1、什么是HashMap
2、源码分析
3、手写实现
4、不足
一、什么是HashMap
hash散列 将一个任意长度通过某种算法(hash函数算法)换成一个固定值
map: 地图x,y 存储
总结: 通过HASH出来的值,然后通过值定位到map,然后value存储到这个map中
二、源码分析
HashMap在源码中的位置
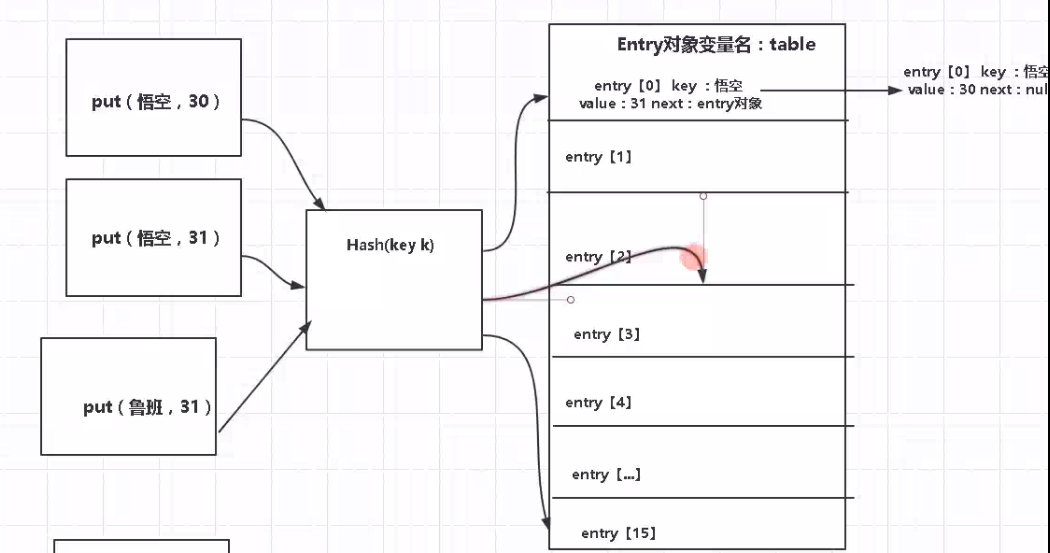
Hash冲突
三、 手写实现
1、创建Map接口
public interface Map<K,V> {
public V put(K k, V v);
public V get(K k);
public int size();
public interface Entry<K, V>{
public K getKey();
public V getValue();
}
}
2、创建hashmap类
package hashmap;
public class HashMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V> {
private static int defaultLength = 16;
private static double defaultLoader = 0.75;
private Entry<K, V>[] table = null;
private int size = 0;
public HashMap() {
this(defaultLength, defaultLoader);
}
public HashMap(int length, double loader) {
defaultLength = length;
defaultLoader = loader;
table = new Entry[defaultLength];
}
@Override
public V put(K k, V v) {
size++;
int index = hash(k);
Entry<K,V> entry = table[index];
if(entry == null){
table[index] = newEntry(k, v, null);
}else {
table[index] = newEntry(k, v, entry);
}
return table[index].getValue();
}
public Entry<K,V> newEntry(K k, V v, Entry<K,V> next) {
return new Entry<K,V>(k,v, next);
}
public int hash(K k){
int m = defaultLength;
int i = k.hashCode() % m;
return i > 0 ? i: -i;
}
@Override
public V get(K k) {
int index = hash(k);
if(table[index] == null){
return null;
}
return find(k, table[index]);
}
private V find(K k, Entry<K, V> entry) {
if(k == entry.getKey() || k.equals(entry.getKey())){
if(entry.next != null) {
System.out.println("1老Value:" + entry.next.getValue());
}
return entry.getValue();
}else {
if(entry.next != null){
System.out.println("2老Value:" + entry.next.getValue());
return find(k, entry.next);
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public int size() {
return size;
}
class Entry<K, V> implements Map.Entry<K,V>{
K k;
V v;
Entry<K,V> next;
public Entry(K k, V v, Entry<K, V> next) {
this.k = k;
this.v = v;
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public K getKey() {
return k;
}
@Override
public V getValue() {
return v;
}
}
}
3、测试
public class TestHashMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("z","1234");
//System.out.println("z:" + map.get("z"));
map.put("z","5678");
System.out.println("z:" + map.get("z"));
}
}
四、不足之处:
每当hashmap扩容的时候需要重新去add entry对象 需要重新Hash。然后放入新的entry table数组里面。影像效率。 如果你知道hashmap需要存多少个值,如几千或者几万的时候,最后就是先指定他们的扩容大小,防止在put的时候再次扩容。
作者:Work Hard Work Smart
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/linlf03/
欢迎任何形式的转载,未经作者同意,请保留此段声明!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号