java中对象的深拷贝和浅拷贝
根据对象成员变量的拷贝程度(基本数据类型、引用类型),可将拷贝分为浅拷贝和深拷贝。
一、浅拷贝
package javaKeyTechnology; class PerSon{ private String name; private int age; PerSon(String name,int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } public void setName(String name){ //私有数据的更改器 this.name = name; } public String getName(){ //私有数据的访问器 return name; } public void setAge(int age){ this.age = age; } public int getAge(){ return age; } public String toString(){ return "Person:["+this.hashCode()+" name:"+name+" age:"+age+"]"; } } public class MyClone implements Cloneable{ PerSon man; private int id; private String gender; public MyClone(String name,int age,String gender,int id){ man = new PerSon(name,age); this.gender = gender; this.id = id; } public void setId(int id){ this.id = id; } public int getId(){ return id; } public void setGender(String gender){ this.gender = gender; } public String getGender(){ return gender; } public String toString(){ return man.toString() + this.hashCode() + " gender:"+gender+" id:"+id; } //浅拷贝 public MyClone clone(){ try { return (MyClone)super.clone(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { return null; } } public static void main(String[] args){ MyClone student1 = new MyClone("LiLi",16,"felman",123456); MyClone student2 = student1.clone(); MyClone student3 = student1; student2.man.setAge(20);//改变student的引用变量的内容 student2.man.setName("Jason"); student2.setId(888888);//改变student的基本类型变量的内容 student2.setGender("man"); System.out.println("浅拷贝"); System.out.println("student1: " + student1.toString()); System.out.println("student1.clone " + student2.toString()); System.out.println("对象拷贝"); System.out.println("student1.copy: " + student1.toString()); } }
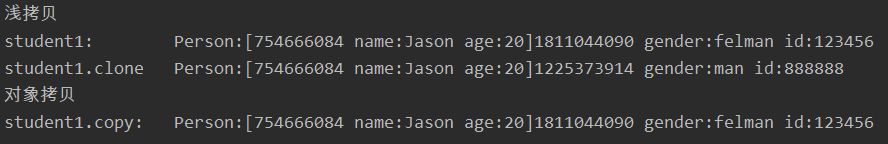
可见,对于浅拷贝:
1.创建了新对象,和原对象的hashcode不同;
2.成员变量中的基本数据类型是是拷贝其值,新对象和原对象中任一对象的基本数据类型发生改变,对另一对象不产生影响。所以原对象的id没有改变。
3.成员变量中的不可变对象的引用类型(如String),虽然是拷贝其地址,由于其引用的对象不可变,改变新对象和原对象任一的该变量(引用),只是让它引用了新的不可变对象,另外一个对象的该变量所引用的对象不变。所以原对象的gender没有改变。
4.成员变量中的可变对象的引用类型是是拷贝地址。新对象和原对象中该变量指向同一对象,所以person的hashCode相同;任一对象的该引用的对象内容发生改变,对另一对象产生影响,所以原对象的person内容也改变了。
5.Object.clone()是浅拷贝,如果在实现了Cloneable接口后只调用Object.clone(),自然也只能是浅拷贝。
对于浅拷贝和对象拷贝的区别:
1.浅拷贝创建了新对象,两对象地址不同。
2.对象拷贝没有创建新对象,两个变量指向的是同一个对象,同一个地址。
二、深拷贝
package javaKeyTechnology; class PerSon implements Cloneable{ private String name; private int age; PerSon(String name,int age){ this.name = name; this.age = age; } public void setName(String name){ //私有数据的更改器 this.name = name; } public String getName(){ //私有数据的访问器 return name; } public void setAge(int age){ this.age = age; } public int getAge(){ return age; } public String toString(){ return "Person:["+this.hashCode()+" name:"+name+" age:"+age+"]"; } public PerSon clone(){ try { return (PerSon)super.clone(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { return null; } } } public class MyClone implements Cloneable{ PerSon man; private int id; private String gender; public MyClone(String name,int age,String gender,int id){ man = new PerSon(name,age); this.gender = gender; this.id = id; } public void setId(int id){ this.id = id; } public int getId(){ return id; } public void setGender(String gender){ this.gender = gender; } public String getGender(){ return gender; } public String toString(){ return man.toString() + this.hashCode() + " gender:"+gender+" id:"+id; } //深拷贝 public MyClone clone(){ try { MyClone tmp = (MyClone)super.clone(); tmp.man = man.clone(); //把现在对象的man克隆 return tmp; } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { return null; } } public static void main(String[] args){ MyClone student1 = new MyClone("LiLi",16,"felman",123456); MyClone student2 = student1.clone(); student2.man.setAge(20);//改变student的引用变量的内容 student2.man.setName("Jason"); student2.setId(888888);//改变student的基本类型变量的内容 student2.setGender("man"); System.out.println("深拷贝"); System.out.println("student1: " + student1.toString()); System.out.println("student1.clone " + student2.toString()); } }

原对象和拷贝后创建的新对象中任一对象的任意成员变量(基本数据类型、不可变对象的引用、可变对象的引用)发生改变,都不影响另一个对象的成员变量。
深拷贝比浅拷贝多做的工作是:让新对象的引用变量 = 该引用所指对象的深拷贝
如果对象有多层对象(成员变量是引用),每层对象所属的类都要实现Cloneable接口并重写clone()。如果类的超类是Object,直接重写clone()。
三、关于以上代码中的异常处理
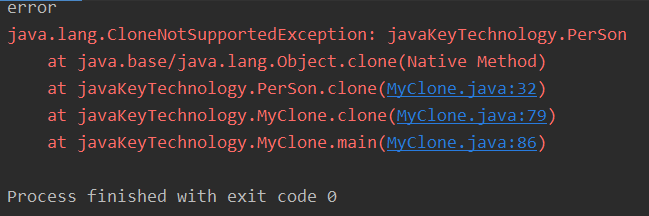
如果一个类没有implement Cloneable接口,该类的对象在调用Object.clone()时,就会抛出CloneNotSupportException(受查异常)。
注意并没有实现Cloneable接口的任何方法,clone()是从Object继承而来的。但是该接口会作为一个标记,允许克隆。
有两种异常处理的方法:
1.在该方法中捕获异常(一、二中的代码采用该方式)
2.声明异常,由该方法的高层调用处理,如果第一层调用不处理,可以继续传递给更高层的调用。这里就用到这一点。
因为这是一个受查异常,所以最好利用throws声明异常,将异常抛给方法的调用者去处理:
1 package javaKeyTechnology; 2 3 //class PerSon implements Cloneable{ //正确写法 4 class PerSon{ //制造一个异常 5 private String name; 6 private int age; 7 PerSon(String name,int age){ 8 this.name = name; 9 this.age = age; 10 } 11 12 public void setName(String name){ //私有数据的更改器 13 this.name = name; 14 } 15 16 public String getName(){ //私有数据的访问器 17 return name; 18 } 19 20 public void setAge(int age){ 21 this.age = age; 22 } 23 24 public int getAge(){ 25 return age; 26 } 27 28 public String toString(){ 29 return "Person:["+this.hashCode()+" name:"+name+" age:"+age+"]"; 30 } 31 32 public PerSon clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException{ 33 return (PerSon)super.clone(); 34 } 35 36 37 } 38 public class MyClone implements Cloneable{ 39 PerSon man; 40 private int id; 41 private String gender; 42 43 public MyClone(String name,int age,String gender,int id){ 44 man = new PerSon(name,age); 45 this.gender = gender; 46 this.id = id; 47 } 48 public void setId(int id){ 49 this.id = id; 50 } 51 52 public int getId(){ 53 return id; 54 } 55 56 public void setGender(String gender){ 57 this.gender = gender; 58 } 59 60 public String getGender(){ 61 return gender; 62 } 63 public String toString(){ 64 return man.toString() + this.hashCode() + " gender:"+gender+" id:"+id; 65 } 66 67 //异常处理方式一: 68 // public MyClone clone(){ 69 // try { 70 // MyClone tmp = (MyClone)super.clone(); 71 // tmp.man = man.clone(); //把现在对象的man克隆 72 // return tmp; 73 // } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { 74 // return null; 75 // } 76 // }
77 //异常处理方式二: 78 public MyClone clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException{ //一旦没有采用Cloneable接口,将抛出异常,由该方法的上层调用处理 79 MyClone tmp = (MyClone)super.clone(); 80 tmp.man = man.clone(); //把现在对象的man克隆,这里将抛出一个异常,但是先不处理继续传递给public MyClone clone()方法。 81 return tmp; 82 83 } 84 public static void main(String[] args){ 85 MyClone student1 = new MyClone("LiLi",16,"felman",123456); 86 try{ //需要调用声明异常的方法时,捕获异常 87 MyClone student2 = student1.clone(); 88 student2.man.setAge(20);//改变student的引用变量的内容 89 student2.man.setName("Jason"); 90 student2.setId(888888);//改变student的基本类型变量的内容 91 student2.setGender("man"); 92 System.out.println("深拷贝"); 93 System.out.println("student1: " + student1.toString()); 94 System.out.println("student1.clone " + student2.toString()); 95 }catch(CloneNotSupportedException e){ 96 System.out.println("error"); 97 e.printStackTrace(); 98 } 99 } 100 }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号