dubbo起停之服务消费
ReferenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor继承了AnnotationInjectedBeanPostProcessors其实现了InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter接口postProcessPropertyValues方法中,扫描带@Reference注解的成员 注入ReferenceBean对象:
@Override public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues( PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeanCreationException { InjectionMetadata metadata = findInjectionMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs); try { metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs); } catch (BeanCreationException ex) { throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of @" + getAnnotationType().getName() + " dependencies is failed", ex); } return pvs; }
findInjectionMetadata会找出所有@Reference的字段和方法并封装成元数据,metadata.inject方法进去,会调用injectElement的inject方法,进而调用AnnotatedFieldElement的inject方法:
public class AnnotatedFieldElement extends InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement { private final Field field; private final A annotation; private volatile Object bean; protected AnnotatedFieldElement(Field field, A annotation) { super(field, null); this.field = field; this.annotation = annotation; } @Override protected void inject(Object bean, String beanName, PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable { Class<?> injectedType = field.getType(); Object injectedObject = getInjectedObject(annotation, bean, beanName, injectedType, this); ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field); field.set(bean, injectedObject); } }
protected Object getInjectedObject(A annotation, Object bean, String beanName, Class<?> injectedType, InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement injectedElement) throws Exception { String cacheKey = buildInjectedObjectCacheKey(annotation, bean, beanName, injectedType, injectedElement); Object injectedObject = injectedObjectsCache.get(cacheKey); if (injectedObject == null) { injectedObject = doGetInjectedBean(annotation, bean, beanName, injectedType, injectedElement); // Customized inject-object if necessary injectedObjectsCache.putIfAbsent(cacheKey, injectedObject); } return injectedObject; }
这里与serviceBean不同 可以看到时直接new可一个实例出来:

其中doGetInjectedBean被ReferenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor重写:
@Override protected Object doGetInjectedBean(Reference reference, Object bean, String beanName, Class<?> injectedType, InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement injectedElement) throws Exception { String referencedBeanName = buildReferencedBeanName(reference, injectedType); ReferenceBean referenceBean = buildReferenceBeanIfAbsent(referencedBeanName, reference, injectedType, getClassLoader()); cacheInjectedReferenceBean(referenceBean, injectedElement); Object proxy = buildProxy(referencedBeanName, referenceBean, injectedType); return proxy; }
可以看到这里构造了一个referenceBean并返回了一个代理,真正注入的其实是这个代理。
仔细观察可以发现这里实际上用的时java原生的代理方法:
private Object buildProxy(String referencedBeanName, ReferenceBean referenceBean, Class<?> injectedType) { InvocationHandler handler = buildInvocationHandler(referencedBeanName, referenceBean); Object proxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(getClassLoader(), new Class[]{injectedType}, handler); return proxy; } private InvocationHandler buildInvocationHandler(String referencedBeanName, ReferenceBean referenceBean) { ReferenceBeanInvocationHandler handler = localReferenceBeanInvocationHandlerCache.get(referencedBeanName); if (handler == null) { handler = new ReferenceBeanInvocationHandler(referenceBean); } if (applicationContext.containsBean(referencedBeanName)) { // Is local @Service Bean or not ? // ReferenceBeanInvocationHandler's initialization has to wait for current local @Service Bean has been exported. localReferenceBeanInvocationHandlerCache.put(referencedBeanName, handler); } else { // Remote Reference Bean should initialize immediately handler.init(); } return handler; }
接下来看下ReferenceBean:

可以看到ReferenceBean也实现了InitializingBean接口,一起看下在初始化的时候做了哪些事情吧
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception { if (getConsumer() == null) { Map<String, ConsumerConfig> consumerConfigMap = applicationContext == null ? null : BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(applicationContext, ConsumerConfig.class, false, false); if (consumerConfigMap != null && consumerConfigMap.size() > 0) { ConsumerConfig consumerConfig = null; for (ConsumerConfig config : consumerConfigMap.values()) { if (config.isDefault() == null || config.isDefault().booleanValue()) { if (consumerConfig != null) { throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate consumer configs: " + consumerConfig + " and " + config); } consumerConfig = config; } } if (consumerConfig != null) { setConsumer(consumerConfig); } } } ......... Boolean b = isInit(); if (b == null && getConsumer() != null) { b = getConsumer().isInit(); } if (b != null && b.booleanValue()) { getObject(); } }
这里的逻辑和serviceBean很相似 一进来会做很多配置检查和启用默认config类的逻辑完了之后我们注意到最后执行了getObject方法:
private void init() { if (initialized) { return; } initialized = true; if (interfaceName == null || interfaceName.length() == 0) { throw new IllegalStateException("<dubbo:reference interface=\"\" /> interface not allow null!"); } // get consumer's global configuration checkDefault(); appendProperties(this); if (getGeneric() == null && getConsumer() != null) { setGeneric(getConsumer().getGeneric()); } if (ProtocolUtils.isGeneric(getGeneric())) { interfaceClass = GenericService.class; } else { try { interfaceClass = Class.forName(interfaceName, true, Thread.currentThread() .getContextClassLoader()); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { throw new IllegalStateException(e.getMessage(), e); } checkInterfaceAndMethods(interfaceClass, methods); } String resolve = System.getProperty(interfaceName); String resolveFile = null; if (resolve == null || resolve.length() == 0) { resolveFile = System.getProperty("dubbo.resolve.file"); if (resolveFile == null || resolveFile.length() == 0) { File userResolveFile = new File(new File(System.getProperty("user.home")), "dubbo-resolve.properties"); if (userResolveFile.exists()) { resolveFile = userResolveFile.getAbsolutePath(); } } if (resolveFile != null && resolveFile.length() > 0) { Properties properties = new Properties(); FileInputStream fis = null; try { fis = new FileInputStream(new File(resolveFile)); properties.load(fis); } catch (IOException e) { throw new IllegalStateException("Unload " + resolveFile + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e); } finally { try { if (null != fis) fis.close(); } catch (IOException e) { logger.warn(e.getMessage(), e); } } resolve = properties.getProperty(interfaceName); } } if (resolve != null && resolve.length() > 0) { url = resolve; if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { if (resolveFile != null) { logger.warn("Using default dubbo resolve file " + resolveFile + " replace " + interfaceName + "" + resolve + " to p2p invoke remote service."); } else { logger.warn("Using -D" + interfaceName + "=" + resolve + " to p2p invoke remote service."); } } } if (consumer != null) { if (application == null) { application = consumer.getApplication(); } if (module == null) { module = consumer.getModule(); } if (registries == null) { registries = consumer.getRegistries(); } if (monitor == null) { monitor = consumer.getMonitor(); } } if (module != null) { if (registries == null) { registries = module.getRegistries(); } if (monitor == null) { monitor = module.getMonitor(); } } if (application != null) { if (registries == null) { registries = application.getRegistries(); } if (monitor == null) { monitor = application.getMonitor(); } } checkApplication(); checkStubAndMock(interfaceClass); Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); Map<Object, Object> attributes = new HashMap<Object, Object>(); map.put(Constants.SIDE_KEY, Constants.CONSUMER_SIDE); map.put(Constants.DUBBO_VERSION_KEY, Version.getProtocolVersion()); map.put(Constants.TIMESTAMP_KEY, String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis())); if (ConfigUtils.getPid() > 0) { map.put(Constants.PID_KEY, String.valueOf(ConfigUtils.getPid())); } if (!isGeneric()) { String revision = Version.getVersion(interfaceClass, version); if (revision != null && revision.length() > 0) { map.put("revision", revision); } String[] methods = Wrapper.getWrapper(interfaceClass).getMethodNames(); if (methods.length == 0) { logger.warn("NO method found in service interface " + interfaceClass.getName()); map.put("methods", Constants.ANY_VALUE); } else { map.put("methods", StringUtils.join(new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(methods)), ",")); } } map.put(Constants.INTERFACE_KEY, interfaceName); appendParameters(map, application); appendParameters(map, module); appendParameters(map, consumer, Constants.DEFAULT_KEY); appendParameters(map, this); String prefix = StringUtils.getServiceKey(map); if (methods != null && !methods.isEmpty()) { for (MethodConfig method : methods) { appendParameters(map, method, method.getName()); String retryKey = method.getName() + ".retry"; if (map.containsKey(retryKey)) { String retryValue = map.remove(retryKey); if ("false".equals(retryValue)) { map.put(method.getName() + ".retries", "0"); } } appendAttributes(attributes, method, prefix + "." + method.getName()); checkAndConvertImplicitConfig(method, map, attributes); } } String hostToRegistry = ConfigUtils.getSystemProperty(Constants.DUBBO_IP_TO_REGISTRY); if (hostToRegistry == null || hostToRegistry.length() == 0) { hostToRegistry = NetUtils.getLocalHost(); } else if (isInvalidLocalHost(hostToRegistry)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Specified invalid registry ip from property:" + Constants.DUBBO_IP_TO_REGISTRY + ", value:" + hostToRegistry); } map.put(Constants.REGISTER_IP_KEY, hostToRegistry); //attributes are stored by system context. StaticContext.getSystemContext().putAll(attributes); ref = createProxy(map); ConsumerModel consumerModel = new ConsumerModel(getUniqueServiceName(), this, ref, interfaceClass.getMethods()); ApplicationModel.initConsumerModel(getUniqueServiceName(), consumerModel); }
方法最后会执行一个init方法如上,大致逻辑是覆盖配置文件,处理config类,将config里必要信息和其他信息给到map用来创建ref的代理
多注册中心会在createProxy中合并成一个Invoker:
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) { //...省略在同一个jvm消费的情况else { if (url != null && url.length() > 0) { // user specified URL, could be peer-to-peer address, or register center's address. String[] us = Constants.SEMICOLON_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(url); if (us != null && us.length > 0) { for (String u : us) { URL url = URL.valueOf(u); if (url.getPath() == null || url.getPath().length() == 0) { url = url.setPath(interfaceName); } if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) { urls.add(url.addParameterAndEncoded(Constants.REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map))); } else { urls.add(ClusterUtils.mergeUrl(url, map)); } } } } else { // assemble URL from register center's configuration List<URL> us = loadRegistries(false); if (us != null && !us.isEmpty()) { for (URL u : us) { URL monitorUrl = loadMonitor(u); if (monitorUrl != null) { map.put(Constants.MONITOR_KEY, URL.encode(monitorUrl.toFullString())); } urls.add(u.addParameterAndEncoded(Constants.REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map))); } } if (urls.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalStateException("No such any registry to reference " + interfaceName + " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ", please config <dubbo:registry address=\"...\" /> to your spring config."); } } if (urls.size() == 1) { invoker = refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, urls.get(0)); } else { List<Invoker<?>> invokers = new ArrayList<Invoker<?>>(); URL registryURL = null; for (URL url : urls) { invokers.add(refprotocol.refer(interfaceClass, url)); if (Constants.REGISTRY_PROTOCOL.equals(url.getProtocol())) { registryURL = url; // use last registry url } } if (registryURL != null) { // registry url is available // use AvailableCluster only when register's cluster is available URL u = registryURL.addParameter(Constants.CLUSTER_KEY, AvailableCluster.NAME); invoker = cluster.join(new StaticDirectory(u, invokers)); } else { // not a registry url invoker = cluster.join(new StaticDirectory(invokers)); } } } Boolean c = check; if (c == null && consumer != null) { c = consumer.isCheck(); } if (c == null) { c = true; // default true } if (c && !invoker.isAvailable()) { throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to check the status of the service " + interfaceName + ". No provider available for the service " + (group == null ? "" : group + "/") + interfaceName + (version == null ? "" : ":" + version) + " from the url " + invoker.getUrl() + " to the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion()); } if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Refer dubbo service " + interfaceClass.getName() + " from url " + invoker.getUrl()); } // create service proxy return (T) proxyFactory.getProxy(invoker); }
首先会得到consumer在注册中心的url,如果发现只有1个url则直接refprotocol.refer获取invokers,否则refprotocol.refer逐个获得invoker实例。最后通过 cluster.join聚合成为一个invoker进一步展开RegistryProtocol的refer():
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException { url = url.setProtocol(url.getParameter(Constants.REGISTRY_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_REGISTRY)).removeParameter(Constants.REGISTRY_KEY); Registry registry = registryFactory.getRegistry(url); if (RegistryService.class.equals(type)) { return proxyFactory.getInvoker((T) registry, type, url); } // group="a,b" or group="*" Map<String, String> qs = StringUtils.parseQueryString(url.getParameterAndDecoded(Constants.REFER_KEY)); String group = qs.get(Constants.GROUP_KEY); if (group != null && group.length() > 0) { if ((Constants.COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(group)).length > 1 || "*".equals(group)) { return doRefer(getMergeableCluster(), registry, type, url); } } return doRefer(cluster, registry, type, url); }
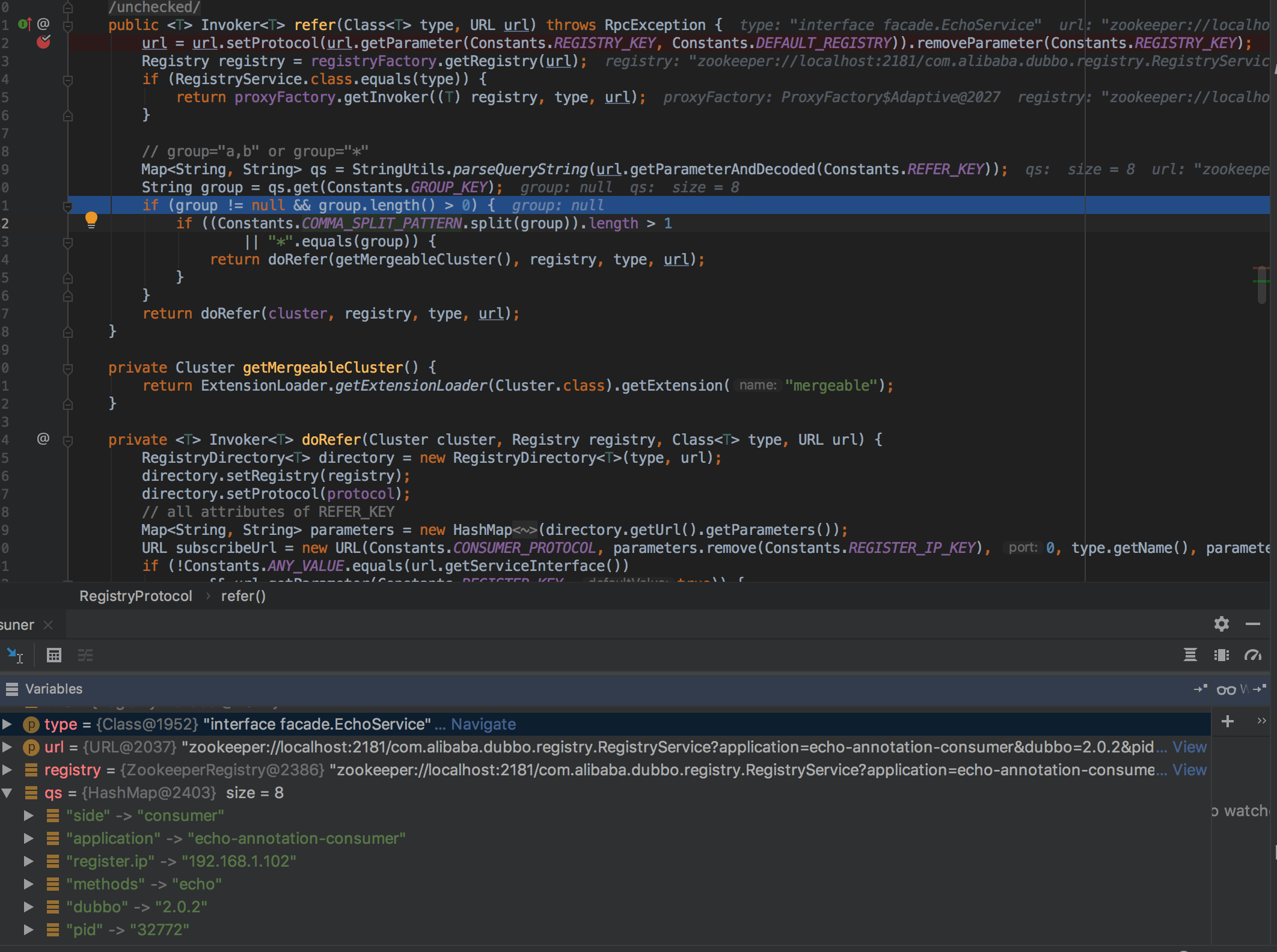
重点看下
directory.subscribe(subscribeUrl.addParameter(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY, Constants.PROVIDERS_CATEGORY + "," + Constants.CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY + "," + Constants.ROUTERS_CATEGORY));
public void subscribe(URL url) { setConsumerUrl(url); registry.subscribe(url, this); }
FailbackRegistry中的subscribe:
public void subscribe(URL url, NotifyListener listener) { super.subscribe(url, listener); removeFailedSubscribed(url, listener); try { // Sending a subscription request to the server side doSubscribe(url, listener); } catch (Exception e) { Throwable t = e; List<URL> urls = getCacheUrls(url); if (urls != null && !urls.isEmpty()) { notify(url, listener, urls); logger.error("Failed to subscribe " + url + ", Using cached list: " + urls + " from cache file: " + getUrl().getParameter(Constants.FILE_KEY, System.getProperty("user.home") + "/dubbo-registry-" + url.getHost() + ".cache") + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t); } else { // If the startup detection is opened, the Exception is thrown directly. boolean check = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.CHECK_KEY, true) && url.getParameter(Constants.CHECK_KEY, true); boolean skipFailback = t instanceof SkipFailbackWrapperException; if (check || skipFailback) { if (skipFailback) { t = t.getCause(); } throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to subscribe " + url + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t); } else { logger.error("Failed to subscribe " + url + ", waiting for retry, cause: " + t.getMessage(), t); } } // Record a failed registration request to a failed list, retry regularly addFailedSubscribed(url, listener); } }
父类中的subscribe仅完成了注册listerner的工作
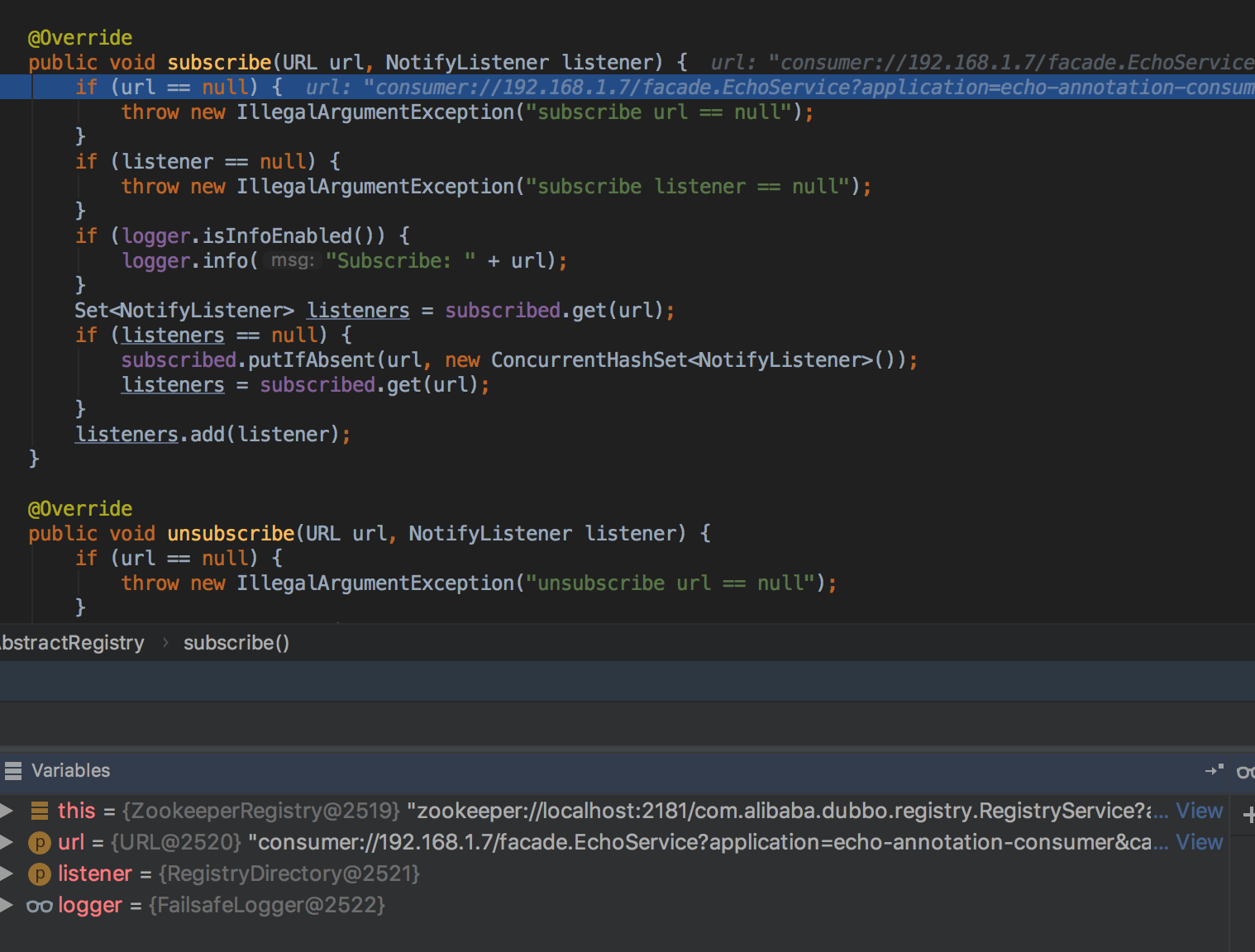
在随后的doSubscribe中我们可以看到这样一段逻辑:
else { List<URL> urls = new ArrayList<URL>(); for (String path : toCategoriesPath(url)) { ConcurrentMap<NotifyListener, ChildListener> listeners = zkListeners.get(url); if (listeners == null) { zkListeners.putIfAbsent(url, new ConcurrentHashMap<NotifyListener, ChildListener>()); listeners = zkListeners.get(url); } ChildListener zkListener = listeners.get(listener); if (zkListener == null) { listeners.putIfAbsent(listener, new ChildListener() { @Override public void childChanged(String parentPath, List<String> currentChilds) { ZookeeperRegistry.this.notify(url, listener, toUrlsWithEmpty(url, parentPath, currentChilds)); } }); zkListener = listeners.get(listener); } zkClient.create(path, false); List<String> children = zkClient.addChildListener(path, zkListener); if (children != null) { urls.addAll(toUrlsWithEmpty(url, path, children)); } } notify(url, listener, urls); }
在用zk客户端写入结点之后,会主动notify一次 最后会调用RegistryDirectory的notify方法
最后看下doRefer方法:
private <T> Invoker<T> doRefer(Cluster cluster, Registry registry, Class<T> type, URL url) { RegistryDirectory<T> directory = new RegistryDirectory<T>(type, url); directory.setRegistry(registry); directory.setProtocol(protocol); // all attributes of REFER_KEY Map<String, String> parameters = new HashMap<String, String>(directory.getUrl().getParameters()); URL subscribeUrl = new URL(Constants.CONSUMER_PROTOCOL, parameters.remove(Constants.REGISTER_IP_KEY), 0, type.getName(), parameters); if (!Constants.ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface()) && url.getParameter(Constants.REGISTER_KEY, true)) { registry.register(subscribeUrl.addParameters(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY, Constants.CONSUMERS_CATEGORY, Constants.CHECK_KEY, String.valueOf(false))); } directory.subscribe(subscribeUrl.addParameter(Constants.CATEGORY_KEY, Constants.PROVIDERS_CATEGORY + "," + Constants.CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY + "," + Constants.ROUTERS_CATEGORY)); Invoker invoker = cluster.join(directory); ProviderConsumerRegTable.registerConsumer(invoker, url, subscribeUrl, directory); return invoker; }
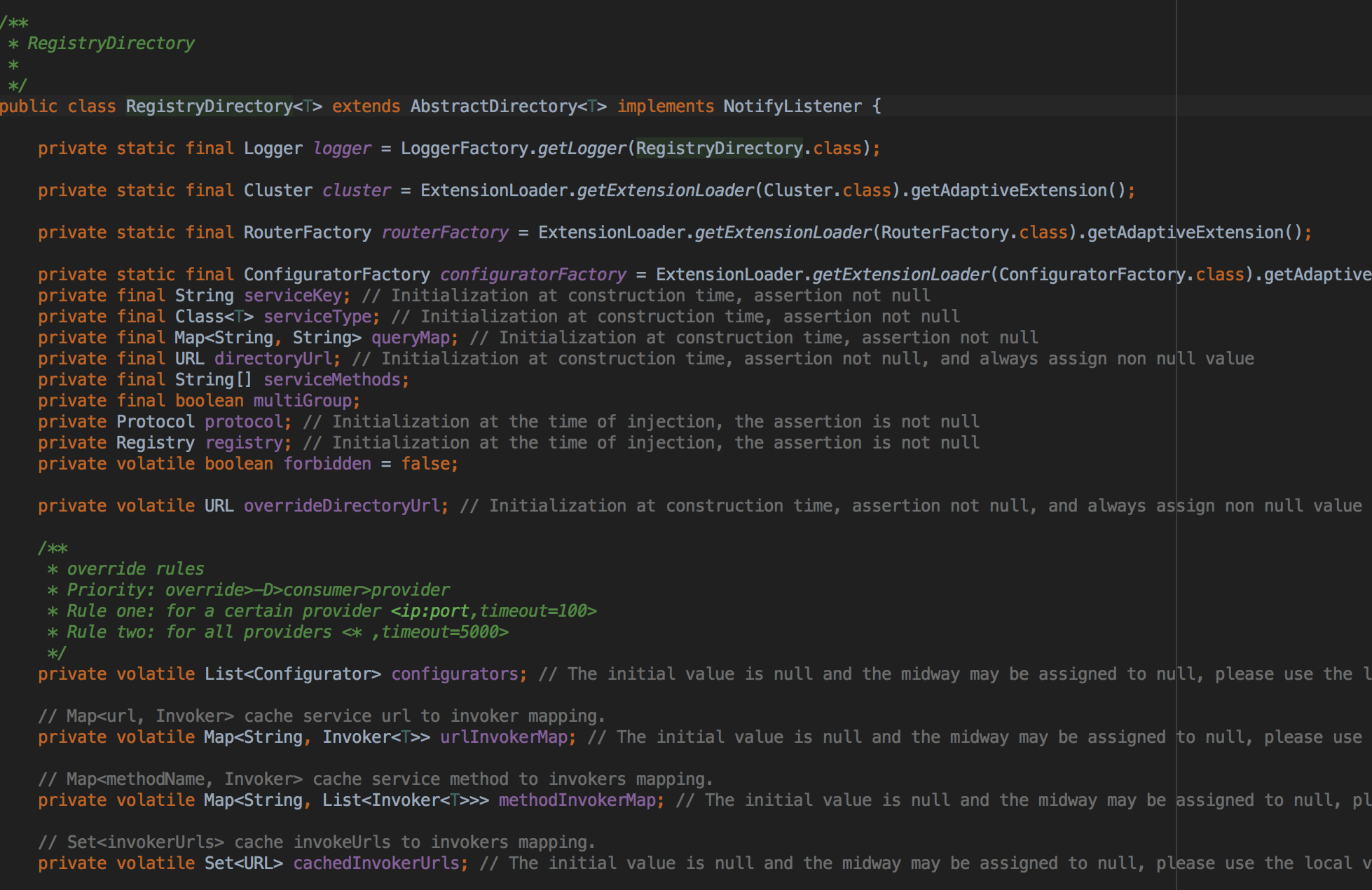
RegistryDirectory持有实际Invoker和接受订阅通知,随后注册消费信息到注册中心,订阅服务提供者,路由和动态配置通过Cluster合并invokers
到此好像只看到与zk的逻辑,具体的远程Invoker是在什么时候哪里创建的呢?
当进行刚刚提到的第一次发器订阅时会进行一次数据拉取操作,同时触发RegistryDirectory#notify方法,当通知providers数据时,在RegistryDirectory#toInvoker方法内完成转换。
private Map<String, Invoker<T>> toInvokers(List<URL> urls) { Map<String, Invoker<T>> newUrlInvokerMap = new HashMap<String, Invoker<T>>(); if (urls == null || urls.isEmpty()) { return newUrlInvokerMap; } Set<String> keys = new HashSet<String>(); String queryProtocols = this.queryMap.get(Constants.PROTOCOL_KEY); for (URL providerUrl : urls) { // If protocol is configured at the reference side, only the matching protocol is selected if (queryProtocols != null && queryProtocols.length() > 0) { boolean accept = false; String[] acceptProtocols = queryProtocols.split(","); for (String acceptProtocol : acceptProtocols) { if (providerUrl.getProtocol().equals(acceptProtocol)) { accept = true; break; } } if (!accept) { continue; } } if (Constants.EMPTY_PROTOCOL.equals(providerUrl.getProtocol())) { continue; } if (!ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).hasExtension(providerUrl.getProtocol())) { logger.error(new IllegalStateException("Unsupported protocol " + providerUrl.getProtocol() + " in notified url: " + providerUrl + " from registry " + getUrl().getAddress() + " to consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + ", supported protocol: " + ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getSupportedExtensions())); continue; } URL url = mergeUrl(providerUrl); String key = url.toFullString(); // The parameter urls are sorted if (keys.contains(key)) { // Repeated url continue; } keys.add(key); // Cache key is url that does not merge with consumer side parameters, regardless of how the consumer combines parameters, if the server url changes, then refer again Map<String, Invoker<T>> localUrlInvokerMap = this.urlInvokerMap; // local reference Invoker<T> invoker = localUrlInvokerMap == null ? null : localUrlInvokerMap.get(key); if (invoker == null) { // Not in the cache, refer again try { boolean enabled = true; if (url.hasParameter(Constants.DISABLED_KEY)) { enabled = !url.getParameter(Constants.DISABLED_KEY, false); } else { enabled = url.getParameter(Constants.ENABLED_KEY, true); } if (enabled) { invoker = new InvokerDelegate<T>(protocol.refer(serviceType, url), url, providerUrl); } } catch (Throwable t) { logger.error("Failed to refer invoker for interface:" + serviceType + ",url:(" + url + ")" + t.getMessage(), t); } if (invoker != null) { // Put new invoker in cache newUrlInvokerMap.put(key, invoker); } } else { newUrlInvokerMap.put(key, invoker); } } keys.clear(); return newUrlInvokerMap; }
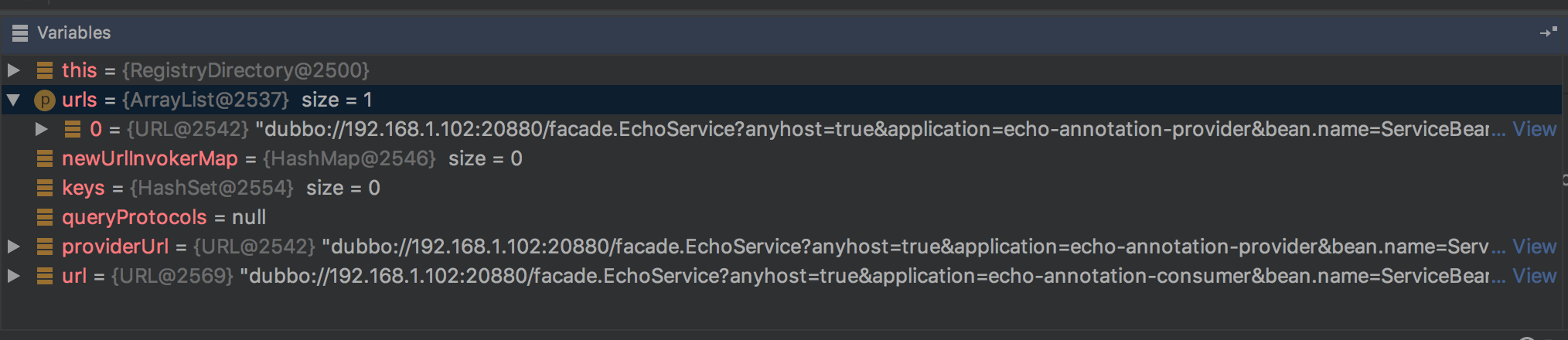
具体的Invoker创建是在DubboProtocol#refer中实现的,refer中initClient:
private ExchangeClient initClient(URL url) { // client type setting. String str = url.getParameter(Constants.CLIENT_KEY, url.getParameter(Constants.SERVER_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_REMOTING_CLIENT)); url = url.addParameter(Constants.CODEC_KEY, DubboCodec.NAME); // enable heartbeat by default url = url.addParameterIfAbsent(Constants.HEARTBEAT_KEY, String.valueOf(Constants.DEFAULT_HEARTBEAT)); // BIO is not allowed since it has severe performance issue. if (str != null && str.length() > 0 && !ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).hasExtension(str)) { throw new RpcException("Unsupported client type: " + str + "," + " supported client type is " + StringUtils.join(ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).getSupportedExtensions(), " ")); } ExchangeClient client; try { // connection should be lazy if (url.getParameter(Constants.LAZY_CONNECT_KEY, false)) { client = new LazyConnectExchangeClient(url, requestHandler); } else { client = Exchangers.connect(url, requestHandler); } } catch (RemotingException e) { throw new RpcException("Fail to create remoting client for service(" + url + "): " + e.getMessage(), e); } return client; }
public static ExchangeClient connect(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException { if (url == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null"); } if (handler == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("handler == null"); } url = url.addParameterIfAbsent(Constants.CODEC_KEY, "exchange"); return getExchanger(url).connect(url, handler); } public static Exchanger getExchanger(URL url) { String type = url.getParameter(Constants.EXCHANGER_KEY, Constants.DEFAULT_EXCHANGER); return getExchanger(type); } public static Exchanger getExchanger(String type) { return ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Exchanger.class).getExtension(type); }
public class HeaderExchanger implements Exchanger { public static final String NAME = "header"; @Override public ExchangeClient connect(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException { return new HeaderExchangeClient(Transporters.connect(url, new DecodeHandler(new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler))), true); } @Override public ExchangeServer bind(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException { return new HeaderExchangeServer(Transporters.bind(url, new DecodeHandler(new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler)))); } }
哎 到了这里有点眼熟有没有,同样我们可以在DubboProtocl里找到这样一个handle人:
private ExchangeHandler requestHandler = new ExchangeHandlerAdapter() { @Override public Object reply(ExchangeChannel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException { if (message instanceof Invocation) { Invocation inv = (Invocation) message; Invoker<?> invoker = getInvoker(channel, inv); // need to consider backward-compatibility if it's a callback if (Boolean.TRUE.toString().equals(inv.getAttachments().get(IS_CALLBACK_SERVICE_INVOKE))) { String methodsStr = invoker.getUrl().getParameters().get("methods"); boolean hasMethod = false; if (methodsStr == null || methodsStr.indexOf(",") == -1) { hasMethod = inv.getMethodName().equals(methodsStr); } else { String[] methods = methodsStr.split(","); for (String method : methods) { if (inv.getMethodName().equals(method)) { hasMethod = true; break; } } } if (!hasMethod) { logger.warn(new IllegalStateException("The methodName " + inv.getMethodName() + " not found in callback service interface ,invoke will be ignored." + " please update the api interface. url is:" + invoker.getUrl()) + " ,invocation is :" + inv); return null; } } RpcContext.getContext().setRemoteAddress(channel.getRemoteAddress()); return invoker.invoke(inv); } throw new RemotingException(channel, "Unsupported request: " + (message == null ? null : (message.getClass().getName() + ": " + message)) + ", channel: consumer: " + channel.getRemoteAddress() + " --> provider: " + channel.getLocalAddress()); }
这里有一个疑问 在服务暴露的时候 我们用的也是这个requestHandler,但是在server端 我们确实是持有业务逻辑的,我们也看到过invoker.invoke执行的是业务逻辑,但是这里的invoker执行的是什么内容呢
总结一下:被标注了@reference的字段,最后会被注入ReferenceBean和Handler生成的代理,在ReferenceBean里最为容器的bean的初始化的时候,会将T ref指向一个代理,具体的过程大概是protocol的refer方法,其中RegistryProtocol的refer会去注册中心注册,订阅,并会主动调用notify,notify最终用拿到的dubbo协议url调用扩展点DubboProtocols的refer方法,DubboProtocols会创建nettyClient 被RegistryDirectory持有,并作为参数给cluster.join()得到一个代理,这个代理会进一步被proxyFactory.getProxy()再包一层 返回给ref引用


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号