Java并发包相关组件(1)
1. CountDownLatch
用于线程计时,完成操作后通过countDownLatch.countDown() 就能让计时减一,直到计时为零之后,执行countDownLatch.await() 后的代码,否则阻塞。
1 class MainThread implements Runnable{ 2 private CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(3); 3 4 @Override 5 public void run() { 6 ReentrantLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantLock(); 7 8 new Thread(()->{ 9 try { 10 reentrantLock.lock(); 11 Thread.sleep(1000); 12 System.out.println("打开冰箱"); 13 countDownLatch.countDown(); 14 reentrantLock.unlock(); 15 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 }).start(); 19 new Thread(()->{ 20 try { 21 reentrantLock.lock(); 22 Thread.sleep(1000); 23 System.out.println("把大象装入冰箱"); 24 countDownLatch.countDown(); 25 reentrantLock.unlock(); 26 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 30 }).start(); 31 new Thread(()->{ 32 try { 33 reentrantLock.lock(); 34 Thread.sleep(1000); 35 System.out.println("关上冰箱"); 36 countDownLatch.countDown(); 37 reentrantLock.unlock(); 38 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 39 e.printStackTrace(); 40 } 41 }).start(); 42 new Thread(()->{ 43 try { 44 countDownLatch.await(); 45 System.out.println("步骤完成"); 46 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 47 e.printStackTrace(); 48 } 49 }).start(); 50 } 51 }
执行结果
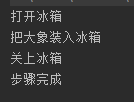
2. CyclicBarrier
只有当规定数量的线程都完成了对应的操作并通过cyclicBarrier.await() 进入的阻塞状态,cyclicBarrier实现的Runable的内容才会执行。
1 //运动员线程 2 class Runner implements Runnable{ 3 private CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier; 4 private int id; 5 private static int allId = 0; 6 7 public Runner(CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier) { 8 this.cyclicBarrier = cyclicBarrier; 9 this.id = allId++; 10 } 11 12 @Override 13 public void run() { 14 try { 15 System.out.println("运动员" + this.id + "号准备中"); 16 TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000) + 500); 17 System.out.println("运动员" + this.id + "号准备完毕"); 18 cyclicBarrier.await(); 19 } 20 catch (Exception e){ 21 e.printStackTrace(); 22 } 23 } 24 } 25 26 //main 27 class Main{ 28 public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { 29 CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(5, new Runnable() { 30 @Override 31 public void run() { 32 System.out.println("所有运动员准备完毕,比赛开始"); 33 } 34 }); 35 36 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); 37 38 for(int i = 0;i < 5;i++){ 39 executorService.submit(new Runner(cyclicBarrier)); 40 } 41 42 } 43 }
3. DelayQueue
延时队列,里面的元素需要实现Delayed接口,只有当元素到达延时时间后才会弹出,否则进行阻塞。
1 class DelayItem implements Delayed{ 2 //必要字段,表示延时的时长 3 private long duration; 4 private String msg; 5 6 public DelayItem(long duration, String msg) { 7 this.duration = duration + System.currentTimeMillis(); 8 this.msg = msg; 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) { 13 return unit.convert(this.duration - System.currentTimeMillis(),TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); 14 } 15 16 @Override 17 public int compareTo(Delayed o) { 18 DelayItem delayItem = (DelayItem) o; 19 20 return this.duration > delayItem.duration ? 1 : -1; 21 } 22 23 public String getMsg(){ 24 return msg; 25 } 26 } 27 28 //main 29 class Main{ 30 public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { 31 DelayQueue delayQueue = new DelayQueue(); 32 33 delayQueue.offer(new DelayItem(3000,"第二紧急事件")); 34 delayQueue.offer(new DelayItem(1000,"第一紧急事件")); 35 delayQueue.offer(new DelayItem(5000,"第三紧急事件")); 36 37 System.out.println(((DelayItem) delayQueue.take()).getMsg()); 38 System.out.println(((DelayItem) delayQueue.take()).getMsg()); 39 System.out.println(((DelayItem) delayQueue.take()).getMsg()); 40 41 42 } 43 }
4. PriorityBlockingQueue
优先级队列,当队列中没有元素时执行取出将会阻塞
class PriorityItem implements Comparable{ private long priority; private String msg; public PriorityItem(long priority,String msg) { this.priority = priority; this.msg = msg; } @Override public int compareTo(Object o) { PriorityItem priorityItem = (PriorityItem) o;
//返回1时会放在尾部,返回-1则放在头部 return this.priority < priorityItem.priority ? 1 : -1; } public String getMsg() { return msg; } } //main class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { PriorityBlockingQueue<PriorityItem> priorityBlockingQueue = new PriorityBlockingQueue(); priorityBlockingQueue.add(new PriorityItem(10,"第二紧急事件")); priorityBlockingQueue.add(new PriorityItem(30,"第一紧急事件")); priorityBlockingQueue.add(new PriorityItem(5,"第三紧急事件")); System.out.println(((PriorityItem) priorityBlockingQueue.take()).getMsg()); System.out.println(((PriorityItem) priorityBlockingQueue.take()).getMsg()); System.out.println(((PriorityItem) priorityBlockingQueue.take()).getMsg()); } }
5. Semaphore
信号量,用于实现同步和互斥,分为公平与非公平信号量。公平信号量根据获取锁的时间长短来进行执行,非公平信号量则根据CPU时间片轮转来随机分配执行。
//信号量解决哲学家吃饭问题 class Reader implements Runnable{ private Semaphore[] semaphore; //哲学家编号 private int id; //筷子个数 private int num; private static int allId = 0; public Reader(Semaphore[] semaphore) { this.semaphore = semaphore; num = semaphore.length; id = allId++; } @Override public void run() { try { while (true){ semaphore[id % num].acquire(); semaphore[(id + 1) % num].acquire(); System.out.println("哲学家" + this.id + "号拿起筷子"); TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000) + 500); System.out.println("哲学家" + this.id + "号结束吃饭"); semaphore[id % num].release(); semaphore[(id + 1) % num].release(); } } catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } } } //main class Main{ public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { Semaphore[] semaphores = new Semaphore[5]; for(int i = 0;i < semaphores.length;i++){
//将信号量设置为公平信号量 semaphores[i] = new Semaphore(1,true); } ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); for(int i = 0;i < 5;i++){ executorService.submit(new Reader(semaphores)); } executorService.shutdown(); } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号