Hashtable的hashcode()(JDK8)
一、简述
Hatable中有一个hashcode(),可以返回当前map的hashcode。为什么要特意提出这个方法呢?请继续往下看。
二、hashcode()
//计算table的hashcode
public synchronized int hashCode() {
int h = 0;
if (count == 0 || loadFactor < 0) //size为0 或 负载因子《0
return h; // Returns zero 返回0
//标记当前table的负载因子,说明正在使用中
loadFactor = -loadFactor; // Mark hashCode computation in progress
Entry<?,?>[] tab = table;
for (Entry<?,?> entry : tab) { //遍历entry
while (entry != null) { //entry不为空
h += entry.hashCode(); //table的hashcode = 所有entry的hashcode相加
entry = entry.next;
}
}
//计算hashcode结束,将负载因子变为原值
loadFactor = -loadFactor; // Mark hashCode computation complete
return h;//返回hashcode
}
通过阅读源码,可以发现有这样一个操作loadFactor = -loadFactor;,将加载因子 x(-1),等计算hashcode结束后,再将加载因子变为原值。这是为什么呢?答案是确保在哈希表本身具有循环引用循环的情况下,代码不会陷入无限循环。
根据源码可以看出,最终的hashcode是由所有entry的hashcode相加得到的,由于有可能存在类似于<key,this>这样的键值对,如果不加以控制,会造成死循环。因此,需要添加一个标志位,当加载因子小于0时,直接返回0。这样就不会进入死循环了。
但是在HashMap中并没有实现hashcode(),如果调用hashcode()则是调了AbstractMap类的hashcode()。
public int hashCode() {
int h = 0;
Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
while (i.hasNext())
h += i.next().hashCode();
return h;
}
可以看出,只是通过迭代entrySet将所有entry的hashcode相加,并没有做死循环处理。
三、实例
@Test
public void testHashcode(){
Hashtable<String, Hashtable> hashtable = new Hashtable<>();
hashtable.put("a",hashtable);
System.out.println(hashtable.hashCode());
HashMap<String, HashMap> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("a",map);
System.out.println(map.hashCode());
}
测试结果
Hashtable
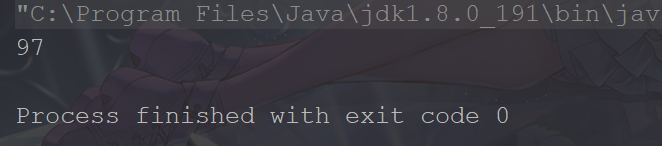
HashMap
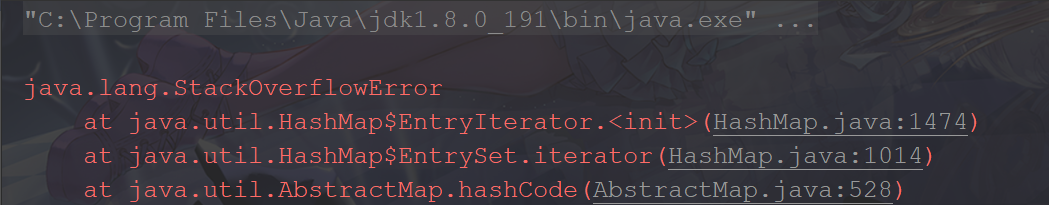
可以看出Hashtable正常输出hashcode,而HashMap则抛出StackOverflowError。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号