线段数维护区间乘,欧拉函数和
The Euler function, φ, is known to be important in math theory. Given a positive integer n, φ(n) is defined as the number of integers in [1,n] that are co-prime with n. For example, φ(1)=1,φ(10)=4,φ(11)=10.
Now, given an array x with n positive integers x1,…,xn, your task is to maintain m operations on x, which can be categorized into two types:
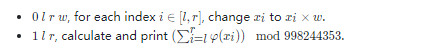
Input
The first line contains two inetegers n,m (1≤n,m≤105).
The second line contains n integers x1,…,xn (1≤xi≤100).
Then m lines follow. The i-th line describes the i-th operation. The input guarantees that 1≤l≤r≤n and 1≤w≤100.
Output
For each operation of type 1, output a single line with a single integer, representing the answer.
Sample Input
5 5
1 2 3 4 5
1 1 5
0 1 3 2
1 1 5
0 2 5 6
1 1 5结尾无空行
Sample Output
10
11
37
这个题就是首先你要先知道欧拉函数的性质,ol[i]=n*(1-1/p1)*(1-1/p2)*(1-1/p3).......*(1-1/pn)
这个题就是用到这个性质,然后这a[i]和乘的每一个数都是<=100的质因子也就25个,可以用一个bitset来维护一下,
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<bitset> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int maxn=5e5+100; const ll mod = 998244353; bitset<30>st[105]; struct node{ bitset<30> st; ll x,lazy; int l,r; }t[maxn]; int n,m; int vis[maxn]; int idx; int a[maxn],pri[100],cnt[105][30]; int f[maxn];//欧拉函数 void inint(){ for(int i=2;i<=100;i++){ if(!vis[i]){ pri[++idx]=i; } for(int j=1;j*pri[i]<maxn&&j<=idx;j++){ vis[i*pri[j]]=1; if(i%pri[j]==0){ break; } } } for(int i=1;i<=100;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=25;j++){ int tmp=i; while(tmp%pri[j]==0){ ++cnt[i][j]; tmp/=pri[j]; } st[i][j]=cnt[i][j]; } } } int ol(int n){ int ans=n; for(int i=2;i*i<=n;i++){ if(n%i==0){ ans=ans/i*(i-1); while(n%i==0){ n/=i; } } } if(n>1){ ans=ans/n*(n-1); } return ans; } void push_up(int p){ t[p].x=(t[2*p].x+t[2*p+1].x)%mod; t[p].st=(t[2*p].st & t[2*p+1].st); } void push_down(int p){ t[2*p].lazy=(t[2*p].lazy*t[p].lazy)%mod; t[2*p+1].lazy=(t[2*p+1].lazy*t[p].lazy)%mod; t[2*p].x=(t[2*p].x*t[p].lazy)%mod; t[2*p+1].x=(t[2*p+1].x*t[p].lazy)%mod; t[p].lazy=1; } void build(int p,int l,int r){ t[p].l=l; t[p].r=r; t[p].lazy=1; if(t[p].l==t[p].r){ t[p].x=1ll*f[a[l]]; t[p].lazy=1; t[p].st=st[a[l]]; return ; } int mid=(l+r)/2; build(2*p,l,mid); build(2*p+1,mid+1,r); push_up(p); } void update(int p,int l,int r,int x,int y){ if(t[p].l>=l&&t[p].r<=r&&t[p].st[x]){ for(int i=1;i<=y;i++){ t[p].x=(t[p].x*pri[x])%mod; t[p].lazy=(t[p].lazy*pri[x])%mod; } return ; } if(t[p].l==t[p].r){ t[p].x=(t[p].x*(pri[x]-1))%mod; t[p].st[x]=1; for(int i=1;i<=y-1;i++){ t[p].x=(t[p].x*pri[x])%mod; } return ; } if(t[p].lazy!=1){ push_down(p); } int mid=(t[p].l+t[p].r)/2; if(l<=mid){ update(2*p,l,r,x,y); } if(r>mid){ update(2*p+1,l,r,x,y); } push_up(p); } ll query(int p,int l,int r){ if(t[p].l>=l&&t[p].r<=r){ return t[p].x; } ll ans=0; if(t[p].lazy!=1){ push_down(p); } int mid=(t[p].l+t[p].r)/2; if(l<=mid){ ans+=query(2*p,l,r); } if(r>mid){ ans+=query(2*p+1,l,r); } return ans; } //ll query(int p, int a, int b) //{ // if(a <= t[p].l && t[p].r <= b) return t[p].x; // // if(t[p].lazy != 1) push_down(p); // int mid = (t[p].l + t[p].r) >> 1; // if(mid >= b) return query(p<<1, a, b); // else if(mid < a) return query(p<<1|1, a, b); // else return (query(p<<1, a, b) + query(p<<1|1, a, b)) % mod; //} int main(){ inint(); f[1]=1; for(int i=2;i<=100;i++){ f[i]=ol(i); } int n,m; cin>>n>>m; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ cin>>a[i]; } build(1,1,n); int op,a,b,c; while(m--){ scanf("%d",&op); if(op==1){ scanf("%d%d",&a,&b); printf("%lld\n",query(1,a,b)%mod); } else{ scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c); for(int i=1;i<=25;i++){ if(cnt[c][i]){ update(1,a,b,i,cnt[c][i]); } } } } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号