Java io流(二)
Java io 缓冲流
1. 字节缓冲流(bos,bis)
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out) | 创建字节缓冲输出流对象 |
| BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) | 创建字节缓冲输入流 |
1.2 字节缓冲流复制视频
package second;
import java.io.*;
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 3.基本字节流-输出流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("code\\1.mp4");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("E:\\javascript代码\\jsBOM和DOM\\day06" +
"\\07.zy.media.js插件的使用\\mov.mp4");
// 1.复制视频,比较各个复制的效率,缓冲输出流
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
// 2.缓冲输入流
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
// 开始时间
long startTime= System.currentTimeMillis();
// method1(bos,bis); 26ms 缓冲区单个字节
// method2(bos,bis); 2ms 缓冲区 字节数组
// method3(fis,fos); 3021ms 基本字节流-单个字节
// method4(fis,fos); 3157 基本字节流-字节数组
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("总时间"+(endTime-startTime));
}
// 一个一个字节的复制
public static void method1(BufferedOutputStream bos,BufferedInputStream bis) throws IOException {
int bt;
while((bt=bis.read())!=-1){
bos.write(bt);
}
}
// 2.使用字节数组获取原来
public static void method2(BufferedOutputStream bos,BufferedInputStream bis) throws IOException {
byte []bts=new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=bis.read(bts))!=-1){
bos.write(bts,0,len);
}
}
// 1.基本字节流一个一个写
public static void method3(FileInputStream fis,FileOutputStream fos) throws IOException {
int bt;
while((bt=fis.read())!=-1){
fos.write(bt);
}
}
// 2.基本字节流字节数组
public static void method4(FileInputStream fis,FileOutputStream fos) throws IOException {
byte []bts=new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=fis.read())!=-1){
fos.write(bts,0,len);
}
}
}
结论
- 缓冲流字节数组效率最高,基本字节流字节数组最慢
2. 字符流
- 定义:字符流=字节流+编码表,便于操作中文
2.1 常见的编码表
-
常见字符集
- ascll字符集
- GBK字符集:常用的中文编码,20000+汉字
- unicode字符集:UTF-8编码:万国码,一至4个字节
-
编码形式:
- ascll:一个字节编码
- 拉丁文等字符,两个字节编码
- 大部分常用字(包含中文),3个字节编码
- 极少使用的Unicode辅助字符,4字节编码
2.2 字符串的编码解码问题
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| bytes[] getBytes() | 使用平台默认字符集编码字节 |
| bytes[] getBytes(String charsetName) | 使用参数里的字符集编码字节 |
| String(bytes[]) | 使用默认字符集解码成字符串 |
| String(bytes[],String charsetName) | 使用参数里的字符集解码成字符串 |
示例
package second;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
public class Demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
// 1.定义一个字符串
String str="中国";
// 2.使用默认字符集编码
byte []arr=str.getBytes();
for(byte i:arr){
System.out.print(i);
System.out.print(",");
}
// 3.使用GBK编码
byte []arr1=str.getBytes("GBK");
System.out.println();
for(byte i:arr){
System.out.print(i+",");
}
// 使用默认的字符集解码
String str1=new String(arr);
System.out.println(str1);
// 使用GBK解码
String str2=new String(arr1,"GBK");
System.out.println(str2);
}
}
- 效果图

2.3 字符流中的编码解码问题
- InputStreamReader:是从字节流到字符流的桥梁
- OutputStreamWriter:是从字符流到字节流的桥梁
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| InputStreamReader(InputStream in) | 使用默认编码创建InputStreamReader对象 |
| InputStreamReader(InputStream in,String chasetName) | 使用参数的编码创建InputStreamReader对象 |
| OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out) | 使用默认编码创建osw对象 |
| OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out,String chasetName) | 使用参数的编码创建osw |
示例
package second;
import java.io.*;
public class Demo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.使用默认的编码创建InputStreamReader对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("code\\2.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("code\\3.txt",true);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
// 2.使用默认的编码创建OutStreamWriter对象
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos,"GBK");
// 直接使用字符写入数据,默认编码
osw.write("中国");
// int bt=isr.read();
// char cbt=(char)bt;
// System.out.println(cbt);
// 2.读取数组
int bt;
while((bt=isr.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)bt);
}
osw.close();
isr.close();
}
}
- 效果图

2.4 字符流写数据的方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| void write(int c) | 写入一个字符 |
| void write(byte []bys) | 写入一个字符数组 |
| void write(byte []bys int off,int len) | 写入字符数组的一部分 |
| void write(String str) | 写入一个字符串 |
| void write(String str,int off,int len) | 写入字符串的一部分 |
- 刷新和关闭的方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| flush() | 刷新流,之后可以继续写数据 |
| close() | 关闭流,释放资源,关闭之前会刷新流 |
示例
package second;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
public class Demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.创建输出流-字符输出流
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("code\\2.txt",true);
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos);
// 写入一个字符
osw.write('a');
// 写入一个字符数组
char []bys=new char[]{'a','b','c','d','e'};
osw.write(bys,1,3);
// 写入一个字符串
osw.write("abcdefgh",2,5);
osw.close();
}
}
- 效果图

2.5 字符流读数据的方法
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| int read() | 一次读一个字符 |
| int read(char[] cbuf) | 一次读一个字符数组 |
示例
package second;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class Demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.创建字符输入流对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("code\\3.txt");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis,"GBK");
// 一次读一个字符
int ch;
while((ch=isr.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)ch);
}
// 一次读一个字符数组
char []chs=new char[1024];
int len;
while((len=isr.read(chs))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(chs,0,len));
}
isr.close();
}
}
- 效果图

2.6 字符流复制文件(isr,osw)
package second;
import java.io.*;
public class Demo7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.创建字符流输入输出对象
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("F:\\BaiduNetdiskDownload\\第八卷生肉.txt");
final FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("code\\4.txt");
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis);
OutputStreamWriter osw = new OutputStreamWriter(fos);
int len;
char []chs=new char[1024];
while((len=isr.read(chs))!=-1){
osw.write(chs,0,len);
}
}
}
- 效果图

2.7 便捷流复制文件(FileReader)
package second;
import java.io.*;
public class Demo8 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.使用便捷流复制文件
// 1.创建便捷流对象
FileReader fr = new FileReader("F:\\BaiduNetdiskDownload\\第八卷生肉.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("code\\5.txt");
int len;
char chs[]=new char[1024];
while((len=fr.read(chs))!=-1){
fw.write(chs,0,len);
}
}
}
- 效果图

2.8 字符缓冲流
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| BufferedWriter(Write out) | 创建字符缓冲输出流对象 |
| BufferedReader(Reader in) | 创建字符缓冲输入流对象 |
示例
package second;
import java.io.*;
public class Demo9 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.字符流缓冲复制文件
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("F:\\BaiduNetdiskDownload\\第八卷生肉.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("code\\6.txt"));
// 以字符数组的形式复制
int len;
char []chs=new char[1024];
while((len=br.read(chs))!=-1){
bw.write(chs,0,len);
}
br.close();
bw.close();
}
}
- 效果图
2.9 字符缓冲流的特有方法
- BufferedWriter
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| void newLine() | 写一行分隔符,行风格字符串由系统属性定义 |
- BufferedReader
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| String readLine() | 读一行文字,结果包含行的内容字符串,不包括任何终止字符,如果流的结尾已经到达,则为null |
示例
package second;
import java.io.*;
public class Demo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.创建字符缓冲流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("code\\5.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("code\\5.txt"));
// 1.往5.txt写数据
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
bw.write("hello"+i);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
// 2.从5.txt中读取数据
String len;
// char []chs=new char[1024];
while((len=br.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println(len);
}
}
}
- 效果图

3. 总结
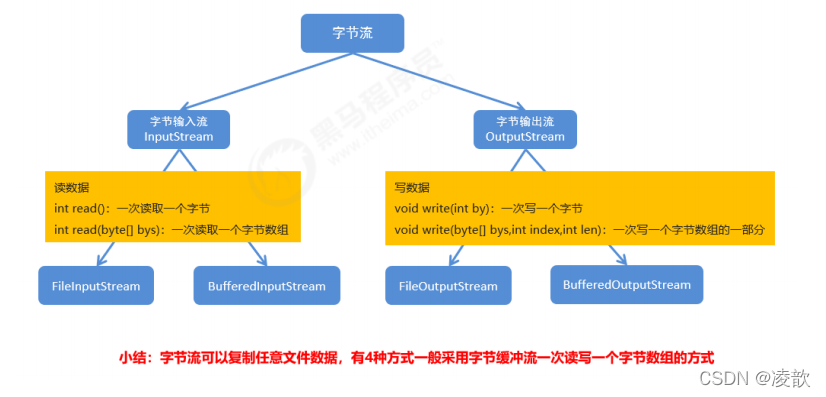

- 更多关于io流的类推荐查看jdk文档
4.案例
4.1 文件内容到集合
package second;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class demo11 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.创建字符缓冲对象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("code\\5.txt"));
ArrayList<String> strs = new ArrayList<String>();
String s;
// 1.每一行添加到集合
while((s=br.readLine())!=null){
strs.add(s);
}
br.close();
// 1.遍历集合
for(String line : strs){
System.out.println(line);
}
}
}
- 效果图

4.2 集合到文件
package second;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Demo12 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1.创建字符缓冲流对象
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("code\\6.txt",true));
ArrayList<String> strs = new ArrayList<String>();
strs.add("hello");
strs.add("world");
strs.add("happy");
// 遍历集合,写数据到文件
for(String s:strs){
bw.write(s);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
}
}
- 效果图

4.3 学生对象到文件
package second;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class StudentsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<Student>();
Student s1=new Student(12,"bob","heima001","北京");
Student s2=new Student(13,"kate","heima002","西安");
Student s3=new Student(14,"peter","heima003","娄底");
Student s4=new Student(15,"judy","heima004","湖南");
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("code\\7.txt"));
students.add(s1);
students.add(s2);
students.add(s3);
students.add(s4);
for(Student s:students){
String str="年龄:"+s.getAge()+" 姓名:"+s.getName()+" 学号:"+s.getSid()+" 地址:"+s.getAddress();
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
}
}
- 效果图

4.4 文件到学生对象
package second;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class StudentsTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ArrayList<Student> students = new ArrayList<Student>();
Student s1=new Student(12,"bob","heima001","北京");
Student s2=new Student(13,"kate","heima002","西安");
Student s3=new Student(14,"peter","heima003","娄底");
Student s4=new Student(15,"judy","heima004","湖南");
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("code\\7.txt"));
students.add(s1);
students.add(s2);
students.add(s3);
students.add(s4);
for(Student s:students){
String str="年龄:"+s.getAge()+" 姓名:"+s.getName()+" 学号:"+s.getSid()+" 地址:"+s.getAddress();
bw.write(str);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
// 文件到对象
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("code\\7.txt"));
String str;
while((str=br.readLine())!=null){
String[] strs = str.split(" ");
Student student = new Student();
int num=0;
for(String s:strs){
s=s.substring(3);
if(num==0){
student.setAge(Integer.parseInt(s));
}else if(num==1){
student.setName(s);
}else if(num==2){
student.setSid(s);
}else if(num==3){
student.setAddress(s);
}
num++;
}
students.add(student);
}
for(Student s:students){
String str1="年龄:"+s.getAge()+" 姓名:"+s.getName()+" 学号:"+s.getSid()+" 地址:"+s.getAddress();
System.out.println(str1);
}
}
}
- 效果图






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号