nn.Conv1d
conv1 = nn.Conv1d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size)
这个是一维卷积
参数
in_channels(int) – 输入信号的通道。在文本分类中,即为词向量的维度(embedding_size)
out_channels(int) – 卷积产生的通道。有多少个out_channels,就需要多少个1维卷积
kernel_size(int or tuple) - 卷积核的尺寸,卷积核的大小为(k,),第二个维度是由in_channels来决定的,所以实际上卷积大小为in_channels*kernel_size
stride(int or tuple, optional) - 卷积步长
padding (int or tuple, optional)- 输入的每一条边补充0的层数
dilation(int or tuple, optional) – 卷积核元素之间的间距
groups(int, optional) – 从输入通道到输出通道的阻塞连接数
bias(bool, optional) - 如果bias=True,添加偏置

这里需要注意的是这个out_channels是有几个卷积核,
然后这个卷积核的大小是in_channels*kernel_sizes,然后这个in_channels是词向量的维度
例子 1:
input1 = torch.randn(20, 16, 50) # 这里的输入是batch_size x embedding_size x text_len
m = nn.Conv1d(16, 33, 3, stride=2) # 这里指的就是有33个卷积核,然后每个卷积核的大小就是16*3步长为2,然后输出就是的最后一维就是⌊50+2*0 - 1*(3-1) -1⌋/2 + 1 =24
output = m(input1) # torch.Size([20, 33, 24])
print(output.shape)
# torch.Size([20, 33, 24])
例子 2:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# 卷积大小为in_channels*kernel_size, 此处也即 4 * 3, 每个卷积核产生一维的输出数据,长度与输入数据的长度和stride有关,根据ouotput可知是3,第二个参数2也就卷积核的数量
m = nn.Conv1d(4, 2, 3, stride=2)
# 第一个参数理解为batch的大小,输入是4 * 9格式
input = torch.randn(1, 4, 9)
print(input)
output = m(input)
print(output)
print(output.size())
输出如下:
tensor([[[-0.2105, -1.0958, 0.7299, 1.1003, 2.3175, 0.8186, -1.7510, -0.1925, 0.8591],
[ 1.0991, -0.3016, 1.5633, 0.6162, 0.3150, 1.0413, 1.0571, -0.7014, 0.2239],
[-0.0658, 0.4755, -0.6653, -0.0696, 0.3483, -0.0360, -0.4665, 1.2606, 1.3365],
[-0.0186, -1.1802, -0.8835, -1.1813, -0.5145, -0.0534, -1.2568, 0.3211, -2.4793]]])
tensor([[[-0.8012, 0.0589, 0.1576, -0.8222],
[-0.8231, -0.4233, 0.7178, -0.6621]]], grad_fn=<SqueezeBackward1>)
torch.Size([1, 2, 4])

得到输出1*4的输出:
[-0.8012, 0.0589, 0.1576, -0.8222]
第二个卷积核进行类似操作:

得到输出1*4的输出:
[-0.8231, -0.4233, 0.7178, -0.6621]
合并得到最后的2*4的结果:
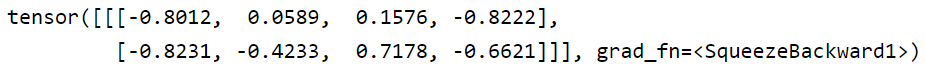
输入的input为 4 * 9 ,输出为 2 * 4。
验证Shape中conv1d 关于输出Lout的公式:Lout =⌊ 9+20 - 1(3-1) -1⌋/2 + 1 = 4
例子3:
conv1 = nn.Conv1d(in_channels=256,out_channels=100,kernel_size=1)
input = torch.randn(32,35,256)
# batch_size x text_len x embedding_size -> batch_size x embedding_size x text_len
input = input.permute(0,2,1)
out = conv1(input)
print(out.size())
torch.Size([32, 100, 35])



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号