time series
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv(r'../data/data.csv')
data
# 数据那么好,为什么不回归呢...
| x1 | x2 | x3 | x4 | x5 | x6 | x7 | x8 | x9 | x10 | x11 | x12 | x13 | y | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 3831732 | 181.54 | 448.19 | 7571.00 | 6212.70 | 6370241 | 525.71 | 985.31 | 60.62 | 65.66 | 120.0 | 1.029 | 5321 | 64.87 |
| 1 | 3913824 | 214.63 | 549.97 | 9038.16 | 7601.73 | 6467115 | 618.25 | 1259.20 | 73.46 | 95.46 | 113.5 | 1.051 | 6529 | 99.75 |
| 2 | 3928907 | 239.56 | 686.44 | 9905.31 | 8092.82 | 6560508 | 638.94 | 1468.06 | 81.16 | 81.16 | 108.2 | 1.064 | 7008 | 88.11 |
| 3 | 4282130 | 261.58 | 802.59 | 10444.60 | 8767.98 | 6664862 | 656.58 | 1678.12 | 85.72 | 91.70 | 102.2 | 1.092 | 7694 | 106.07 |
| 4 | 4453911 | 283.14 | 904.57 | 11255.70 | 9422.33 | 6741400 | 758.83 | 1893.52 | 88.88 | 114.61 | 97.7 | 1.200 | 8027 | 137.32 |
| 5 | 4548852 | 308.58 | 1000.69 | 12018.52 | 9751.44 | 6850024 | 878.26 | 2139.18 | 92.85 | 152.78 | 98.5 | 1.198 | 8549 | 188.14 |
| 6 | 4962579 | 348.09 | 1121.13 | 13966.53 | 11349.47 | 7006896 | 923.67 | 2492.74 | 94.37 | 170.62 | 102.8 | 1.348 | 9566 | 219.91 |
| 7 | 5029338 | 387.81 | 1248.29 | 14694.00 | 11467.35 | 7125979 | 978.21 | 2841.65 | 97.28 | 214.53 | 98.9 | 1.467 | 10473 | 271.91 |
| 8 | 5070216 | 453.49 | 1370.68 | 13380.47 | 10671.78 | 7206229 | 1009.24 | 3203.96 | 103.07 | 202.18 | 97.6 | 1.560 | 11469 | 269.10 |
| 9 | 5210706 | 533.55 | 1494.27 | 15002.59 | 11570.58 | 7251888 | 1175.17 | 3758.62 | 109.91 | 222.51 | 100.1 | 1.456 | 12360 | 300.55 |
| 10 | 5407087 | 598.33 | 1677.77 | 16884.16 | 13120.83 | 7376720 | 1348.93 | 4450.55 | 117.15 | 249.01 | 101.7 | 1.424 | 14174 | 338.45 |
| 11 | 5744550 | 665.32 | 1905.84 | 18287.24 | 14468.24 | 7505322 | 1519.16 | 5154.23 | 130.22 | 303.41 | 101.5 | 1.456 | 16394 | 408.86 |
| 12 | 5994973 | 738.97 | 2199.14 | 19850.66 | 15444.93 | 7607220 | 1696.38 | 6081.86 | 128.51 | 356.99 | 102.3 | 1.438 | 17881 | 476.72 |
| 13 | 6236312 | 877.07 | 2624.24 | 22469.22 | 18951.32 | 7734787 | 1863.34 | 7140.32 | 149.87 | 429.36 | 103.4 | 1.474 | 20058 | 838.99 |
| 14 | 6529045 | 1005.37 | 3187.39 | 25316.72 | 20835.95 | 7841695 | 2105.54 | 8287.38 | 169.19 | 508.84 | 105.9 | 1.515 | 22114 | 843.14 |
| 15 | 6791495 | 1118.03 | 3615.77 | 27609.59 | 22820.89 | 7946154 | 2659.85 | 9138.21 | 172.28 | 557.74 | 97.5 | 1.633 | 24190 | 1107.67 |
| 16 | 7110695 | 1304.48 | 4476.38 | 30658.49 | 25011.61 | 8061370 | 3263.57 | 10748.28 | 188.57 | 664.06 | 103.2 | 1.638 | 29549 | 1399.16 |
| 17 | 7431755 | 1700.87 | 5243.03 | 34438.08 | 28209.74 | 8145797 | 3412.21 | 12423.44 | 204.54 | 710.66 | 105.5 | 1.670 | 34214 | 1535.14 |
| 18 | 7512997 | 1969.51 | 5977.27 | 38053.52 | 30490.44 | 8222969 | 3758.39 | 13551.21 | 213.76 | 760.49 | 103.0 | 1.825 | 37934 | 1579.68 |
| 19 | 7599295 | 2110.78 | 6882.85 | 42049.14 | 33156.83 | 8323096 | 4454.55 | 15420.14 | 228.46 | 852.56 | 102.6 | 1.906 | 41972 | 2088.14 |
AutoGluon : Regression
train_data_reg = data.iloc[0:-2,:]
test_data_reg = data.iloc[-2:,:]
from autogluon.tabular import TabularDataset, TabularPredictor
train_data_reg_auto = TabularDataset(train_data_reg)
test_data_reg_auto = TabularDataset(test_data_reg)
predictor = TabularPredictor(label='y').fit(train_data=train_data_reg_auto)
predictions = predictor.predict(test_data_reg_auto)
## AutoGluon infers your prediction problem is: 'regression'
## (because dtype of label-column == float and many unique label-values observed).
No path specified. Models will be saved in: "AutogluonModels/ag-20220331_070120\"
Beginning AutoGluon training ...
AutoGluon will save models to "AutogluonModels/ag-20220331_070120\"
AutoGluon Version: 0.4.0
Python Version: 3.9.7
Operating System: Windows
Train Data Rows: 18
Train Data Columns: 13
Label Column: y
Preprocessing data ...
AutoGluon infers your prediction problem is: 'regression' (because dtype of label-column == float and many unique label-values observed).
Label info (max, min, mean, stddev): (1535.14, 64.87, 482.99222, 462.62691)
If 'regression' is not the correct problem_type, please manually specify the problem_type parameter during predictor init (You may specify problem_type as one of: ['binary', 'multiclass', 'regression'])
Using Feature Generators to preprocess the data ...
Fitting AutoMLPipelineFeatureGenerator...
Available Memory: 693.54 MB
Train Data (Original) Memory Usage: 0.0 MB (0.0% of available memory)
Inferring data type of each feature based on column values. Set feature_metadata_in to manually specify special dtypes of the features.
Stage 1 Generators:
Fitting AsTypeFeatureGenerator...
Stage 2 Generators:
Fitting FillNaFeatureGenerator...
Stage 3 Generators:
Fitting IdentityFeatureGenerator...
Stage 4 Generators:
Fitting DropUniqueFeatureGenerator...
Types of features in original data (raw dtype, special dtypes):
('float', []) : 10 | ['x2', 'x3', 'x4', 'x5', 'x7', ...]
('int', []) : 3 | ['x1', 'x6', 'x13']
Types of features in processed data (raw dtype, special dtypes):
('float', []) : 10 | ['x2', 'x3', 'x4', 'x5', 'x7', ...]
('int', []) : 3 | ['x1', 'x6', 'x13']
0.1s = Fit runtime
13 features in original data used to generate 13 features in processed data.
Train Data (Processed) Memory Usage: 0.0 MB (0.0% of available memory)
Data preprocessing and feature engineering runtime = 0.09s ...
AutoGluon will gauge predictive performance using evaluation metric: 'root_mean_squared_error'
To change this, specify the eval_metric parameter of Predictor()
Automatically generating train/validation split with holdout_frac=0.2, Train Rows: 14, Val Rows: 4
Fitting 11 L1 models ...
Fitting model: KNeighborsUnif ...
-61.9471 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.01s = Training runtime
0.02s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: KNeighborsDist ...
-29.1196 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.01s = Training runtime
0.01s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: LightGBMXT ...
-334.4967 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.2s = Training runtime
0.01s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: LightGBM ...
-334.4967 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.22s = Training runtime
0.0s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: RandomForestMSE ...
-54.861 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.67s = Training runtime
0.05s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: CatBoost ...
-31.2363 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.94s = Training runtime
0.0s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: ExtraTreesMSE ...
-23.7411 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.65s = Training runtime
0.1s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: NeuralNetFastAI ...
No improvement since epoch 0: early stopping
-290.8096 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.35s = Training runtime
0.02s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: XGBoost ...
-30.2997 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.2s = Training runtime
0.02s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: NeuralNetTorch ...
Warning: Exception caused NeuralNetTorch to fail during training... Skipping this model.
float division by zero
Detailed Traceback:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "D:\miniConda_Python\lib\site-packages\autogluon\core\trainer\abstract_trainer.py", line 1074, in _train_and_save
model = self._train_single(X, y, model, X_val, y_val, **model_fit_kwargs)
File "D:\miniConda_Python\lib\site-packages\autogluon\core\trainer\abstract_trainer.py", line 1032, in _train_single
model = model.fit(X=X, y=y, X_val=X_val, y_val=y_val, **model_fit_kwargs)
File "D:\miniConda_Python\lib\site-packages\autogluon\core\models\abstract\abstract_model.py", line 577, in fit
out = self._fit(**kwargs)
File "D:\miniConda_Python\lib\site-packages\autogluon\tabular\models\tabular_nn\torch\tabular_nn_torch.py", line 196, in _fit
self._train_net(train_dataset=train_dataset,
File "D:\miniConda_Python\lib\site-packages\autogluon\tabular\models\tabular_nn\torch\tabular_nn_torch.py", line 350, in _train_net
f"Train loss: {round(total_train_loss / total_train_size, 4)}, "
ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero
Fitting model: LightGBMLarge ...
-43.8279 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.32s = Training runtime
0.01s = Validation runtime
Fitting model: WeightedEnsemble_L2 ...
-4.0605 = Validation score (root_mean_squared_error)
0.4s = Training runtime
0.0s = Validation runtime
AutoGluon training complete, total runtime = 4.9s ... Best model: "WeightedEnsemble_L2"
TabularPredictor saved. To load, use: predictor = TabularPredictor.load("AutogluonModels/ag-20220331_070120\")
predictions
18 1409.151489
19 1405.571655
Name: y, dtype: float32
## AutoGluon training complete, total runtime = 11.11s ... Best model: "WeightedEnsemble_L2"
import joblib
model = joblib.load("AutogluonModels/ag-20220331_035208/models/WeightedEnsemble_L2/model.pkl")
y_test = test_data_reg_auto.iloc[:,0:-1]
y_true = test_data_reg_auto.iloc[:,-1]
y_pred = model.predict(y_test)
y_pred
array([1190.105 , 1180.3666], dtype=float32)
y_true
18 1579.68
19 2088.14
Name: y, dtype: float64
## 才注意到py编写函数不用指定参数类型的.......
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error,mean_absolute_error
def metrics(y_true,y_pred):
mae = mean_absolute_error(y_true,y_pred)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_true,y_pred)
print("mae = {} , mse = {}".format(mae,mse))
## 挺夸张的,不过好像也正常
## std 后数据会好看点,但都autogluon了,就懒得操作了
metrics(y_true,y_pred)
mae = 648.6742211914062 , mse = 487910.64153920766
Time_Series
import numpy as np
data_time_series = np.array(data.iloc[:,-1])
import seaborn as sns
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
ax = sns.lineplot(data = data_time_series)
plt.show()
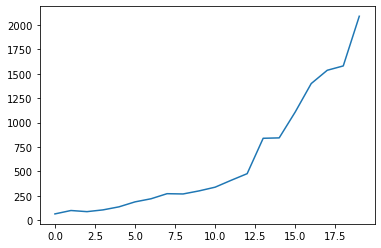
加权移动平均 : 蠢
data_time_series_train = data_time_series[0:-2]
data_time_series_test = data_time_series[-2:]
data_time_series_train_array = np.array(data_time_series_train).reshape(1,18)
weight = np.array([0.1,0.2,0.2,0.5])
record = []
for x in range(2,0,-1):
series = data_time_series_train_array[0,-5-x:-1-x],
res = np.multiply(series,weight)
record.append(np.sum(res) + 0.5 * np.sum(res))
print(" %d : %f" %(2015 - x + 1 , np.sum(res) + 0.5 * np.sum(res)))
## res + 0.5res : 加权和 和 提升 蠢
metrics(y_true,record)
2014 : 1088.397000
2015 : 1406.899500
mae = 586.26175 , mse = 352723.802464625
Torch : Lstm
补充成任务数据的样式,反归一化输出
我自己怎么可能写得出来呢
# data_time_series : 切出来的 y 一列
data_time_series_lstm = data_time_series
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
scaler = MinMaxScaler()
max_value = np.max(data_time_series_lstm)
min_value = np.min(data_time_series_lstm)
data_time_series_lstm = (data_time_series_lstm - min_value) / (max_value - min_value)
# std
import seaborn as sns
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
ax = sns.lineplot(data = data_time_series_lstm)
plt.show()
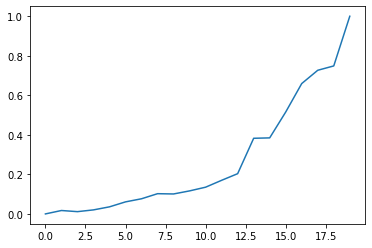
import torch
DAYS_FOR_TRAIN = 5
def create_dataset(data, days_for_train=5) -> (np.array, np.array):
"""
根据给定的序列data,生成数据集
数据集分为输入和输出,每一个输入的长度为days_for_train,每一个输出的长度为1。
也就是说用days_for_train天的数据,对应下一天的数据。
若给定序列的长度为d,将输出长度为(d-days_for_train+1)个输入/输出对
数据形式:[x1,x2,x3,x4,y]
"""
dataset_x, dataset_y= [], []
for i in range(len(data)-days_for_train):
_x = data[i:(i+days_for_train)]
dataset_x.append(_x)
dataset_y.append(data[i+days_for_train])
return (np.array(dataset_x), np.array(dataset_y))
dataset_x, dataset_y = create_dataset(data_time_series_lstm, DAYS_FOR_TRAIN)
dataset_y
array([0.06092612, 0.07662843, 0.1023294 , 0.10094056, 0.1164847 ,
0.13521675, 0.17001685, 0.20355662, 0.38260835, 0.38465949,
0.51540328, 0.65947204, 0.72668008, 0.74869395, 1. ])
dataset_y
array([0.06092612, 0.07662843, 0.1023294 , 0.10094056, 0.1164847 ,
0.13521675, 0.17001685, 0.20355662, 0.38260835, 0.38465949,
0.51540328, 0.65947204, 0.72668008, 0.74869395, 1. ])
# 划分训练集和测试集,70%作为训练集
train_size = int(len(dataset_x) * 0.7)
train_x = dataset_x[:train_size]
train_y = dataset_y[:train_size]
# 将数据改变形状,RNN 读入的数据维度是 (seq_size, batch_size, feature_size)
train_x = train_x.reshape(-1, 1, DAYS_FOR_TRAIN)
train_y = train_y.reshape(-1, 1, 1)
# 转为pytorch的tensor对象
train_x = torch.from_numpy(train_x).to(torch.float32)
train_y = torch.from_numpy(train_y).to(torch.float32)
import torch
from torch import nn
class LSTM_Regression(nn.Module):
"""
使用LSTM进行回归
参数:
- input_size: feature size
- hidden_size: number of hidden units
- output_size: number of output
- num_layers: layers of LSTM to stack
"""
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size=1, num_layers=2):
super().__init__()
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size, hidden_size, num_layers)
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_size, output_size)
def forward(self, _x):
x, _ = self.lstm(_x) # _x is input, size (seq_len, batch, input_size)
s, b, h = x.shape # x is output, size (seq_len, batch, hidden_size)
x = x.view(s*b, h)
x = self.fc(x)
x = x.view(s, b, -1) # 把形状改回来
return x
model = LSTM_Regression(DAYS_FOR_TRAIN, 8, output_size=1, num_layers=2)
loss_function = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-2)
for i in range(100):
out = model(train_x)
loss = loss_function(out, train_y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
if (i+1) % 10 == 0:
print('Epoch: {}, Loss:{:.5f}'.format(i+1, loss.item()))
Epoch: 10, Loss:0.00674
Epoch: 20, Loss:0.00327
Epoch: 30, Loss:0.00204
Epoch: 40, Loss:0.00116
Epoch: 50, Loss:0.00085
Epoch: 60, Loss:0.00071
Epoch: 70, Loss:0.00064
Epoch: 80, Loss:0.00059
Epoch: 90, Loss:0.00057
Epoch: 100, Loss:0.00055
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
model = model.eval() # 转换成测试模式
# 注意这里用的是全集 模型的输出长度会比原数据少DAYS_FOR_TRAIN 填充使长度相等再作图
dataset_x = dataset_x.reshape(-1, 1, DAYS_FOR_TRAIN) # (seq_size, batch_size, feature_size)
dataset_x = torch.tensor(dataset_x).to(torch.float32)
pred_test = model(dataset_x) # 全量训练集的模型输出 (seq_size, batch_size, output_size)
pred_test = pred_test.view(-1).data.numpy()
pred_test = np.concatenate((np.zeros(DAYS_FOR_TRAIN), pred_test)) # 填充0 使长度相同
assert len(pred_test) == len(data_time_series_lstm)
plt.plot(pred_test, 'r', label='prediction')
plt.plot(data_time_series_lstm, 'b', label='real')
plt.plot((train_size, train_size), (0, 1), 'g--')
plt.legend(loc='best')
plt.show()
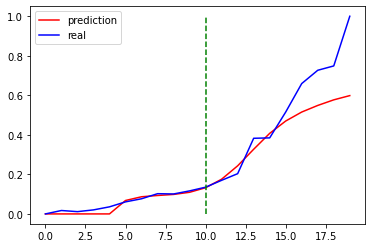
### 数据反归一化
pred_test = pred_test * (max_value - pred_test) + pred_test
ax = sns.lineplot(data = pred_test)
plt.show(ax)
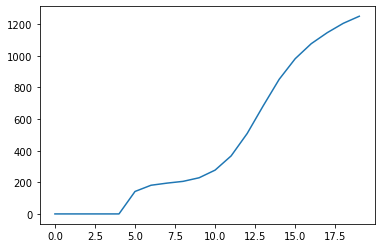
pred_test
array([ 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. ,
0. , 141.97164252, 181.31122203, 194.75042542,
205.88793585, 228.55081975, 277.00616729, 366.82627218,
508.25917347, 683.14472015, 851.27406525, 981.55267148,
1076.44698354, 1146.16705891, 1205.26890924, 1250.06205714])
寄
metrics(data_time_series_lstm, pred_test)
mae = 464.65907024157497 , mse = 414380.31475062034




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号