IO流-字节流
IO流-字节流



/*
FileOutputStream: 文件输出流用于将数据写入File
FileOutputStream(String name): 创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件
*/
package IO.ByteStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class FileOutputStream_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节流输出对象
FileOutputStream fops = new FileOutputStream("D:\\2\\fops.txt");
/*
做了三件事:
1. 调用系统功能创建了文件
2. 创建字节流输出对象
3. 让字节流输出对象指向创建好的文件
*/
// void write (int b): 将指定的字节写入此文件输出流
fops.write(97);//a
fops.write(57);//9
fops.write(55);//7
//在相关IO操作时,最后都要释放资源.
// void close(): 关闭此文件输出流并释放与此流相关联的任何系统资源.
fops.close();
}
}
/*
构造方法:
FileOutputStream(String name):创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件
FileOutputStream(File file):创建文件输出流以写入由指定的 File对象表示的文件
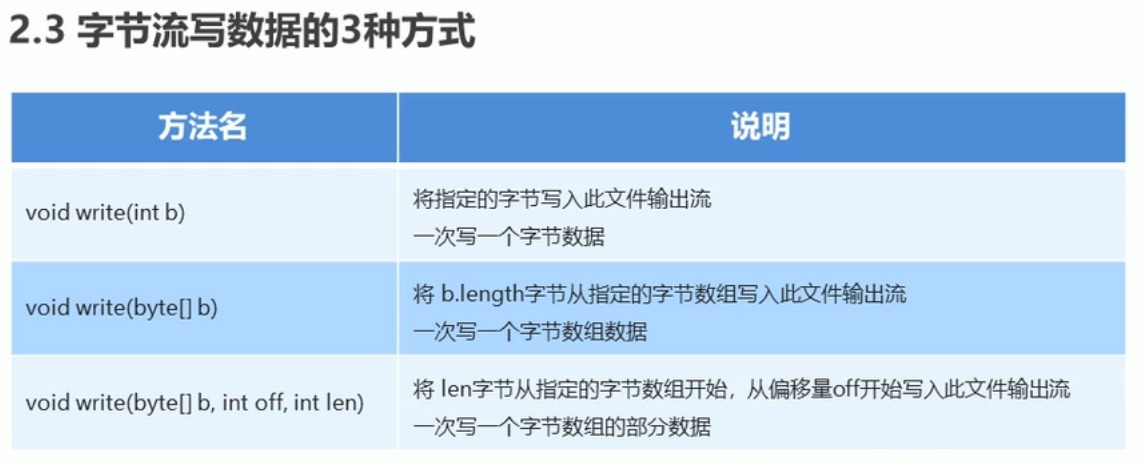
写数据的三种方式:
void write (int b):将指定的字节写入此文件输出流
一次写一个字节数据
void write (byte[] b):将 b.length字节从指定的字节数组写入此文件输出流
一次写一个字节数组数据
void write (byte[] b, int off, int Len):将 Len字节从指定的字节数组开始,从偏移量off开始写入此文件输出流
一次写一个字节数组的部分数据
*/
package IO.ByteStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class ByteStream_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//FileOutputStream(String name):创建文件输出流以指定的名称写入文件
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("d:\\2\\abc.txt");
//FileOutputStream(File file):创建文件输出流以写入由指定的 File对象表示的文件
// FileOutputStream fos1 = new FileOutputStream(new File("d:\\2\\abc1"));
//这两个构造方法作用是一样的,用第一个比较方便
/*写数据的三种方式:
void write (int b):将指定的字节写入此文件输出流
一次写一个字节数据*/
// fos.write(97);
// fos.write(98);
// fos.write(99);
// fos.write(100);
/*void write (byte[] b):将 b.length字节从指定的字节数组写入此文件输出流
一次写一个字节数组数据*/
byte [] arr = {97,98,99,100,101};
// fos.write(arr);
//String类中的getByet方法可以把字符串转成byet数组
byte[] bytes = "abcde(f)g_+!@".getBytes();
// fos.write(bytes);//写入文件 abcde(f)g_+!@
/*void write (byte[] b, int off, int Len):将 Len字节从指定的字节数组开始,从偏移量off开始写入此文件输出流
一次写一个字节数组的部分数据 */
fos.write(bytes,1,6); // 就是按数组指定的索引开始写入指定长度的数据, bcde(f
//最后不要忘了释放资源
fos.close();
}
}
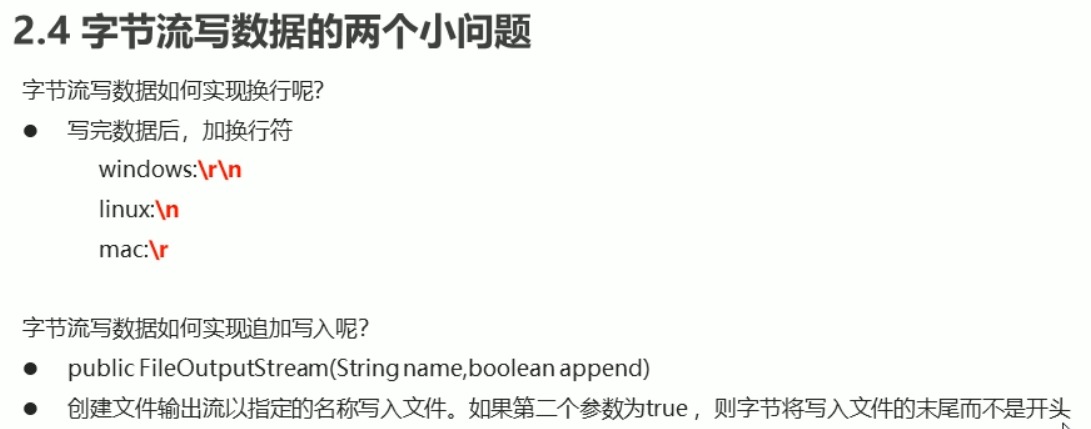
/*字节流写数据的两个小问题:
1: 字节流写数据如何实现换行?
写入换行符就能换行了
不同系统对换行符识别不同
Windows :\r \n
Linux : \n
mac : \r
2: 字节流写数据如何实现追加写入?
使用这个构造方法就能实现追加写入:
public FileOutputStream(String name, boolean append)如果第二个参数为true,
字节将写入文件的末尾而不是开头.
*/
package IO.ByteStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteStream_3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输出流对象 第二个参数为true就追加写入
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("d:\\2\\fileOutputStream.txt",true);
//写数据
for (int i = 0;i<3;i++){
fos.write("Hello,World!".getBytes());
fos.write("\r\n".getBytes()); //再写入\r\n就会换行
}
//释放资源
fos.close();
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号