【Spring MVC】MVC请求的处理过程一览-HandlerExceptionResolver异常处理器以及常见异常404、400、500的经历过程
1 前言
上节【Spring MVC】MVC请求的处理过程一览-HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler结果处理器或者说前面,我们基本看过了请求的整体处理过程,请求参数的解析,业务逻辑的执行以及上节结果返回的处理,那么在看的过程中,发现都没有对异常进行一些特殊处理,异常都是在哪处理呢,就是我们本节要看的 HandlerExceptionResolver。
2 HandlerExceptionResolver
2.1 概述
HandlerExceptionResolver 用于解析请求处理过程中所产生的异常,我们看一下类图:
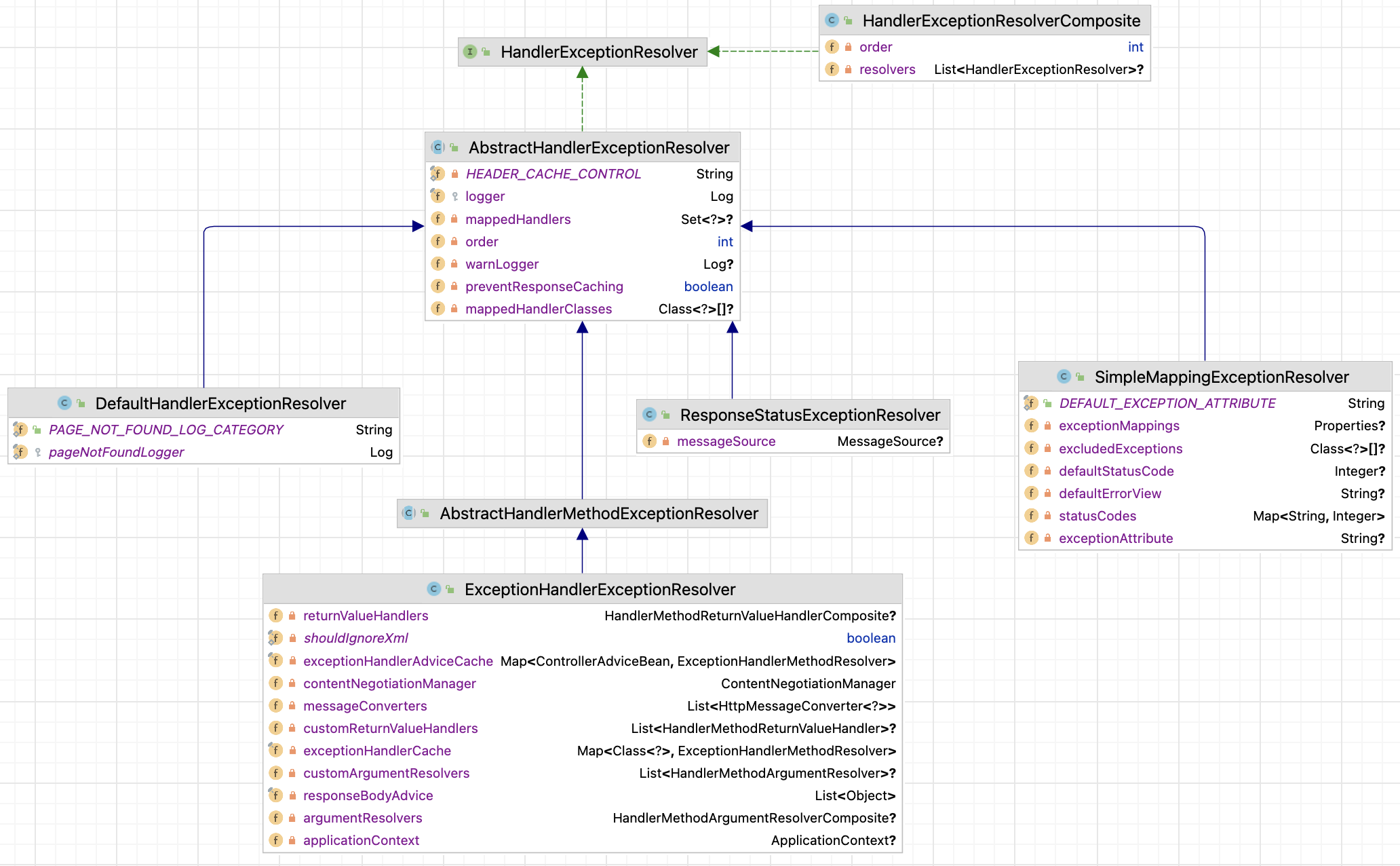
其中 HandlerExceptionResolverComposite 作为容器使用,可以封装别的Resolver,前面已经多次介绍过,这里就不再叙述了。
HandlerExceptionResolver 的主要实现都继承自抽象类 AbstractlandlerExceptionResolver,它有五个子类,其中的 AnnotationMethodHandlerExceptionResolver 已经被弃用,剩下的还有四个:
(1)AbstractHandlerMethodExceptionResolver:和其子类 ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver一起完成使用 @ExceptionHandler 注释的方法进行异常解析的功能。
(2)DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver: 按不同类型分别对异常进行解析。
(3)ResponseStatusExceptionResolver:解析有 @ResponseStatus 注释类型的异常。
(4)SimpleMappingExceptionResolver:通过配置的异常类和view 的对应关系来解析异常。
异常解析过程主要包含两部分内容:给ModelAndView 设置相应内容、设置 response 的相关属性。当然还可能有一些辅助功能,如记录日志等,在自定义的 ExceptionHandler 里还可以做更多的事情。
2.2 异常的处理入口
在看具体异常处理器逻辑之前, 我们先回顾下统一处理异常的入口,其实他是在 DispatcherServlet 的 doDispatch 方法中,我们回顾下:
// DispatchServlet#doDispatch protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; // 处理请求 handler 我们的 controller 里的每个方法一般都会解析为某个 mappedHandler 但注意这里是执行链对象 // 会有拦截器的相关处理 HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; // 是否是文件上传的请求 boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; // 异步请求的处理 暂且不看 WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { // 检查是否是上传文件的请求 主要是通过请求的请求头里的 content-type 的值中是否有 multipart // 这个里边会有文件大小的限制 比如我们常见的 MaxUploadSizeExceededException processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // 获得当前请求的一个处理链 mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); // 如果为空的话 就是我们常见看到的 404 not found异常 if (mappedHandler == null) { // 这里方法里边也是抛出一个 NoHandlerFoundException 异常 noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // 找不到适配器的时候 也是抛出一个 ServletException 异常 HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // ... // 执行处理器的前置处理 如果有一个 拦截器返回false 就直接返回 if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // 执行实际的业务逻辑 // Actually invoke the handler. // 执行过程中抛出各种各样的异常 mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); // 执行后置处理 mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } // 捕获异常 catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } // 捕获异常 catch (Throwable err) { // As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); } // 这里就是统一处理异常的入口 processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } // 当 dispatch 出现异常的时候 才会执行拦截器的 afterCompletion 方法 catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Throwable err) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); } finally { //... }
可以看到最后统一处理异常的入口方法 processDispatchResult,那我们继续看看它内部的逻辑:
// DispatcherServlet#processDispatchResult private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv, @Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception { boolean errorView = false; // 当发生异常时 if (exception != null) { // 视图异常处理 if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) { logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception); mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView(); } else { // 调用异常处理器进行异常处理 Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null); mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception); errorView = (mv != null); } } // Did the handler return a view to render? if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) { render(mv, request, response); if (errorView) { WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request); } } else { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned."); } } if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Concurrent handling started during a forward return; } // 最后执行钩子函数 triggerAfterCompletion 拦截器的某个阶段 if (mappedHandler != null) { // Exception (if any) is already handled.. mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null); } }
可以看到当异常不为空的情况下,并且不是视图异常的话,就会调用我们的异常处理器进行响应处理,最后执行拦截器的 triggerAfterCompletion。
所以我们要知道处理请求过程中发生的异常最后都是在 DispatcherServlet 的 doDispatch 方法中,通过一个大 try catch 代码块捕获发生的异常,最后交给 processDispatchResult 方法处理,调用我们的异常处理器进行异常的处理。
2.3 异常处理类
2.3.1 AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver 模版模式基础类
AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver 是所有直接解析异常类的父类,里面定义了通用的解析流程,并使用了模板模式,子类只需要覆盖相应的方法即可,resolveException 方法如下:
// AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver#resolveException public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) { // 判断是否可以解析 if (shouldApplyTo(request, handler)) { prepareResponse(ex, response); ModelAndView result = doResolveException(request, response, handler, ex); if (result != null) { // Print debug message when warn logger is not enabled. if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && (this.warnLogger == null || !this.warnLogger.isWarnEnabled())) { logger.debug(buildLogMessage(ex, request) + (result.isEmpty() ? "" : " to " + result)); } // Explicitly configured warn logger in logException method. logException(ex, request); } return result; } else { return null; } }
首先使用 shouldApplyTo 方法判断当前 ExceptionResolver 是否可以解析所传入处理器所抛出的异常(可以指定只能处理指定的处理器抛出的异常),如果不可以则返回 null,交给下一个 ExceptionResolver 解析,如果可以则调用logException 方法打印日志,接着调用 prepareResponse 设置 response,最后调用 doResolveException 实际解析异常,doResolveException 是个模板方法,留给子类实现。
shouldApplyTo 方法的代码如下:
// AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver#shouldApplyTo protected boolean shouldApplyTo(HttpServletRequest request, @Nullable Object handler) { if (handler != null) { if (this.mappedHandlers != null && this.mappedHandlers.contains(handler)) { return true; } if (this.mappedHandlerClasses != null) { for (Class<?> handlerClass : this.mappedHandlerClasses) { if (handlerClass.isInstance(handler)) { return true; } } } } return !hasHandlerMappings(); }
这里使用了两个属性:mappedHandlers 和 mappedHandlerClasses,这两个属性可以在定义HandlerExceptionResolver 的时候进行配置,用于指定可以解析处理器抛出的哪些异常,也就是如果设置了这两个值中的一个,那么这个 ExceptionResolver 就只能解析所设置的处理器抛出的异常。mappedHandlers 用于配置处理器的集合,mappedHandlerClasses 用于配置处理器类型的集合。检查方法非常简单,在此就不细说了,如果西个属性都没配置则将处理所有异常。
logException 是默认记录日志的方法,代码如下:
// AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver#logException protected void logException(Exception ex, HttpServletRequest request) { if (this.warnLogger != null && this.warnLogger.isWarnEnabled()) { this.warnLogger.warn(buildLogMessage(ex, request)); } } // AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver#buildLogMessage protected String buildLogMessage(Exception ex, HttpServletRequest request) { return "Resolved [" + LogFormatUtils.formatValue(ex, -1, true) + "]"; }
logException 方法首先调用 buildLogMessage 创建了日志消息,然后使用 warnLogger 将其记录下来。
prepareResponse 方法根据 preventResponseCaching 标示判断是否给 response 设置禁用缓存的属性,preventResponseCaching 默认 false,代码如下:
// AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver#prepareResponse protected void prepareResponse(Exception ex, HttpServletResponse response) { if (this.preventResponseCaching) { preventCaching(response); } } // AbstractHandlerExceptionResolver#preventCaching protected void preventCaching(HttpServletResponse response) { response.addHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL, "no-store"); }
最后的 doResolveException 方法是模板方法,子类使用它具体完成异常的解析工作。
2.3.2 ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver 继 承 自 AbstractHandler MethodExceptionResolver,后者继承自 AbstractHlandlerException Resolver。
AbstractHandlerMethodExceptionResolver 重写了shouldApplyTo 方法,并在处理请求的 doResolveException 方法中将实际处理请求的过程交给了模板方法 doResolveHandlerMethodException。代码如下:
// AbstractHandlerMethodExceptionResolver#shouldApplyTo @Override protected boolean shouldApplyTo(HttpServletRequest request, @Nullable Object handler) { if (handler == null) { return super.shouldApplyTo(request, null); } else if (handler instanceof HandlerMethod) { HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod) handler; handler = handlerMethod.getBean(); return super.shouldApplyTo(request, handler); } else if (hasGlobalExceptionHandlers() && hasHandlerMappings()) { return super.shouldApplyTo(request, handler); } else { return false; } }
AbstractHandlerMethodExceptionResolver 的作用其实相当于一个适配器。一般的处理器是类的形式,但 HandlerMethod 其实是将方法作为处理器来使用的,所以需要进行适配。首先在 shouldApplyTo 中判断如果处理器是 HandlerMethod 类型则将处理器设置为其所在的类,然后再交给父类判断,如果空则直接交给父类判断,如果既不 空也不是 HandlerMethod类型则返回 false 不处理。
doResolveException 将处理传递给 doResolveHandlerMethodException 方法具体处理,这样做主要是为了层次更加合理,而且这样设计后如果有多个子类还可以在doResolveException 中统一做一些事情。
// AbstractHandlerMethodExceptionResolver#resolveException protected final ModelAndView doResolveException( HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) { HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (handler instanceof HandlerMethod ? (HandlerMethod) handler : null); return doResolveHandlerMethodException(request, response, handlerMethod, ex); }
下面来看 ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,它其实就是一个简化版的 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter,它的执行也是使用的 ServletlnvocableHandlerMethod,首先根据 handlerMethod和 exception 将其创建出来(大致过程是在处理器类里找出所有注释了@ExceptionHandler 的方法,然后再根据其配置中的异常和需要解析的异常进行匹配),然后设置了argumentResolvers 和 returnValueHandlers,接着调用其 invokeAndHandle 方法执行处理,最后将处理结果封装成 ModelAndView 返回。如果 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter 理解了,再来看它就会觉得非常简单。代码如下:
// ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver#doResolveHandlerMethodException protected ModelAndView doResolveHandlerMethodException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Exception exception) { // 获取异常处理方法 构造ServletInvocableHandlerMethod对象 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod exceptionHandlerMethod = getExceptionHandlerMethod(handlerMethod, exception); if (exceptionHandlerMethod == null) { return null; } // 参数解析器 if (this.argumentResolvers != null) { exceptionHandlerMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers); } // 结果处理器 if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) { exceptionHandlerMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers); } // 封装请求和响应 ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response); ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer(); ArrayList<Throwable> exceptions = new ArrayList<>(); try { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Using @ExceptionHandler " + exceptionHandlerMethod); } // Expose causes as provided arguments as well Throwable exToExpose = exception; while (exToExpose != null) { exceptions.add(exToExpose); Throwable cause = exToExpose.getCause(); exToExpose = (cause != exToExpose ? cause : null); } Object[] arguments = new Object[exceptions.size() + 1]; exceptions.toArray(arguments); // efficient arraycopy call in ArrayList arguments[arguments.length - 1] = handlerMethod; // 调用异常处理方法 exceptionHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer, arguments); } catch (Throwable invocationEx) { // Any other than the original exception (or a cause) is unintended here, // probably an accident (e.g. failed assertion or the like). if (!exceptions.contains(invocationEx) && logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Failure in @ExceptionHandler " + exceptionHandlerMethod, invocationEx); } // Continue with default processing of the original exception... return null; } if (mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) { return new ModelAndView(); } else { ModelMap model = mavContainer.getModel(); HttpStatus status = mavContainer.getStatus(); ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView(mavContainer.getViewName(), model, status); mav.setViewName(mavContainer.getViewName()); if (!mavContainer.isViewReference()) { mav.setView((View) mavContainer.getView()); } if (model instanceof RedirectAttributes) { Map<String, ?> flashAttributes = ((RedirectAttributes) model).getFlashAttributes(); RequestContextUtils.getOutputFlashMap(request).putAll(flashAttributes); } return mav; } }
这里只是返回了 ModelAndView,并没有对 response 进行设置,如果需要可以自己在异常处理器中设置。
2.3.3 DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver 的解析过程是根据异常类型的不同,使用不同的方法进行处理,doResolveException 代码如下:
// DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver#resolveException protected ModelAndView doResolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) { try { if (ex instanceof HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException) { return handleHttpRequestMethodNotSupported( (HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException) { return handleHttpMediaTypeNotSupported( (HttpMediaTypeNotSupportedException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException) { return handleHttpMediaTypeNotAcceptable( (HttpMediaTypeNotAcceptableException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof MissingPathVariableException) { return handleMissingPathVariable( (MissingPathVariableException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof MissingServletRequestParameterException) { return handleMissingServletRequestParameter( (MissingServletRequestParameterException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof ServletRequestBindingException) { return handleServletRequestBindingException( (ServletRequestBindingException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof ConversionNotSupportedException) { return handleConversionNotSupported( (ConversionNotSupportedException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof TypeMismatchException) { return handleTypeMismatch( (TypeMismatchException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof HttpMessageNotReadableException) { return handleHttpMessageNotReadable( (HttpMessageNotReadableException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof HttpMessageNotWritableException) { return handleHttpMessageNotWritable( (HttpMessageNotWritableException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof MethodArgumentNotValidException) { return handleMethodArgumentNotValidException( (MethodArgumentNotValidException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof MissingServletRequestPartException) { return handleMissingServletRequestPartException( (MissingServletRequestPartException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof BindException) { return handleBindException((BindException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof NoHandlerFoundException) { return handleNoHandlerFoundException( (NoHandlerFoundException) ex, request, response, handler); } else if (ex instanceof AsyncRequestTimeoutException) { return handleAsyncRequestTimeoutException( (AsyncRequestTimeoutException) ex, request, response, handler); } } catch (Exception handlerEx) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Failure while trying to resolve exception [" + ex.getClass().getName() + "]", handlerEx); } } return null; }
具体的解析方法也非常简单,主要是设置 response 的相关属性,下面介绍前两个异常的处理方法,也就是没找到处理器执行方法和 request 的Method 类型不支持的异常处理,代码如下:
// DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver#handleHttpRequestMethodNotSupported protected ModelAndView handleHttpRequestMethodNotSupported(HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException ex, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler) throws IOException { String[] supportedMethods = ex.getSupportedMethods(); if (supportedMethods != null) { response.setHeader("Allow", StringUtils.arrayToDelimitedString(supportedMethods, ", ")); } response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_METHOD_NOT_ALLOWED, ex.getMessage()); return new ModelAndView(); } // DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver#handleBindException protected ModelAndView handleBindException(BindException ex, HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler) throws IOException { response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_BAD_REQUEST); return new ModelAndView(); }
可以看到其处理方法就是给response 设置了相应属性,然后返回一个空的ModelAndView。其中 response 的 sendError 方法用于设置错误类型,它有两个重载方法 sendBrror(int)和 sendError(int, String),int 参数用于设置404)500等错误类型,String类型的参数用于设置附加的错误信息,可以在页面中获取到。sendError 和 setStatus 方法的区别是前者会返回web.xml 中定义的相应错误页面,后者只是设置了 status 而不会返回相应错误页面。其他处理方法也都大同小异,就不解释了。
2.3.4 ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver 用来解析注释了 @ResponseStatus 的异常(如自定义的注释了@ResponseStatus 的异常),代码如下:
// ResponseStatusExceptionResolver#resolveException protected ModelAndView doResolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) { try { if (ex instanceof ResponseStatusException) { return resolveResponseStatusException((ResponseStatusException) ex, request, response, handler); } ResponseStatus status = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(ex.getClass(), ResponseStatus.class); if (status != null) { return resolveResponseStatus(status, request, response, handler, ex); } if (ex.getCause() instanceof Exception) { return doResolveException(request, response, handler, (Exception) ex.getCause()); } } catch (Exception resolveEx) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Failure while trying to resolve exception [" + ex.getClass().getName() + "]", resolveEx); } } return null; }
doResolveException 方法中首先使用 AnnotationUtils 找到 ResponseStatus 注释,然后调用 resolveResponseStatus 方法进行解析,后者使用注释里的value 和 reason 作力参数调用了response 的sendError 方法。
2.3.5 SimpleMappingExceptionResolver
SimpleMappingExceptionResolver 需要提前配置异常类和view 的对应关系然后才能使用,doResolveException 代码如下:
// SimpleMappingExceptionResolver#resolveException protected ModelAndView doResolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Object handler, Exception ex) { // Expose ModelAndView for chosen error view. // 根据异常获取错误页面的逻辑视图 String viewName = determineViewName(ex, request); if (viewName != null) { // 检查是否配置了所找到的视图对应的状态码 // Apply HTTP status code for error views, if specified. // Only apply it if we're processing a top-level request. Integer statusCode = determineStatusCode(request, viewName); if (statusCode != null) { applyStatusCodeIfPossible(request, response, statusCode); } return getModelAndView(viewName, ex, request); } else { return null; } }
这里首先调用 determineViewName 方法根据异常找到显示异常的逻辑视图,然后调用determineStatusCode 方法判断逻辑视图是否有对应的statusCode,如果有则调用 applyStatusCodeifPossible 方法设置到 response,最后调用getModelAndView 将异常和解析出的 viewName封装成ModelAndView 并返回。
查找视图的 determineViewName 方法如下:
// SimpleMappingExceptionResolver#determineViewName protected String determineViewName(Exception ex, HttpServletRequest request) { String viewName = null; // 如果异常在设置的 excludedExceptions 中所包含那么返回null if (this.excludedExceptions != null) { for (Class<?> excludedEx : this.excludedExceptions) { if (excludedEx.equals(ex.getClass())) { return null; } } } // 调用 findMatchingViewName 进行查找 // Check for specific exception mappings. if (this.exceptionMappings != null) { viewName = findMatchingViewName(this.exceptionMappings, ex); } // 如果没找到并且配置了 defaultErrorView 则用 defaultErrorView // Return default error view else, if defined. if (viewName == null && this.defaultErrorView != null) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Resolving to default view '" + this.defaultErrorView + "'"); } viewName = this.defaultErrorView; } return viewName; }
这里首先检查异常是不是配置在 excludedExceptions 中(excludedExceptions 用于配置不处理的异常),如果是则返回 null,否则调用 findMatching ViewName 实际查找 viewName,如果没找到而且配置了 defaultErrorView,则使用 defaultErrorView。 findMatchingViewName 从传入的参数就可以看出来它是根据配置的 exceptionMappings 参数匹配当前异常的,不过并不是直接完全匹配的,而是只要配置异常的字符在当前处理的异常或其父类中存在就可以了,如配置“BindingException”可以匹配“xxx.UserBindingException”“xxx.DeptBindingException” 等,而“java.lang.Exception”可以匹配所有它的子类,即所有“CheckedExceptions”,其代码如下:
// SimpleMappingExceptionResolver#findMatchingViewName @Nullable protected String findMatchingViewName(Properties exceptionMappings, Exception ex) { String viewName = null; String dominantMapping = null; int deepest = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (Enumeration<?> names = exceptionMappings.propertyNames(); names.hasMoreElements();) { String exceptionMapping = (String) names.nextElement(); int depth = getDepth(exceptionMapping, ex); if (depth >= 0 && (depth < deepest || (depth == deepest && dominantMapping != null && exceptionMapping.length() > dominantMapping.length()))) { deepest = depth; dominantMapping = exceptionMapping; viewName = exceptionMappings.getProperty(exceptionMapping); } } if (viewName != null && logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Resolving to view '" + viewName + "' based on mapping [" + dominantMapping + "]"); } return viewName; }
大致过程就是遍历配置文件,然后调用 getDepth 查找,如果返回值大于等于0则说明可以匹配,而且如果有多个匹配项则选择最优的,选择方法是判断两项内容:①匹配的深度;②匹配的配置项文本的长度。深度越浅越好,配置的文本越长越好。深度是指如果匹配的是异常的父类而不是异常本身,那么深度就是异常本身到被匹配的父类之间的继承层数。getDepth 方法的代码如下:
protected int getDepth(String exceptionMapping, Exception ex) { return getDepth(exceptionMapping, ex.getClass(), 0); } private int getDepth(String exceptionMapping, Class<?> exceptionClass, int depth) { if (exceptionClass.getName().contains(exceptionMapping)) { // Found it! return depth; } // If we've gone as far as we can go and haven't found it... if (exceptionClass == Throwable.class) { return -1; } return getDepth(exceptionMapping, exceptionClass.getSuperclass(), depth + 1); }
getDepth 中调用了同名的带 depth 参数的递归方法 getDepth,并给 depth 传入了0。后面的getDepth 方法判断传入的类名中是否包含匹配的字符串,如果找到则返回相应的depth,如果没有则对 depth 加1后递归检查异常的父类,直到检查的类变成 Throwable 还不匹配则返回-1。
分析完 determine ViewName,再回过头去分析 determineStatusCode,代码如下:
// SimpleMappingExceptionResolver#determineStatusCode protected Integer determineStatusCode(HttpServletRequest request, String viewName) { if (this.statusCodes.containsKey(viewName)) { return this.statusCodes.get(viewName); } return this.defaultStatusCode; }
determineStatusCode 方法非常简单,就是直接从配置的 statusCodes 中用 viewName 获取,如果获取不到则返回默认值 defaultStatusCode,statusCodes 和 defaultStatusCode 都可以在定义 SimpleMappingExceptionResolver 的时候进行配置。找到 statusCode 后会调用 applyStatusCodelfPossible 方法将其设置到 response 上,代码如下:
// SimpleMappingExceptionResolver#applyStatusCodeIfPossible protected void applyStatusCodeIfPossible(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, int statusCode) { if (!WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Applying HTTP status " + statusCode); } response.setStatus(statusCode); request.setAttribute(WebUtils.ERROR_STATUS_CODE_ATTRIBUTE, statusCode); } }
最后调用 getModelAndView 生成 ModelAndView 并返回,生成过程是将解析出的viewName设置为 View,如果 exceptionAttribute 不为空则将异常添加到 Model,代码如下:
// SimpleMappingExceptionResolver#getModelAndView protected ModelAndView getModelAndView(String viewName, Exception ex, HttpServletRequest request) { return getModelAndView(viewName, ex); } protected ModelAndView getModelAndView(String viewName, Exception ex) { ModelAndView mv = new ModelAndView(viewName); if (this.exceptionAttribute != null) { mv.addObject(this.exceptionAttribute, ex); } return mv; }
SimpleMappingExceptionResolver 就分析完了,这里面有不少可配置的选项,总结如下:
(1)exceptionMappings:用于配置异常类(字符串类型)和 viewName 的对应关系,异常类可以是异常(包含包名的完整名)的一部分,还可以是异常父类的一部分。
(2)excludedExceptions:用于配置不处理的异常。
(3)defaultErrorView:用于配置当无法从 exceptionMappings 中解析出视图时使用的默认视图
(4)statusCodes:用于配置解析出的 viewName 和 statusCode 对应关系。
(5)defaultStatusCode:用于配置 statusCodes 中没有配置相应的viewName 时使用的默认statusCode。
(6)exceptionAttribute:用于配置异常在 Model 中保存的参数名,默认为"exception"如果为 null,异常将不保存到 Model 中。
2.4 常见错误
2.4.1 404 Not Found
我们启动一个服务,然后随便输入一个路径就会出现 404,比如:
localhost:8088/demo/testServlet222222
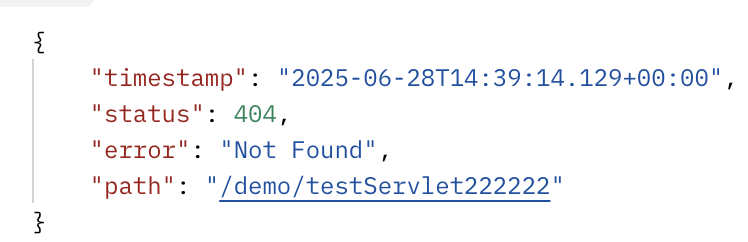
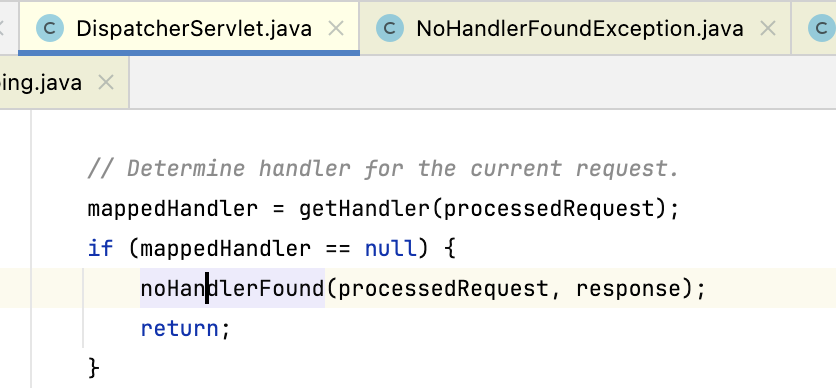
那我们看下这个404的出现过程。首先我刚开始以为是在 getHandler 也就是获取某个 handler 的时候匹配不到一个所以报的 404, 也就是在下边这个位置抛出的异常
其实不是的,因为有一个能匹配 /** 的 ResourceHttpRequestHandler 处理器(它是由HttpRequestHandlerAdapter这个适配器执行的,适配器执行逻辑非常简单就是直接调用前边的 Handler进行处理),如下:
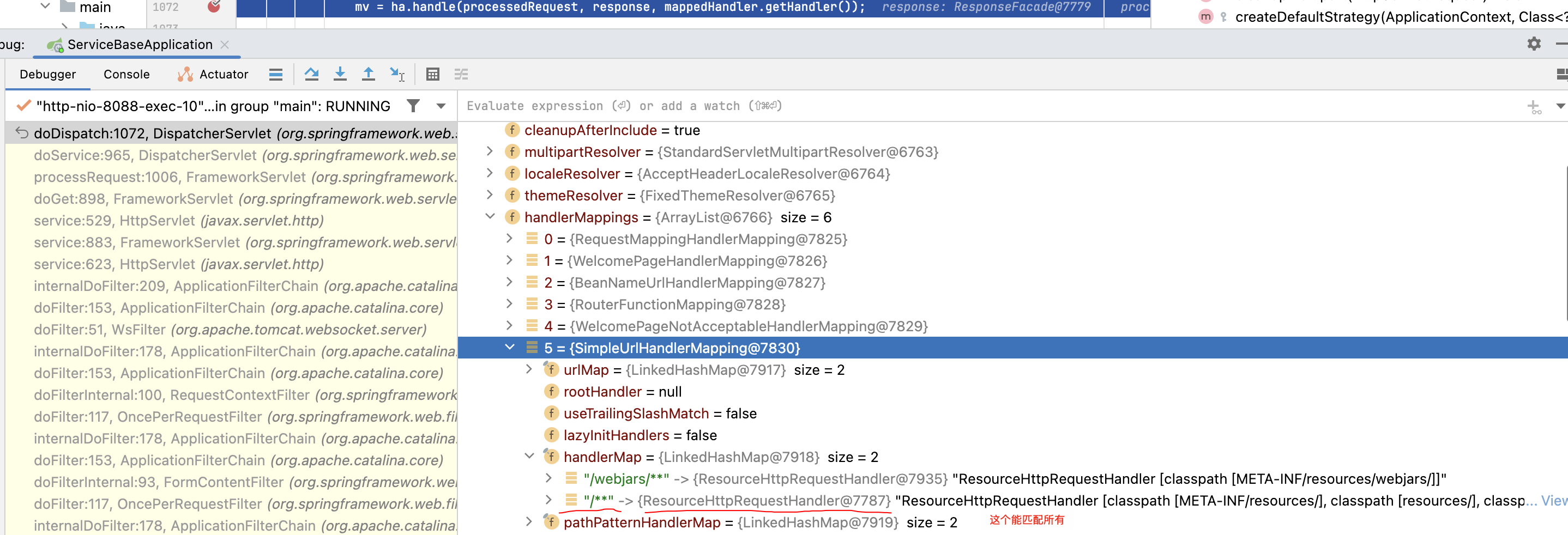
HttpRequestHandlerAdapter 适配器执行,也就是直接调用 ResourceHttpRequestHandler 的 handleRequest 方法:
public class HttpRequestHandlerAdapter implements HandlerAdapter { @Override public boolean supports(Object handler) { return (handler instanceof HttpRequestHandler); } @Override @Nullable public ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { ((HttpRequestHandler) handler).handleRequest(request, response); return null; }
然后是因为这个处理器找不到对应的路径资源所以报的 404:
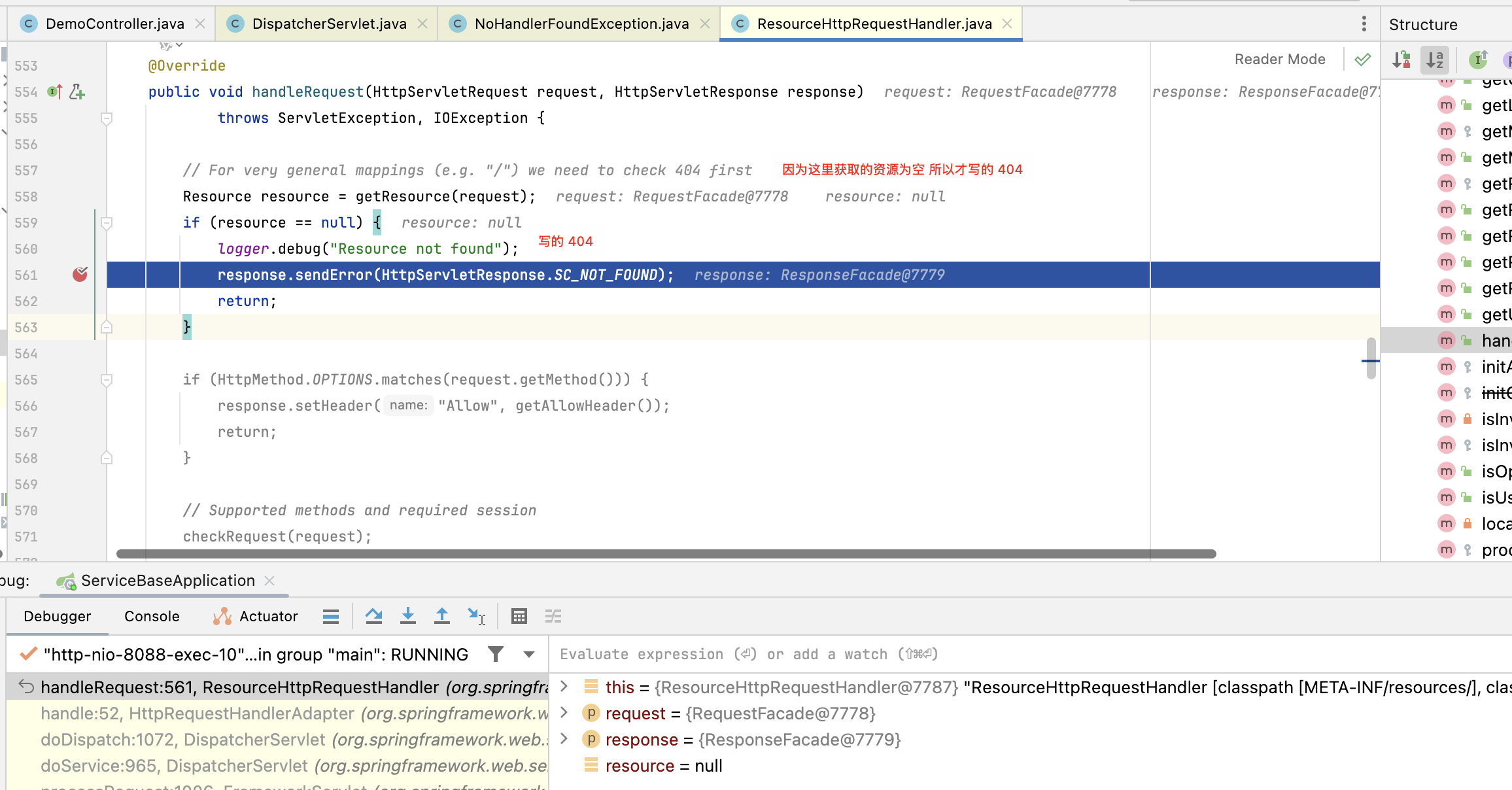
但是你 debug 调试的话,会发现它是经过回调路径 /error,经过 BasicErrorController 这个 controller 的处理返回的,并没有经过上边的异常处理器。
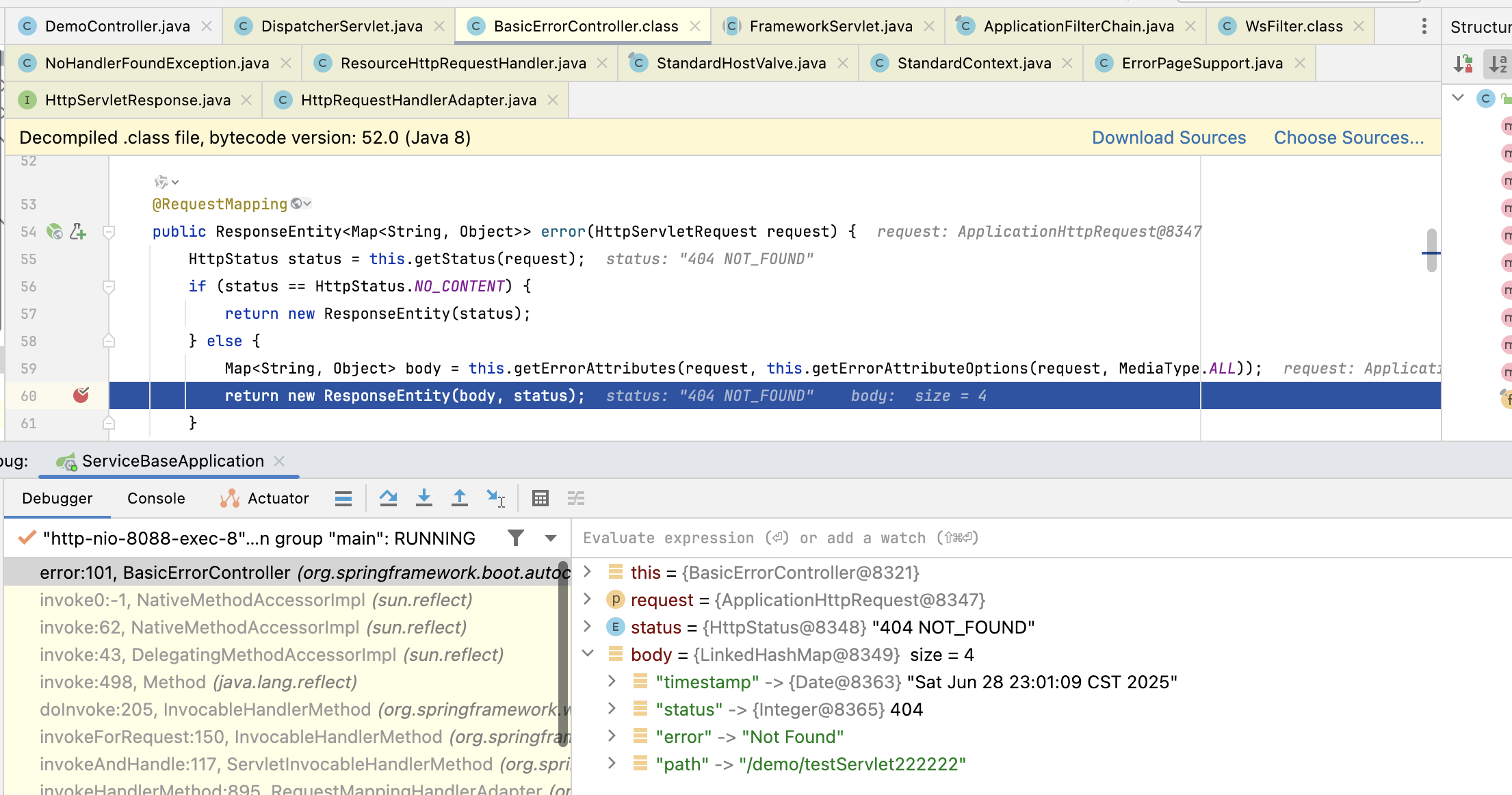
也就是说 DispatcherServlet 里的 doDispatch方法就没有异常抛出,但是 doDispatch 方法被调用了两次,一次是我们的请求 /demo/testServlet222222,另一次是一个 /error 进来的。
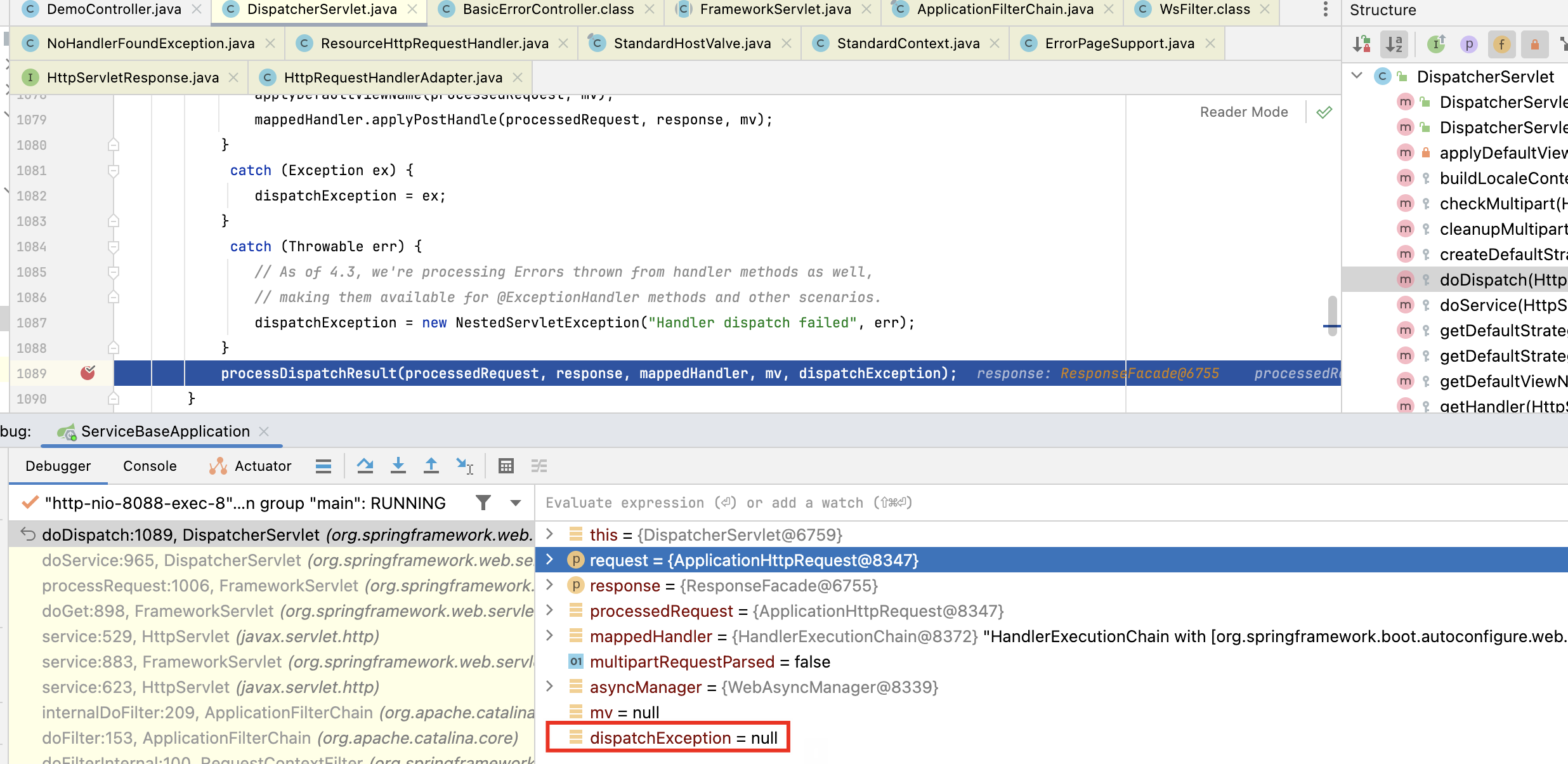
那我们看一下 /error 是咋进来的,其实这个就跟 Tomcat 有关系了,我用的是 Tomcat,在 StandardHostValue 这个类中,会检查响应状态码,
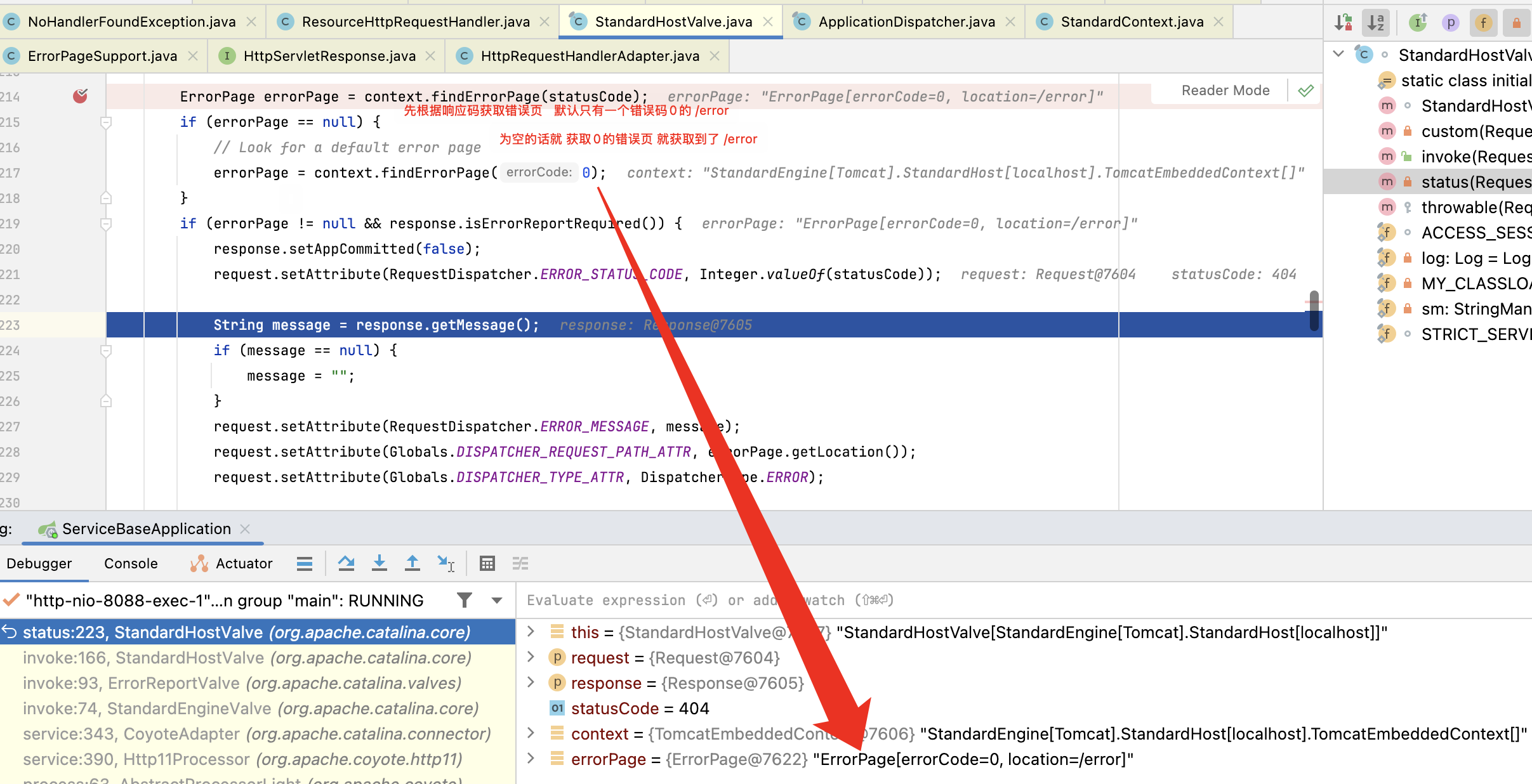
获取到错误页路径/error, 然后走到 custom 里经过转发请求重新处理当前请求了。

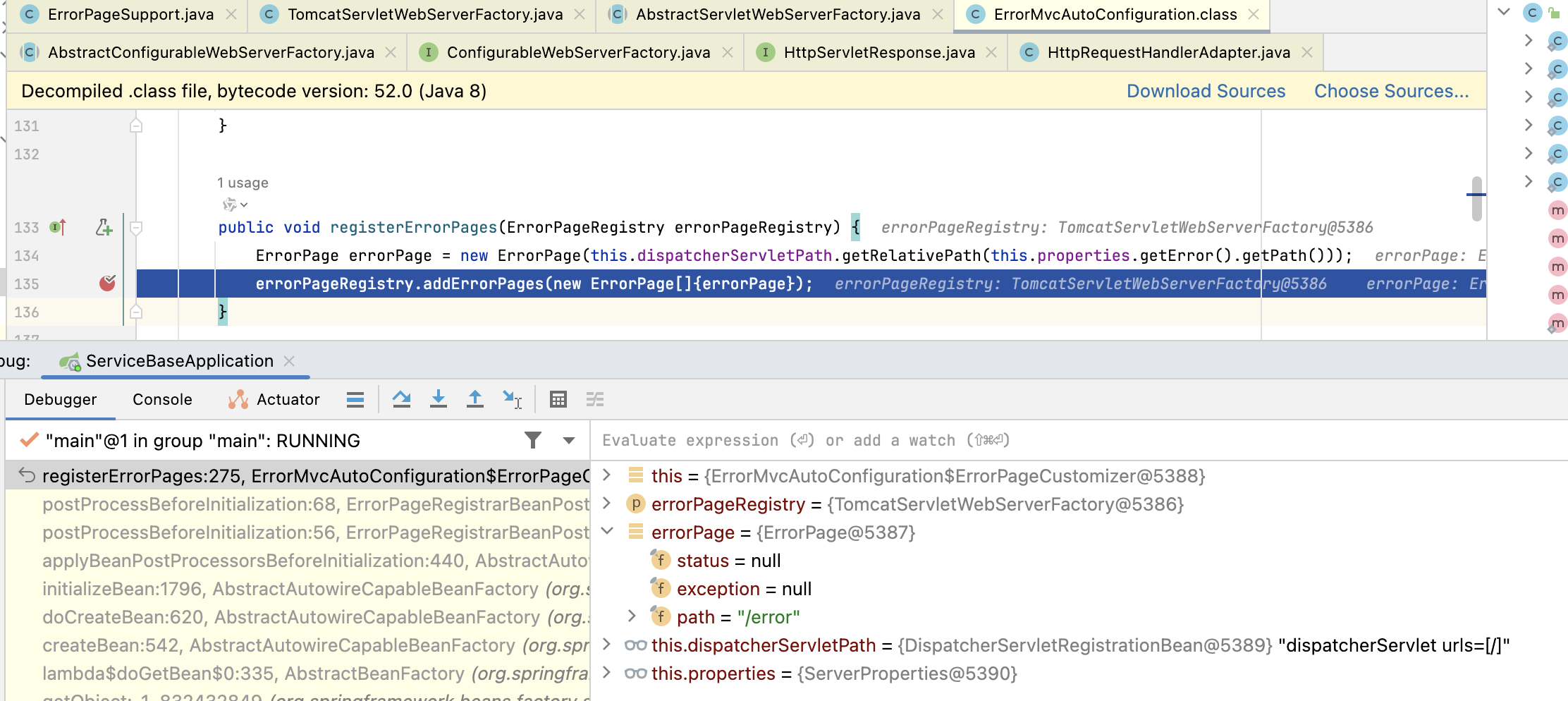
再延伸一点,那么 Tomcat 里的 error page是怎么来的呢?
首先是 ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration 往 TomcatServletWebServerFactory 里注册了一个 错误页:
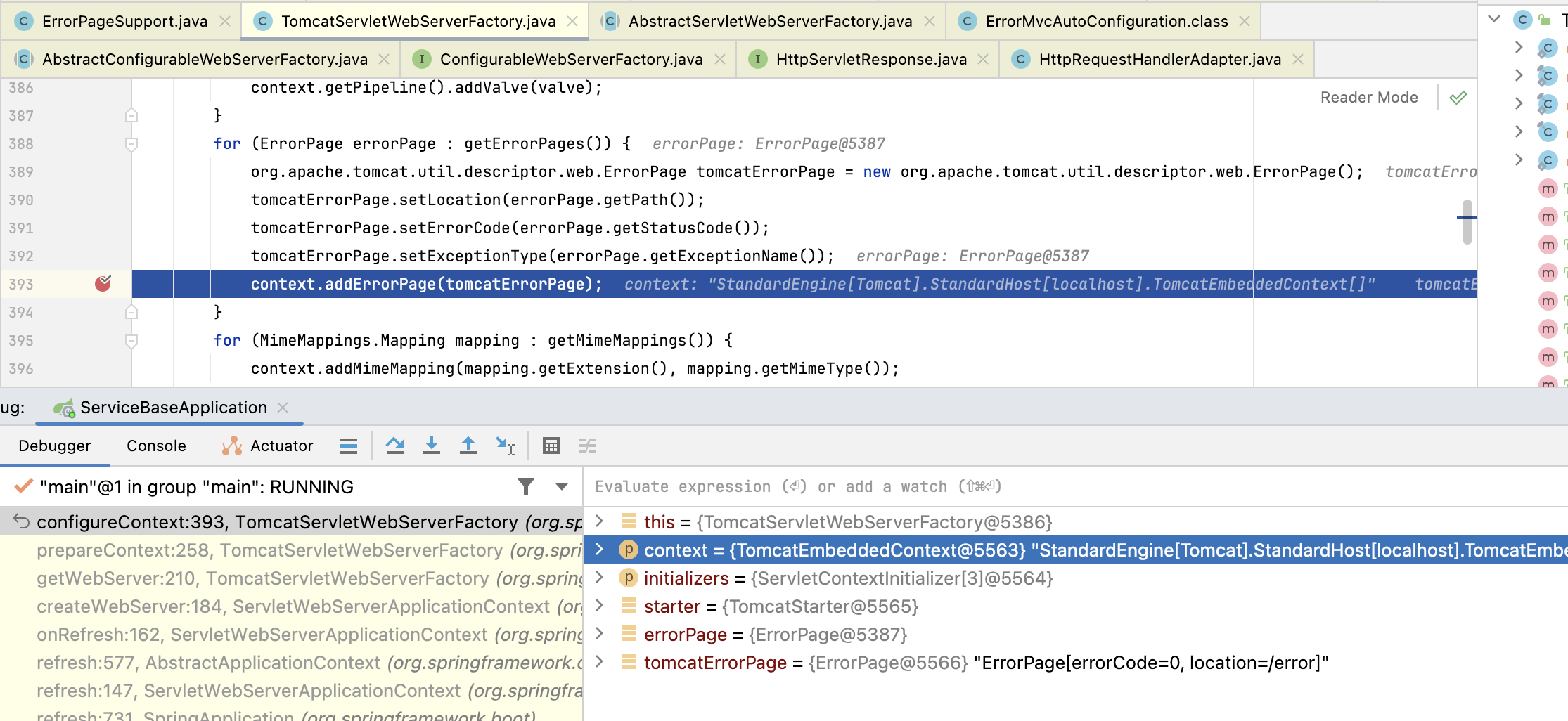
然后在创建 Tomcat 的时候,把它放进了 Tomcat 里的 context 对象里:
画个图捋一下,大家可能会看的比较清晰点,过程还是比较长的:

大家可以自己 debug 看看哈,
2.4.2 400 Bad Request
400的情况我们可以将请求头里添加很长很长的字符串就可以触发:
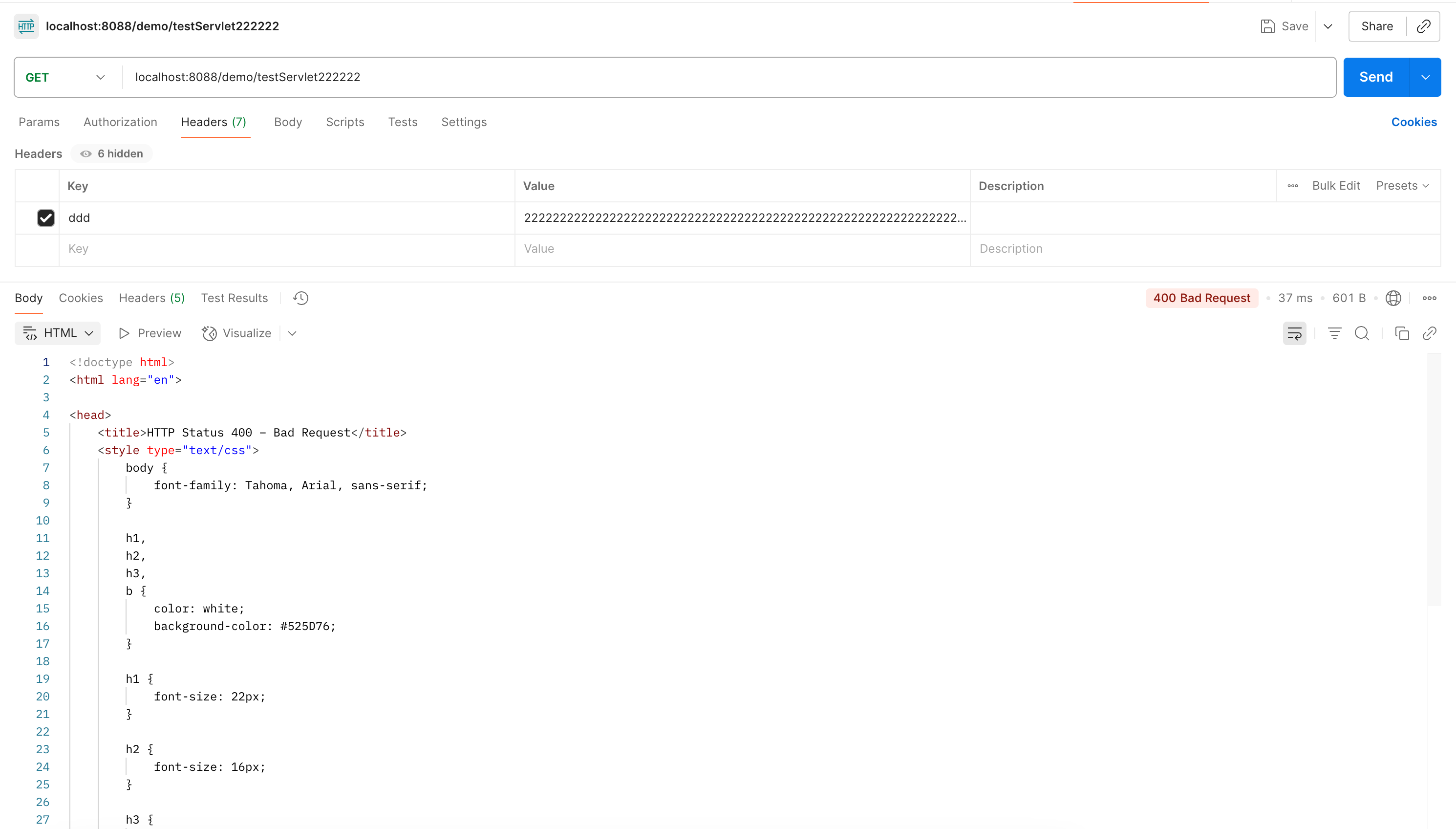
但是这个400并不是 mvc 框架层面报出来的哈,这个可以看我之前的这篇,【问题记录】【SpringBoot】【Tomcat】请求头大小的限制以及配置过程原理 应该是 tomcat层面直接报出的错。
那我们想让 mvc 层面报一个的话,可以这样比如有一个 post的请求,当我们的请求体为空的话就可以报出:
@PostMapping("/receiveByRequestBody")
public OrderDto receiveByRequestBody(@RequestBody OrderDto orderDto) {
log.info("orderDto={}", orderDto);
return orderDto;
}
效果如下:
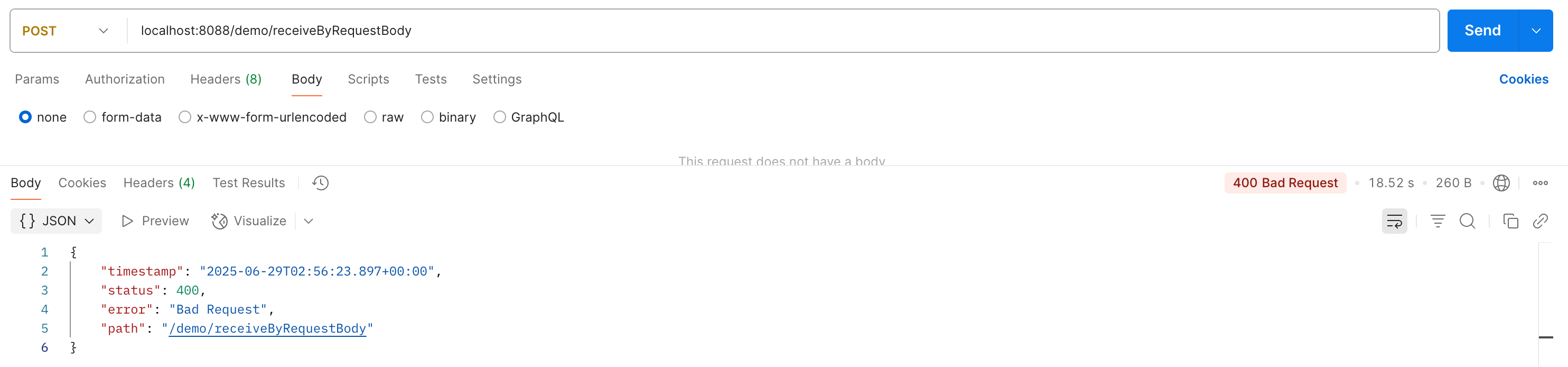
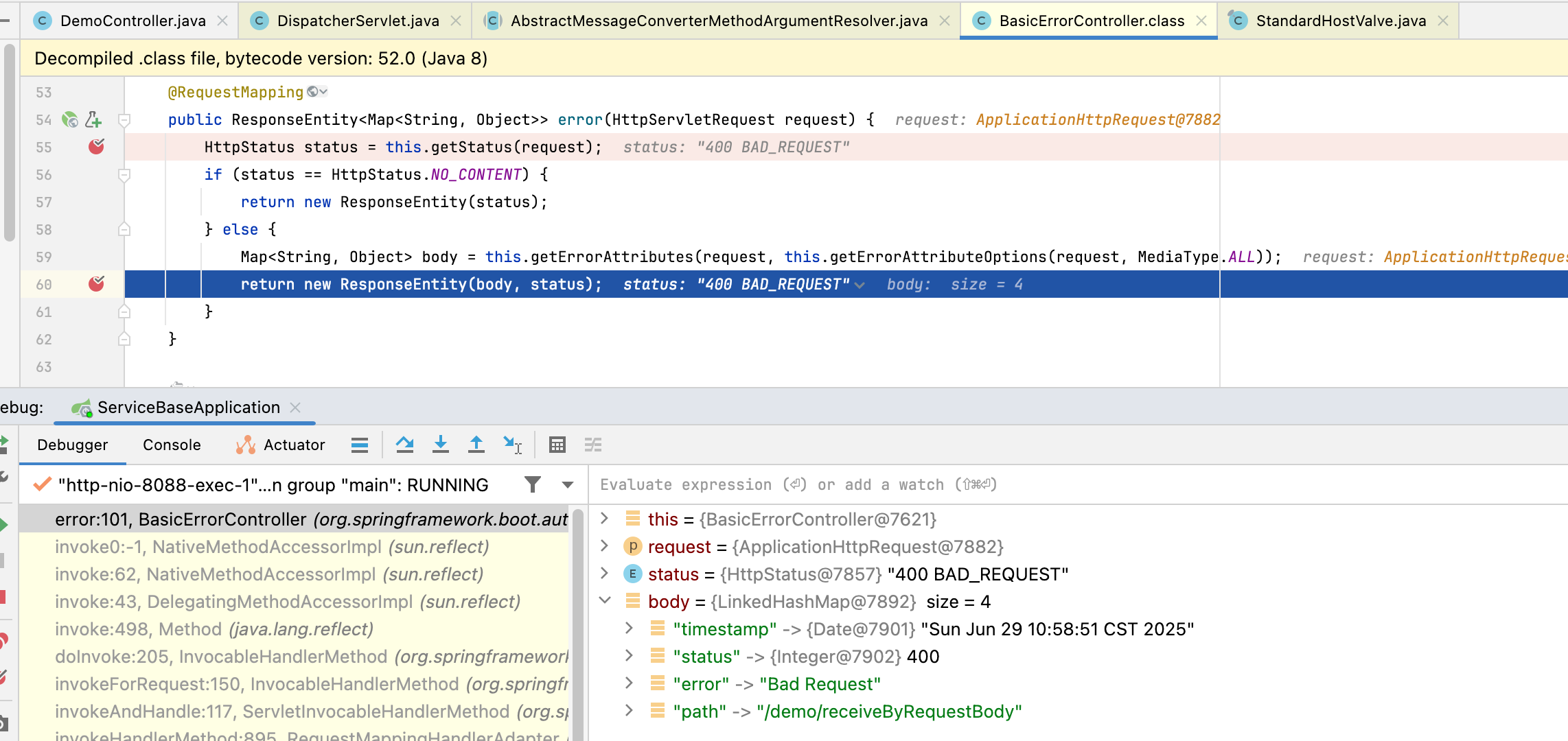
他的原理就跟 404的处理过程差不多,也是经历了一次转发到 error,我们这里就不详细看了哈,看一下到 basicErrorController 的debug如下哈:
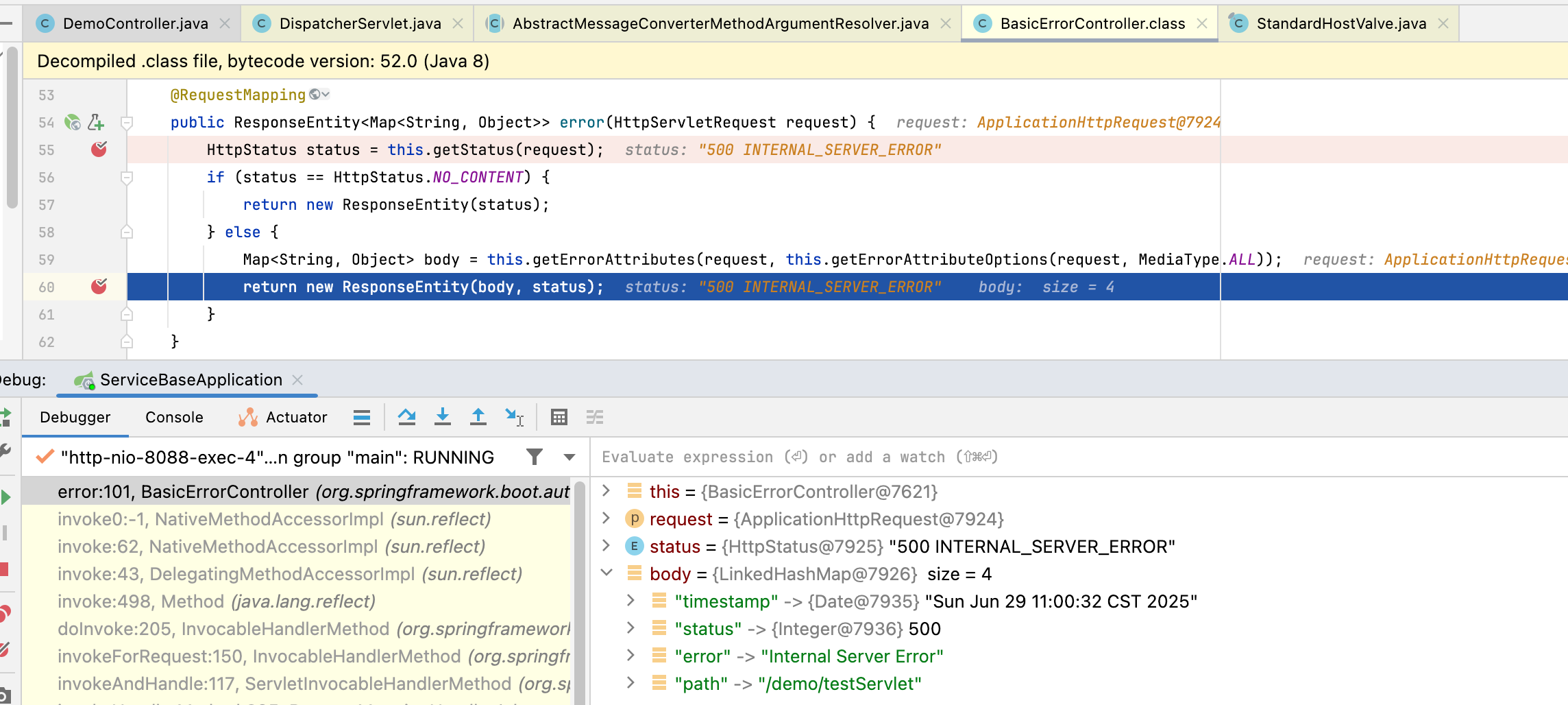
2.4.3 500 Internal Server Error
这个500的异常应该也很常见,比如下边的例子,我直接抛出一个异常:
@GetMapping("/testServlet")
public List testServlet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
log.info("request={}, response={}", request, response);
log.info("name={}", name);
throw new RuntimeException("测试异常");
}
效果如下:
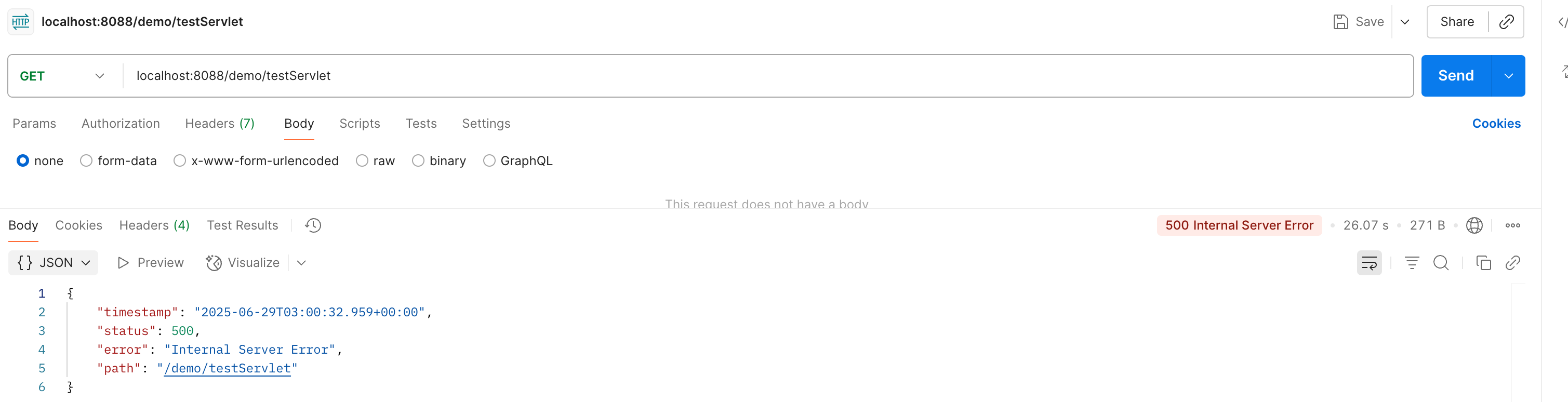
他的过程也是跟404差不多哈,我们也是 debug看下 basicErrorController看一下:
3 概述
好啦,本节异常处理器就看到这里哈,有理解不对的地方还请指正哈。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号