yaml
yaml
普通语法
- 空格不能省略
- 用缩进来控制层级关系,只要是左边对齐的一列数据都是同一个层级的
- 属性和值的大小写都十分敏感
# 普通KV键值对
name: lct
# 对象
student:
name: lct
age: 23
student: {name: zhj, age: 18}
# 数组
pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig
pets: [cat, dog, pig]
注入配置文件
yaml文件强大的地方在于,可以给我们的实体类直接注入匹配值!
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
- 非必要,加了的话就没报错;不加也不影响功能
样例
Dog.java
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "dog")
public class Dog {
private String name;
private int age;
// 有参、无参、getter/setter、toString
}
Person.java
/*
@ConfigurationProperties作用:
将配置文件中配置的每一个属性的值,映射到这个组件中;
告诉SpringBoot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中相关的配置进行绑定
参数 prefix = “person” : 将配置文件中的person下面的所有属性一一对应
*/
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean happy;
private Date birth;
private Map<String, Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
// 有参、无参、getter/setter、toString
}
application.yaml
person:
name: lct
age: 18
happy: false
birth: 2023/07/12
maps: {k1: v1, k2: v2}
lists: [a, b, c, d, e]
dog: {name: Wang, age: 3}
结果
Test.java
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot02ConfigApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Person person;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(person);
}
}
Person{name='lct', age=18, happy=false, birth=Wed Jul 12 00:00:00 CST 2023, maps={k1=v1, k2=v2}, lists=[a, b, c, d, e], dog=Dog{name='Wang', age=3}}
加载指定的配置文件
person.properties
name = lct
Person.java
@Component
// 加载指定配置文件
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:person.properties")
public class Person {
@Value("${name}")
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Boolean happy;
private Date birth;
private Map<String, Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
private Dog dog;
}
结果
Person{name='lct', age=null, happy=null, birth=null, maps=null, lists=null, dog=null}
配置文件占位符
person:
name: lct${random.uuid} # 随机uuid
age: ${random.int(100)} # 随机数,最大100
happy: false
hello: hi
birth: 2023/07/12
maps: {k1: v1, k2: v2}
lists: [a, b, c, d, e]
dog:
name: ${person.hello:hello}_Wang # 如果存在前值则为前值;否则为后值
age: 3
结果
Person{name='lcta1735883-3cba-4258-82d6-829087ac276e', age=61, happy=false, birth=Wed Jul 12 00:00:00 CST 2023, maps={k1=v1, k2=v2}, lists=[a, b, c, d, e], dog=Dog{name='hi_Wang', age=3}}
松散绑定
-或_可以自动转化为对象内的驼峰命名
对象内的属性
private String lastName;
private String firstName;
yaml内对象的属性
person:
last-name: lct_${random.uuid}
# ...
dog:
first_name: ${person.hello:hello}_Wang
# ...
结果
Person(lastName=lct_2d992523-2730-498b-b6b9-fd695d399e35, .... , dog=Dog(firstName=hi_Wang, age=3))
JSR303
- Springboot中可以用@validated来校验数据,如果数据异常则会统一抛出异常,方便异常中心统一处理
样例
Person.java
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@Validated
public class Person {
@Email(message = "邮箱格式错误")
private String lastName;
}
application.yaml
person:
last-name: lct_${random.uuid}
age: ${random.int(100)}
happy: false
hello: hi
birth: 2023/07/12
maps: {k1: v1, k2: v2}
lists: [a, b, c, d, e]
dog:
first_name: ${person.hello:hello}_Wang
age: 3
- 此时进行数据注入,原数据会报错(未满足邮箱格式)
常见参数
- 可在包中查看所有支持的配置
@NotNull(message="名字不能为空")
private String userName;
@Max(value=120,message="年龄最大不能查过120")
private int age;
@Email(message="邮箱格式错误")
private String email;
空检查
@Null 验证对象是否为null
@NotNull 验证对象是否不为null, 无法查检长度为0的字符串
@NotBlank 检查约束字符串是不是Null还有被Trim的长度是否大于0,只对字符串,且会去掉前后空格.
@NotEmpty 检查约束元素是否为NULL或者是EMPTY.
Booelan检查
@AssertTrue 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 true
@AssertFalse 验证 Boolean 对象是否为 false
长度检查
@Size(min=, max=) 验证对象(Array,Collection,Map,String)长度是否在给定的范围之内
@Length(min=, max=) string is between min and max included.
日期检查
@Past 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之前
@Future 验证 Date 和 Calendar 对象是否在当前时间之后
@Pattern 验证 String 对象是否符合正则表达式的规则
.......等等
除此以外,我们还可以自定义一些数据校验规则
多环境配置
配置文件位置
application.yaml/.properties
- 根目录的
config文件夹 - 根目录
resources目录下的config文件夹resources目录
- 配置文件优先级与上面的顺序相同,
1最优先
环境切换
多文件
- application.yaml
- application-dev.yaml
- application-test.yaml
通过在application.yaml中更改该配置,可以选择性的激活对应环境
# SpringBoot多环境配置, 可选择激活哪个配置文件
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
单文件(推荐)
application.yaml
server:
port: 8080
spring:
profiles:
active: test
---
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles: dev
---
server:
port: 8082
spring:
profiles: test
对比Properties
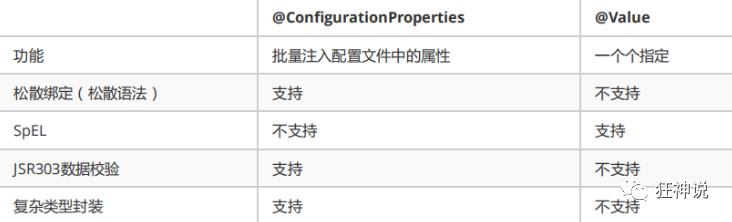
- @ConfigurationProperties只需要写一次即可,@Value则需要每个字段都添加
- 支持松散绑定和JSR303校验
- yaml中可以实现复杂类型封装
- yaml可以封装对象,使用@Value就不支持


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号