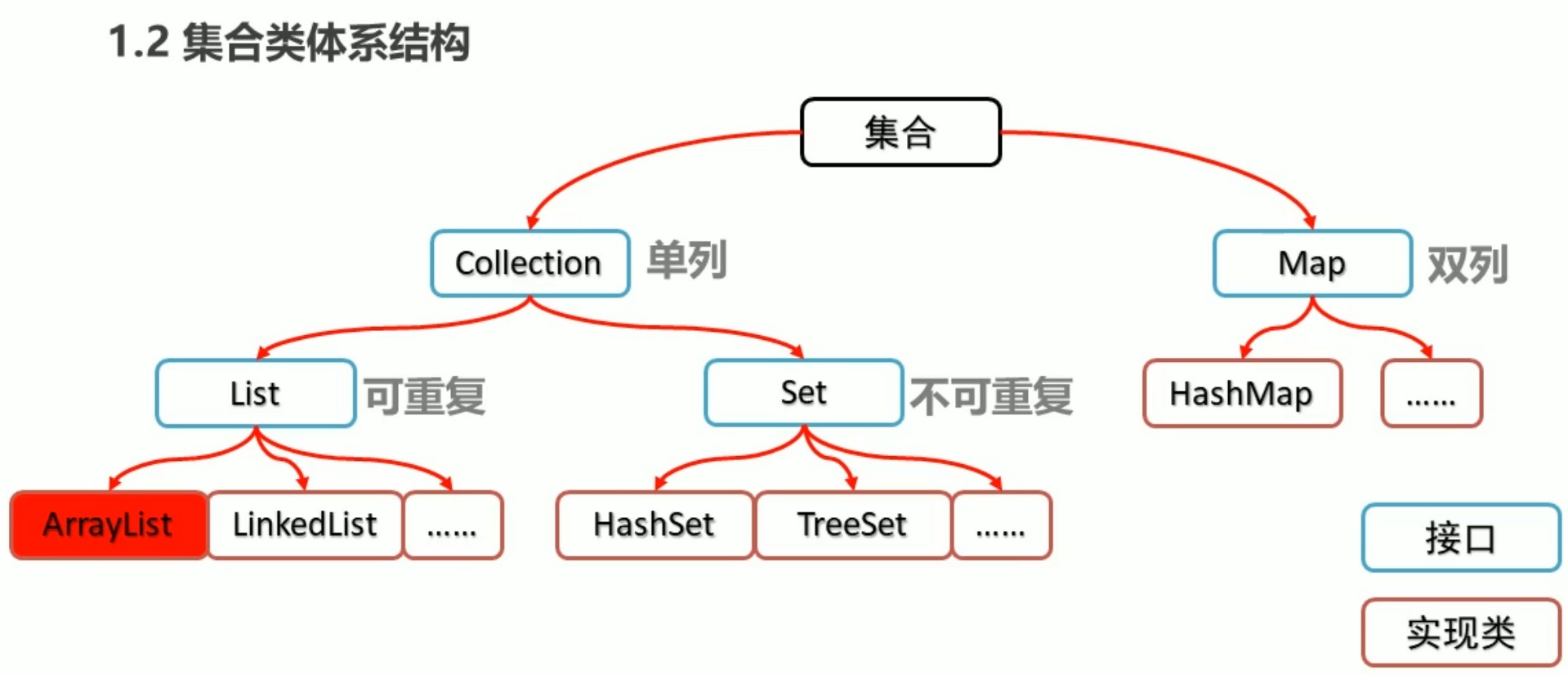
Collection集合
Collection 集合
package Collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
public class ArrayListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//用多态的方式来创建Collection集合的对象
Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<String>();
//boolean add(E e)方法用来添加元素
c.add("hello");
c.add("world");
c.add("Java");
System.out.println(c);
}//控制台输出:[hello, world, Java]
}
package Collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
/*
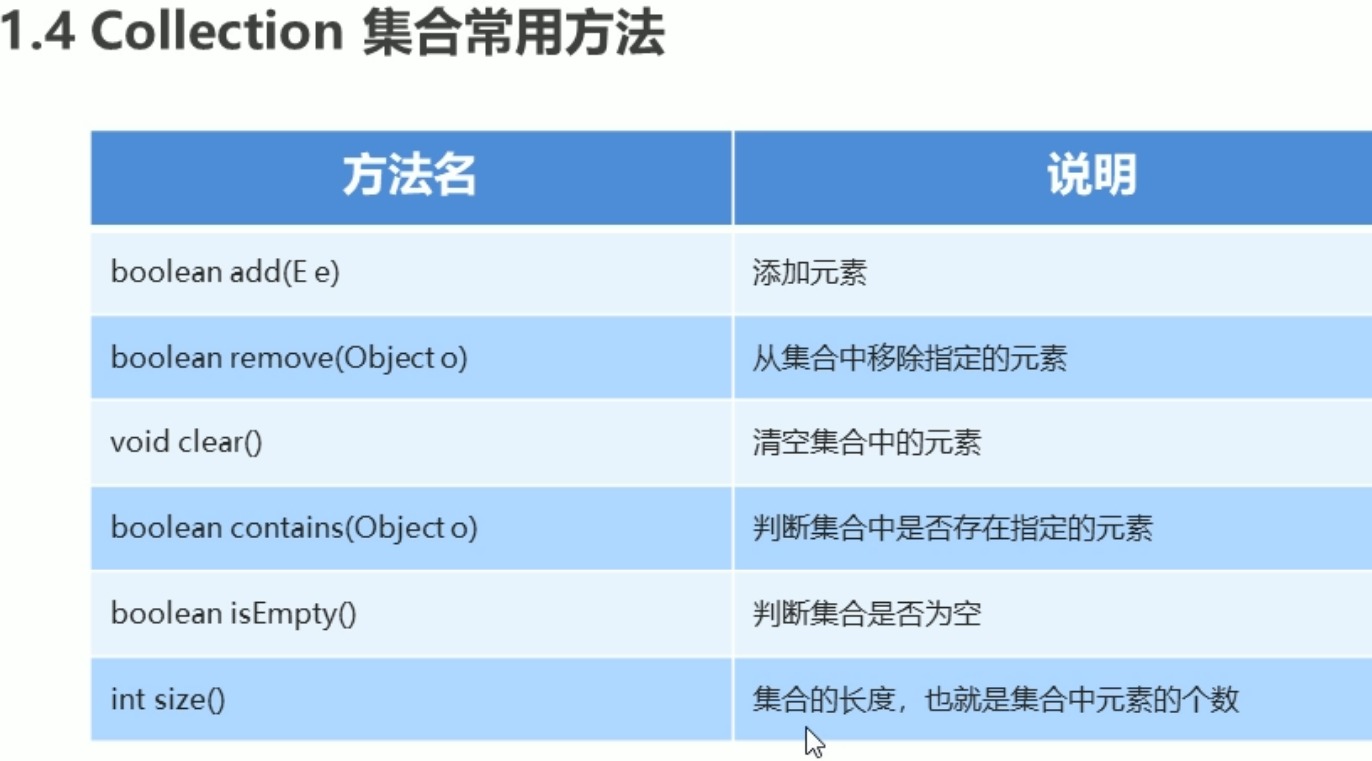
Collection集合的常用方法:
boolean add(E e):添加元素
boolean remove(Object o):从集合中删除指定元素
void clear():清空集合中元素
boolean contains(Object o):判断集合中是否存在指定元素
boolean isEmpty():判断集合是否为空
int size():集合的长度,就是集合中元素的个数
Alt+7 或View->Tool Windows->Structure 打开类的结构信息窗口
*/
public class ArrayListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//用多态的方式来创建Collection集合的对象
Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<String>();
//boolean add(E e)方法用来添加元素 永远返回true
c.add("hello");
c.add("world");
c.add("Java");
//boolean remove(Object o):从集合中删除指定元素
c.remove("world");
//void clear():清空集合中元素
c.clear();
//boolean contains(Object o):判断集合中是否存在指定元素
System.out.println(c.contains("hello"));
// boolean isEmpty():判断集合是否为空
System.out.println(c.isEmpty());
//int size():集合的长度,就是集合中元素的个数
System.out.println(c.size());
System.out.println(c);
}
}
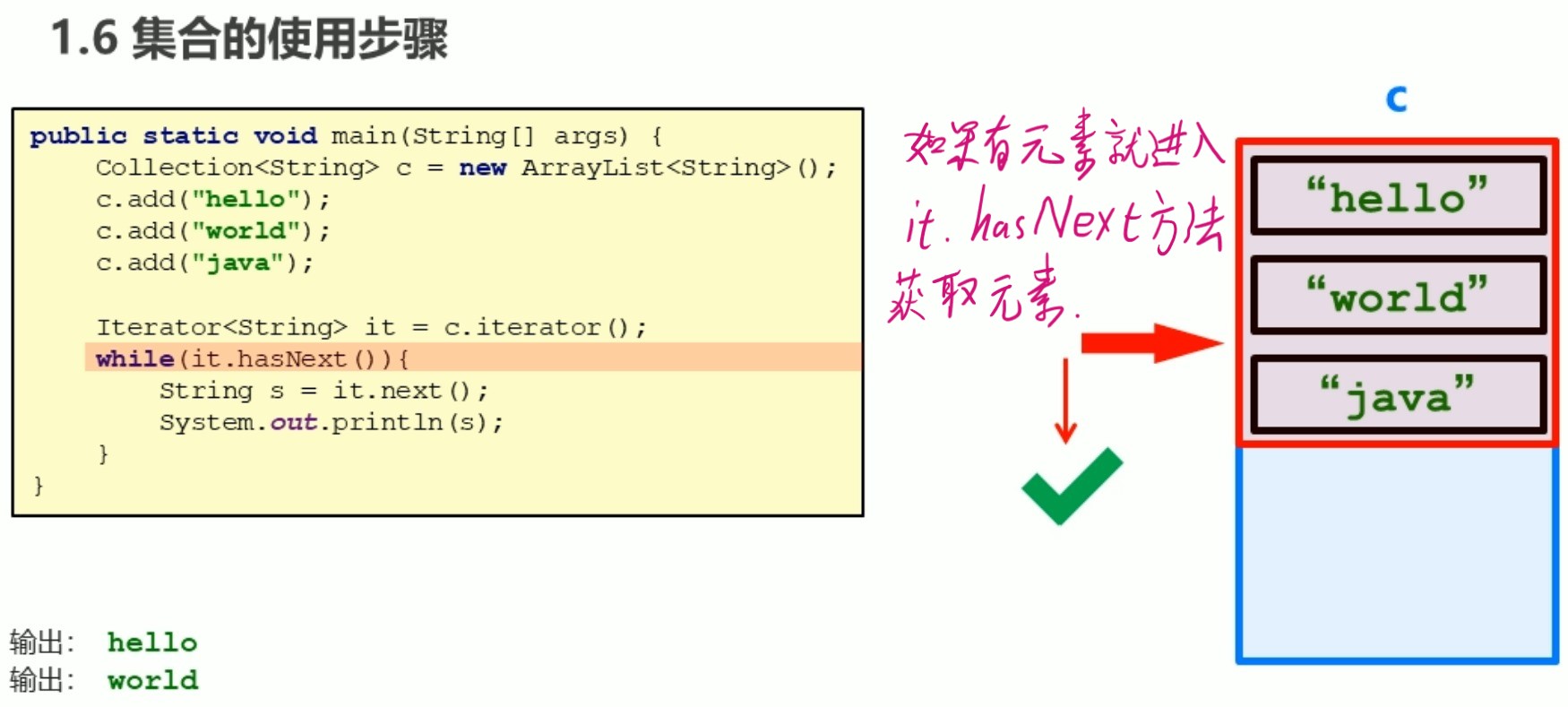
Collection集合的遍历
iterator 迭代器: 集合的专用遍历方式

package Collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/*
Iterator <E> . iterator() 返回集合中元素的迭代器, 通过iterator()方法
<E> next(): 返回迭代器中下一个元素
*/
public class IteratorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<>();//创建Collection集合
c.add("hello"); //添加元素
c.add("world");
c.add("java");
//Iterator <E> . iterator() 返回集合中元素的迭代器, 通过iterator()方法
Iterator<String> it = c.iterator();
//<E> next(): 返回迭代器中下一个元素
// System.out.println(it.next());
// System.out.println(it.next());
// System.out.println(it.next());
// System.out.println(it.next()); 报错!NoSuchElementException:被请求的元素不存在!
//控制台输出:hello world java
//------------------------------------------------------
//boolean hasNext():如果迭代器还有更多元素, 则返回true
// if(it.hasNext()){ //如果还有更多元素, 则返回true
// System.out.println(it.next());
// }
// if(it.hasNext()){
// System.out.println(it.next());
// }
// if(it.hasNext()){
// System.out.println(it.next());
// }
// if(it.hasNext()){ //已经没有更多元素, 则返回false
// System.out.println(it.next());
// }
//------------------------------------------------------
System.out.println("----------------");
//用循环来改进
while (it.hasNext()) {
String next = it.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
}
}
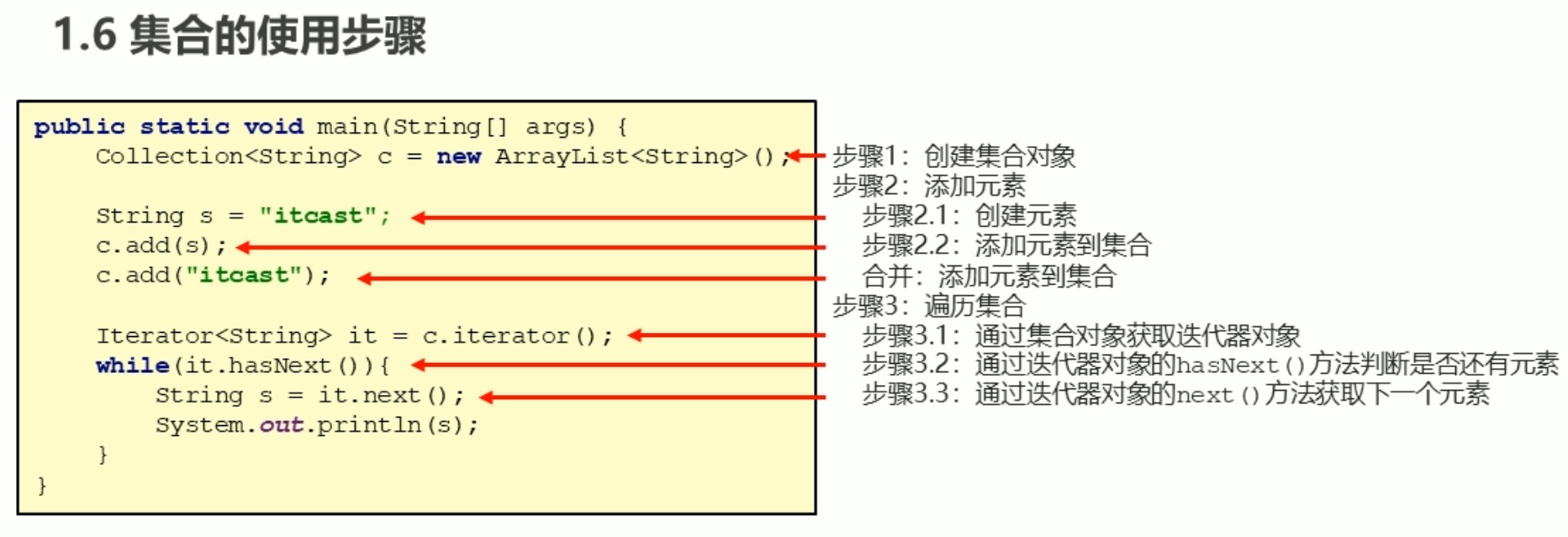
集合使用步骤的图解
案例: 创建一个储存学生对象的集合,存储3个学生对象,在控制台遍历
/*
案例: 创建一个储存学生对象的集合,存储3个学生对象,在控制台遍历
思路:
1. 定义学生类,
2. 创建Collection集合对象
3. 创建学生对象
4. 把学生添加到集合
5. 遍历集合(迭代器方式)
*/
package Collection;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class CollectionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Collection集合对象
Collection<Student> s = new ArrayList<Student>();
//创建学生对象
Student s1 = new Student("Peppa",6);
Student s2 = new Student("George",3);
Student s3 = new Student("Mike", 5);
//把学生添加到集合
s.add(s1);
s.add(s2);
s.add(s3);
//遍历集合(迭代器方式)
Iterator<Student> it = s.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Student student = it.next();
System.out.println(student.getName()+","+student.getAge());
}
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号