哈希表-集合-映射
哈希表-集合-映射
874. 模拟行走机器人
机器人在一个无限大小的 XY 网格平面上行走,从点 (0, 0) 处开始出发,面向北方。该机器人可以接收以下三种类型的命令 commands :
-2:向左转90度-1:向右转90度1 <= x <= 9:向前移动x个单位长度
在网格上有一些格子被视为障碍物 obstacles 。第 i 个障碍物位于网格点 obstacles[i] = (xi, yi) 。
机器人无法走到障碍物上,它将会停留在障碍物的前一个网格方块上,但仍然可以继续尝试进行该路线的其余部分。
返回从原点到机器人所有经过的路径点(坐标为整数)的最大欧式距离的平方。(即,如果距离为 5 ,则返回 25 )
注意:
- 北表示
+Y方向。 - 东表示
+X方向。 - 南表示
-Y方向。 - 西表示
-X方向。
示例 1:
输入:commands = [4,-1,3], obstacles = []
输出:25
解释:
机器人开始位于 (0, 0):
1. 向北移动 4 个单位,到达 (0, 4)
2. 右转
3. 向东移动 3 个单位,到达 (3, 4)
距离原点最远的是 (3, 4) ,距离为 32 + 42 = 25
示例 2:
输入:commands = [4,-1,4,-2,4], obstacles = [[2,4]]
输出:65
解释:机器人开始位于 (0, 0):
1. 向北移动 4 个单位,到达 (0, 4)
2. 右转
3. 向东移动 1 个单位,然后被位于 (2, 4) 的障碍物阻挡,机器人停在 (1, 4)
4. 左转
5. 向北走 4 个单位,到达 (1, 8)
距离原点最远的是 (1, 8) ,距离为 12 + 82 = 65
提示:
1 <= commands.length <= 104commands[i]is one of the values in the list[-2,-1,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9].0 <= obstacles.length <= 104-3 * 104 <= xi, yi <= 3 * 104- 答案保证小于
231
解题思路
1. 把障碍物位置存储到set中,hash实现,实现时间复杂度为O(1),即输入一个值,hash函数处理,得到值(可以理解为下标),看是否能在set集合中找到下标是否存了值O(1)
2. 每走一步,确定下一步是否有障碍物,没有,继续行走,计算一个最大值
/**
* @param {number[]} commands
* @param {number[][]} obstacles
* @return {number}
*/
var robotSim = function(commands, obstacles) {
// 使用set集合存放障碍物
let set=new Set()
for(let i=0;i<obstacles.length;i++){
set.add(obstacles[i][0]+","+obstacles[i][1])
}
// 定义一个方向数组,即机器人往某个方向移动时,x,y的变化
// 0 N 1 E 2 S 3 W
let dx=[0,1,0,-1]
let dy=[1,0,-1,0]
// 初始方向北
let dir=0
// 开始运行指令
let x=0
let y=0
let res=0
commands.forEach((command)=>{
// console.log(command,index)
if(command===-1){
// 右转
dir=(dir+1)%4
}else if(command===-2){
// 左转
dir=(dir+3)%4
}else{
// 正常行走
// console.log(dir)
for(let j=0;j<command;j++){
let nextX=x+dx[dir]
let nextY=y+dy[dir]
// 判断下一步的地方是否存在障碍物
if(set.has(nextX+","+nextY)){
// console.log(1)
break
}else{
x=nextX
y=nextY
res=Math.max(res,x*x+y*y)
}
}
}
})
// console.log(x,y)
return res
};
-
注意点
- 方向数组(这个可以记忆,作为一个解决方案,因为判断每次行走的下一步位置比较复杂(使用if,eles))
// 定义一个方向数组,即机器人往某个方向移动时,x,y的变化 // 0 N 1 E 2 S 3 W let dx=[0,1,0,-1] let dy=[1,0,-1,0] // 初始方向北 let dir=0
49. 字母异位词分组(模板题)
给你一个字符串数组,请你将 字母异位词 组合在一起。可以按任意顺序返回结果列表。
字母异位词 是由重新排列源单词的字母得到的一个新单词,所有源单词中的字母通常恰好只用一次。
示例 1:
输入: strs = ["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"]
输出: [["bat"],["nat","tan"],["ate","eat","tea"]]
示例 2:
输入: strs = [""]
输出: [[""]]
示例 3:
输入: strs = ["a"]
输出: [["a"]]
提示:
1 <= strs.length <= 1040 <= strs[i].length <= 100strs[i]仅包含小写字母
解题思路
1. 一个单词字母出现次数相同,排列不同,我们把它分为一组
3. 那我们把单词的字母顺序都排好,创建排好序的str==>[]的映射
4. 遇到一个排好序的与str(key)相同,把排序前的字符串push到映射数组中
5. 最后我们把拍好序的映射数组输出
完整代码
/**
* @param {string[]} strs
* @return {string[][]}
*/
var groupAnagrams = function(strs) {
// 字母相同,排列不同,我们让它们的排列相同
// 我们设置排序字符串 和 其字符串数组的映射(如果排序后字符串与key相同,则push)
let m=new Map()
for(let str of strs){
let sortStr=str.split("")
sortStr.sort((a,b)=>{
return a.charCodeAt()-b.charCodeAt()
})
sortStr=sortStr.join("")
// 设置映射关系
// let res=m.has(sortStr) ? m.get(sortStr).push(str) : [].push(str)
if(m.has(sortStr)){
// console.log(m.get(sortStr))
let arr=m.get(sortStr)
arr.push(str)
m.set(sortStr,arr)
}else{
let arr=[]
arr.push(str)
m.set(sortStr,arr)
}
}
let keys=m.keys()
let res=[]
for(let key of keys){
res.push(m.get(key))
}
return res
};
30. 串联所有单词的子串
给定一个字符串 s 和一个字符串数组 words。 words 中所有字符串 长度相同。
s 中的 串联子串 是指一个包含 words 中所有字符串以任意顺序排列连接起来的子串。
- 例如,如果
words = ["ab","cd","ef"], 那么"abcdef","abefcd","cdabef","cdefab","efabcd", 和"efcdab"都是串联子串。"acdbef"不是串联子串,因为他不是任何words排列的连接。
返回所有串联字串在 s 中的开始索引。你可以以 任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:s = "barfoothefoobarman", words = ["foo","bar"]
输出:[0,9]
解释:因为 words.length == 2 同时 words[i].length == 3,连接的子字符串的长度必须为 6。
子串 "barfoo" 开始位置是 0。它是 words 中以 ["bar","foo"] 顺序排列的连接。
子串 "foobar" 开始位置是 9。它是 words 中以 ["foo","bar"] 顺序排列的连接。
输出顺序无关紧要。返回 [9,0] 也是可以的。
示例 2:
输入:s = "wordgoodgoodgoodbestword", words = ["word","good","best","word"]
输出:[]
解释:因为 words.length == 4 并且 words[i].length == 4,所以串联子串的长度必须为 16。
s 中没有子串长度为 16 并且等于 words 的任何顺序排列的连接。
所以我们返回一个空数组。
示例 3:
输入:s = "barfoofoobarthefoobarman", words = ["bar","foo","the"]
输出:[6,9,12]
解释:因为 words.length == 3 并且 words[i].length == 3,所以串联子串的长度必须为 9。
子串 "foobarthe" 开始位置是 6。它是 words 中以 ["foo","bar","the"] 顺序排列的连接。
子串 "barthefoo" 开始位置是 9。它是 words 中以 ["bar","the","foo"] 顺序排列的连接。
子串 "thefoobar" 开始位置是 12。它是 words 中以 ["the","foo","bar"] 顺序排列的连接。
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 1041 <= words.length <= 50001 <= words[i].length <= 30words[i]和s由小写英文字母组成
解题思路
-
这题和49(上题思路一致)
-
这题我们把单词作为字母
-
计算单词出现的次数和给定的words数组中字母的出现次数是否相同
完整代码
/**
* @param {string} s
* @param {string[]} words
* @return {number[]}
*/
var findSubstring = function(s, words) {
let res=[]
// words数组每个单词出现次数对象
let wordsObj={}
for(let i=0;i<words.length;i++){
wordsObj[words[i]]=wordsObj[words[i]]===undefined? 1:wordsObj[words[i]]+1
}
// words数组每个单词出现次数对象
// 比较两个对象是否相同
const compareObj=(obj1,obj2)=>{
let obj1Props=Object.getOwnPropertyNames(obj1)
let obj2Props=Object.getOwnPropertyNames(obj2)
// 属性长度是否相同
if(obj1Props.length!==obj2Props.length){
return false
}
for(let i=0;i<obj1Props.length;i++){
propName=obj1Props[i]
let a=obj1[propName]
let b=obj2[propName]
if(a!==b){
return false
}
}
return true
}
// 枚举可能的字串
// 字串长度
let length=words.length*words[0].length
for(let i=0;i<=s.length-length;i++){
let sObj={}
for(let j=i;j<i+length;j+=words[0].length){
// 判断i到i+length这个字串是否包含words数组
// 把字符串切成words.length份
// let subStr=s.slice(i+j*words.length,i+((j+1)*words.length))
let subStr=s.slice(j,j+words[0].length)
sObj[subStr]=sObj[subStr]===undefined? 1:sObj[subStr]+1
}
// 判断一下sObj 与wordsObj是否相同
// console.log(sObj,wordsObj)
if(compareObj(wordsObj,sObj)){
res.push(i)
}
}
return res
};
146. LRU 缓存(高频题)
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity)以 正整数 作为容量capacity初始化 LRU 缓存int get(int key)如果关键字key存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回-1。void put(int key, int value)如果关键字key已经存在,则变更其数据值value;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组key-value。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过capacity,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。
函数 get 和 put 必须以 O(1) 的平均时间复杂度运行。
示例:
输入
["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"]
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
输出
[null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]
解释
LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2);
lRUCache.put(1, 1); // 缓存是 {1=1}
lRUCache.put(2, 2); // 缓存是 {1=1, 2=2}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 1
lRUCache.put(3, 3); // 该操作会使得关键字 2 作废,缓存是 {1=1, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(2); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.put(4, 4); // 该操作会使得关键字 1 作废,缓存是 {4=4, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(1); // 返回 -1 (未找到)
lRUCache.get(3); // 返回 3
lRUCache.get(4); // 返回 4
提示:
1 <= capacity <= 30000 <= key <= 100000 <= value <= 105- 最多调用
2 * 105次get和put
解题思路
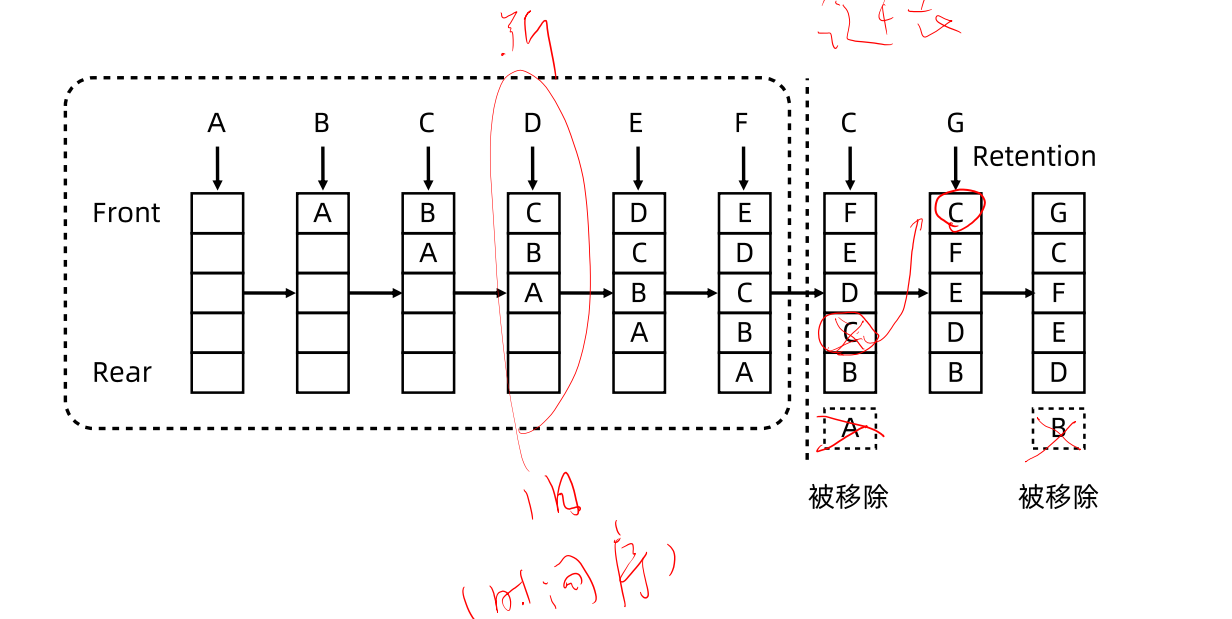
1. 最近最少使用,当容量达到最大时,每次挤出的都停留时间最长的===>可以使用最大堆(优先队列)
2. 使用双向链表+hash表,双向链表在删除和插入时为O(1),而在查询是为O(n) ,我们可以维护一个地址hash表(key==>node) node为链表节点地址
每次进入一个元素时(超出容量),看是否在hash表中,如果存在,则把hash表对应的节点删除,在重新在头部插入
不存在则删除最后一个节点,把新节点存入链表头部
同时保存hash映射 key==>node
完整代码(双向链表+hash)
// 解题思路
// 最近最少使用
// get和put都会算作访问最新的
// 1. 使用优先队列(最大堆),每次返回停留时间最长的
// 2. 使用双向链表+hash表(存放存入cache的地址),方便查询操作为O(1)
// node的数据结构
var Node = function (key, value, pre, next) {
this.key = key === undefined ? undefined : key
this.value = value === undefined ? undefined : value
this.pre = pre === undefined ? undefined : pre
this.next = next === undefined ? undefined : next
}
/**
* @param {number} capacity
*/
// 全局变量,存储一下cache最大值
// var capacity = 0
var LRUCache = function (capacity) {
this.maxCapacity = capacity
// 链表,我们创建保护节点
this.capacity = 0
this.map = new Map()
this.protectHead = new Node(-1, -1)
this.protectTail = new Node(-2, -2)
this.protectHead.next = this.protectTail
this.protectTail.pre = this.protectHead
}
/**
* @param {number} key
* @return {number}
*/
LRUCache.prototype.get = function (key) {
if (this.map.get(key)) {
// 刷新访问
let node = this.removeNode(this.map.get(key))
this.insertNode(key, node.value)
return node.value
} else {
return -1
}
}
/**
* @param {number} key
* @param {number} value
* @return {void}
*/
LRUCache.prototype.put = function (key, value) {
//这里使用头插法,最新的protectHead指向
if (this.map.has(key)) {
// 删除该节点,再重新插入
let node = this.removeNode(this.map.get(key))
// node.value=value
delete node
this.insertNode(key, value)
} else {
if (this.capacity + 1 > this.maxCapacity) {
// 超出cache最大值
// 把链表的尾部节点去除
this.removeNode(this.protectTail.pre)
// 新的插入
this.insertNode(key, value)
} else {
this.capacity++
this.insertNode(key, value)
}
}
}
LRUCache.prototype.insertNode = function (key, value) {
let node = new Node(key, value)
this.map.set(key, node)
// 头插入链表
this.protectHead.next.pre = node
node.next = this.protectHead.next
this.protectHead.next = node
node.pre = this.protectHead
}
LRUCache.prototype.removeNode = function (node) {
this.map.delete(node.key)
node.pre.next = node.next
node.next.pre = node.pre
return node
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号