import tensorflow as tf
w = tf.constant(1.)
x = tf.constant(2.)
y = x*w
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch([w])
y2 = x*w
grad1 = tape.gradient(y,[w])
print(grad1)
结果为[None]
因为 y= x* w 没有放在 with tf.GradientTape() as tape:中。所以无法计算.如果w 已经是tf.Variable类型,就不需要放在GradientType中了
import tensorflow as tf
w = tf.constant(1.)
x = tf.constant(2.)
y = x*w
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch([w])
y2 = x*w
grad2 = tape.gradient(y2,[w])
print(grad2)
结果 为:[<tf.Tensor: id=6, shape=(), dtype=float32, numpy=2.0>].
注意 [w] 中的w必须放在tape.watch()中.因为这个w不是tf.Variable型。
import tensorflow as tf
x = tf.random.normal([2,4])
w = tf.random.normal([4,3])
b = tf.zeros([3])
y = tf.constant([2,0])
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
tape.watch([w,b])
logits = x@w + b
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy(tf.one_hot(y,depth=3),logits,from_logits = True))
grads = tape.gradient(loss,[w,b])
print(grads)
x =tf.random.normal([2,4])
w = tf.Variable(tf.random.normal([4,3]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([3]))
y = tf.constant([2,0])
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# tape.watch([w,b]) 注意 w,b 已经是 tf.Variable类型了。就不需要watch了。
logits = x@w + b
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.categorical_crossentropy(tf.one_hot(y,depth=3),logits,from_logits = True))
grads = tape.gradient(loss,[w,b])
print(grads)
第三点:Persistent 参数.为True才可以连续求梯度.否则会报错.
with tf.GradientTape( persistent = True) as tape:
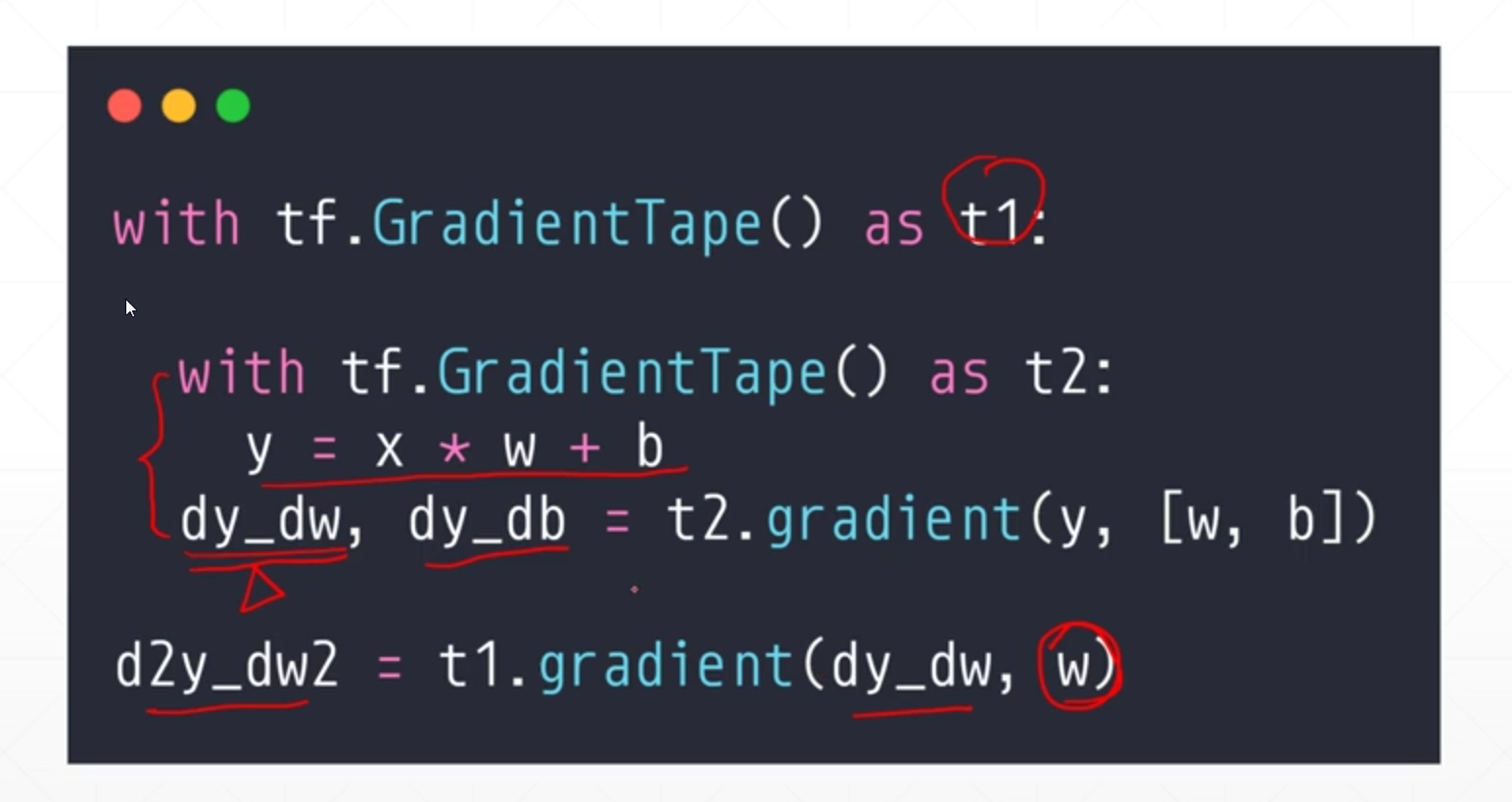
第4点。二阶求导:DMEO.一般很少用到。
![]()
![]()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号