Sentiment analysis in nlp
The goal of the program is to analysis the article title is Sarcasm or not, i use tensorflow 2.5 to solve this problem.
Dataset download url: https://www.kaggle.com/rmisra/news-headlines-dataset-for-sarcasm-detection/home
{ "article_link": "https://www.huffingtonpost.com/entry/versace-black-code_us_5861fbefe4b0de3a08f600d5", "headline": "former versace store clerk sues over secret 'black code' for minority shoppers", "is_sarcastic": 0 }
we want to depend on headline to predict the is_sarcastic, 1 means True,0 means False.
preprocessing
-
use pandas to read json file.
import pandas as pd # lines = True means headle the json for each line df = pd.read_json("Sarcasm_Headlines_Dataset_v2.json" ,lines="True") df ''' is_sarcastic headline article_link 0 1 thirtysomething sci... https://www.theonion.co... 1 0 dem rep. totally ... https://www.huffingtonpos.. '''
-
build list for each column
labels = [] sentences = [] urls = [] # a tips for convert series to list ''' type(df['is_sarcastic']) # Series type(df['is_sarcastic'].values) # ndarray type(df['is_sarcastic'].values.tolist()) # list ''' labels = df['is_sarcastic'].values.tolist() sentences = df['headline'].values.tolist() urls = df['article_link'].values.tolist() len(labels) # 28619 len(sentences) # 28619
-
split dataset into train set and test set
# train size is the 2/3 of the all dataset. train_size = int(len(labels) / 3 * 2) train_sentences = sentences[0: train_size] test_sentences = sentences[train_size:] train_y = labels[0:train_size] test_y = labels[train_size:]
-
init some parameter
# some parameter vocab_size = 10000 # input layer to embedding embedding_dim = 16 # each input sentence length max_length = 100 # padding method trunc_type='post' padding_type='post' # token the unfamiliar word oov_tok = "<OOV>"
-
preprocessing on train set and test set
# processing on train set and test set import numpy as np from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences tokenizer = Tokenizer(oov_token = oov_tok) tokenizer.fit_on_texts(train_sentences) train_X = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(train_sentences) # padding the data train_X = pad_sequences(train_X, maxlen = max_length, truncating = trunc_type, padding = padding_type) train_X[:2] # convery the list to nparray train_y = np.array(train_y) # same operator to test set test_X = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(test_sentences) test_X = pad_sequences(test_X , maxlen = max_length, truncating = trunc_type, padding = padding_type) test_y = np.array(test_y)
build the model
some important functions and args:
-
tf.keras.layers.Dense # Dense
implements the operation:output = activation(dot(input, kernel) + bias) , a NN layer-
activation # Activation function to use. If you don't specify anything, no activation is applied (ie. "linear" activation:
a(x) = x). -
use_bias # Boolean, whether the layer uses a bias vector.
-
-
tf.keras.Sequential # contain a linear stack of layer into a
tf.keras.Model. -
tf.keras.Model # to train and predict
-
config the model with losses and metrics with
model.compile(args)-
optimizer
-
some args
AdamRMSpropSGDAdagrad
-
-
loss # The loss value that will be minimized by the model will then be the sum of all individual losses.
-
some args
-
-
metrices # List of metrics to be evaluated by the model during training and testing.
-
some args
-
-
-
train the model with
model.fit(x=None,y=None)-
batch_size # Number of samples per gradient update. If unspecified,
batch_sizewill default to 32. -
epochs # Number of epochs to train the model
-
verbose # Verbosity mode. 0 = silent, 1 = progress bar, 2 = one line per epoch,verbose=2 is recommended when not running interactively
-
validation_data #( valid_X, valid_y )
-
-
-
tf.keras.layers.Embedding # Turns positive integers (indexes) into dense vectors of fixed size. as shown in following figure
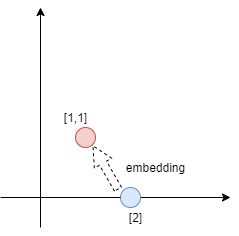
-
the purpose of the embedding is making the 1-dim integer proceed the muti-dim vectors add. can find the hide feature and connect to predict the labels. in this program ,every word's emotion direction can be trained many times.
-
-
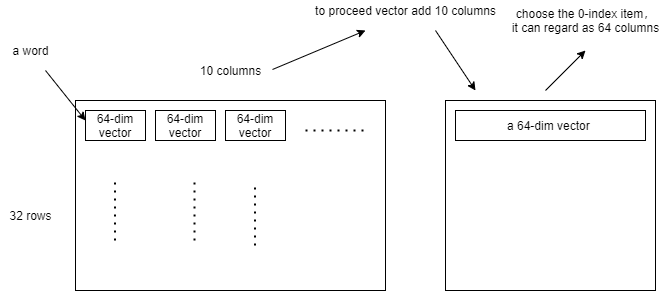
tf.keras.layer.GlobalAveragePooling1D # add all muti-dim vectors ,if the output layer shape is (32, 10, 64), after the pooling, the shape will be changed as (32,64), as shown in following figure
-
code is more simple then theory
# build the model model = tf.keras.Sequential( [ # make a word became a 64-dim vector tf.keras.layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim, input_length = max_length), # add all word vector tf.keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling1D(), # NN tf.keras.layers.Dense(24, activation = 'relu'), tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation = 'sigmoid') ] ) model.compile(loss = 'binary_crossentropy', optimizer = 'adam' , metrics = ['accuracy'])
train the model
num_epochs = 30 history = model.fit(train_X, train_y, epochs = num_epochs, validation_data = (test_X, test_y), verbose = 2)
after the 30 epochs
Epoch 30/30 597/597 - 8s - loss: 1.8816e-04 - accuracy: 1.0000 - val_loss: 1.2858 - val_accuracy: 0.8216
predict our sentence
mytest_sentence = ["you are so cute", "you are so cute but looks like stupid"] mytest_X = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(mytest_sentence) mytest_X = pad_sequences(mytest_X , maxlen = max_length, truncating = trunc_type, padding = padding_type) mytest_y = model.predict(mytest_X) # if result is bigger then 0.5 ,it means the title is Sarcasm print(mytest_y > 0.5) ''' [[False] [ True]] '''
reference:
tensorflow API: https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/Sequential
colab: bit.ly/tfw-sarcembed



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号