E. Boring Segments(线段树覆盖问题)
You are given n segments on a number line, numbered from 1 to n. The ii-th segments covers all integer points from li to ri and has a value wi.
You are asked to select a subset of these segments (possibly, all of them). Once the subset is selected, it's possible to travel between two integer points if there exists a selected segment that covers both of them. A subset is good if it's possible to reach point m starting from point 1 in arbitrary number of moves.
The cost of the subset is the difference between the maximum and the minimum values of segments in it. Find the minimum cost of a good subset.
In every test there exists at least one good subset.
The first line contains two integers nn and mm (1≤n≤3⋅10^5; 2≤m≤10^6) — the number of segments and the number of integer points.
Each of the next nn lines contains three integers lili, riri and wiwi (1≤li<ri≤m; 1≤wi≤10^6) — the description of the ii-th segment.
In every test there exists at least one good subset.
Print a single integer — the minimum cost of a good subset.
5 12 1 5 5 3 4 10 4 10 6 11 12 5 10 12 3
3
1 10 1 10 23
0
题目大意
这个题的题目意思就是给你一些线段,每一个线段都有一个权值,让选出一些线段,能够覆盖[1,m],并且这些线段(最大权值-最小权值)的最小值
题解
将线段按照w从小到大排序. 然后从左到右枚举线段r, 尺取维护一个最大的l,满足[l,r]能够覆盖[1,m], 判断[l,r]中的线段能否覆盖[1,m],可以用线段树区间加法, 维护每个点被覆盖的次数,同时维护区间最小值, 如果最小值>0,说明全覆盖了. 对于满足条件的区间,用w的差值更新答案即可. 算法总复杂度O(n*log) ps: 这题其实说的不是区间覆盖,而是能够连通, 例如[1,3]和[4,5]是不连通的,因为线段之间没有相交 而[1,3]和[3,5]是连通的. 处理方法是将m--,每条线段的右端点r--, 这样的话就不需要判相交,只需要判断是否覆盖了[1,m]就行了.
代码
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> const int maxn=5e6+100; using namespace std; struct node{ int l,r,mi;//与其说是最小值,还不如说是和,就是取有一个最小值 int lazy; }t[maxn]; struct Node{ int l,r,w; bool friend operator<(Node a,Node b){ return a.w<b.w; } }save[maxn]; void pushdown(int p){ if(t[p].lazy){ t[2*p].lazy+=t[p].lazy; t[2*p+1].lazy+=t[p].lazy; t[2*p].mi+=t[p].lazy; t[2*p+1].mi+=t[p].lazy; t[p].lazy=0; } } void pushup(int p){ t[p].mi=min(t[2*p].mi,t[2*p+1].mi); } void build(int p,int l,int r){ t[p].l=l; t[p].r=r; t[p].mi=t[p].lazy=0; if(l==r){ return ; } int mid=(l+r)/2; build(2*p,l,mid); build(2*p+1,mid+1,r); pushup(p); } void update(int p,int l,int r,int val){ if(t[p].l>=l&&t[p].r<=r){ t[p].mi+=val; t[p].lazy+=val; return ; } int mid=(t[p].l+t[p].r)/2; pushdown(p); if(l<=mid){ update(2*p,l,r,val); } if(r>mid){ update(2*p+1,l,r,val); } pushup(p); } int main(){ int n,m; cin>>n>>m; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ scanf("%d%d%d",&save[i].l,&save[i].r,&save[i].w); save[i].r--; } sort(save+1,save+1+n); build(1,1,m-1); int ans=0x3f3f3f3f; for(int R=1,L=1;R<=n;R++){ update(1,save[R].l,save[R].r,1); while(t[1].mi){//这里的t[1].mi就是区间1-m的最小值 ans=min(ans,save[R].w-save[L].w); update(1,save[L].l,save[L].r,-1); L++; } } cout<<ans<<endl; }
题目二:
在数轴上有 n 个闭区间从 1 至 n 编号,第 i 个闭区间为 [li,ri] 。
现在要从中选出 m 个区间,使得这 m 个区间共同包含至少一个位置。换句话说,就是使得存在一个 x ,使得对于每一个被选中的区间[li,ri],都有li≤x≤ri 。
对于一个合法的选取方案,它的花费为被选中的最长区间长度减去被选中的最短区间长度。
区间[li,ri] 的长度定义为 (ri−li) ,即等于它的右端点的值减去左端点的值。
求所有合法方案中最小的花费。如果不存在合法的方案,输出 −1。
输入格式
第一行包含两个整数,分别代表 n 和 m。
第 2 到第 (n+1) 行,每行两个整数表示一个区间,第(i+1) 行的整数 i,ri 分别代表第 i 个区间的左右端点。
输出格式
输出一行一个整数表示答案。
输入输出样例
6 3 3 5 1 2 3 4 2 2 1 5 1 4
2
说明/提示
样例输入输出 1 解释
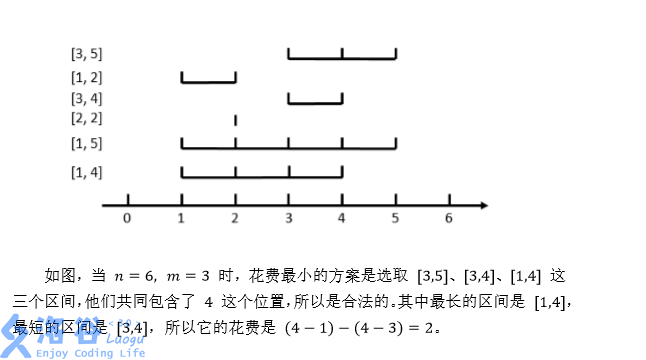
对于全部的测试点,保证1≤n≤5×10^5,1≤m≤2×10^5,0≤li≤ri≤10^9。
解题思路:
这个题其实和上面的那个题是一样的,就是这个题的li和ri都很大,需要离散化,然后按照长度排个序,然后再用尺取,
这个为啥能用出去呢?因为你是按照长度排好序的,就是如果[L,R]是满足条件的,然后R向右移动,然后是可以保证这个L也是向右
移动的,向左移动只会答案增加。然后还有一个问题就是判断怎么样判断是否满足条件呢,这个是可以用线段树来维护的,
这个每次可以在[li,ri]区间+1,然后判断[1,cnt]的最大值是不是>=m,这个max[1,cnt]就是t[1].ma
代码
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<vector> #include<map> using namespace std; const int maxn=4e6+100; int n,m; struct node{ int l,r; int ma,lazy; }t[maxn]; struct Node{ int l,r,w; bool friend operator<(Node x,Node y){ return x.w<y.w; } }save[maxn]; int id[maxn]; int cnt=0; int getid(int x){ return lower_bound(id+1,id+cnt+1,x)-id; } void pushup(int p){ t[p].ma=max(t[2*p].ma,t[2*p+1].ma); } void build(int p,int l,int r){ t[p].l=l; t[p].r=r; t[p].lazy=0,t[p].ma=0; if(l==r){ return ; } int mid=(l+r)/2; build(2*p,l,mid); build(2*p+1,mid+1,r); pushup(p); } void pushdown(int p){ if(t[p].lazy){ t[2*p].ma+=t[p].lazy; t[2*p+1].ma+=t[p].lazy; t[2*p].lazy+=t[p].lazy; t[2*p+1].lazy+=t[p].lazy; t[p].lazy=0; } } void update(int p,int l,int r,int val){ if(t[p].l>=l&&t[p].r<=r){ t[p].ma+=val; t[p].lazy+=val; return ; } int mid=(t[p].l+t[p].r)/2; pushdown(p); if(l<=mid){ update(2*p,l,r,val); } if(r>mid){ update(2*p+1,l,r,val); } pushup(p); } int main(){ cin>>n>>m; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ scanf("%d%d",&save[i].l,&save[i].r); id[++cnt]=save[i].l,id[++cnt]=save[i].r; save[i].w=(save[i].r-save[i].l); } sort(save+1,save+1+n); sort(id+1,id+cnt+1); cnt=unique(id+1,id+1+cnt)-(id+1); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ save[i].l=getid(save[i].l); save[i].r=getid(save[i].r); } build(1,1,cnt); int ans=0x3f3f3f3f; for(int R=1,L=1;R<=n;R++){ update(1,save[R].l,save[R].r,1); while(t[1].ma>=m){ ans=min(ans,save[R].w-save[L].w); //cout<<ans<<endl; update(1,save[L].l,save[L].r,-1); L++; } } if(ans==0x3f3f3f3f){ cout<<-1<<endl; } else{ cout<<ans<<endl; } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号