0-n BFS总结
最近看到几个关于Dijkstra变形题,都是边权在限定范围内,用规则保证最小性,而不需要从优先队列中取。
例如:
- 0-1 BFS: 0-1 BFS (Shortest Path in a Binary Weight Graph)
- 1-2 BFS: https://codetop.cc/discuss/135
- 1-5 BFS: 【求助】如何用线性时间复杂度解决单源最短路径问题
参考 0-1 BFS [Tutorial] 里有一句最重要的话,
引理: “在 BFS 执行期间,持有顶点的队列仅包含来自 BFS 树的最多两个连续级别的元素。”
解释: 因为在执行 BFS 的每个点,我们只遍历到一个顶点的相邻顶点,因此队列中的每个顶点都与队列中的所有其他顶点最多相距一层。
推论:对于边权为0-n的图,BFS过程中,队列中元素的差值不会超过n
我们以0-2 BFS为例,可以用三层来表示BFS过程中的队列情况,利用三个数组滚动进行,可以O(1)入队,O(1)得到当前最小值
例如:
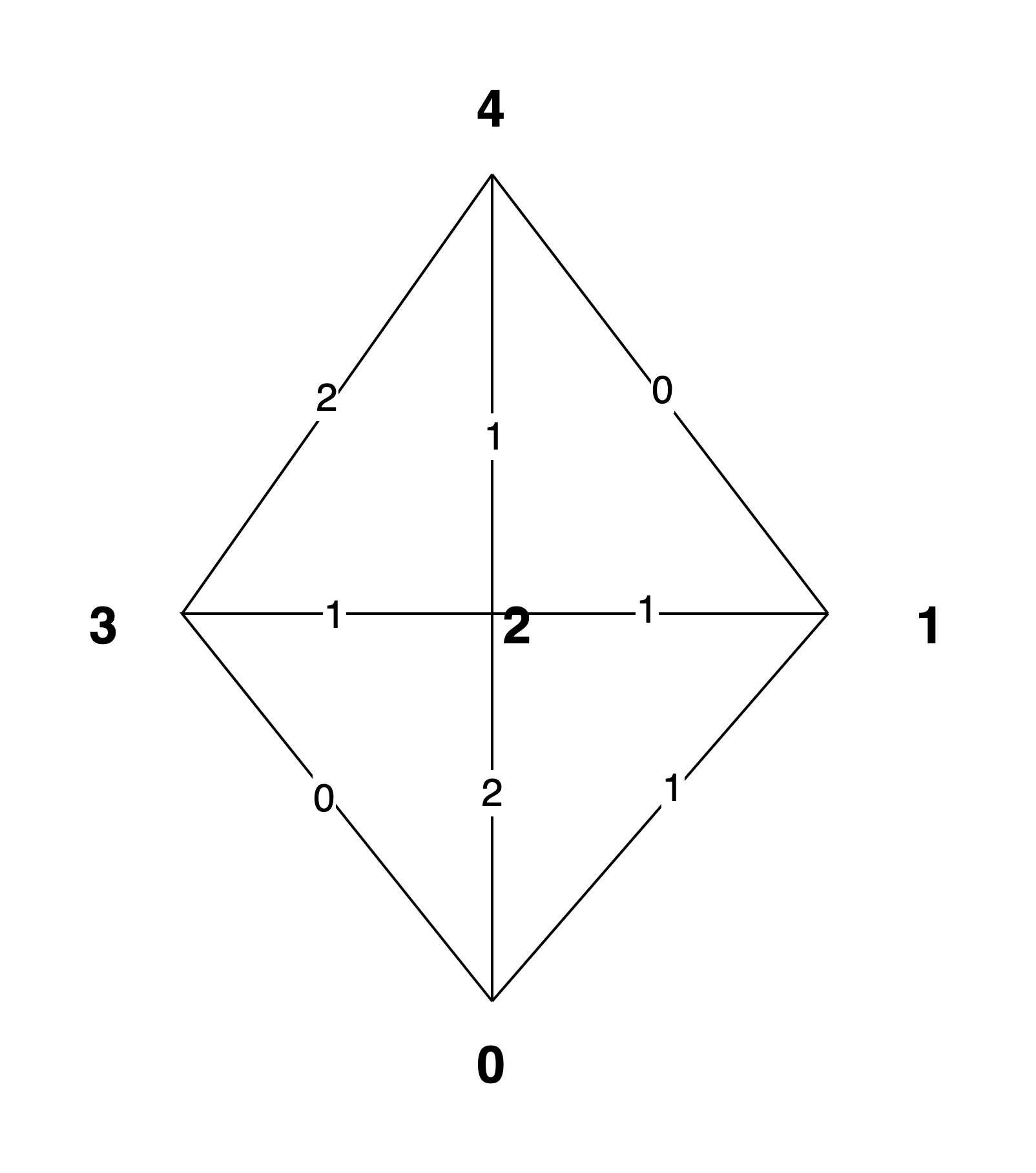
求节点0到其他节点的最短路
三层列表的更新过程如下:
首先0加入0号队列,并将更新的节点放入对应的队列...,cur号队列取完了就取cur+1号队列,直到三个队列都为空
| 0号队列 | 0 | 3 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1号队列 | 1 | 1,2 | 2,4 | 4 | |||||
| 2号队列 | 2 | 2,4 | 2,4 | 2,4 | 2,4 | 2,4 | 4 |
最终最短距离分别为:0 1 1 0 1
代码实现:
参考了 https://codetop.cc/discuss/135
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int V = 100000+5;
struct Node {
int id, w;
Node(int id_, int w_): id(id_), w(w_) {}
};
// 查看队列详情
// void print_que(const queue<int>& que_) {
// queue<int> que = que_;
// while (!que.empty()) {
// cout << que.front() << " ";
// que.pop();
// }
// cout << endl;
// }
vector<Node>edges[V];
queue<int> q[3];
void three_shortest_path(int n, int s, int t) {
vector<int>dist(V, INT_MAX);
dist[s] = 0;
int cur = 0;
q[cur].push(s);
while(!(q[0].empty() && q[1].empty() && q[2].empty())) {
// for(int i = 0;i < 3;i++) {
// cout << "i: " << i << endl;
// print_que(q[i]);
// }
if(!q[cur].empty()) {
int u = q[cur].front();
q[cur].pop();
for(auto &e: edges[u]) {
if(dist[e.id] > dist[u] + e.w) {
dist[e.id] = dist[u] + e.w;
q[(cur+e.w)%3].push(e.id);
}
}
} else {
cur = (cur+1)%3;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // 打印结果
if(dist[i] == INT_MAX) {
printf("-1\n");
} else {
printf("%d\n", dist[i]);
}
}
// printf("%d\n", dist[t]);
}
int main() {
int n, m, s, t;
scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &m, &s, &t);
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
int u, v, w;
scanf("%d%d%d", &u, &v, &w);
edges[u].push_back(Node(v, w));
edges[v].push_back(Node(u, w));
}
three_shortest_path(n, s, t);
return 0;
}
个性签名:时间会解决一切


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号