redis安装和参数配置-基于Windows
1.先下载redis包并完成安装 .
2.打开cmd黑窗口 , 找到本地redis的安装地址
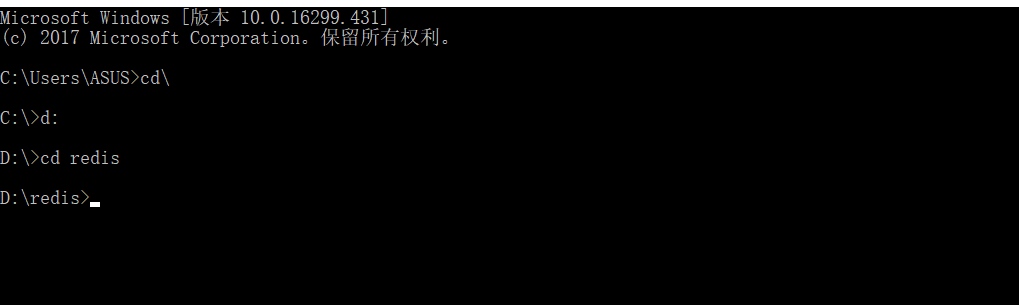
3.输入[redis-server.exe] , 回车 , 运行redis测试是否安装成功,
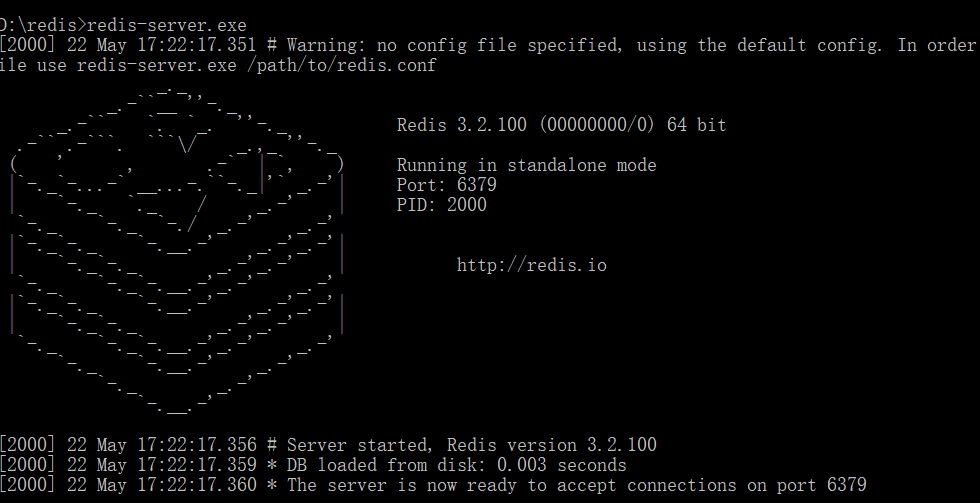
4.这时候 , 原窗口不要关闭 (关闭了已经在运行的redis服务就停掉了) , 打开新的窗口 , 找到redis安装目录 , 输入本机IP及端口号回车启动
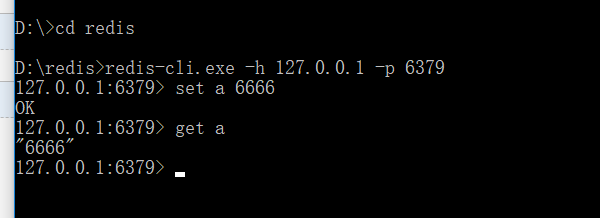
可以测试下设值取值 , 判断是否真的安装成功了
5.假如需要经常使用本地的redis服务的话可以把本机的redis注册到电脑的服务中 , 并设置为自启动 , 这样就可以有效避免每次跑项目都要重新手动去黑窗口启动的弊端.而且黑窗口启动有个弊端在于 , 窗口不可关闭 , 关掉服务就停了
我这边是使用的黑窗口配置redis服务的方法 . 记录下来 , 避免忘记
首先要在黑窗口中把redis基础服务跑起来 .
分别是 :
1.进入redis安装目录 , 输入redis-server.exe , 然后回车 , 会出现如下页面 , 否则估计是安装失败
2.保持当前窗口打开 , 打开另一个黑窗口 , 进入redis安装页面 , 输入redis-server --service-install redis.windows-service.conf --service-name redis(此处为注册的服务名) --port 6379(默认端口号 , 假如重新配置端口号 , 则输入自己配置的端口号)
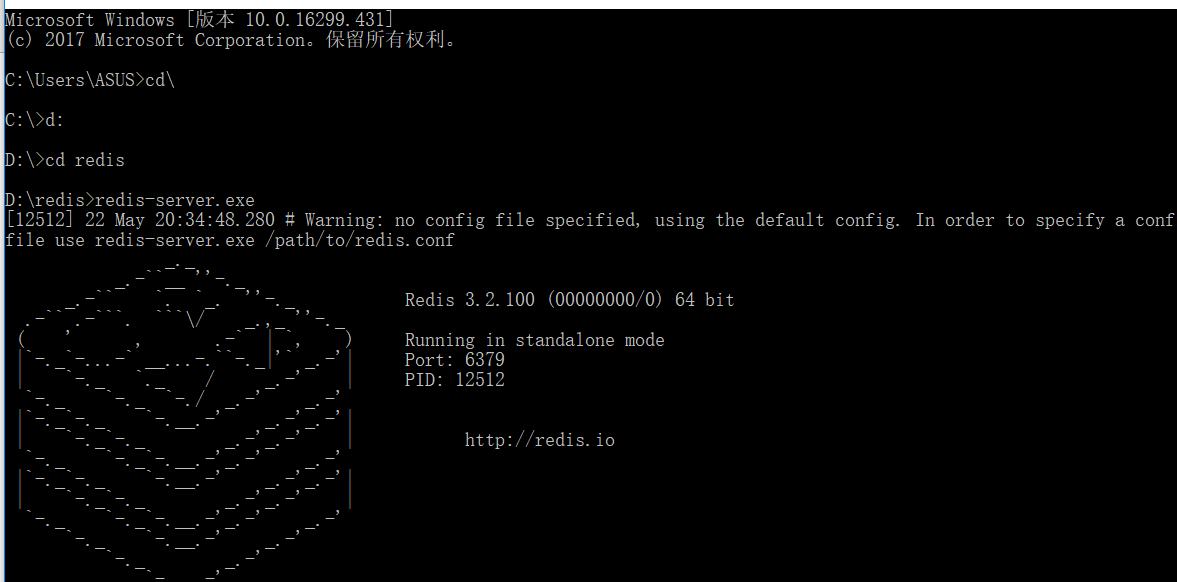
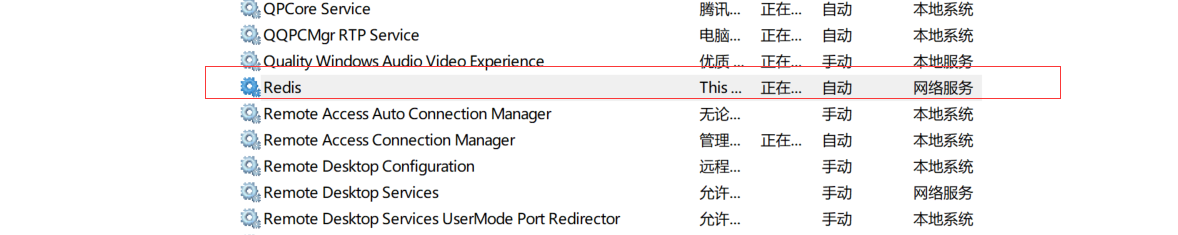
这时候 , 去服务列表中查看 , 是否完成服务注册 , 若已存在redis服务 , 则注册成功 , 为了方便 ,可以设置为自启动 , 以后在本地测试就不需要重新去黑窗口启动了 .
6.redis停止命令
redis-cli shutdown
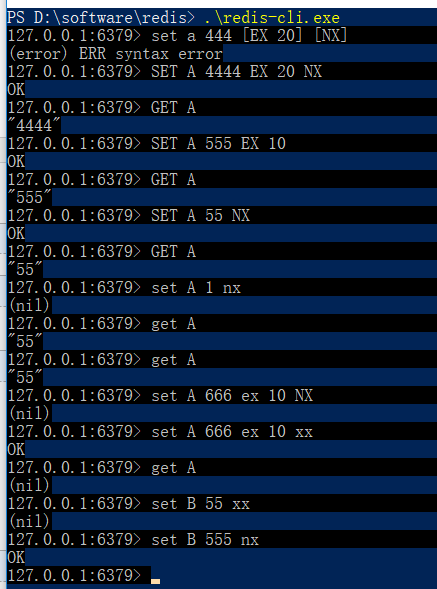
7. redis执行set时的命令 :
set key value ex 10[秒] / px 100 [毫秒] nx[key不存在时set命令起作用] / xx[key存在时命令起作用]
基本配置
# Redis configuration file example # Note on units: when memory size is needed, it is possible to specify # it in the usual form of 1k 5GB 4M and so forth: # # 1k => 1000 bytes # 1kb => 1024 bytes # 1m => 1000000 bytes # 1mb => 1024*1024 bytes # 1g => 1000000000 bytes # 1gb => 1024*1024*1024 bytes # # units are case insensitive so 1GB 1Gb 1gB are all the same. ################################## INCLUDES ################################### # Include one or more other config files here. This is useful if you # have a standard template that goes to all Redis servers but also need # to customize a few per-server settings. Include files can include # other files, so use this wisely. # # Notice option "include" won't be rewritten by command "CONFIG REWRITE" # from admin or Redis Sentinel. Since Redis always uses the last processed # line as value of a configuration directive, you'd better put includes # at the beginning of this file to avoid overwriting config change at runtime. # # If instead you are interested in using includes to override configuration # options, it is better to use include as the last line. # # include .\path\to\local.conf # include c:\path\to\other.conf ################################## NETWORK ##################################### # By default, if no "bind" configuration directive is specified, Redis listens # for connections from all the network interfaces available on the server. # It is possible to listen to just one or multiple selected interfaces using # the "bind" configuration directive, followed by one or more IP addresses. # # Examples: # # bind 192.168.1.100 10.0.0.1 # bind 127.0.0.1 ::1 # # ~~~ WARNING ~~~ If the computer running Redis is directly exposed to the # internet, binding to all the interfaces is dangerous and will expose the # instance to everybody on the internet. So by default we uncomment the # following bind directive, that will force Redis to listen only into # the IPv4 lookback interface address (this means Redis will be able to # accept connections only from clients running into the same computer it # is running). # # IF YOU ARE SURE YOU WANT YOUR INSTANCE TO LISTEN TO ALL THE INTERFACES # JUST COMMENT THE FOLLOWING LINE. # ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ bind 127.0.0.1 # Protected mode is a layer of security protection, in order to avoid that # Redis instances left open on the internet are accessed and exploited. # # When protected mode is on and if: # # 1) The server is not binding explicitly to a set of addresses using the # "bind" directive. # 2) No password is configured. # # The server only accepts connections from clients connecting from the # IPv4 and IPv6 loopback addresses 127.0.0.1 and ::1, and from Unix domain # sockets. # # By default protected mode is enabled. You should disable it only if # you are sure you want clients from other hosts to connect to Redis # even if no authentication is configured, nor a specific set of interfaces # are explicitly listed using the "bind" directive. protected-mode yes # Accept connections on the specified port, default is 6379 (IANA #815344). # If port 0 is specified Redis will not listen on a TCP socket. port 6379 # TCP listen() backlog. # # In high requests-per-second environments you need an high backlog in order # to avoid slow clients connections issues. Note that the Linux kernel # will silently truncate it to the value of /proc/sys/net/core/somaxconn so # make sure to raise both the value of somaxconn and tcp_max_syn_backlog # in order to get the desired effect. tcp-backlog 511 # Unix socket. # # Specify the path for the Unix socket that will be used to listen for # incoming connections. There is no default, so Redis will not listen # on a unix socket when not specified. # # unixsocket /tmp/redis.sock # unixsocketperm 700 # Close the connection after a client is idle for N seconds (0 to disable) timeout 0 # TCP keepalive. # # If non-zero, use SO_KEEPALIVE to send TCP ACKs to clients in absence # of communication. This is useful for two reasons: # # 1) Detect dead peers. # 2) Take the connection alive from the point of view of network # equipment in the middle. # # On Linux, the specified value (in seconds) is the period used to send ACKs. # Note that to close the connection the double of the time is needed. # On other kernels the period depends on the kernel configuration. # # A reasonable value for this option is 60 seconds. tcp-keepalive 0 ################################# GENERAL ##################################### # By default Redis does not run as a daemon. Use 'yes' if you need it. # Note that Redis will write a pid file in /var/run/redis.pid when daemonized. # NOT SUPPORTED ON WINDOWS daemonize no # If you run Redis from upstart or systemd, Redis can interact with your # supervision tree. Options: # supervised no - no supervision interaction # supervised upstart - signal upstart by putting Redis into SIGSTOP mode # supervised systemd - signal systemd by writing READY=1 to $NOTIFY_SOCKET # supervised auto - detect upstart or systemd method based on # UPSTART_JOB or NOTIFY_SOCKET environment variables # Note: these supervision methods only signal "process is ready." # They do not enable continuous liveness pings back to your supervisor. # NOT SUPPORTED ON WINDOWS supervised no # If a pid file is specified, Redis writes it where specified at startup # and removes it at exit. # # When the server runs non daemonized, no pid file is created if none is # specified in the configuration. When the server is daemonized, the pid file # is used even if not specified, defaulting to "/var/run/redis.pid". # # Creating a pid file is best effort: if Redis is not able to create it # nothing bad happens, the server will start and run normally. # NOT SUPPORTED ON WINDOWS pidfile /var/run/redis.pid # Specify the server verbosity level. # This can be one of: # debug (a lot of information, useful for development/testing) # verbose (many rarely useful info, but not a mess like the debug level) # notice (moderately verbose, what you want in production probably) # warning (only very important / critical messages are logged) loglevel notice # Specify the log file name. Also 'stdout' can be used to force # Redis to log on the standard output. logfile "" # To enable logging to the Windows EventLog, just set 'syslog-enabled' to # yes, and optionally update the other syslog parameters to suit your needs. # If Redis is installed and launched as a Windows Service, this will # automatically be enabled. # syslog-enabled no # 数据库 databases 16 ################################ SNAPSHOTTING ################################ # 900s内有一条变更时持久化 save 900 1 # 300s内有至少10条变化时触发持久化 save 300 10 # 60s内有10000条变更时触发持久化 save 60 10000 # 当执行BGSAVE命令异常时停止数据写入,以警示异常. stop-writes-on-bgsave-error yes # redis在进行RDB持久化的过程中,如果遇到字符串对象并且其中的字符串占用超过20个字节,就会对数据进行LZF算法压缩 rdbcompression yes # redis是否使用CRC64算法校验生成的RDB文件是否发生损坏,默认开启,如果要提示性能,可关闭 rdbchecksum yes # RDB文件名 dbfilename dump.rdb # 快照保存目录 dir ./ ################################# REPLICATION ################################# # 作为从服务,配置对应的主服务的IP和端口 # slaveof <masterip> <masterport> # 配置主节点的数据库的密码,主从复制过程中要保持一致 # masterauth <master-password> # 1.如果slave-serve-stale-data设置为yes(默认设置),从库会继续响应客户端的请求。 # 2.如果slave-serve-stale-data设置为no,除去INFO和SLAVOF命令之外的任何请求都会返回一个错误”SYNC with master in progress”。 slave-serve-stale-data yes # 从服务器作为只读,但是当客户端连接该节点进行set等命令时,仍会将数据保存至相应的主节点上,并不会直接拒绝 slave-read-only yes # Replication SYNC strategy: disk or socket. # # ------------------------------------------------------- # WARNING: DISKLESS REPLICATION IS EXPERIMENTAL CURRENTLY # ------------------------------------------------------- # # 是否使用无盘同步RDB文件,默认为no,no为不使用无盘,需要将RDB文件保存到磁盘后再发送给slave,yes为支持无盘, # 支持无盘就是RDB文件不需要保存至本地磁盘,而且直接通过socket文件发送给slave repl-diskless-sync no # diskless时[即repl-diskless-sync YES时]复制的服务器等待的延迟时间. repl-diskless-sync-delay 5 # slave端向server端发送ping的时间间隔,默认为10秒 # repl-ping-slave-period 10 # 主从ping连接超时时间,超过此值无法连接,master_link_status显示为down,并记录错误日志 # repl-timeout 60 # 是否启用TCP_NODELAY,如设置成yes,则redis会合并小的TCP包从而节省带宽, 但会增加同步延迟(40ms), # 造成master与slave数据不一致,假如设置成no,则redis master会立即发送同步数据,没有延迟,yes关注网络性能,no关注redis服务中的数据一致性 repl-disable-tcp-nodelay no # master的写入数据缓冲区,用于记录自上一次同步后到下一次同步过程中间的写入命令, # 计算公式:repl-backlog-size = 允许从节点最大中断时长 * 主实例offset每秒写入量, # 比如master每秒最大写入64mb,最大允许60秒,那么就要设置为64mb*60秒=3840MB(3.8G),建议此值是设置的足够大 # repl-backlog-size 1mb # 如果一段时间后没有slave连接到master,则backlog size的内存将会被释放。如果值为0则 表示永远不释放这部份内存。 # repl-backlog-ttl 3600 # slave端的优先级设置,值是一个整数,数字越大表示优先级越高。 # 当master故障时将会按照优先级来选择slave端进行恢复,如果值设置为0,则表示该slave永远不会被选择。 slave-priority 100 # 至少有多少台机器才能写入成功 # min-slaves-to-write 3 # 从节点最大延迟时间,即延迟时间小于10S的才被认为是健康的 # min-slaves-max-lag 10 # # Setting one or the other to 0 disables the feature. # # By default min-slaves-to-write is set to 0 (feature disabled) and # min-slaves-max-lag is set to 10. ################################## SECURITY ################################### # redis数据库密码,主从复制时从节点的masterauth和此应保持一致 # requirepass foobared # 在生产环境中,将一些敏感的、危险的命令进行重新命名,以防止被误执行, # 同时一定程度上提升了rediser server的安全性。但是主从节点中,容易出一些问题 # rename-command CONFIG b840fc02d524045429941cc15f59e41cb7be6c52 # # rename-command CONFIG "" ################################### LIMITS #################################### # redis server能够接受的client连接数最大值,默认为10000 # # maxclients 10000 # 开启或者关闭持久化功能,默认[yes]即开启,如果要关闭持久化则配置成 [no]。 # 说明:如果存在slave,则就算关闭了持久化功能,依然会生成rdb文件并同步给salve。这一点要注意区别。 # persistence-available [(yes)|no] # # 最大占用内存 # maxmemory <bytes> # 从已设置过期时间的数据集(server.db[i].expires)中挑选最近最少使用的数据淘汰 # volatile-lru -> remove the key with an expire set using an LRU algorithm # 从数据集(server.db[i].dict)中挑选最近最少使用的数据淘汰 # allkeys-lru -> remove any key according to the LRU algorithm # 从已设置过期时间的数据集(server.db[i].expires)中任意选择数据淘汰 # volatile-random -> remove a random key with an expire set # 从数据集(server.db[i].dict)中任意选择数据淘汰 # allkeys-random -> remove a random key, any key # 从已设置过期时间的数据集(server.db[i].expires)中挑选将要过期的数据淘汰 # volatile-ttl -> remove the key with the nearest expire time (minor TTL) # 禁止驱逐数据 # noeviction -> don't expire at all, just return an error on write operations # maxmemory-policy noeviction # 基于lru或者ttl时,redis并不是在所有符合条件的key中的执行淘汰策略,而是随机选出一批数据出来基于lru或者ttl策略进行淘汰。 # redis之所以没有使用真正的lru或者ttl算法来执行,是为了节省内存使用,在效果上他们几乎是等价的。 # 这个值配置的越大,那么内存淘汰的精度就越高,但是会更消耗内存和CPU,这个值配置的越小,那么速度就越快,相应的会牺牲一定的精度。 # maxmemory-samples 5 ############################## APPEND ONLY MODE ############################### # AOF是否启用.默认不开启 appendonly no # AOF文件名 appendfilename "appendonly.aof" # appendfsync always # 每次执行完毕都立持久化 appendfsync everysec # 每秒一次持久化 # appendfsync no # 随内存自己决定何时进行持久化 # 当appendonly=yes && appendfsync=always/everysec时,redis后台会执行大量的I/O操作保存命令, # 此时如果:即aof文件在重写或者执行BGSAVE命令时会停止持久化命令.会导致数据丢失. no-appendfsync-on-rewrite no # 表示本次重写的aof的文件大小和上次aof文件大小的比值,设置越小,redis持久化的文件大小越小. auto-aof-rewrite-percentage 100 # 表示运行AOF重写时文件最小体积, 默认为64MB。 auto-aof-rewrite-min-size 64mb # 当aof文件最后一条命令因为内存已满或者服务宕机导致保存失败时,启动redis恢复数据时会显示为异常aof文件, # 此时设置该属性为YES,可以忽略该异常指令,保证正常启动 aof-load-truncated yes ################################ LUA SCRIPTING ############################### # lua脚本执行最大时间 lua-time-limit 5000 ################################ REDIS CLUSTER ############################### # # 开启cluster模式。默认为no # 一个普通的redis server无法成为cluster集群的一部分,如果要让一个节点成为cluster一部分的话,则需要开启此节点。 # cluster-enabled yes # 集群中每个节点都有一个集群配置文件,这个文件不需要人为编辑,它有redis自己维护,我们只需要指定其配置文件名称即可。 # cluster-config-file nodes-6379.conf # 在集群中,节点故障判断时长,默认为15000ms。 # # cluster-node-timeout 15000 # redis集群在进行故障转移时,除了会衡量从节点的优先级(slave-priority配置)之外会衡量从节点的数据“老旧”程度, # 如果某个从节点的数据太老,则它也不会被升级为主节点。 # 判断从节点的数据老旧程度从两方面来判断: # 1.判断增量数据的复制偏移量,根据增量数据偏移量得出从节点的数据新旧程度。 # 2.判断最近连接时间,如果从节点和主节点的交互太旧,则该从节点也不会参与故障转移。 # 第1点有redis集群决定,用户无法干预;第2点则可以根据配置来进行干预。 # 具体干预如下:如果从节点自上次交互以来的时间 > cluster-node-timeout * cluster-slave-validity-factor + repl-ping-slave-period. # 那么该从节点是不会参与故障转移(即不会被选举为master的) # cluster-slave-validity-factor 10 # 集群分配从节点时的“移民障碍”, 默认为1,即要保证master至少有1个slave节点。 # 在集群中,为了尽量让从节点分配均匀,采用了“移民障碍”的方式,即只要保证master有指定个数的从节点, # 在满足这个条件的前提下,如果master有多余的从节点,则可以根据需要被分配到其他master下。 # cluster-migration-barrier 1 # cluster集群中总共有16384个slot,如果该配置为yes,则分片要覆盖所有的slot,否则整个集群不可用。 # cluster-require-full-coverage yes # In order to setup your cluster make sure to read the documentation # available at http://redis.io web site. ################################## SLOW LOG ################################### # 慢日志记录条数,当超过该配置时,采用FIFO的方式移除旧记录。默认值为128 slowlog-max-len 128 ################################ LATENCY MONITOR ############################## # 延迟监控默认是关闭状态,即使延迟监控处理几乎不耗时。然而,当延迟监控只需非常小的内存时,则没有必要为一个运行良好的Redis实例提高基线内存使用量 latency-monitor-threshold 0 ############################# EVENT NOTIFICATION ############################## # Redis can notify Pub/Sub clients about events happening in the key space. # This feature is documented at http://redis.io/topics/notifications # # For instance if keyspace events notification is enabled, and a client # performs a DEL operation on key "foo" stored in the Database 0, two # messages will be published via Pub/Sub: # # PUBLISH __keyspace@0__:foo del # PUBLISH __keyevent@0__:del foo # # It is possible to select the events that Redis will notify among a set # of classes. Every class is identified by a single character: # # K Keyspace events, published with __keyspace@<db>__ prefix. # E Keyevent events, published with __keyevent@<db>__ prefix. # g Generic commands (non-type specific) like DEL, EXPIRE, RENAME, ... # $ String commands # l List commands # s Set commands # h Hash commands # z Sorted set commands # x Expired events (events generated every time a key expires) # e Evicted events (events generated when a key is evicted for maxmemory) # A Alias for g$lshzxe, so that the "AKE" string means all the events. # # The "notify-keyspace-events" takes as argument a string that is composed # of zero or multiple characters. The empty string means that notifications # are disabled. # # Example: to enable list and generic events, from the point of view of the # event name, use: # # notify-keyspace-events Elg # # Example 2: to get the stream of the expired keys subscribing to channel # name __keyevent@0__:expired use: # # notify-keyspace-events Ex # # By default all notifications are disabled because most users don't need # this feature and the feature has some overhead. Note that if you don't # specify at least one of K or E, no events will be delivered. notify-keyspace-events "" ############################### ADVANCED CONFIG ############################### # Hashes are encoded using a memory efficient data structure when they have a # small number of entries, and the biggest entry does not exceed a given # threshold. These thresholds can be configured using the following directives. hash-max-ziplist-entries 512 hash-max-ziplist-value 64 # Lists are also encoded in a special way to save a lot of space. # The number of entries allowed per internal list node can be specified # as a fixed maximum size or a maximum number of elements. # For a fixed maximum size, use -5 through -1, meaning: # -5: max size: 64 Kb <-- not recommended for normal workloads # -4: max size: 32 Kb <-- not recommended # -3: max size: 16 Kb <-- probably not recommended # -2: max size: 8 Kb <-- good # -1: max size: 4 Kb <-- good # Positive numbers mean store up to _exactly_ that number of elements # per list node. # The highest performing option is usually -2 (8 Kb size) or -1 (4 Kb size), # but if your use case is unique, adjust the settings as necessary. list-max-ziplist-size -2 # Lists may also be compressed. # Compress depth is the number of quicklist ziplist nodes from *each* side of # the list to *exclude* from compression. The head and tail of the list # are always uncompressed for fast push/pop operations. Settings are: # 0: disable all list compression # 1: depth 1 means "don't start compressing until after 1 node into the list, # going from either the head or tail" # So: [head]->node->node->...->node->[tail] # [head], [tail] will always be uncompressed; inner nodes will compress. # 2: [head]->[next]->node->node->...->node->[prev]->[tail] # 2 here means: don't compress head or head->next or tail->prev or tail, # but compress all nodes between them. # 3: [head]->[next]->[next]->node->node->...->node->[prev]->[prev]->[tail] # etc. list-compress-depth 0 # Sets have a special encoding in just one case: when a set is composed # of just strings that happen to be integers in radix 10 in the range # of 64 bit signed integers. # The following configuration setting sets the limit in the size of the # set in order to use this special memory saving encoding. set-max-intset-entries 512 # Similarly to hashes and lists, sorted sets are also specially encoded in # order to save a lot of space. This encoding is only used when the length and # elements of a sorted set are below the following limits: zset-max-ziplist-entries 128 zset-max-ziplist-value 64 # HyperLogLog sparse representation bytes limit. The limit includes the # 16 bytes header. When an HyperLogLog using the sparse representation crosses # this limit, it is converted into the dense representation. # # A value greater than 16000 is totally useless, since at that point the # dense representation is more memory efficient. # # The suggested value is ~ 3000 in order to have the benefits of # the space efficient encoding without slowing down too much PFADD, # which is O(N) with the sparse encoding. The value can be raised to # ~ 10000 when CPU is not a concern, but space is, and the data set is # composed of many HyperLogLogs with cardinality in the 0 - 15000 range. hll-sparse-max-bytes 3000 # Active rehashing uses 1 millisecond every 100 milliseconds of CPU time in # order to help rehashing the main Redis hash table (the one mapping top-level # keys to values). The hash table implementation Redis uses (see dict.c) # performs a lazy rehashing: the more operation you run into a hash table # that is rehashing, the more rehashing "steps" are performed, so if the # server is idle the rehashing is never complete and some more memory is used # by the hash table. # # The default is to use this millisecond 10 times every second in order to # actively rehash the main dictionaries, freeing memory when possible. # # If unsure: # use "activerehashing no" if you have hard latency requirements and it is # not a good thing in your environment that Redis can reply from time to time # to queries with 2 milliseconds delay. # # use "activerehashing yes" if you don't have such hard requirements but # want to free memory asap when possible. activerehashing yes # The client output buffer limits can be used to force disconnection of clients # that are not reading data from the server fast enough for some reason (a # common reason is that a Pub/Sub client can't consume messages as fast as the # publisher can produce them). # # The limit can be set differently for the three different classes of clients: # # normal -> normal clients including MONITOR clients # slave -> slave clients # pubsub -> clients subscribed to at least one pubsub channel or pattern # # The syntax of every client-output-buffer-limit directive is the following: # # client-output-buffer-limit <class> <hard limit> <soft limit> <soft seconds> # # A client is immediately disconnected once the hard limit is reached, or if # the soft limit is reached and remains reached for the specified number of # seconds (continuously). # So for instance if the hard limit is 32 megabytes and the soft limit is # 16 megabytes / 10 seconds, the client will get disconnected immediately # if the size of the output buffers reach 32 megabytes, but will also get # disconnected if the client reaches 16 megabytes and continuously overcomes # the limit for 10 seconds. # # By default normal clients are not limited because they don't receive data # without asking (in a push way), but just after a request, so only # asynchronous clients may create a scenario where data is requested faster # than it can read. # # Instead there is a default limit for pubsub and slave clients, since # subscribers and slaves receive data in a push fashion. # # Both the hard or the soft limit can be disabled by setting them to zero. client-output-buffer-limit normal 0 0 0 client-output-buffer-limit slave 256mb 64mb 60 client-output-buffer-limit pubsub 32mb 8mb 60 # Redis calls an internal function to perform many background tasks, like # closing connections of clients in timeot, purging expired keys that are # never requested, and so forth. # # Not all tasks are perforemd with the same frequency, but Redis checks for # tasks to perform according to the specified "hz" value. # # By default "hz" is set to 10. Raising the value will use more CPU when # Redis is idle, but at the same time will make Redis more responsive when # there are many keys expiring at the same time, and timeouts may be # handled with more precision. # # The range is between 1 and 500, however a value over 100 is usually not # a good idea. Most users should use the default of 10 and raise this up to # 100 only in environments where very low latency is required. hz 10 # When a child rewrites the AOF file, if the following option is enabled # the file will be fsync-ed every 32 MB of data generated. This is useful # in order to commit the file to the disk more incrementally and avoid # big latency spikes. aof-rewrite-incremental-fsync yes ################################## INCLUDES ################################### # Include one or more other config files here. This is useful if you # have a standard template that goes to all Redis server but also need # to customize a few per-server settings. Include files can include # other files, so use this wisely. # # include /path/to/local.conf # include /path/to/other.conf




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号