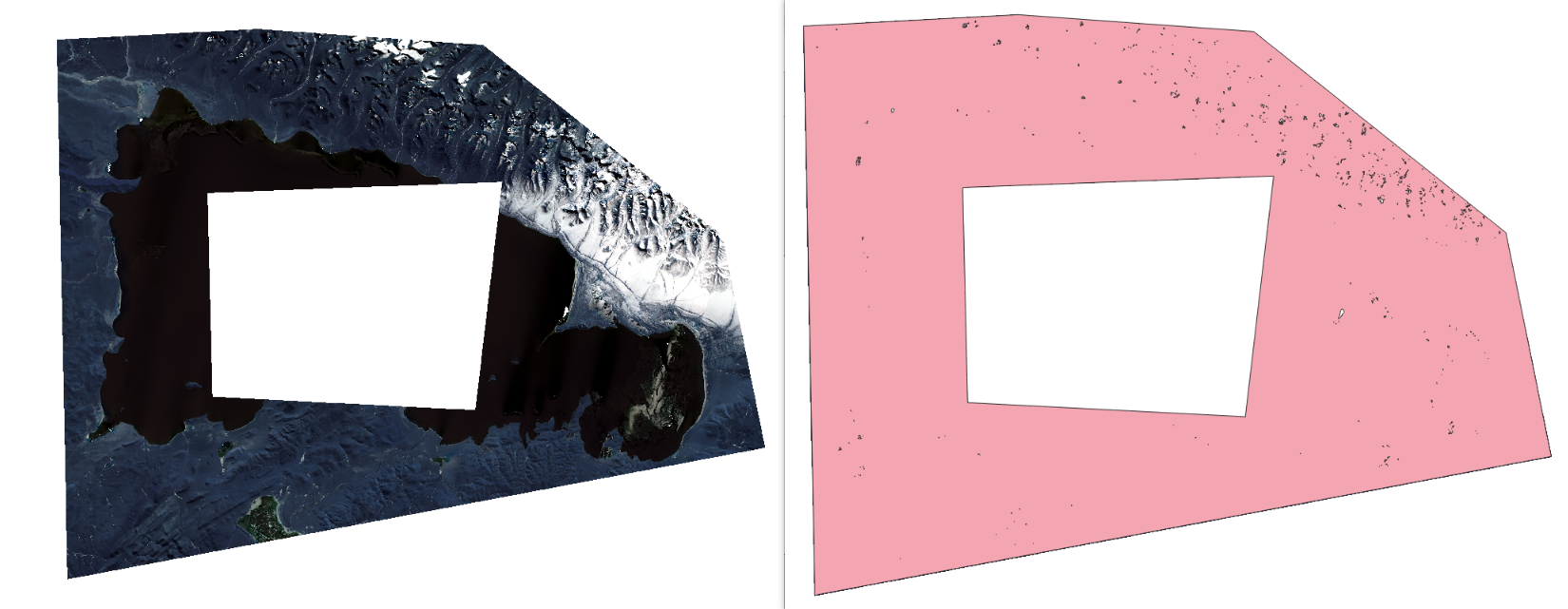
栅格数据来源:微信公众号,小白说遥感
目标:获取栅格的矢量边界
逻辑:
1. 获取栅格基本信息;
2. 判断是否需要进行多进程、分块处理;
3. 从栅格数据创建掩膜;
4. 将掩膜矢量化;
5. 过滤有效的多边形(DN值为1的多边形,即有数据的区域)。
代码:https://github.com/Lth1121/lth/blob/main/raster_to_vector.py
简易示例
from raster_to_vector import RasterToVector
import os
input = r"E:\code_git\gis_learning\raster_process\rasterfootprint\LC09_L2SP_138039_20230101_20230315_02_T1_SR_B2_rgb_clip.tif"
output = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(input), "output.shp")
if __name__ == '__main__':
processor = RasterToVector()
processor.process_raster(input, output)
代码实现
类注册
# !/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 栅格数据转矢量边界工具
# 支持处理栅格数据中的空洞,输出为Shapefile或GeoJSON格式
# 支持超大栅格的分块处理和加速优化
import os
import sys
import argparse
import time
import gc
from multiprocessing import Pool, cpu_count
from osgeo import gdal, ogr, osr
import numpy as np
class RasterToVector:
"""栅格转矢量类"""
def __init__(self, chunk_size=512, max_memory_mb=256, use_multiprocessing=True):
"""
初始化栅格转矢量处理器
"""
gdal.UseExceptions() # 启用GDAL异常
self.chunk_size = chunk_size # 分块大小(像素)
self.max_memory_mb = max_memory_mb # 最大内存使用量(MB)
self.use_multiprocessing = use_multiprocessing # 是否使用多进程
self.cpu_cores = cpu_count()
获取栅格基本信息
def get_raster_info(self, raster_path):
"""
获取栅格基本信息
Args:
raster_path (str): 栅格文件路径
Returns:
dict: 栅格信息字典
"""
dataset = gdal.Open(raster_path, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
if dataset is None:
raise ValueError(f"无法打开栅格文件: {raster_path}")
info = {
'width': dataset.RasterXSize,
'height': dataset.RasterYSize,
'bands': dataset.RasterCount,
'geotransform': dataset.GetGeoTransform(),
'projection': dataset.GetProjection(),
'datatype': dataset.GetRasterBand(1).DataType,
'nodata': dataset.GetRasterBand(1).GetNoDataValue()
}
# 计算文件大小(估算)
pixel_count = info['width'] * info['height']
bytes_per_pixel = gdal.GetDataTypeSize(info['datatype']) // 8
estimated_size_mb = (pixel_count * bytes_per_pixel) / (1024 * 1024)
info['estimated_size_mb'] = estimated_size_mb
dataset = None
return info
判断是否分块处理
def should_use_chunked_processing(self, raster_info):
"""
判断是否需要使用分块处理
Args:
raster_info (dict): 栅格信息
Returns:
bool: 是否需要分块处理
"""
# 如果估算内存使用超过阈值,或者像素数量过大,则使用分块处理
print(f"估算内存需求: {raster_info['estimated_size_mb']:.1f} MB")
return (raster_info['estimated_size_mb'] > self.max_memory_mb or
raster_info['width'] > self.chunk_size * 4 or
raster_info['height'] > self.chunk_size * 4)
单栅格创建掩膜
def create_mask_from_raster(self, raster_path, nodata_value=None):
"""
从栅格数据创建掩膜
Args:
raster_path (str): 栅格文件路径
nodata_value (float): 无数据值,如果为None则从栅格文件读取
Returns:
tuple: (mask_array, geotransform, projection, width, height)
"""
# 打开栅格文件
dataset = gdal.Open(raster_path, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
if dataset is None:
raise ValueError(f"无法打开栅格文件: {raster_path}")
# 获取栅格信息
width = dataset.RasterXSize
height = dataset.RasterYSize
geotransform = dataset.GetGeoTransform()
projection = dataset.GetProjection()
print(f"栅格信息:{width} x {height},投影坐标projection:{projection}")
# 获取第一个波段
band = dataset.GetRasterBand(1)
# 获取无数据值
if nodata_value is None:
nodata_value = band.GetNoDataValue()
# 读取数据
data = band.ReadAsArray()
# 创建掩膜:有效数据为1,无效数据为0
if nodata_value is not None:
mask = np.where(np.isclose(data, nodata_value, equal_nan=True), 0, 1)
else:
# 如果没有无数据值,则将NaN视为无数据
mask = np.where(np.isnan(data), 0, 1)
# 转换为uint8类型
mask = mask.astype(np.uint8)
dataset = None # 关闭数据集
return mask, geotransform, projection, width, height
分块创建掩膜
def create_mask_chunked(self, raster_path, nodata_value=None):
"""
分块创建掩膜(用于超大栅格)
Args:
raster_path (str): 栅格文件路径
nodata_value (float): 无数据值
Returns:
tuple: (mask_array, geotransform, projection, width, height)
"""
print("使用分块处理模式...")
start_time = time.time()
# 打开栅格文件
dataset = gdal.Open(raster_path, gdal.GA_ReadOnly)
if dataset is None:
raise ValueError(f"无法打开栅格文件: {raster_path}")
# 获取栅格信息
width = dataset.RasterXSize
height = dataset.RasterYSize
geotransform = dataset.GetGeoTransform()
projection = dataset.GetProjection()
print(f"栅格信息:{width} x {height},投影坐标projection:{projection}")
# 获取第一个波段
band = dataset.GetRasterBand(1)
# 获取无数据值
if nodata_value is None:
nodata_value = band.GetNoDataValue()
# 创建输出掩膜数组
mask = np.zeros((height, width), dtype=np.uint8)
# 计算分块参数
x_chunks = (width + self.chunk_size - 1) // self.chunk_size
y_chunks = (height + self.chunk_size - 1) // self.chunk_size
total_chunks = x_chunks * y_chunks
print(f"分块处理:{x_chunks} x {y_chunks} = {total_chunks} 个块")
# 分块处理
processed_chunks = 0
for y_chunk in range(y_chunks):
for x_chunk in range(x_chunks):
# 计算当前块的范围
x_start = x_chunk * self.chunk_size
y_start = y_chunk * self.chunk_size
x_size = min(self.chunk_size, width - x_start)
y_size = min(self.chunk_size, height - y_start)
# 读取数据块
data_chunk = band.ReadAsArray(x_start, y_start, x_size, y_size)
# 创建掩膜块
if nodata_value is not None:
mask_chunk = np.where(np.isclose(data_chunk, nodata_value, equal_nan=True), 0, 1)
else:
mask_chunk = np.where(np.isnan(data_chunk), 0, 1)
# 写入到总掩膜中
mask[y_start:y_start+y_size, x_start:x_start+x_size] = mask_chunk.astype(np.uint8)
processed_chunks += 1
if processed_chunks % 100 == 0 or processed_chunks == total_chunks:
progress = (processed_chunks / total_chunks) * 100
elapsed = time.time() - start_time
print(f"进度: {processed_chunks}/{total_chunks} ({progress:.1f}%), 耗时: {elapsed:.1f}s")
# 强制垃圾回收
del data_chunk, mask_chunk
if processed_chunks % 50 == 0:
gc.collect()
dataset = None # 关闭数据集
print(f"分块处理完成,总耗时: {time.time() - start_time:.1f}s")
return mask, geotransform, projection, width, height
掩膜矢量化
def polygonize_mask(self, mask, geotransform, projection, output_path, output_format='ESRI Shapefile'):
"""
将掩膜矢量化
Args:
mask (numpy.ndarray): 掩膜数组
geotransform (tuple): 地理变换参数
projection (str): 投影信息
output_path (str): 输出文件路径
output_format (str): 输出格式 ('ESRI Shapefile' 或 'GeoJSON')
"""
# 创建内存中的栅格数据集
mem_driver = gdal.GetDriverByName('MEM')
mem_dataset = mem_driver.Create('', mask.shape[1], mask.shape[0], 1, gdal.GDT_Byte)
mem_dataset.SetGeoTransform(geotransform)
mem_dataset.SetProjection(projection)
# 写入掩膜数据
mem_band = mem_dataset.GetRasterBand(1)
mem_band.WriteArray(mask)
mem_band.SetNoDataValue(0)
# 创建输出矢量数据集
if output_format == 'GeoJSON':
driver_name = 'GeoJSON'
if not output_path.endswith('.geojson'):
output_path += '.geojson'
else:
driver_name = 'ESRI Shapefile'
if not output_path.endswith('.shp'):
output_path += '.shp'
# 删除已存在的输出文件
if os.path.exists(output_path):
vector_driver = ogr.GetDriverByName(driver_name)
vector_driver.DeleteDataSource(output_path)
# 创建矢量数据源
vector_driver = ogr.GetDriverByName(driver_name)
vector_dataset = vector_driver.CreateDataSource(output_path)
# 创建空间参考系统
srs = osr.SpatialReference()
srs.ImportFromWkt(projection)
# 创建图层
layer = vector_dataset.CreateLayer('footprint', srs, ogr.wkbPolygon)
# 添加字段
field_def = ogr.FieldDefn('DN', ogr.OFTInteger)
layer.CreateField(field_def)
# 执行矢量化
gdal.Polygonize(mem_band, mem_band, layer, 0, [], callback=None)
# 清理
mem_dataset = None
vector_dataset = None
print(f"矢量化完成,输出文件: {output_path}")
超大掩膜转矢量
def polygonize_mask_optimized(self, mask, geotransform, projection, output_path, output_format='ESRI Shapefile'):
"""
优化的矢量化方法,支持大型掩膜
Args:
mask (numpy.ndarray): 掩膜数组
geotransform (tuple): 地理变换参数
projection (str): 投影信息
output_path (str): 输出文件路径
output_format (str): 输出格式
"""
print("开始优化矢量化...")
start_time = time.time()
# 检查掩膜大小,决定是否需要特殊处理
mask_size_mb = mask.nbytes / (1024 * 1024)
print(f"掩膜大小: {mask_size_mb:.1f} MB")
# 创建内存中的栅格数据集
mem_driver = gdal.GetDriverByName('MEM')
mem_dataset = mem_driver.Create('', mask.shape[1], mask.shape[0], 1, gdal.GDT_Byte)
mem_dataset.SetGeoTransform(geotransform)
mem_dataset.SetProjection(projection)
# 写入掩膜数据
mem_band = mem_dataset.GetRasterBand(1)
mem_band.WriteArray(mask)
mem_band.SetNoDataValue(0)
# 设置缓存大小以优化性能
gdal.SetCacheMax(min(512 * 1024 * 1024, int(mask_size_mb * 2 * 1024 * 1024))) # 设置为掩膜大小的2倍或512MB
# 创建输出矢量数据集
if output_format == 'GeoJSON':
driver_name = 'GeoJSON'
if not output_path.endswith('.geojson'):
output_path += '.geojson'
else:
driver_name = 'ESRI Shapefile'
if not output_path.endswith('.shp'):
output_path += '.shp'
# 删除已存在的输出文件
if os.path.exists(output_path):
vector_driver = ogr.GetDriverByName(driver_name)
vector_driver.DeleteDataSource(output_path)
# 创建矢量数据源
vector_driver = ogr.GetDriverByName(driver_name)
vector_dataset = vector_driver.CreateDataSource(output_path)
# 创建空间参考系统
srs = osr.SpatialReference()
srs.ImportFromWkt(projection)
# 创建图层
layer = vector_dataset.CreateLayer('footprint', srs, ogr.wkbPolygon)
# 添加字段
field_def = ogr.FieldDefn('DN', ogr.OFTInteger)
layer.CreateField(field_def)
# 执行矢量化(带进度回调)
def progress_callback(complete, message, data):
if complete % 0.1 < 0.01: # 每10%显示一次进度
elapsed = time.time() - start_time
print(f"矢量化进度: {complete*100:.1f}%, 耗时: {elapsed:.1f}s")
return 1 # 继续处理
gdal.Polygonize(mem_band, mem_band, layer, 0, [], callback=progress_callback)
# 清理
mem_dataset = None
vector_dataset = None
elapsed = time.time() - start_time
print(f"优化矢量化完成,耗时: {elapsed:.1f}s,输出文件: {output_path}")
过滤有效多边形
def filter_valid_polygons(self, input_path, output_path, output_format='ESRI Shapefile'):
"""
过滤有效的多边形(DN值为1的多边形,即有数据的区域)
Args:
input_path (str): 输入矢量文件路径
output_path (str): 输出矢量文件路径
output_format (str): 输出格式
"""
# 打开输入数据源
input_dataset = ogr.Open(input_path, 0)
input_layer = input_dataset.GetLayer()
# 创建输出数据源
if output_format == 'GeoJSON':
driver_name = 'GeoJSON'
if not output_path.endswith('.geojson'):
output_path += '.geojson'
else:
driver_name = 'ESRI Shapefile'
if not output_path.endswith('.shp'):
output_path += '.shp'
# 删除已存在的输出文件
if os.path.exists(output_path):
output_driver = ogr.GetDriverByName(driver_name)
output_driver.DeleteDataSource(output_path)
# 创建输出数据源
output_driver = ogr.GetDriverByName(driver_name)
output_dataset = output_driver.CreateDataSource(output_path)
# 创建输出图层
output_layer = output_dataset.CreateLayer(
'footprint',
input_layer.GetSpatialRef(),
ogr.wkbPolygon
)
# 复制字段定义
input_layer_defn = input_layer.GetLayerDefn()
for i in range(input_layer_defn.GetFieldCount()):
field_defn = input_layer_defn.GetFieldDefn(i)
output_layer.CreateField(field_defn)
# 过滤并复制要素
valid_count = 0
for feature in input_layer:
dn_value = feature.GetField('DN')
if dn_value == 1: # 只保留有数据的区域
output_layer.CreateFeature(feature)
valid_count += 1
# 清理
input_dataset = None
output_dataset = None
print(f"过滤完成,保留了 {valid_count} 个有效多边形")
智能处理策略
def process_raster(self, input_raster, output_vector, output_format='ESRI Shapefile', nodata_value=None):
"""
处理栅格文件,生成矢量边界(智能选择处理策略)
Args:
input_raster (str): 输入栅格文件路径
output_vector (str): 输出矢量文件路径
output_format (str): 输出格式 ('ESRI Shapefile' 或 'GeoJSON')
nodata_value (float): 无数据值
"""
try:
print(f"开始处理栅格文件: {input_raster}")
start_time = time.time()
# 0. 获取栅格信息并选择处理策略
print("分析栅格文件...")
raster_info = self.get_raster_info(input_raster)
print(f"栅格大小: {raster_info['width']} x {raster_info['height']}")
print(f"估算内存需求: {raster_info['estimated_size_mb']:.1f} MB")
use_chunked = self.should_use_chunked_processing(raster_info)
if use_chunked:
print("检测到大型栅格,使用分块处理模式")
else:
print("使用标准处理模式")
# 1. 创建掩膜
print("创建掩膜...")
if use_chunked:
mask, geotransform, projection, width, height = self.create_mask_chunked(
input_raster, nodata_value
)
else:
mask, geotransform, projection, width, height = self.create_mask_from_raster(
input_raster, nodata_value
)
# 2. 矢量化掩膜
print("矢量化掩膜...")
temp_output = output_vector + '_temp'
# 根据掩膜大小选择矢量化方法
mask_size_mb = mask.nbytes / (1024 * 1024)
if mask_size_mb > 100: # 大于100MB使用优化方法
self.polygonize_mask_optimized(mask, geotransform, projection, temp_output, output_format)
else:
self.polygonize_mask(mask, geotransform, projection, temp_output, output_format)
# 3. 过滤有效多边形
print("过滤有效多边形...")
if output_format == 'GeoJSON':
temp_output += '.geojson'
else:
temp_output += '.shp'
self.filter_valid_polygons(temp_output, output_vector, output_format)
# 4. 清理临时文件
if output_format == 'ESRI Shapefile':
# 删除shapefile相关文件
for ext in ['.shp', '.shx', '.dbf', '.prj']:
temp_file = temp_output.replace('.shp', ext)
if os.path.exists(temp_file):
os.remove(temp_file)
else:
if os.path.exists(temp_output):
os.remove(temp_output)
# 5. 清理内存
del mask
gc.collect()
total_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"处理完成!总耗时: {total_time:.1f}s")
except Exception as e:
import traceback
error_details = traceback.format_exc()
print(f"处理过程中发生错误: {str(e)}")
print(f"详细错误信息:")
print(error_details)
raise
主函数
def main():
"""主函数"""
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='栅格数据转矢量边界工具(支持超大栅格优化处理)')
parser.add_argument('input', help='输入栅格文件路径 (.tif)')
parser.add_argument('output', help='输出矢量文件路径 (.shp 或 .geojson)')
parser.add_argument('--format', choices=['shapefile', 'geojson'], default='shapefile',
help='输出格式 (默认: shapefile)')
parser.add_argument('--nodata', type=float, help='无数据值 (如果不指定则从栅格文件读取)')
parser.add_argument('--chunk-size', type=int, default=2048,
help='分块大小(像素),用于大型栅格处理 (默认: 2048)')
parser.add_argument('--max-memory', type=int, default=1024,
help='最大内存使用量(MB) (默认: 1024)')
parser.add_argument('--no-multiprocessing', action='store_true',
help='禁用多进程处理')
args = parser.parse_args()
# 检查输入文件是否存在
if not os.path.exists(args.input):
print(f"错误: 输入文件不存在: {args.input}")
sys.exit(1)
# 确定输出格式
output_format = 'GeoJSON' if args.format == 'geojson' else 'ESRI Shapefile'
# 创建处理器并执行
processor = RasterToVector(
chunk_size=args.chunk_size,
max_memory_mb=args.max_memory,
use_multiprocessing=not args.no_multiprocessing
)
print(f"处理器配置:")
print(f" 分块大小: {args.chunk_size} 像素")
print(f" 最大内存: {args.max_memory} MB")
print(f" 多进程: {'启用' if not args.no_multiprocessing else '禁用'}")
print(f" CPU核心数: {processor.cpu_cores}")
print()
processor.process_raster(args.input, args.output, output_format, args.nodata)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号