Spark Sql==>自定义函数简单应用
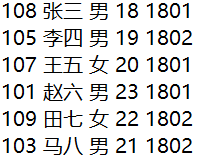
学生信息表数据如下图所示,字段依次为学号、姓名、性别、年龄、班级,字段间以空格分隔:
1 需求描述: 2 3 正确读入数据并注册成表 4 5 自定义UDF函数,实现将“男”转换成“male”,将“女”转换成“famale”功能 6 7 应用上述自定义UDF函数,求性别为“famale”的年龄最大的学生姓名和班级,并将学生的姓名和班级信息打印到控制台 8 9 自定义UDAF函数,实现求平均值功能 10 11 应用上述自定义UDAF函数,求1801班男生的最大年龄,并将班级和最大年龄打印到控制台 12 查询出比学号为103的学生年龄小的所有人员信息,将其姓名、性别、年龄打印到控制台
package com.lq.scala import org.apache.spark.sql.{DataFrame, SparkSession} import org.apache.spark.sql.{Row, SparkSession} import org.apache.spark.sql.expressions.MutableAggregationBuffer import org.apache.spark.sql.expressions.UserDefinedAggregateFunction import org.apache.spark.sql.types._ object Test01 { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val ssc: SparkSession = SparkSession.builder() .master("local[*]") .appName("Test01") .getOrCreate() ssc.sparkContext.setLogLevel("WARN") //正确读入数据并注册成表 val dataDF: DataFrame = ssc.read .option("sep", " ") .schema("id int,name String,sex String,age int,clazz String") .csv("data/day05.txt") //注册临时表 dataDF.createTempView("day05") //数据展示 ssc.sql("select * from day05").show() //自定义UDF函数,实现将“男”转换成“male”,将“女”转换成“famale”功能 ssc.udf.register("MyUDF",(sex:String)=>{ if (sex.equals("男")){ "male" }else if(sex.equals("女")){ "famale" }else{ "" } }) //应用上述自定义UDF函数,求性别为“famale”的年龄最大的学生姓名和班级,并将学生的姓名和班级信息打印到控制台 ssc.sql( """ |select | d.name,d.clazz |from | day05 d, | (select max(age) ages from day05 d where MyUDF(d.sex)='famale') d1 |where d.age=d1.ages and MyUDF(d.sex)='famale' |""".stripMargin).show() //自定义UDAF函数,实现求平均值功能 ssc.udf.register("MyUDAF",MyAverage) //应用上述自定义UDAF函数,求1801班男生的最大年龄,并将班级和最大年龄打印到控制台 ssc.sql( """ |select | d.clazz,d.age |from | day05 d, | (select max(age) ages from day05 d where d.clazz='1801' and MyUDF(d.sex)='male') d1 |where d.age=d1.ages and MyUDF(d.sex)='male' |""".stripMargin).show() //查询出比学号为103的学生年龄小的所有人员信息,将其姓名、性别、年龄打印到控制台 ssc.sql( """ |select | d.name,d.sex,d.age | from | day05 d, | (select age from day05 d where d.id=103) d1 | where d.age < d1.age |""".stripMargin).show() ssc.close() } } object MyAverage extends UserDefinedAggregateFunction { // Data types of input arguments of this aggregate function def inputSchema: StructType = StructType(StructField("inputColumn", LongType) :: Nil) // Data types of values in the aggregation buffer def bufferSchema: StructType = { StructType(StructField("sum", LongType) :: StructField("count", LongType) :: Nil) } // The data type of the returned value def dataType: DataType = DoubleType // Whether this function always returns the same output on the identical input def deterministic: Boolean = true // Initializes the given aggregation buffer. The buffer itself is a `Row` that in addition to // standard methods like retrieving a value at an index (e.g., get(), getBoolean()), provides // the opportunity to update its values. Note that arrays and maps inside the buffer are still // immutable. def initialize(buffer: MutableAggregationBuffer): Unit = { buffer(0) = 0L buffer(1) = 0L } // Updates the given aggregation buffer `buffer` with new input data from `input` def update(buffer: MutableAggregationBuffer, input: Row): Unit = { if (!input.isNullAt(0)) { buffer(0) = buffer.getLong(0) + input.getLong(0) buffer(1) = buffer.getLong(1) + 1 } } // Merges two aggregation buffers and stores the updated buffer values back to `buffer1` def merge(buffer1: MutableAggregationBuffer, buffer2: Row): Unit = { buffer1(0) = buffer1.getLong(0) + buffer2.getLong(0) buffer1(1) = buffer1.getLong(1) + buffer2.getLong(1) } // Calculates the final result def evaluate(buffer: Row): Double = buffer.getLong(0).toDouble / buffer.getLong(1) }
我有一杯酒,足以慰风尘。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号