Day8
一、Dynamic type——动态类型
1、Creating a dynamic object with properties——创建具有属性的动态对象
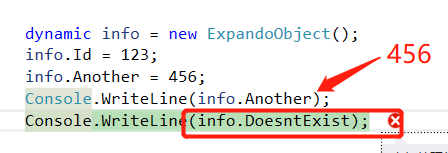
dynamic 类型是一种静态类型,但类型为 dynamic 的对象会跳过静态类型检查。因此,不会报告编译器错误。 但是,该错误不会被无限期疏忽。 它将在运行时被捕获,并导致运行时异常。
2、Creating a dynamic variable——创建动态变量

3、Returning dynamic
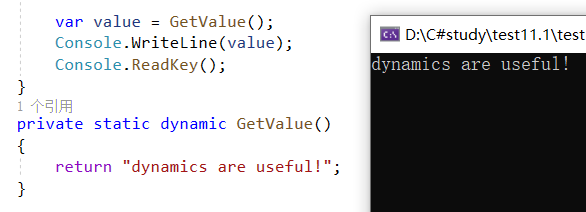
二、Type Conversion——类型转换
一般可以直接用类型家括号的形式,强转。或者用convert.类型。进行转换。
1、Explicit Type Conversion——显示类型转换
1 using System; 2 namespace TypeConversionApplication 3 { 4 class ExplicitConversion 5 { 6 static void Main(string[] args) 7 { 8 double d = 5673.74; 9 int i; 10 i = (int)d; 11 Console.WriteLine(i);// 结果: i = 5673 12 Console.ReadKey(); 13 } 14 } 15 }
2、隐式转换
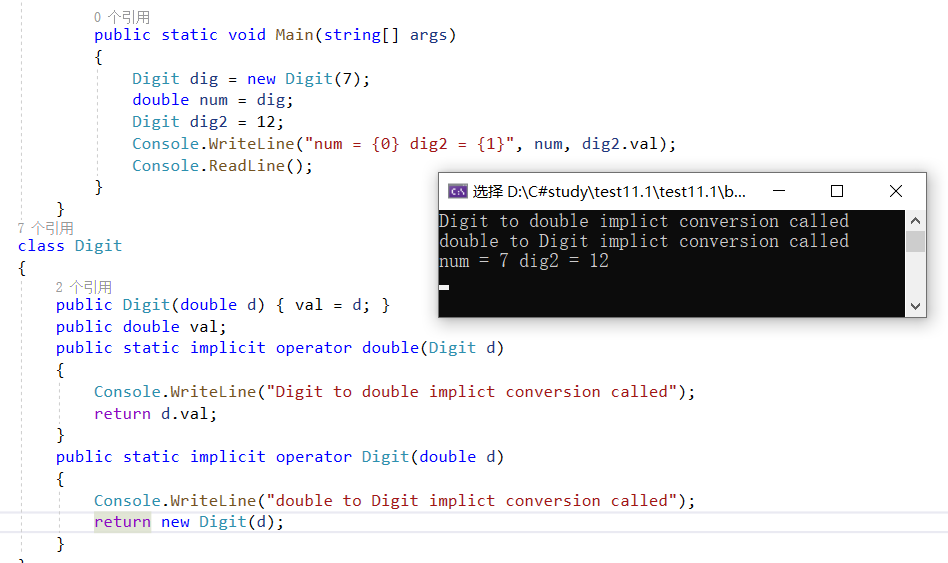
3、 LINQ Casting operations
1 double[] doubles = new[]{1,2,3}.Cast<double>().ToArray();//报错 2 double[] doubles = new[]{1,2,3}.Select(i => (double)i).ToArray();//正解
三、Casting
1、Checking compatibility without casting
1 if(value is int) 2 { 3 Console.WriteLine(value + "is an int"); 4 }
2、Cast an object to a base type
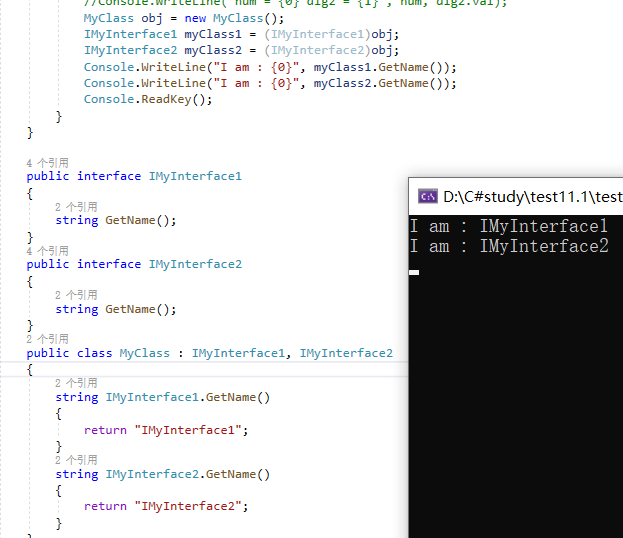
3、Explicit Casting
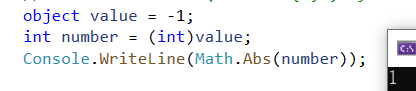
4、Safe Explicit Casting (`as` operator)
如果不确定一个值是否属于您认为的类型,您可以使用作为运算符安全地强制转换它。如果该值不是该类型的值,则生成的值将为空
1 object value = "-1"; 2 int? number = value as int?; 3 if(number != null) 4 { 5 Console.WriteLine(Math.Abs(number.Value)); 6 }
四、Nullable types
1: Initialising a nullable
下面都是判断是否i为null
1 Nullable<int> i = null; 2 int? i = null; 3 var i = (int?)null; 4 Nullable<int> i = 0; 5 int? i = 0;
2: Check if a Nullable has a value
1 int? i = null; 2 if (i != null) 3 { 4 Console.WriteLine("i is not null"); 5 } 6 else 7 { 8 Console.WriteLine("i is null"); 9 } 10 11 //———————————— 12 13 14 if (i.HasValue) 15 { 16 Console.WriteLine("i is not null"); 17 } 18 else 19 { 20 Console.WriteLine("i is null"); 21 }
3、Get the value of a nullable type
1 int? i = 10; 2 int j = i ?? 0; 3 int j = i.GetValueOrDefault(0); 4 int j = i.HasValue ? i.Value : 0;
4、Getting a default value from a nullable
1 class Program 2 { 3 static void Main() 4 { 5 int? nullableExample = null; 6 int result = nullableExample.GetValueOrDefault(); 7 Console.WriteLine(result); // will output the default value for int - 0 8 int secondResult = nullableExample.GetValueOrDefault(1); 9 Console.WriteLine(secondResult) // will output our specified default - 1 10 int thirdResult = nullableExample ?? 1; 11 Console.WriteLine(secondResult) // same as the GetValueOrDefault but a bit shorter 12 } 13 }
5、Default value of nullable types is null
1 public class NullableTypesExample 2 { 3 static int? _testValue; 4 public static void Main() 5 { 6 if(_testValue == null) 7 Console.WriteLine("null"); 8 else 9 Console.WriteLine(_testValue.ToString()); 10 } 11 }
输出:null
五、Interfaces——接口
1、Implementing an interface——实现一个接口
1 public interface INoiseMaker 2 { 3 string MakeNoise(); 4 } 5 public class Cat : INoiseMaker 6 { 7 public string MakeNoise() 8 { 9 return "Nyan"; 10 } 11 } 12 public class Dog : INoiseMaker 13 { 14 public string MakeNoise() 15 { 16 return "Woof"; 17 } 18 }
2、Implementing multiple interfaces
1 public interface IAnimal 2 { 3 string Name { get; set; } 4 } 5 public interface INoiseMaker 6 { 7 string MakeNoise(); 8 } 9 public class Cat : IAnimal, INoiseMaker 10 { 11 public Cat() 12 { 13 Name = "Cat"; 14 } 15 public string Name { get; set; } 16 public string MakeNoise() 17 { 18 return "Nyan"; 19 } 20 }
3、使用多接口
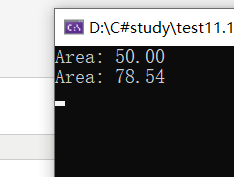
1 using System; 2 using System.Collections.Generic; 3 4 delegate T NumberChanger<T>(T n); 5 6 namespace test11._1 7 { 8 public interface IShape 9 { 10 double ComputeArea(); 11 } 12 class Program 13 { 14 public static void Main(string[] args) 15 { 16 var shapes = new List<IShape>() { new Rectangle(5, 10), new Circle(5) }; 17 ComputeArea(shapes); 18 Console.ReadKey(); 19 } 20 private static void ComputeArea(IEnumerable<IShape> shapes) 21 { 22 foreach (var shape in shapes) 23 { 24 Console.WriteLine("Area: {0:N}", shape.ComputeArea());25 } 26 } 28 } 29 public class Rectangle : IShape 30 { 31 private double length; 32 private double width; 33 34 public Rectangle(double length, double width) 35 { 36 this.length = length; 37 this.width = width; 38 } 39 40 public double ComputeArea() 41 { 42 return length * width; 43 } 44 } 45 public class Circle : IShape 46 { 47 private double radius; 48 public Circle(double radius) 49 { 50 this.radius = radius; 51 } 52 public double ComputeArea() 53 { 54 return Math.Pow(radius, 2.0) * Math.PI; 55 } 56 } 57 58 }
运行结果:
六、静态类
1、静态类
“静态”关键字在一个类有三个效果:
1.您不能创建一个静态类的实例(这甚至删除了默认的构造函数)
2.类中的所有属性和方法也必须是静态的。
3.一个静态类是一个密封的类,这意味着它不能被继承。
2、静态类等级
静态类在成员访问上延迟初始化,并在应用程序域期间一直存在。
3、静态类关键字
静态关键字意味着两件事:
1。这个值不会从对象改变到对象,而是在一个类上改变。
2。静态属性和方法不需要一个实例。
1 public class Foo 2 { 3 public Foo{ 4 Counter++; 5 NonStaticCounter++; 6 } 7 public static int Counter { get; set; } 8 public int NonStaticCounter { get; set; } 9 } 10 public class Program 11 { 12 static void Main(string[] args) 13 { 14 //创建实例 15 var foo1 = new Foo(); 16 Console.WriteLine(foo1.NonStaticCounter); //结果 "1" 17 //这个下一个调用并不访问实例,而是通过类名进行调用。 18 Console.WriteLine(Foo.Counter); //结果 "1" 19 //创建第二个实例 20 var foo2 = new Foo(); 21 Console.WriteLine(foo2.NonStaticCounter); //结果 "1" 22 Console.WriteLine(Foo.Counter); //结果 "2" 23 //静态属性在两个实例上都递增,并且可以对整个类持续化 24 }
七、Singleton Implementation——单例实现
1、Statically Initialized Singleton——静态初始化的实例
1 public class Singleton 2 { 3 private readonly static Singleton instance = new Singleton(); 4 private Singleton() { } 5 public static Singleton Instance => instance; 6 }
这个实现是线程安全的,因为在这种情况下,实例对象是在静态构造函数中初始化的。CLR已经确保了所有静态构造函数都是以线程安全执行的。突变实例不是一个线程安全的操作,因此只读属性保证了初始化后的不变性。
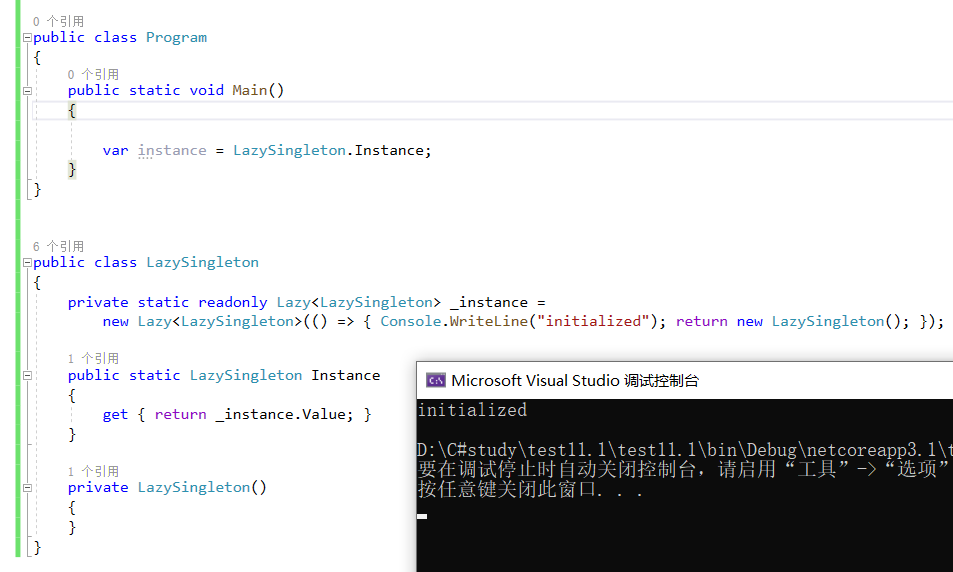
2、 Lazy, thread-safe Singleton (using Lazy<T>)
八、依赖注入
1、Dependency Injection C# and ASP.NET with Unity
首先,为什么我们要在代码中使用依赖注入?我们希望将其他组件从其他我们程序中的类。例如,我们有一个类AnimalController,它有这样的代码:
1 public class AnimalController() 2 { 3 private SantaAndHisReindeer _SantaAndHisReindeer = new SantaAndHisReindeer(); 4 public AnimalController(){ 5 Console.WriteLine(""); 6 } 7 }
九、部分类和方法
1、部分类
部分类提供了将类声明(通常分割为单独的文件)的能力。可以用部分类解决的一个常见问题是,允许用户修改自动生成的代码,而不用担心如果重新生成代码,他们的更改会被覆盖。此外,多个开发人员还可以使用同一个类或方法。

2、 Partial classes inheriting from a base class
您不能在多个部分类中指定不同的基类,这将导致编译器错误。例如:
1 public partial class PartialClass : BaseClass {} ;//错误 2 public partial class PartialClass : OtherBaseClass {} ;//错误
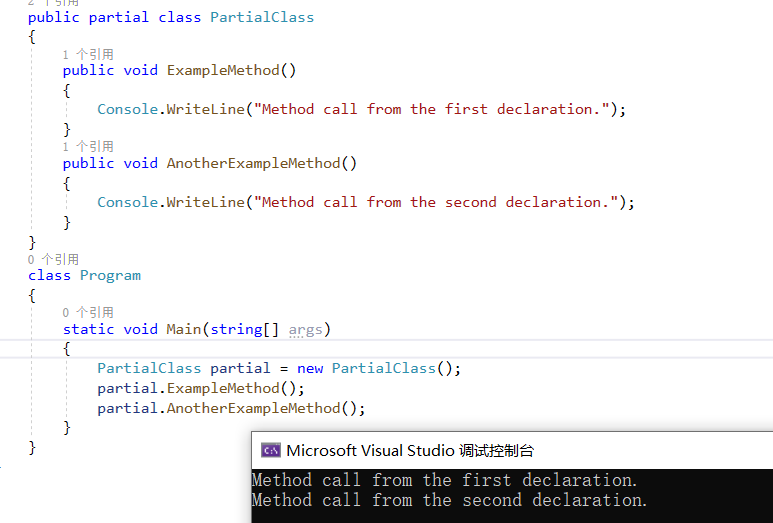
3、Partial methods
部分方法由一个部分类声明中的定义(作为一个常见的场景-在自动生成的场景中)和在另一个部分类声明中的实现组成。
1 using System; 2 namespace PartialClassAndMethods 3 { 4 public partial class PartialClass // 自动生成 5 { 6 partial void PartialMethod(); 7 } 8 public partial class PartialClass // 人为写的 9 { 10 public void PartialMethod() 11 { 12 Console.WriteLine("Partial method called."); 13 } 14 } 15 class Program 16 { 17 static void Main(string[] args) 18 { 19 PartialClass partial = new PartialClass(); 20 partial.PartialMethod(); // outputs "Partial method called." 21 } 22 } 23 }
十、方法
1、 Calling a Method——调用方法
调用静态方法
1 System.Console.WriteLine("Hello World"); 2 3 string name = "User"; 4 System.Console.WriteLine("Hello, {0}!", name);
调用一个静态方法并存储其返回值:
1 string input = System.Console.ReadLine();
调用实例方法
1 int x = 42; 2 string xAsString = x.ToString();
2、Anonymous method
匿名方法提供了一种将代码块作为委托参数传递的技术。它们是带有身体的方法,但没有名字。
1 delegate int IntOp(int lhs, int rhs); 2 class Program 3 { 4 static void Main(string[] args) 5 { 6 // C# 2.0 definition 7 IntOp add = delegate(int lhs, int rhs) 8 { 9 return lhs + rhs; 10 }; 11 // C# 3.0 definition 12 IntOp mul = (lhs, rhs) => 13 { 14 return lhs * rhs; 15 }; 16 // C# 3.0 definition - shorthand 17 IntOp sub = (lhs, rhs) => lhs - rhs; 18 // Calling each method 19 Console.WriteLine("2 + 3 = " + add(2, 3)); 20 Console.WriteLine("2 * 3 = " + mul(2, 3)); 21 Console.WriteLine("2 - 3 = " + sub(2, 3)); 22 } 23 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号