python 数据加载
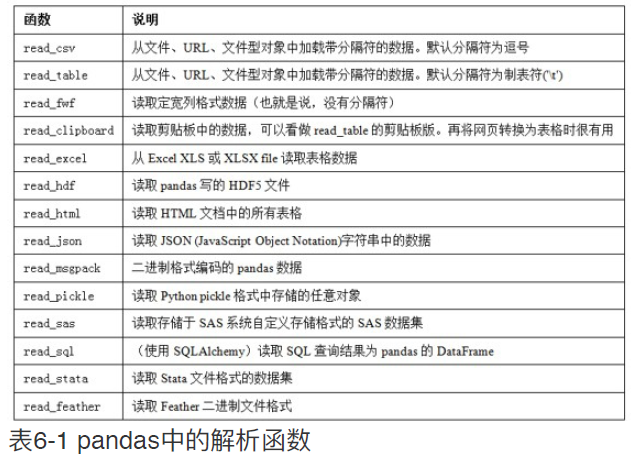
pandas提供了⼀些⽤于将表格型数据读取为DataFrame对象的
函数。表6-1对它们进⾏了总结,其中read_csv和read_table可能
会是你今后⽤得最多的。
1.read_csv

1. In [9]: df = pd.read_csv('examples/ex1.csv') In [10]: df Out[10]: a b c d message 0 1 2 3 4 hello 1 5 6 7 8 world 2 9 10 11 12 foo 2. 我们还可以使⽤read_table,并指定分隔符: In [11]: pd.read_table('examples/ex1.csv', sep=',') Out[11]: a b c d message 0 1 2 3 4 hello 1 5 6 7 8 world 2 9 10 11 12 foo 3. 并不是所有⽂件都有标题⾏。看看下⾯这个⽂件: In [12]: !cat examples/ex2.csv 1,2,3,4,hello 5,6,7,8,world 9,10,11,12,foo 读⼊该⽂件的办法有两个。你可以让pandas为其分配默认的列 名,也可以⾃⼰定义列名: In [13]: pd.read_csv('examples/ex2.csv', header=None) Out[13]: 0 1 2 3 4 0 1 2 3 4 hello 1 5 6 7 8 world 2 9 10 11 12 foo In [14]: pd.read_csv('examples/ex2.csv', names=['a', 'b', 'c', Out[14]: a b c d message 0 1 2 3 4 hello 1 5 6 7 8 world 2 9 10 11 12 foo 假设你希望将message列做成DataFrame的索引。你可以明确表 示要将该列放到索引4的位置上,也可以通过index_col参数指 定"message": a=pd.read_csv('D:/pyworkspace/githubdata/ex2.csv',names=names,index_col='message') print(a) Out[16]: a b c d message hello 1 2 3 4 world 5 6 7 8 foo 9 10 11 12 4. 如果希望将多个列做成⼀个层次化索引,只需传⼊由列编号或列 名组成的列表即可: In [17]: !cat examples/csv_mindex.csv key1,key2,value1,value2 one,a,1,2 one,b,3,4 one,c,5,6 one,d,7,8 two,a,9,10 two,b,11,12 two,c,13,14 two,d,15,16 In [18]: parsed = pd.read_csv('examples/csv_mindex.csv', ....: index_col=['key1', 'key2']) In [19]: parsed Out[19]: value1 value2 key1 key2 one a 1 2 b 3 4 c 5 6 d 7 8 two a 9 10 b 11 12 c 13 14 d 15 16 5.有些情况下,有些表格可能不是⽤固定的分隔符去分隔字段的 (⽐如空⽩符或其他模式)。有些表格可能不是⽤固定的分隔符 去分隔字段的(⽐如空⽩符或其他模式来分隔字段)。看看下⾯ 这个⽂本⽂件: In [20]: list(open('examples/ex3.txt')) Out[20]: [' A B C\n', 'aaa -0.264438 -1.026059 -0.619500\n', 'bbb 0.927272 0.302904 -0.032399\n', 'ccc -0.264273 -0.386314 -0.217601\n', 'ddd -0.871858 -0.348382 1.100491\n'] In [21]: result = pd.read_table('examples/ex3.txt', sep='\s+') In [22]: result Out[22]: A B C aaa -0.264438 -1.026059 -0.619500 bbb 0.927272 0.302904 -0.032399 ccc -0.264273 -0.386314 -0.217601 ddd -0.871858 -0.348382 1.100491

a=pd.read_table('D:/pyworkspace/githubdata/ex4.csv',skiprows=[0,2,3]) 1.skiprows:忽略某行 2.na_values=['4']指定某个值为参数 3.pd.isnull() In [27]: result Out[27]: something a b c d message 0 one 1 2 3.0 4 NaN 1 two 5 6 NaN 8 world 2 three 9 10 11.0 12 foo In [28]: pd.isnull(result) Out[28]: something a b c d message 0 False False False False False True 1 False False False True False False 2 False False False False False False 4.字典的各列可以使⽤不同的NA标记值: In [31]: sentinels = {'message': ['foo', 'NA'], 'something': ['one']} In [32]: pd.read_csv('examples/ex5.csv', na_values=sentinels) something a b c d message 0 one 1 2 3.0 4 NaN 1 NaN 5 6 NaN 8 world 2 three 9 10 11.0 12 NaN
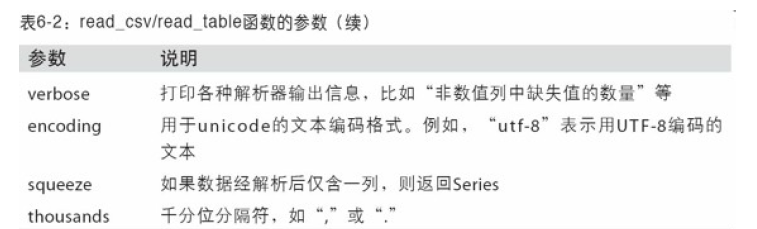
2.pandas.read_csv和pandas.read_table常⽤的选
项。



在处理很⼤的⽂件时,或找出⼤⽂件中的参数集以便于后续处理 时,你可能只想读取⽂件的⼀⼩部分或逐块对⽂件进⾏迭代。 在看⼤⽂件之前,我们先设置pandas显示地更紧些: pd.options.display.max_rows=10 In [34]: result = pd.read_csv('examples/ex6.csv') In [35]: result Out[35]: one two three four key 0 0.467976 -0.038649 -0.295344 -1.824726 L 1 -0.358893 1.404453 0.704965 -0.200638 B 2 -0.501840 0.659254 -0.421691 -0.057688 G 3 0.204886 1.074134 1.388361 -0.982404 R 4 0.354628 -0.133116 0.283763 -0.837063 Q ... ... ... ... ... .. 9995 2.311896 -0.417070 -1.409599 -0.515821 L 9996 -0.479893 -0.650419 0.745152 -0.646038 E 9997 0.523331 0.787112 0.486066 1.093156 K 9998 -0.362559 0.598894 -1.843201 0.887292 G 9999 -0.096376 -1.012999 -0.657431 -0.573315 0 [10000 rows x 5 columns] 如果只想读取⼏⾏(避免读取整个⽂件),通过nrows进⾏指定 即可: In [36]: pd.read_csv('examples/ex6.csv', nrows=5) Out[36]: one two three four key 0 0.467976 -0.038649 -0.295344 -1.824726 L 1 -0.358893 1.404453 0.704965 -0.200638 B 2 -0.501840 0.659254 -0.421691 -0.057688 G 3 0.204886 1.074134 1.388361 -0.982404 R 4 0.354628 -0.133116 0.283763 -0.837063 Q 要逐块读取⽂件,可以指定chunksize(⾏数): In [874]: chunker = pd.read_csv('ch06/ex6.csv', chunksize=1000) In [875]: chunker Out[875]: <pandas.io.parsers.TextParser at 0x8398150>
3.输出数据到文件

In [41]: data = pd.read_csv('examples/ex5.csv') In [42]: data Out[42]: something a b c d message 0 one 1 2 3.0 4 NaN 1 two 5 6 NaN 8 world 2 three 9 10 11.0 12 foo sep分割符 利⽤DataFrame的to_csv⽅法,我们可以将数据写到⼀个以逗号 分隔的⽂件中: In [43]: data.to_csv('examples/out.csv',sep='|') |something|a|b|c|d|message 0|one|1|2|3.0|4| 1|two|5|6||8|world 2|three|9|10|11.0|12|foo na_rep='我为空'方法 In [47]: data.to_csv('examples/out.csv', na_rep='我为空') Unnamed: 0 something a b c d message 0 0 one 1 2 3.0 4 我为空 1 1 two 5 6 我为空 8 world 2 2 three 9 10 11.0 12 foo




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号