ConcurrentMap
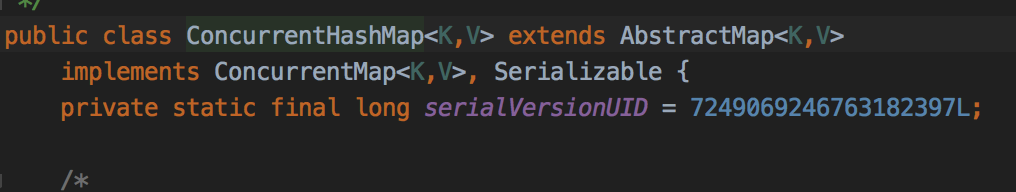
一样的先看看成员有哪些:
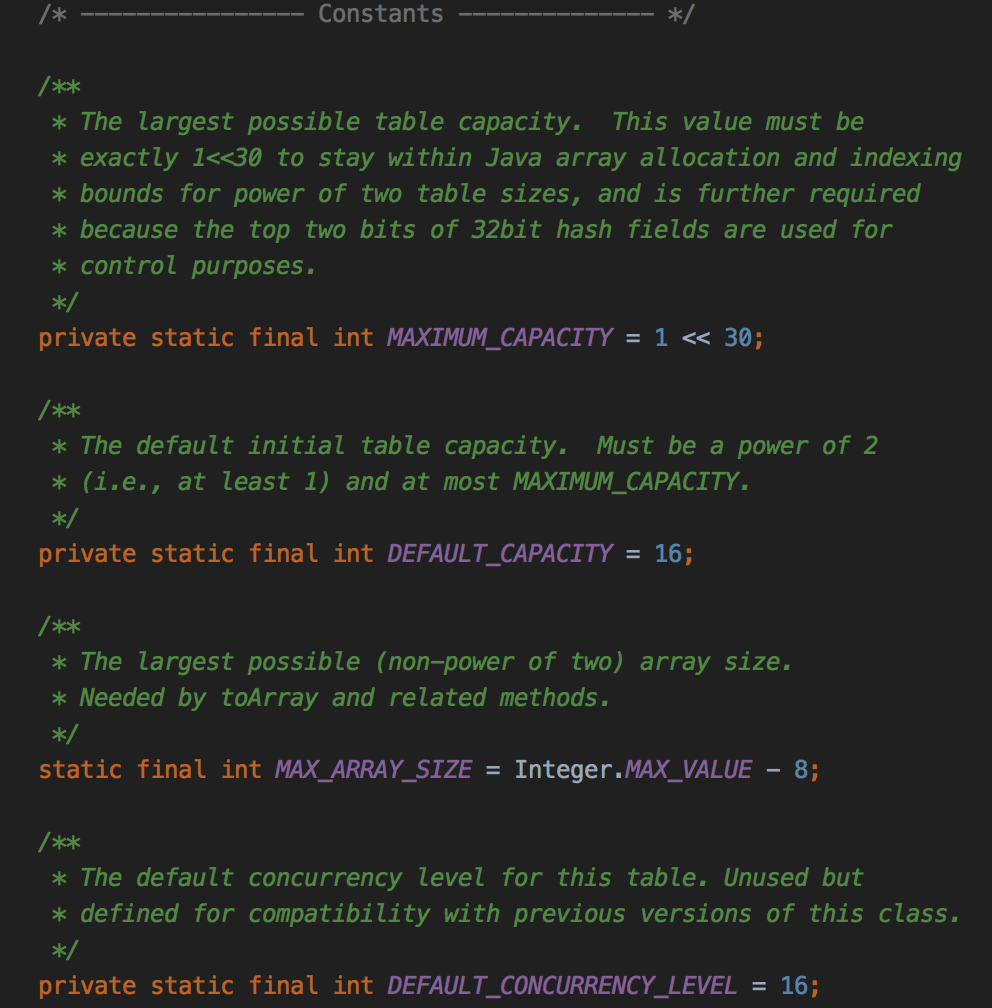
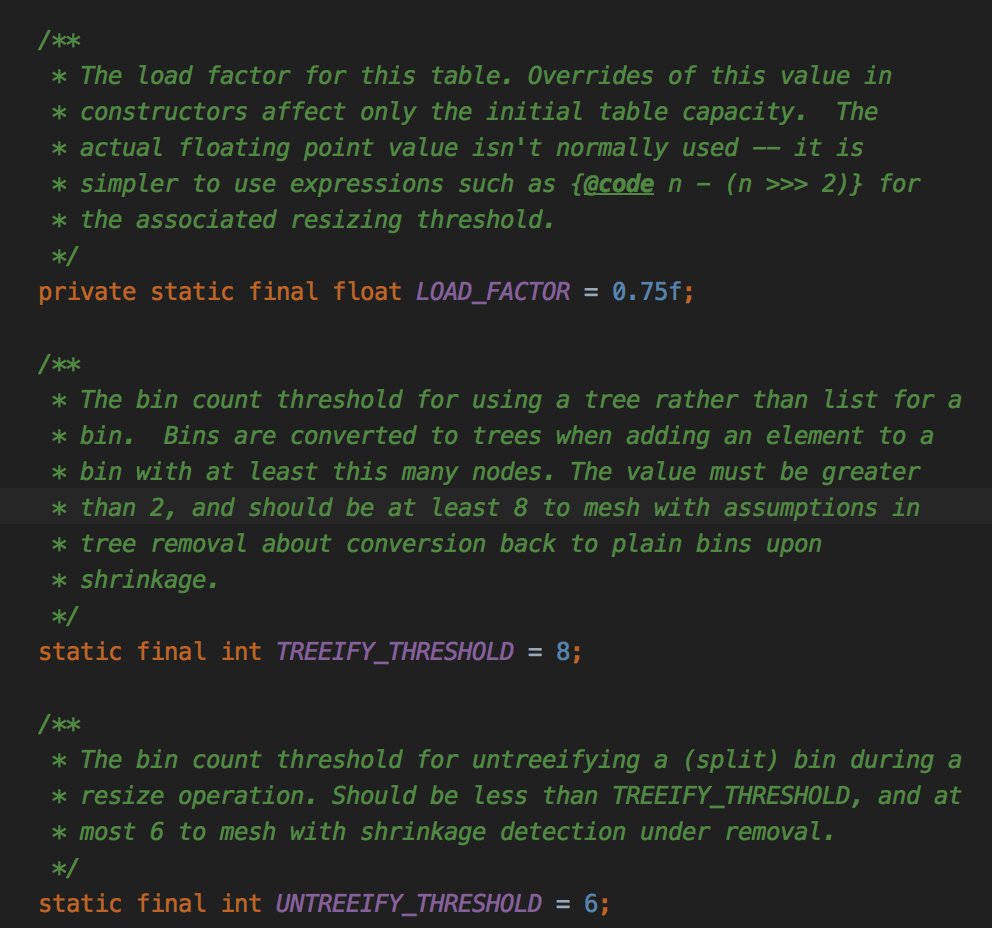

以上都是hashmap中有的成员下面是一些新的:
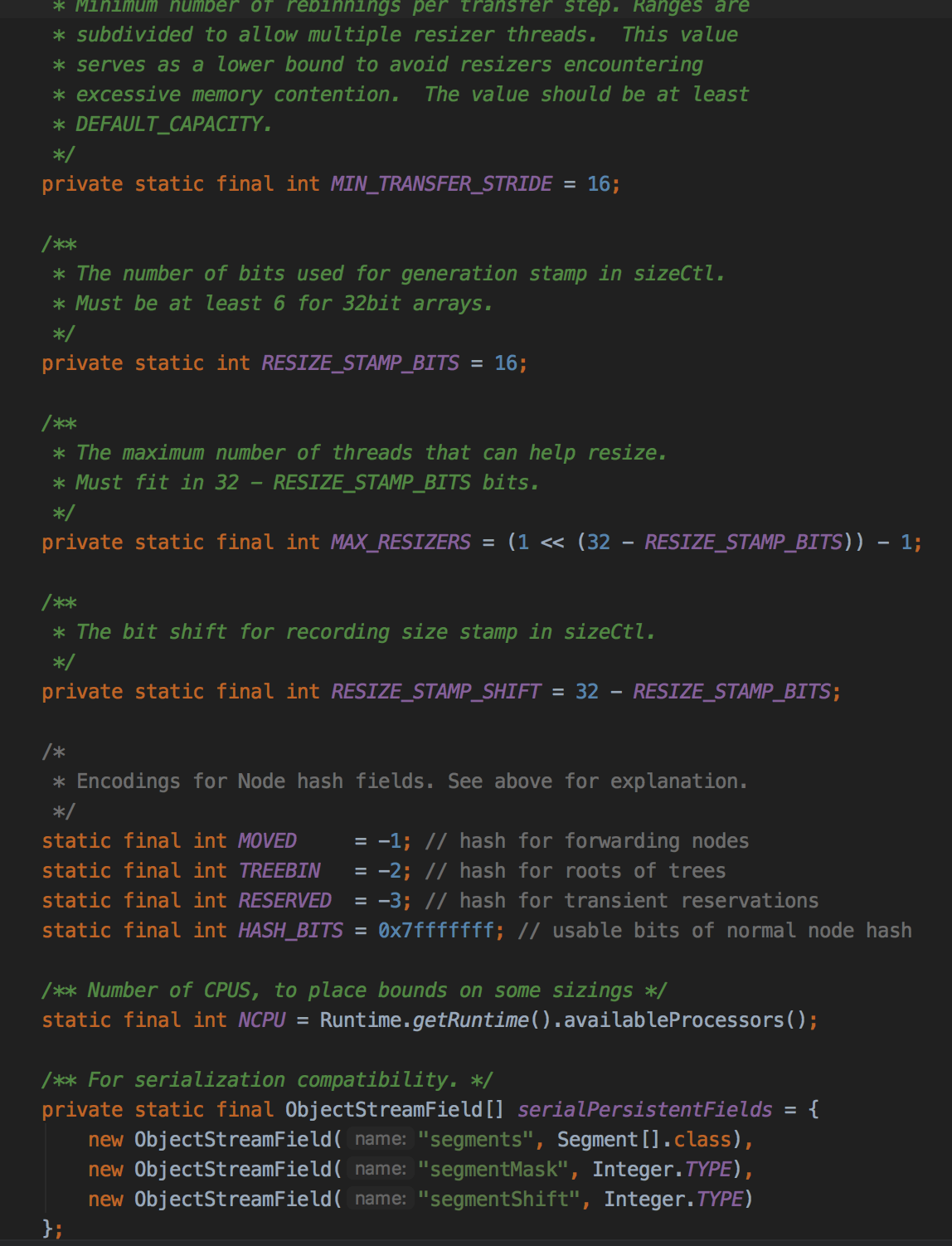
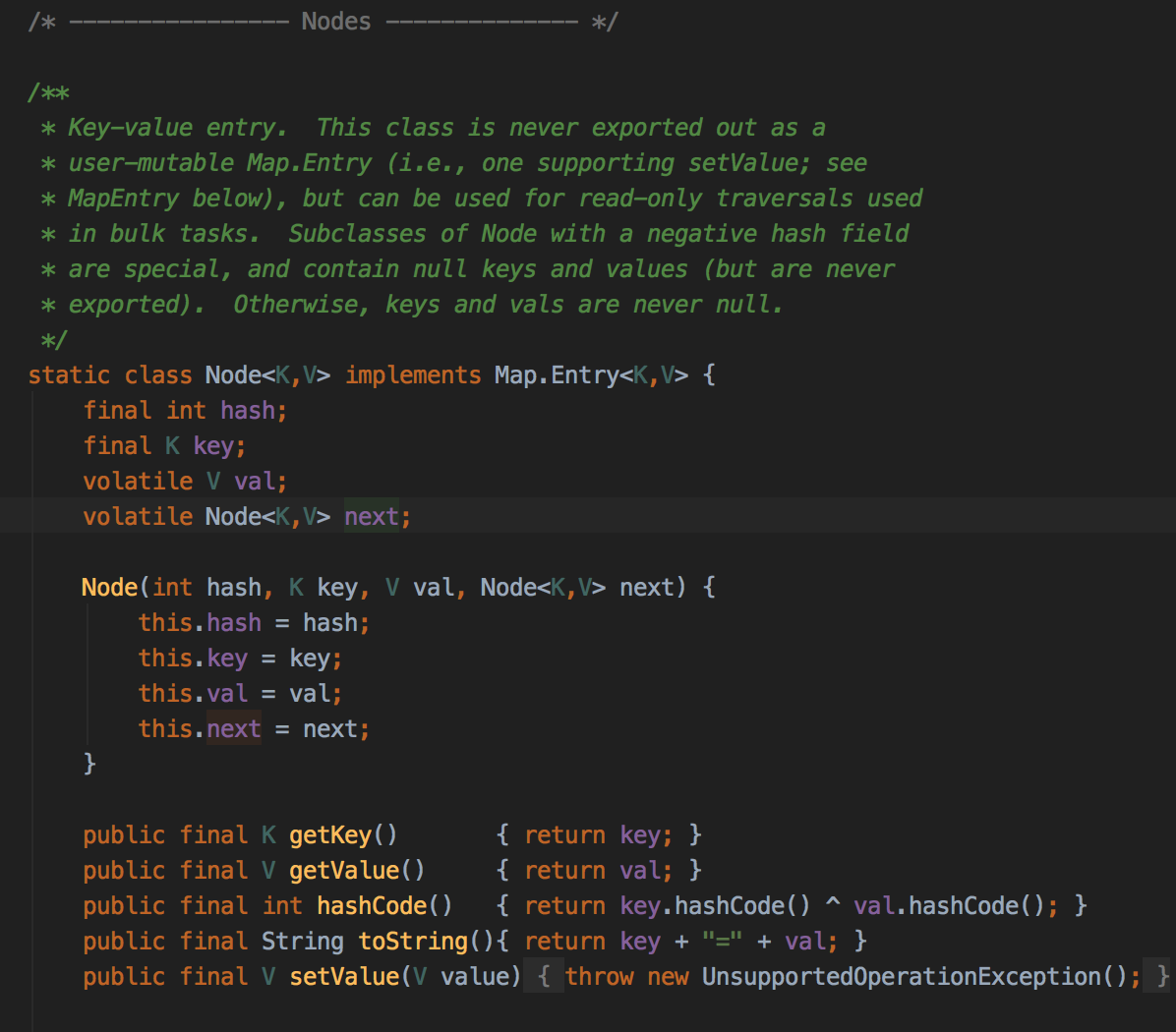
再来看节点信息:
构造方法:
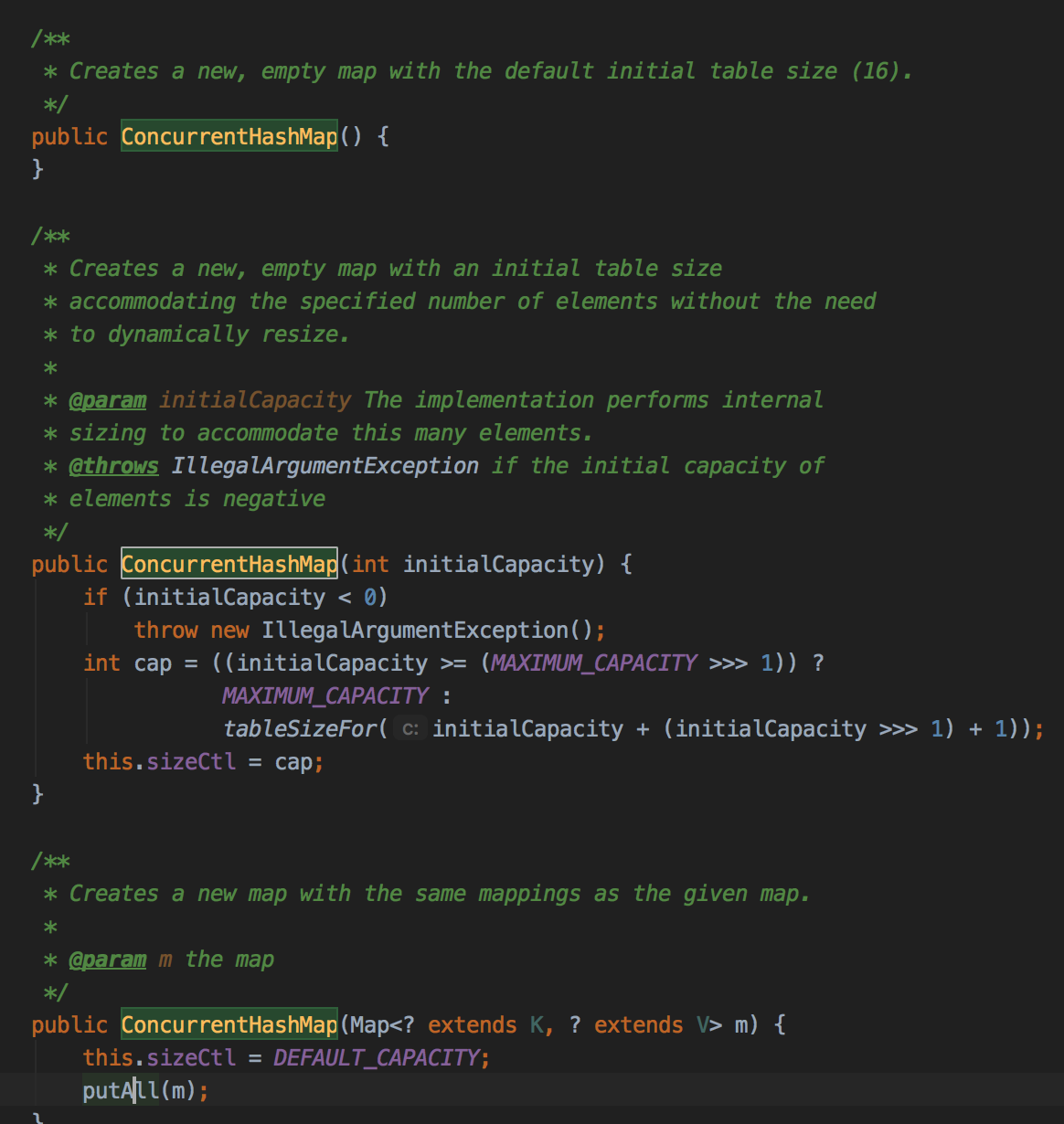
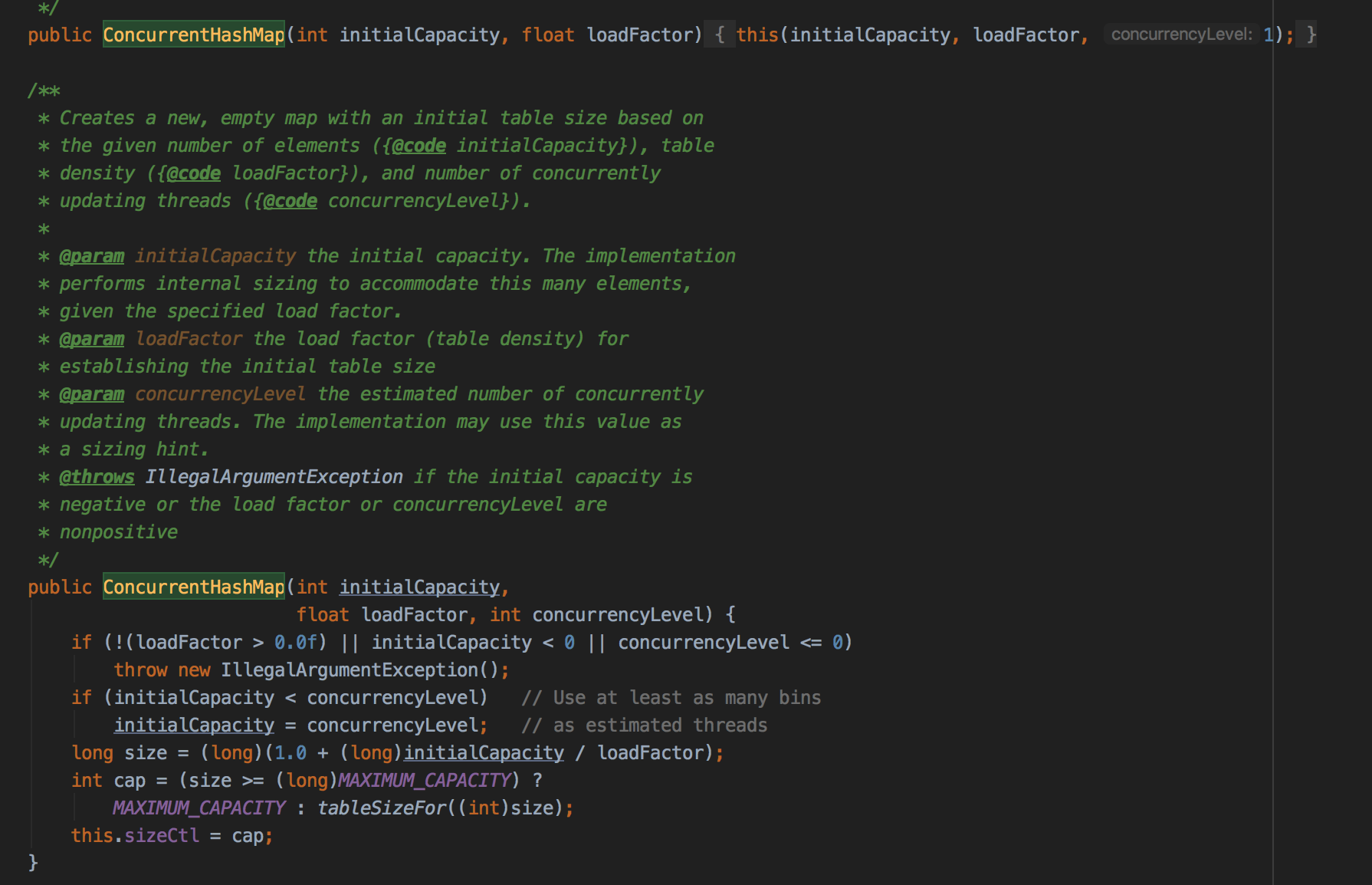
可以看到currentHashMap在初始化的时候用的size并不是像hashmap那样直接用initialCapacity,而是用除以负载因子之后容量或者1.5倍为基础选择最小的2的次幂。
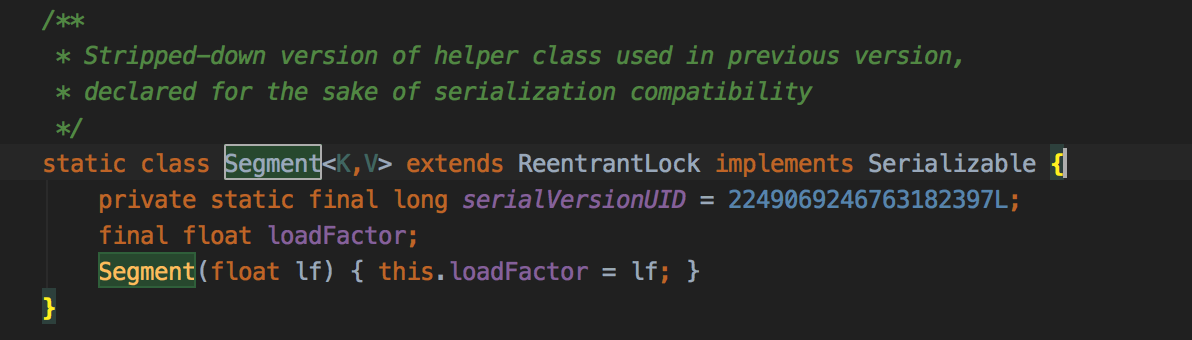
Segment对象。
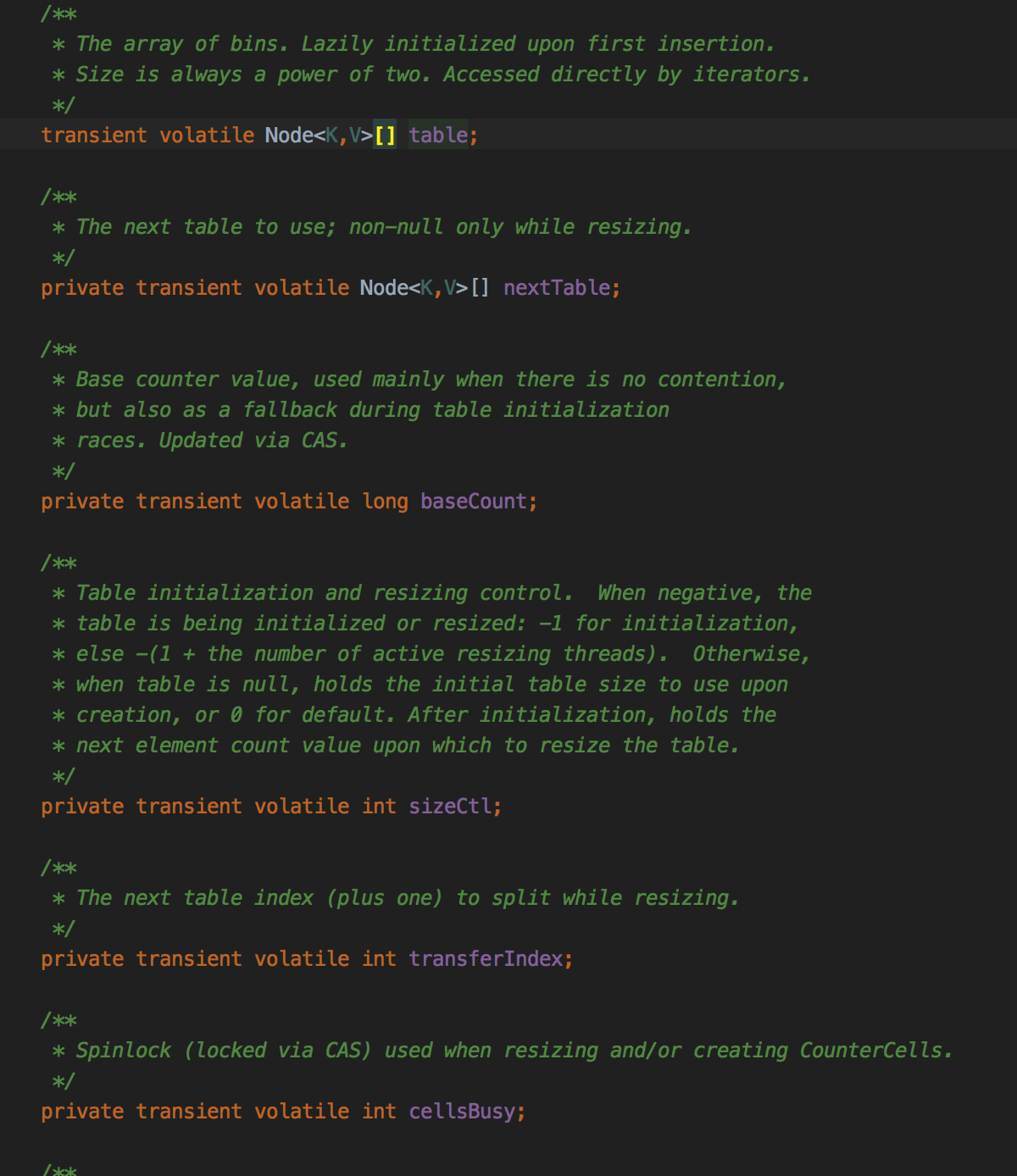
看一下put final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();
//计算hash值跟hashmap一样 int hash = spread(key.hashCode()); int binCount = 0; for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) { Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh; if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
//比较相似都是懒加载初始化 hashmap是resize。 tab = initTable(); else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {
//如果当前槽还没有元素,则cas到第一个元素,如果失败则一直自旋到成功为止 if (casTabAt(tab, i, null, new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null))) break; // no lock when adding to empty bin }
//如果第一位已经移除了 else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
//卧槽,看不懂了 tab = helpTransfer(tab, f); else { V oldVal = null;
//所第一个 synchronized (f) {
//可见 if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) { if (fh >= 0) {
binCount = 1;
//从第一个元素开始 for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) { K ek;
//hash和key都对应上直接替换 if (e.hash == hash && ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) { oldVal = e.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) e.val = value; break; } Node<K,V> pred = e;
//插入到链表尾部 if ((e = e.next) == null) { pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null); break; } } }
//如果hash<0检查是不是红黑树 else if (f instanceof TreeBin) { Node<K,V> p; binCount = 2; if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key, value)) != null) { oldVal = p.val; if (!onlyIfAbsent) p.val = value; } } } }
//链表转树 if (binCount != 0) { if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD) treeifyBin(tab, i); if (oldVal != null) return oldVal; break; } } } addCount(1L, binCount); return null; }
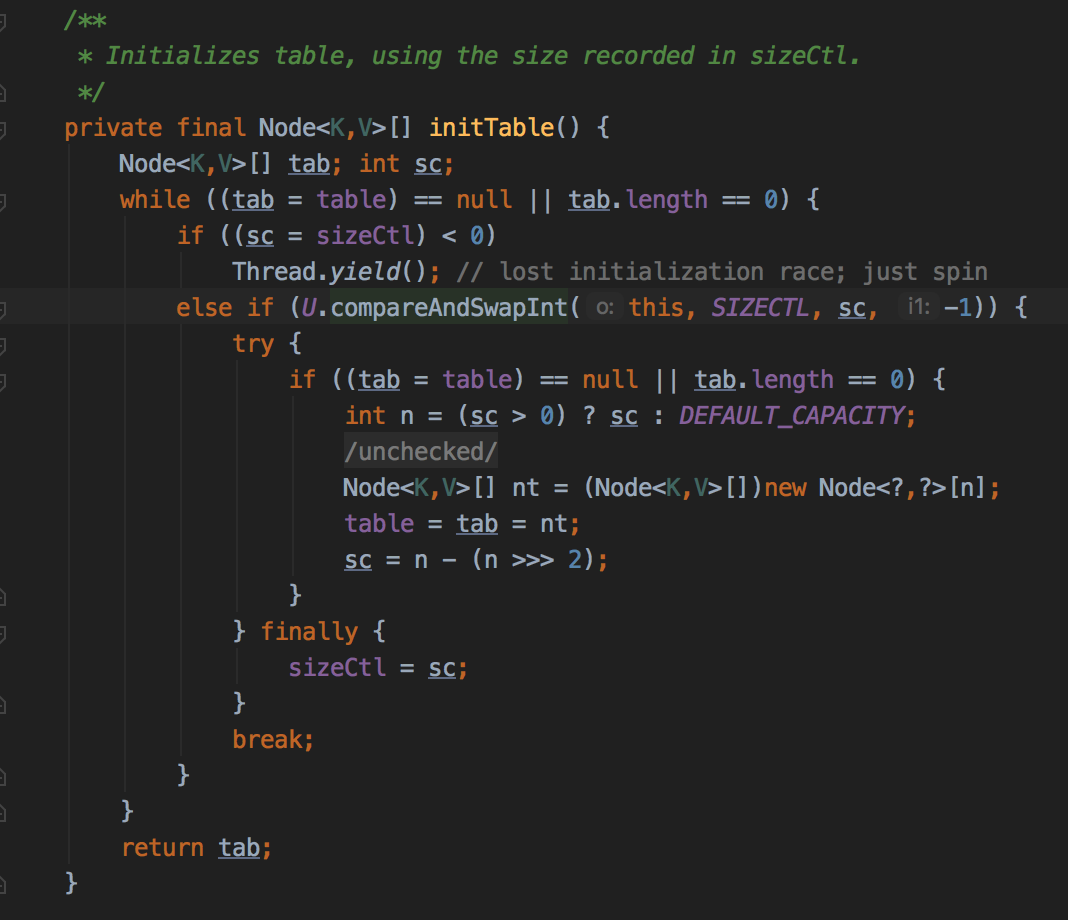
initTable在获取cas成功之后会初始化一个node数组。sizeCtrl会被设置为数组大小的0.75。
扩容:
addCount里:
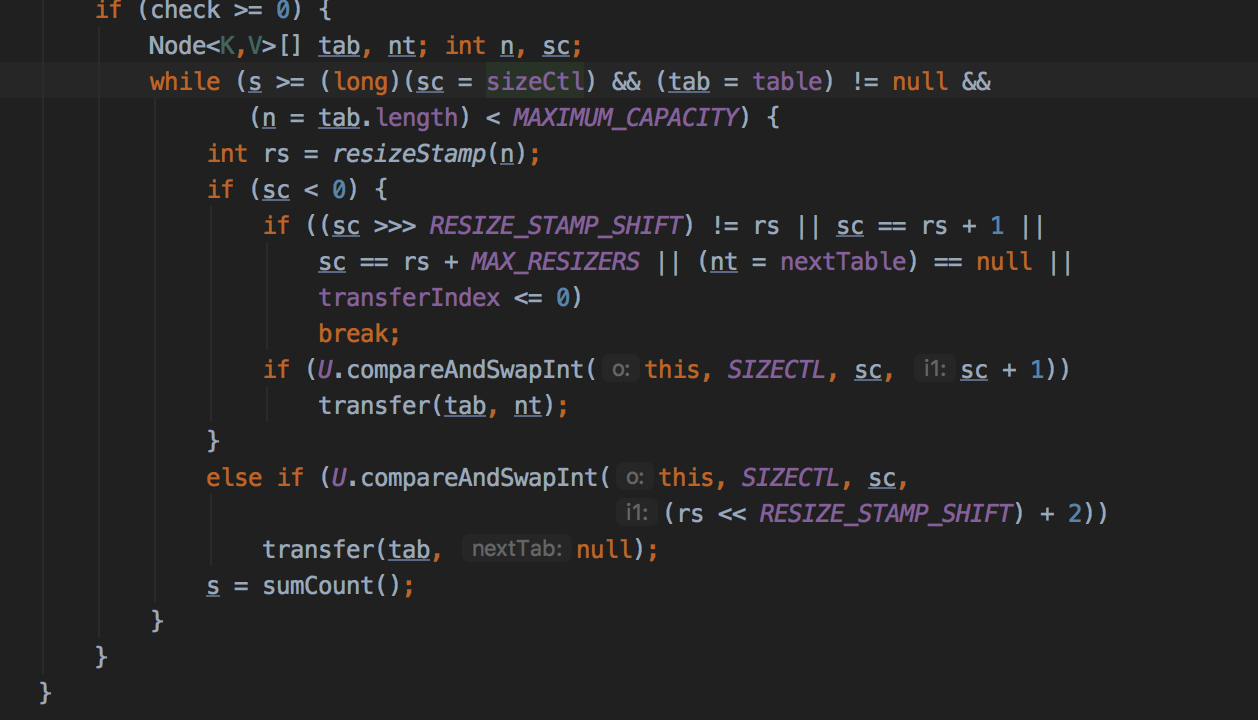
sizeCtl不通的状态居然代表不同的含义,大佬是真的敢,
sizeCtl>=0说明未处在扩容的状态(-1正在初始化和扩容,-n参与到扩容的线程数,>0已初始化,=0未初始化默认值)
resizeStamp()的返回值(简称为rs) 高16位置0,第16位为1,低15位存放当前容量n扩容标识,用于表示是对n的扩容。
rs与RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT配合可以求出新的sizeCtl的值,分情况如下:
sc >= 0
表示没有线程在扩容,使用CAS将sizeCtl的值改为(rs << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) + 2)。高15位为容量n扩容标识,并行扩容线程数+1。
sc < 0
已经有线程在扩容,将sizeCtl+1并调用transfer()让当前线程参与扩容。
private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) {
int n = tab.length, stride;
//检查cpu核心数,如果大于1,n*8/核心数,否则就是n。计算结果小于16 取16
if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)
stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide range
if (nextTab == null) {
// initiating
//如果是第一个扩容的线程进来,nextTab=null先进行初始化
try {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
//大小为n两倍的数组
Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1];
nextTab = nt;
} catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOME
sizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
return;
}
//记录nextTable,和分割点transferIndex
nextTable = nextTab;
transferIndex = n;
}
int nextn = nextTab.length;
ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab);
boolean advance = true;
boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTab
for (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) {
Node<K,V> f; int fh;
while (advance) {
int nextIndex, nextBound;
//--i>=bound当前没处理完继续处理(线程负责处理bound~nextIndex之间的槽,从nextIndex递减处理到bound)
if (--i >= bound || finishing)
advance = false;
else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {
i = -1;
advance = false;
}
//cas nextIndex替换为nextBound。但是这里会成功吗?nextIndex会被compare成功?
else if (U.compareAndSwapInt
(this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex,
nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ?
nextIndex - stride : 0))) {
bound = nextBound;
i = nextIndex - 1;
advance = false;
}
}
if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {
int sc;
if (finishing) {
nextTable = null;
table = nextTab;
sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1);
return;
}
if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) {
if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)
return;
finishing = advance = true;
i = n; // recheck before commit
}
}
else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)
advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd);
else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)
advance = true; // already processed
else {
synchronized (f) {
if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {
Node<K,V> ln, hn;
if (fh >= 0) {
int runBit = fh & n;
Node<K,V> lastRun = f;
for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
int b = p.hash & n;
if (b != runBit) {
runBit = b;
lastRun = p;
}
}
if (runBit == 0) {
ln = lastRun;
hn = null;
}
else {
hn = lastRun;
ln = null;
}
for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val;
if ((ph & n) == 0)
ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln);
else
hn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn);
}
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
//在旧的table中留一个ForwardingNode,在新的线程hash到这个槽的时候,参与到扩容中来
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {
TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;
TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null;
TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null;
int lc = 0, hc = 0;
for (Node<K,V> e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) {
int h = e.hash;
TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>
(h, e.key, e.val, null, null);
if ((h & n) == 0) {
if ((p.prev = loTail) == null)
lo = p;
else
loTail.next = p;
loTail = p;
++lc;
}
else {
if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null)
hi = p;
else
hiTail.next = p;
hiTail = p;
++hc;
}
}
ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) :
(hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t;
hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) :
(lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t;
setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);
setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);
setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);
advance = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
转载一下查个眼,这块代码有点难啃:
https://blog.csdn.net/tp7309/article/details/76532366
看下get方法:
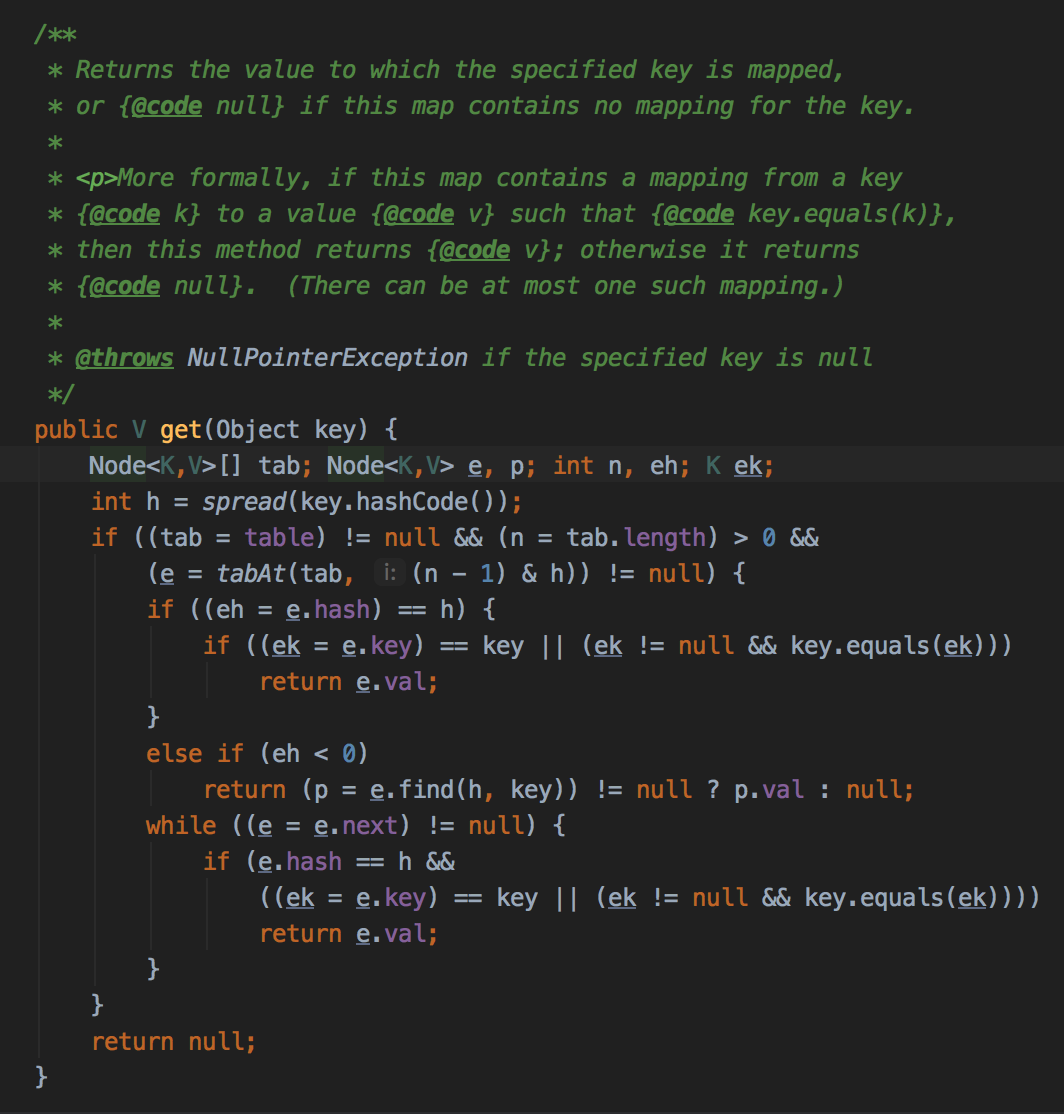
常规操作注意下,当对比的数据的hash值<0,表示在扩容中时:
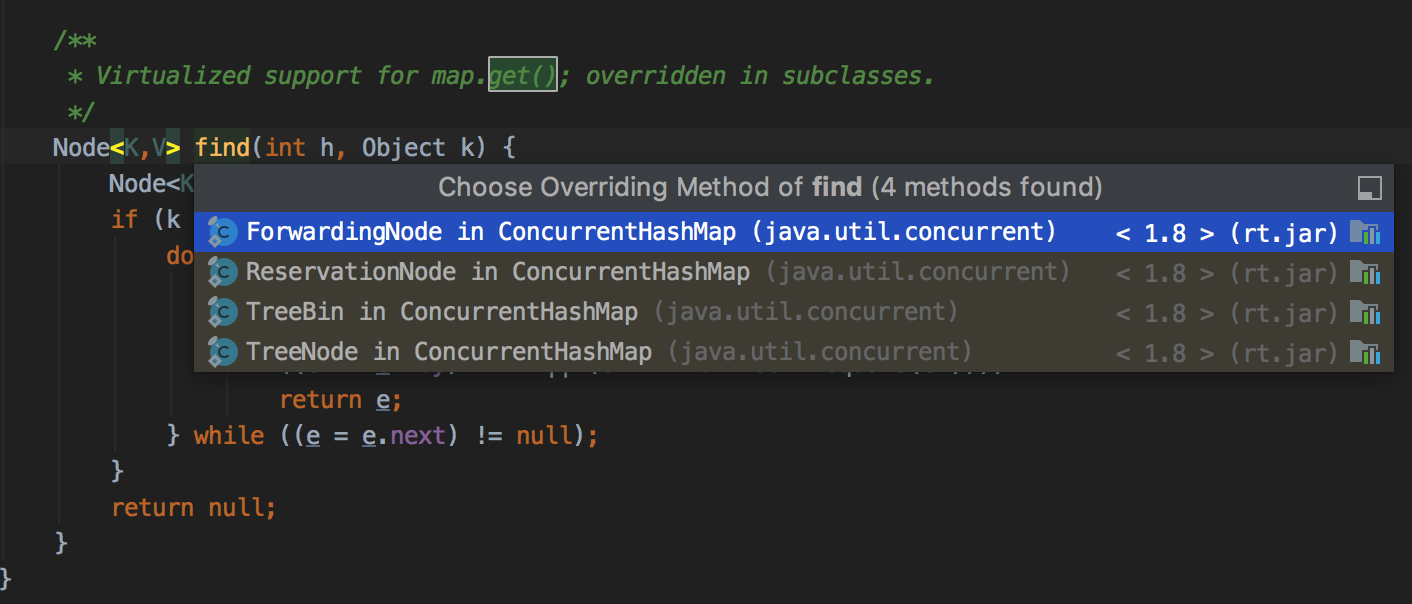
find方法被不同的内部子类override:
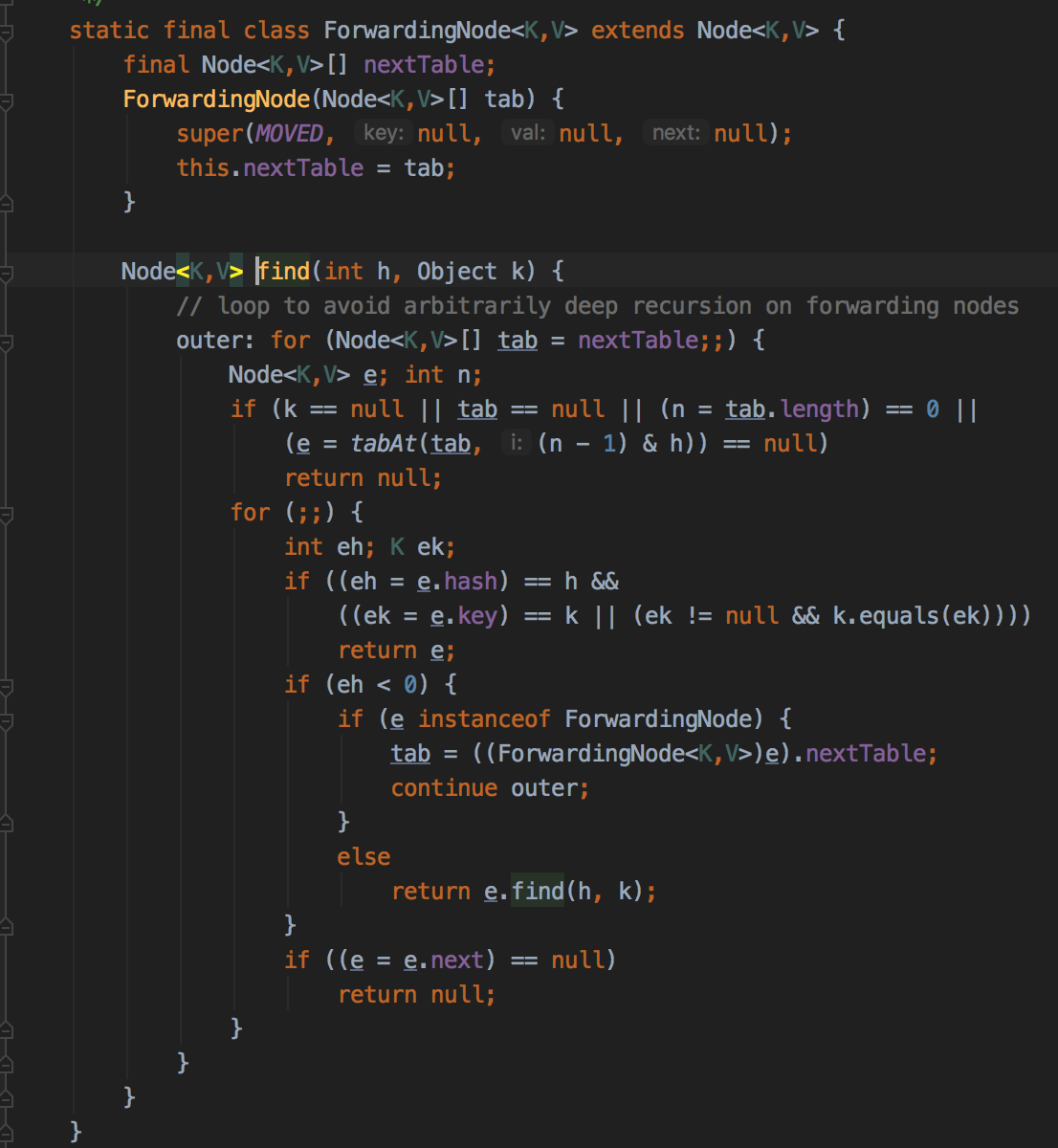
可以看到命中正在扩容中的槽时,回去nextTable查找结果。
size方法:
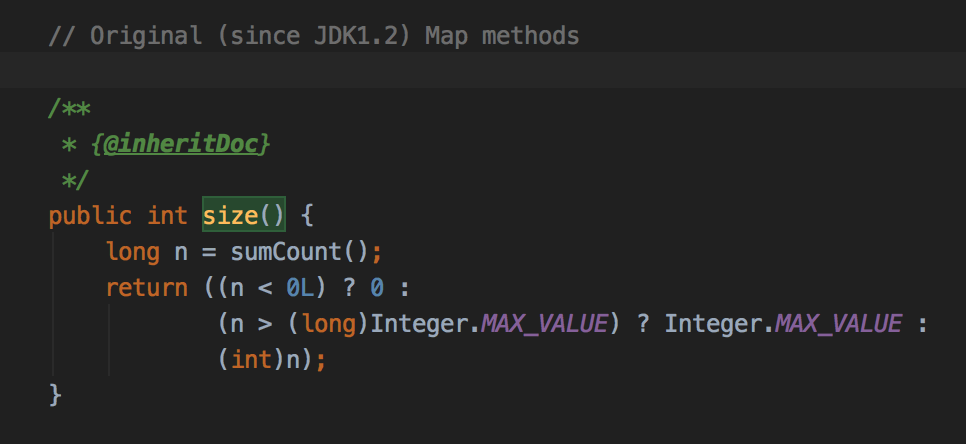
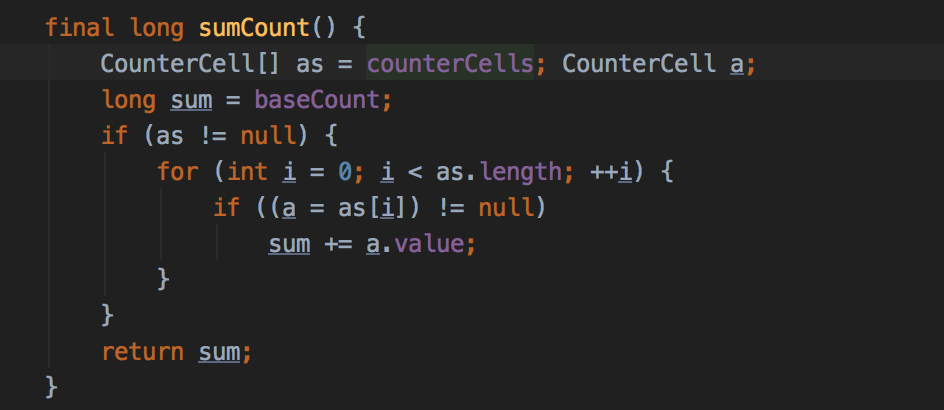
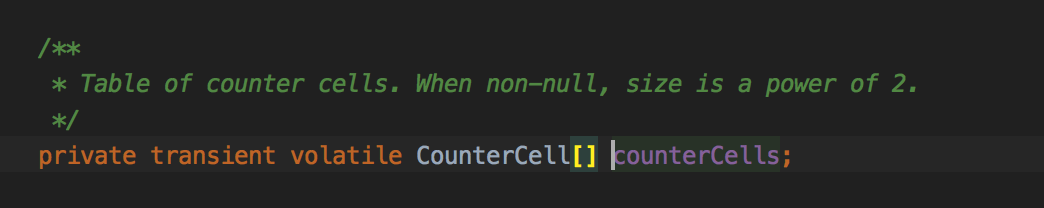
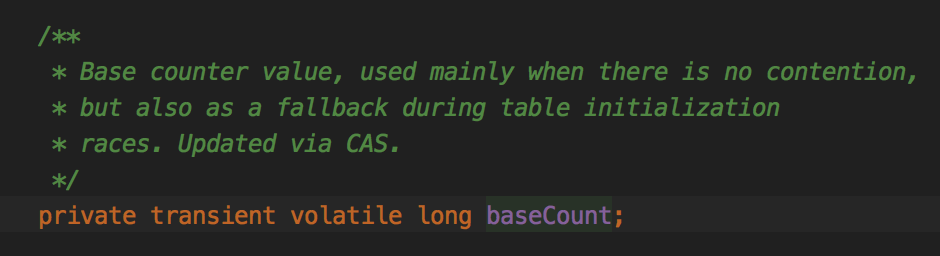
回顾下addCount()的非扩容部分:
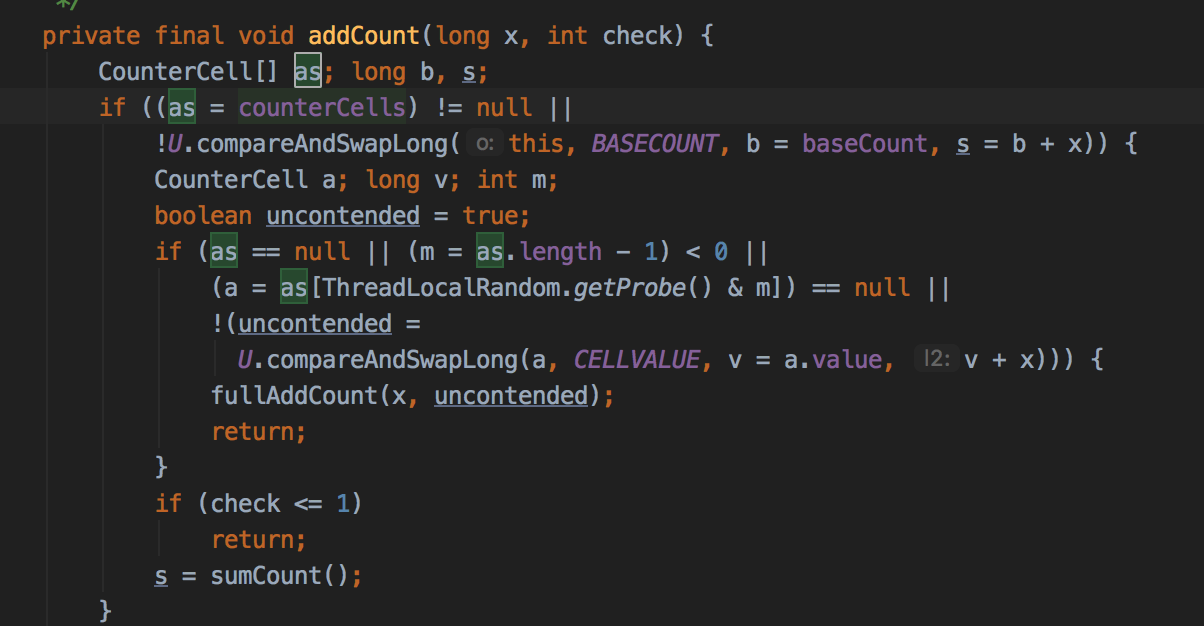
总结:与hashMap很像
- 默认大小为16
- sizeCtl
- 扩容时,每个线程先cas分若干桶(与核心数有关最小为16),对每个桶锁第一个元素,然后同样用高位链和低位链的方式完成重hash,并在最后在第一个桶出放一个ForwardingNode表示此桶已结束扩容迁移到新tab中。如果另外的线程在put的时候遇到ForwardingNode则会加入到扩容工作,每一个线程完成分给自己的段(bound)之后,会去拿另一段bound直至扩容全部完成。更改tab的引用到新的tab。如果另一个线程get的时候碰到ForwardingNode,则会调用ForwardingNode的find方法在新的tab中进行查找




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号