Day7
一、Looping
1、for 循环
1 for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) 2 { 3 Console.WriteLine(i); 4 } 5 //输出: 6 //0 7 //1 8 //2 9 //3 10 //4
2、do-while循环
1 int[] numbers = new int[] { 6, 7, 8, 10 }; 2 int sum = 0; 3 int i = 0; 4 do 5 { 6 sum += numbers[i]; 7 i++; 8 } while (sum <= 10 && i < numbers.Length); 9 10 System.Console.WriteLine(sum); //输出 13
3、Foreach 循环
1 var list = new List<string>(); 2 list.Add("Ion"); 3 list.Add("Andrei"); 4 foreach(var name in list) 5 { 6 Console.WriteLine("Hello " + name); 7 } 8 9 //相当于 10 var list = new List<string>(); 11 list.Add("Ion"); 12 list.Add("Andrei"); 13 IEnumerator enumerator; 14 try 15 { 16 enumerator = list.GetEnumerator(); 17 while(enumerator.MoveNext()) 18 { 19 string name = (string)enumerator.Current; 20 Console.WriteLine("Hello " + name); 21 } 22 } 23 finally 24 { 25 if (enumerator != null) 26 enumerator.Dispose(); 27 }
4、循环样式
While
1 while(条件) 2 { 3 4 }
Do
1 do 2 { 3 4 } while(条件)
For
1 for ( int i = 0; i < array.Count; i++ ) 2 { 3 var currentItem = array[i]; 4 }
Foreach
1 foreach ( var item in someList ) 2 { 3 }
Foreach Method
1 list.ForEach(item => item.DoSomething()); 2 //或者 3 list.ForEach(item => DoSomething(item)); 4 // 或使用一个方法组 5 list.ForEach(Console.WriteLine); 6 // 使用一个数组 7 Array.ForEach(myArray, Console.WriteLine);
5、嵌套循环
双层for
1 for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) 2 { 3 for (int j = 1; j <= 5; j++) 4 { 5 int product = i * j; 6 Console.WriteLine("{0} times {1} is {2}", i, j, product); 7 } 8 }
6、continue
结束当前循环
1 for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++) 2 { 3 if (i < 9) 4 continue; 5 Console.WriteLine(i); 6 } 7 //结果是9(换行)10
7、while循环
1 int n = 0; 2 while (n < 5) 3 { 4 Console.WriteLine(n); 5 n++; 6 } 8 /*结果 9 0 10 1 11 2 12 3 13 4 14 */
8、break
结束本次循环。
六、指类型与参考类型
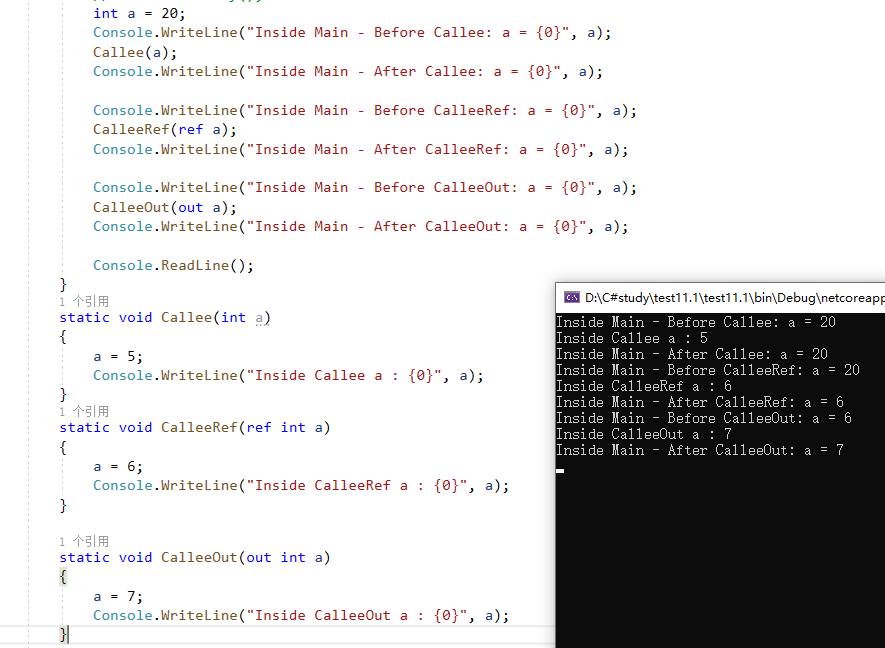
1、 Passing by reference using ref keyword——使用ref关键字通过引用传递
2、Changing values elsewhere
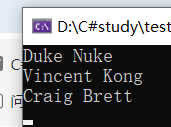
1 class Program 2 { 3 public static void Main() 4 { 5 var studentList = new List<Student>(); 6 studentList.Add(new Student("Scott", "Nuke")); 7 studentList.Add(new Student("Vincent", "King")); 8 studentList.Add(new Student("Craig", "Bertt")); 9 studentList[0].FirstName = "Duke"; 10 studentList[1].LastName = "Kong"; 11 studentList[2].LastName = "Brett"; 12 PrintPrintingList(studentList); 13 14 Console.ReadKey(); 15 } 16 private static void PrintPrintingList(List<Student> students) 17 { 18 foreach (Student student in students) 19 { 20 Console.WriteLine(string.Format("{0} {1}", student.FirstName, student.LastName)); 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 public class Student 25 { 26 public string FirstName { get; set; } 27 public string LastName { get; set; } 28 public Student(string firstName, string lastName) 29 { 30 this.FirstName = firstName; 31 this.LastName = lastName; 32 } 33 }
结果:
3、Assignment
分配给List<int>的变量不会创建List<int>的副本。相反,它将引用复制到List<int>。我们调用以这种方式的类型引用类型。
1 var a = new List<int>(); 2 var b = a; 3 a.Add(5); 4 Console.WriteLine(a.Count); // 结果: 1 5 Console.WriteLine(b.Count); // 结果: 1
4、 Passing by reference——通过引用值传递
1 public static void Main(string[] args) 2 { 3 ... 4 DoubleNumber(ref number); 5 Console.WriteLine(number); // 输出8 6 ... 7 } 8 public void DoubleNumber(ref int number) 9 { 10 number += number; 11 }
七、Built-in Types——内置类型
1、Conversion of boxed value types——盒装值类型的转换(像强制转换)

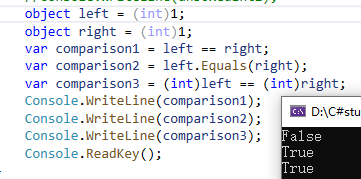
2、Comparisons with boxed value types
3、Immutable reference type - string——不可变的引用类型-字符串
以下三种,s的输出都是hello.
// assign string from a string literal string s = "hello"; // assign string from an array of characters char[] chars = new char[] { 'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o' }; string s = new string(chars, 0, chars.Length); // assign string from a char pointer, derived from a string string s; unsafe { fixed (char* charPointer = "hello") { s = new string(charPointer); } }
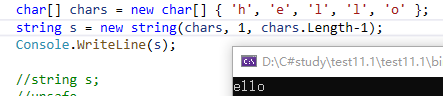
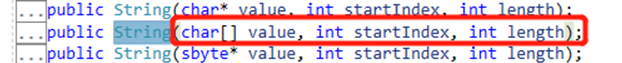
此处string 是重写的,以下是里面参数。第二个startIndex,字符开始的地方,同样的,第几个开始,后面对应的字符的长度就要对应的减去。
八、Aliases of built-in types
1、Built-In Types Table——内置类型表
常用的:
1 //C# Type .NET Framework Type 2 bool System.Boolean 3 byte System.Byte 4 sbyte System.SByte 5 char System.Char 6 decimal System.Decimal 7 double System.Double 8 float System.Single 9 int System.Int32 10 uint System.UInt32 11 long System.Int64 12 ulong System.UInt64 13 object System.Object 14 short System.Int16 15 ushort System.UInt16 16 string System.String
1 int number = 123; 2 System.Int32 number = 123;
int和Syetem.Int32之间可以相互替换
九、Anonymous types——匿名类型
1、Creating an anonymous type
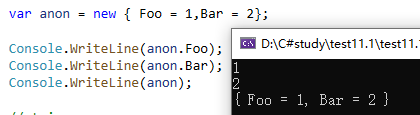
1 string foo = "some string"; 2 var anon3 = new { foo.Length }; 3 // anon3.Length == 11 4 var anon4 = new { foo.Length <= 10 ? "short string" : "long string" }; 5 // compiler error - Invalid anonymous type member declarator. 6 var anon5 = new { Description = foo.Length <= 10 ? "short string" : "long string" }; 7 // OK
2、Anonymous type equalit
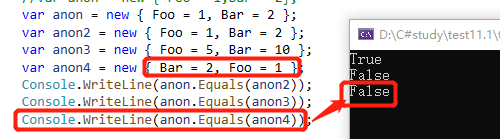
注意:当且仅当两种匿名类型的属性具有相同的名称和类型,且以相同的顺序出现时,才认为这两种匿名类型是相同的。
3、Generic methods with anonymous types
泛型方法允许通过类型推理来使用匿名类型。这意味着LINQ表达式可以与匿名类型一起使用:
1 var products = new[] { 2 new { Amount = 10, Id = 0 }, 3 new { Amount = 20, Id = 1 }, 4 new { Amount = 15, Id = 2 } 5 }; 6 var idsByAmount = products.OrderBy(x => x.Amount).Select(x => x.Id); 7 // 这里idsByAmount: 0, 2, 1
4、Instantiating generic types with anonymous types ——使用匿名类型实例化泛型类型(见泛型&匿名中的例子)
1 var anon = new { Foo = 1, Bar = 2 }; 2 var anon2 = new { Foo = 5, Bar = 10 }; 3 List<T> CreateList<T>(params T[] items) { 4 return new List<T>(items); 5 } 6 var list1 = CreateList(anon, anon2);
5、Implicitly typed arrays ——隐式类型的数组
var arr = new[] { new { Id = 0 }, new { Id = 1 } };



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号