Linux动态库编译与引用
动态库编译
新建一个hello.c和hello.h,待会会将它编译成动态库
#include <stdio.h> void hello (void) { printf("this is hello\r\n"); }
#ifndef __HELLO_H #define __HELLO_H void hello (void); #endif
使用"gcc -shared -fPIC -o libhello.so hello.c"命令生成动态库libhello.so。
动态库引用
新建main.c并引用hello函数。
#include <stdio.h> #include "hello.h" int main (int argc, int **argv[]) { printf("this is main\r\n"); hello(); return 0; }
使用"gcc main.c -L . -lhello -I /home/kmpro/study/ -o main" 生成应用程序main。
如果此时直接”./main“运行,会报如下错误,意思是找不到动态库

此时有三种解决方法:
1.临时设置动态库的查找路径,这种方法在关闭shell终端会失效。
export LD_LIBRARAY_PATH = /home/kmpro/study(库绝对路径)
当然也可以将以上命令放到~/.bashrc或者是/etc/profile,这样就不会失效了。
2.将动态库文件拷贝到系统动态库目录/usr/lib下,这是Linux默认的动态库查找路径。
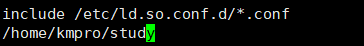
3.修改/etc/ld.so.conf文件,在文件中添加自己的动态库所在路径,修改后使用sudo ldconfig -v更新设置。
总结
1.在编译时需要使用-L指定链接的动态库所在路径,但是该路径只用于编译,编译之后动态库的查找路径需要用户用上面的3方法指定。
2.编译生成的动态库文件名字为libxxx.so,实际在使用-l链接库时名字不需要加lib和.so,仅为xxx。
3.库引用路径用-L,库引用用-l(小写的L),头文件引用路径用-I(大写i)。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号