leetcode回溯算法刷题笔记
回溯是递归的副产品,只要有递归就会有回溯。
回溯算法的本质是穷举,穷举所有可能,为了使其高效,会根据条件对其进行剪枝
回溯法解决的问题都可以抽象为树形结构,因为回溯法解决的都是在集合中递归查找⼦集,集合的⼤⼩就构成了树的宽度,递归的深度,都构成的树的深度。
递归就要有终⽌条件,所以必然是⼀颗⾼度有限的树(N叉树)。
回溯算法解决的类型
- 组合问题:N个数⾥⾯按⼀定规则找出k个数的集合
- 切割问题:⼀个字符串按⼀定规则有⼏种切割⽅式
- ⼦集问题:⼀个N个数的集合⾥有多少符合条件的⼦集
- 排列问题:N个数按⼀定规则全排列,有⼏种排列⽅式
- 棋盘问题:N皇后,解数独等等
组合是不强调元素顺序的,排列是强调元素顺序。
回溯模板
逐步确定回溯函数模板->返回值->参数
在回溯算法中,一般函数起名字为backtracking,
回溯算法中函数返回值⼀般为void。
针对参数,因为回溯算法需要的参数可不像⼆叉树递归的时候那么容易⼀次性确定下来,所以⼀般是先写逻辑,然后需要什么参数,就填什么参数。
伪代码如下:
void backtracking(参数) {
if (终⽌条件) {
存放结果;
return;
}
for (选择:本层集合中元素(树中节点孩⼦的数量就是集合的⼤⼩)) {
处理节点;
backtracking(路径,选择列表); // 递归
回溯,撤销处理结果
}
}
for循环可以理解是横向遍历,即树形结构中的同一层节点,backtracking(递归)就是纵向遍历
集合的⼤⼩构成了树的宽度,递归的深度构成的树的深度
组合问题
切割问题
子集问题
78.子集(子集问题基础模板 无重复 降重由深搜搜索index位置元素)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subsets/
题目
给你一个整数数组 nums ,数组中的元素 互不相同 。返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
解集 不能 包含重复的子集。你可以按 任意顺序 返回解集。
用例
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3]
输出:[[],[1],[2],[1,2],[3],[1,3],[2,3],[1,2,3]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0]
输出:[[],[0]]
思路
子集问题可以看作是寻找树的所有结点
但由于集合是无序的,⼦集{1,2} 和 ⼦集{2,1}是⼀样的,因此需要降重
那么既然是⽆序,取过的元素不会重复取,写回溯算法的时候,for就要从Index开始,⽽不是从0开始!
代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> subsets(vector<int>& nums) {
ans.clear();
sonans.clear();
backtraking(nums,0);
return ans;
}
private:
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<int> sonans;
void backtraking(vector<int>nums,int index){
for(int i= index;i<nums.size();i++)
{
sonans.push_back(nums[i]);
backtraking(nums,i+1);
sonans.pop_back();
}
ans.push_back(sonans);
}
};
90.子集2(有重复 去重靠判定前后重复)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subsets-ii/
题目
给你一个整数数组 nums ,其中可能包含重复元素,请你返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
解集 不能 包含重复的子集。返回的解集中,子集可以按 任意顺序 排列。
用例
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,2]
输出:[[],[1],[1,2],[1,2,2],[2],[2,2]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0]
输出:[[],[0]]
思路
本题与子集1的区别主要在于候选集合存在重复,如何去重是本题的关键。
去重,其实就是使用过的元素不能重复选取。
本题的去重的是的是同一树层上的“使用过”,同一树枝上的都是一个组合里的元素,不用去重
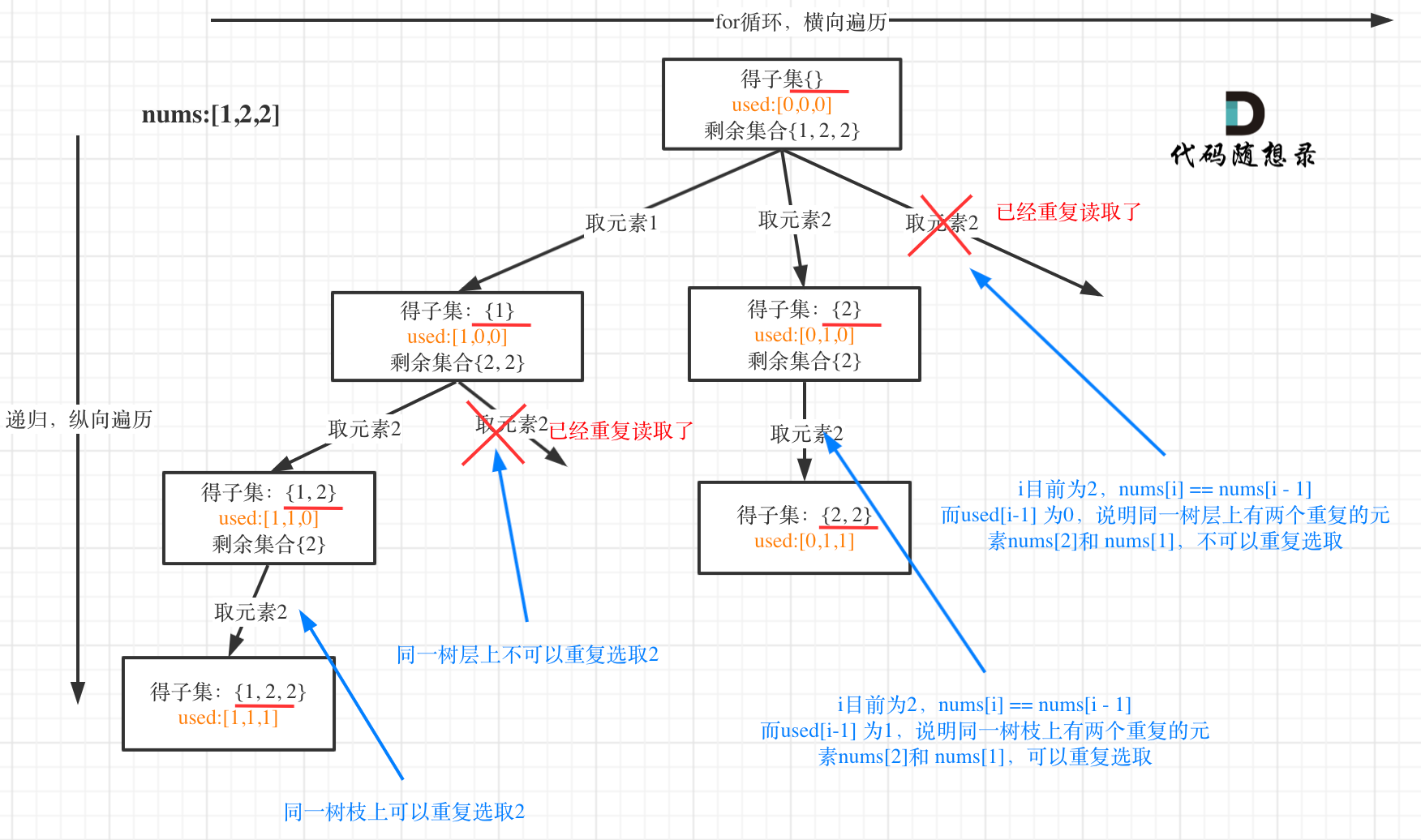
代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> subsetsWithDup(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
ans.clear();
sonans.clear();
backtraink(nums,0);
return ans;
}
private:
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<int >sonans;
void backtraink(vector<int>nums,int index)
{
int judge=1;
for(int i=index;i<nums.size();i++)
{
if(judge)
{
sonans.push_back(nums[i]);
backtraink(nums,i+1);
sonans.pop_back();}
if(i+1<nums.size()&&nums[i]==nums[i+1])
{
judge=0;
}else
judge=1;
}
ans.push_back(sonans);
}
};
dalao版本题解
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<int>> result;
vector<int> path;
void backtracking(vector<int>& nums, int startIndex) {
result.push_back(path);
for (int i = startIndex; i < nums.size(); i++) {
// 而我们要对同一树层使用过的元素进行跳过
if (i > startIndex && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] ) { // 注意这里使用i > startIndex
//这个判断条件我在一开始写没想到i》startindex这个条件 只考虑了i必须大于0 导致过不了
continue;
}
path.push_back(nums[i]);
backtracking(nums, i + 1);
path.pop_back();
}
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> subsetsWithDup(vector<int>& nums) {
result.clear();
path.clear();
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end()); // 去重需要排序
backtracking(nums, 0);
return result;
}
};
排列问题
棋盘问题
79.单词搜索
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/word-search/
题目
给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个字符串单词 word 。如果 word 存在于网格中,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。
用例
示例 1:
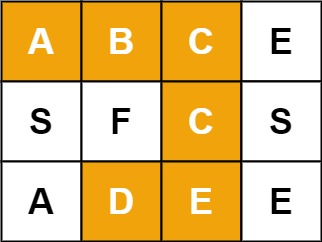
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED"
输出:true
示例 2:
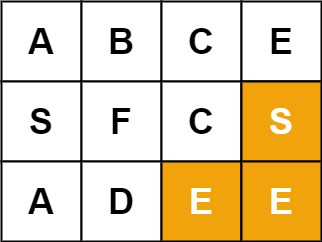
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "SEE"
输出:true
示例 3:
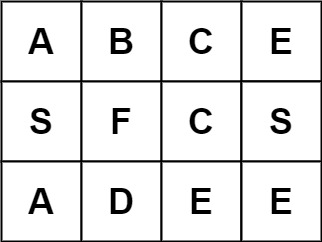
输入:board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCB"
输出:false
思路
棋盘格搜索模板题,就是遍历搜索每一个可能起点,再对可以走的方向进行判断,如字符相等,则对下个位置字符进行递归搜索。
主要要注意结束递归的判断 以及判断走过位置的数组可以再原数组上进行修改(board[x][y]=0)
代码
class Solution {
public:
bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) {
path.assign(board.size(), vector<int>(board[0].size(), 0));
for (int i = 0; i<board.size(); i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j<board[0].size(); j++)
{
path[i][j] = 1;
backtracking(word, 0, board, i, j);
path[i][j] = 0;
if (judge)
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private:
vector<int> p = { -1, 0, 1, 0, -1 };
//vector<char> ans;
bool judge = false;
vector<vector<int>>path;
void backtracking(string word, int index, vector<vector<char>>& board, int x, int y)
{
if(judge==true)
return;
if(word.size()-1==index && word[index] == board[x][y])
judge = true;
if (word[index] != board[x][y])
{
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i<4; i++){
if (x + p[i]<0 || x + p[i]>board.size() - 1 || y + p[i + 1] > board[0].size() - 1 || y + p[i + 1] < 0)
continue;
if (path[x + p[i]][y + p[i + 1]] != 1)
{
path[x + p[i]][y + p[i + 1]] = 1;
backtracking(word, index + 1, board, x +p[i] , y + p[i + 1]);
path[x + p[i]][y + p[i + 1]] = 0;
}
}
}
};
dalao代码
class Solution {
public:
bool exist(vector<vector<char>>& board, string word) {
for(int i = 0; i < board.size(); i++){
for(int j = 0; j < board[0].size(); j++){
if(backtrack(board, word, 0, i , j)){ // 从二维表格的每一个格子出发
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
private:
bool backtrack(vector<vector<char>>& board, string& word, int wordIndex, int x, int y){
if( board[x][y] != word[wordIndex]){ // 当前位的字母不相等,此路不通
return false;
}
if(word.size() - 1 == wordIndex){ // 最后一个字母也相等, 返回成功
return true;
}
char tmp = board[x][y];
board[x][y] = 0; // 避免该位重复使用
wordIndex++;
if((x > 0 && backtrack(board, word, wordIndex, x - 1, y)) // 往上走 (此处多谢笑川兄指正)
|| (y > 0 && backtrack(board, word, wordIndex, x, y - 1)) // 往左走
|| (x < board.size() - 1 && backtrack(board, word, wordIndex, x + 1, y)) // 往下走
|| (y < board[0].size() - 1 && backtrack(board, word, wordIndex, x, y + 1))){ // 往右走
return true; // 其中一条能走通,就算成功
}
board[x][y] = tmp; // 如果都不通,则回溯上一状态
return false;
}
};
51.N皇后
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/n-queens/
题目
n 皇后问题 研究的是如何将 n 个皇后放置在 n×n 的棋盘上,并且使皇后彼此之间不能相互攻击。
给你一个整数 n ,返回所有不同的 n 皇后问题 的解决方案。
每一种解法包含一个不同的 n 皇后问题 的棋子放置方案,该方案中 'Q' 和 '.' 分别代表了皇后和空位。
示例
示例 1:
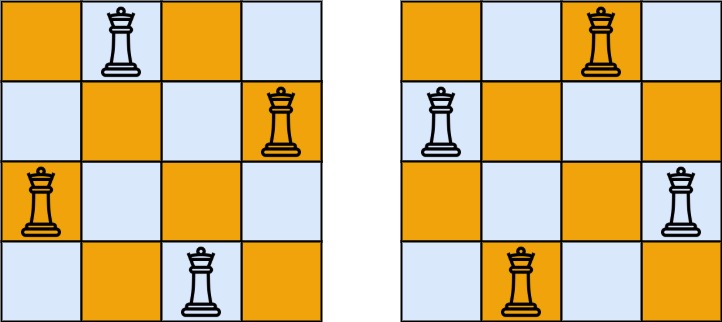
输入:n = 4
输出:[[".Q..","...Q","Q...","..Q."],["..Q.","Q...","...Q",".Q.."]]
解释:如上图所示,4 皇后问题存在两个不同的解法。
示例 2:
输入:n = 1
输出:[["Q"]]
思路
n皇后的约束条件:
- 不能同⾏
- 不能同列
- 不能同斜线
画搜索树如下图(3皇后无解)
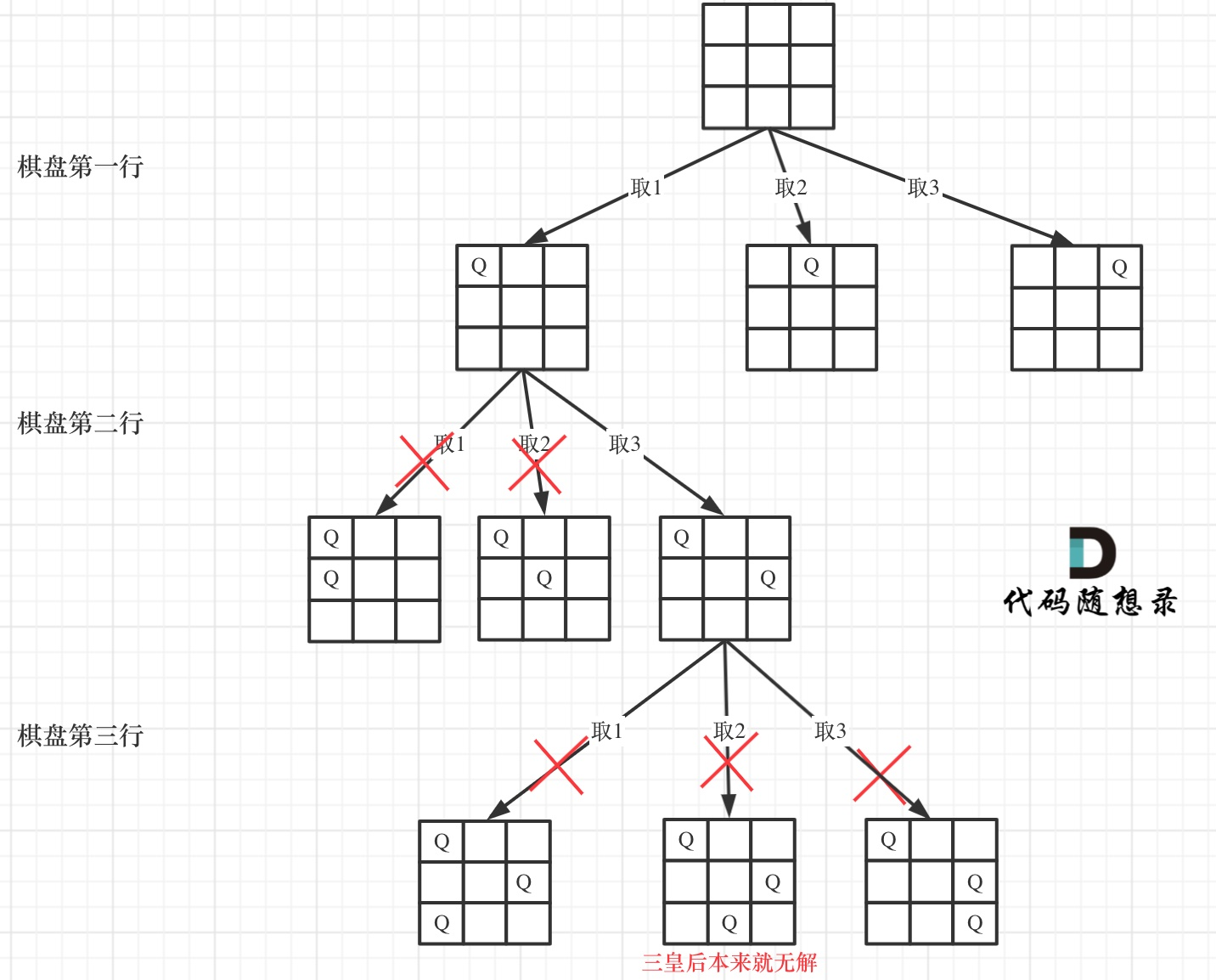
⼆维矩阵中矩阵的⾼就是这颗树的⾼度,矩阵的宽就是树形结构中每⼀个节点的宽度。通过使⽤皇后们的约束条件,来回溯搜索这颗树,只要搜索到了树的叶⼦节点,说明就找到了皇后们的合理位置了。
代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) {
if (n == 1)
{
return{ { "Q" } };
}
backtreacking(n, 0);
return dans;
}
private:
vector<string> ans;
vector<vector<string>> dans;
void backtreacking(int n, int index)
{
if (index == n)
{
dans.push_back(ans);
return;
}
string sonans(n, '.');
for (int i = 0; i<n; i++)//横向搜索
{
int judge = 1;
for (int j = -1; j<2; j++)//左中右三个位置横坐标变化量
{
int num = index;
int num1 = j;
while (num - 1 >= 0)//纵坐标变化
{
if (num1<0 && i + num1<0)
break;
else if (num1>0 && i + num1>n - 1)
break;
else if (ans[num - 1][i + num1] == 'Q')
{
judge = 0;
break;
}
num1+=j;
num--;
}
}
if (judge)
{
sonans[i] = 'Q';
ans.push_back(sonans);
backtreacking(n, index + 1);//回溯
ans.pop_back();
sonans[i] = '.';//注意Q要恢复
}
}
}
};
dalao代码
class Solution {
private:
vector<vector<string>> result;
// n 为输⼊的棋盘⼤⼩
// row 是当前递归到棋牌的第⼏⾏了
void backtracking(int n, int row, vector<string>& chessboard) {
if (row == n) {
result.push_back(chessboard);
return;
}
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++) {
if (isValid(row, col, chessboard, n)) { // 验证合法就可以放
chessboard[row][col] = 'Q'; // 放置皇后
backtracking(n, row + 1, chessboard);
chessboard[row][col] = '.'; // 回溯,撤销皇后
}
}
}
bool isValid(int row, int col, vector<string>& chessboard, int n) {
int count = 0;
// 检查列
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++) { // 这是⼀个剪枝
if (chessboard[i][col] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 检查 45度⻆是否有皇后
for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i >=0 && j >= 0; i--, j--) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
// 检查 135度⻆是否有皇后
for(int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i >= 0 && j < n; i--, j++) {
if (chessboard[i][j] == 'Q') {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
public:
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) {
result.clear();
std::vector<std::string> chessboard(n, std::string(n, '.'));
backtracking(n, 0, chessboard);
return result;
}
};
37.读数独
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sudoku-solver/
题目
编写一个程序,通过填充空格来解决数独问题。
数独的解法需 遵循如下规则:
数字 1-9 在每一行只能出现一次。
数字 1-9 在每一列只能出现一次。
数字 1-9 在每一个以粗实线分隔的 3x3 宫内只能出现一次。(请参考示例图)
数独部分空格内已填入了数字,空白格用 '.' 表示。
用例
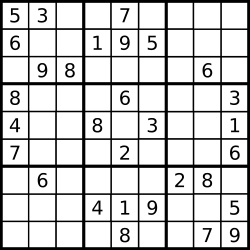
输入:board = [
["5","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."],
["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."],
[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."],
["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"],
["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"],
["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"],
[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."],
[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"],
[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]]
输出:
[["5","3","4","6","7","8","9","1","2"],
["6","7","2","1","9","5","3","4","8"],
["1","9","8","3","4","2","5","6","7"],
["8","5","9","7","6","1","4","2","3"],
["4","2","6","8","5","3","7","9","1"],
["7","1","3","9","2","4","8","5","6"],
["9","6","1","5","3","7","2","8","4"],
["2","8","7","4","1","9","6","3","5"],
["3","4","5","2","8","6","1","7","9"]]
解释:输入的数独如上图所示,唯一有效的解决方案如下所示:
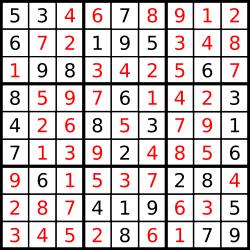
思路
读数独手撕了两小时才勉强调出来,难顶。
与之前的棋盘问题不同,因为熟读要对整个棋盘每个位置进行检测是否数字,是否合法,所以在模板的基础上需要用到二维递归(即两重循环进行遍历)
合法条件横竖 3*3区域检测,注意 判断合法的函数可以分开写!!!
解数独找到⼀个符合的条件(就在树的叶⼦节点上)⽴刻就返回,相当于找从根节点到叶⼦节点⼀条唯⼀路径,递归的结束条件可以通过定义返回bool值判定,一旦没有数符合 返回false,遍历完成返回true,递归成功返回true。
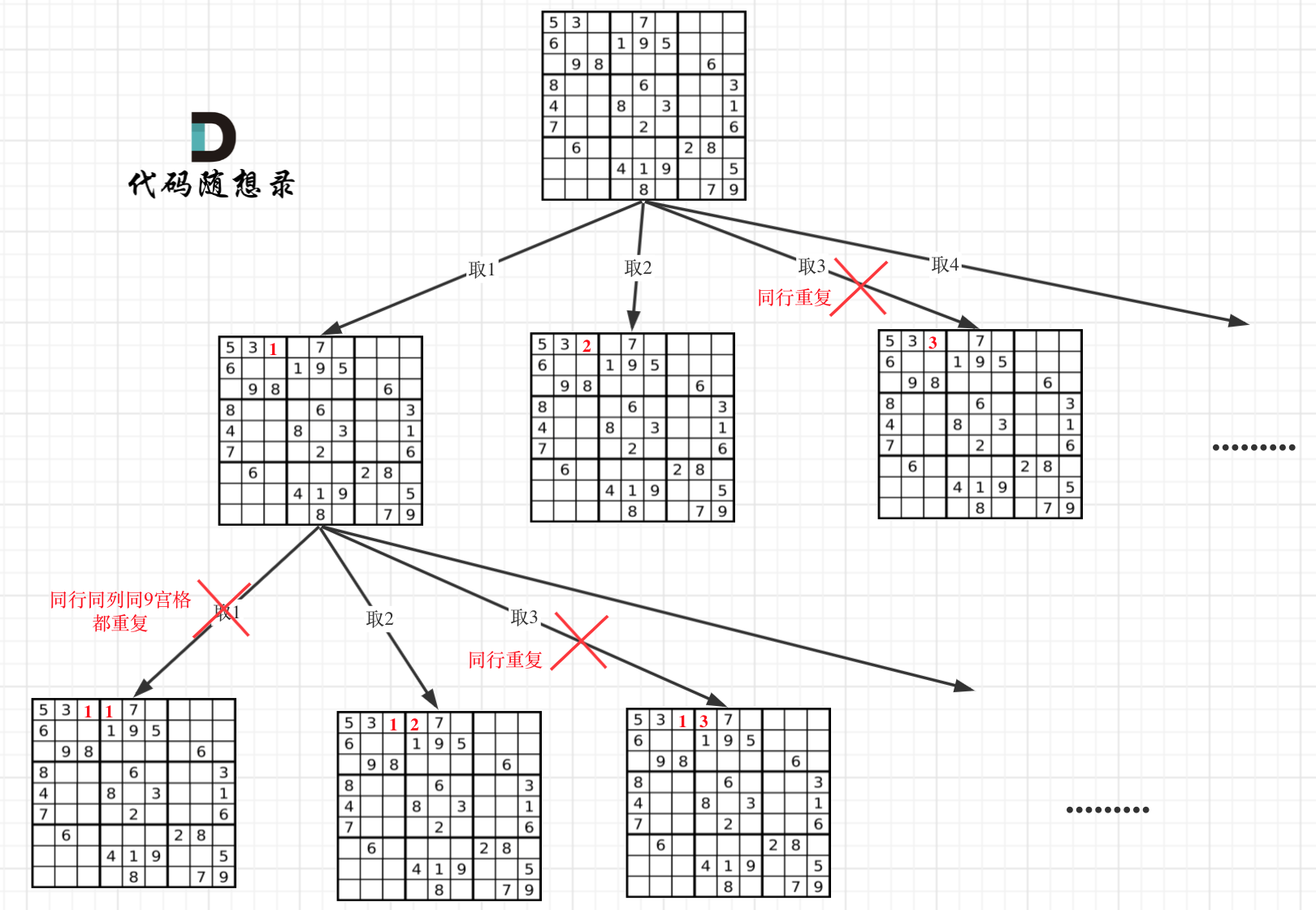
代码
class Solution {
public:
void solveSudoku(vector<vector<char>>& board) {
backtracking(board);
}
bool backtracking(vector<vector<char>>&board)
{
for(int i =0;i<board.size();i++)
{
for(int j =0;j<board[0].size();j++)
{
if(board[i][j]!='.')
continue;
for(char k='1';k<='9';k++){
if(isValid(i,j,k,board))
{
board[i][j]=k;
if(backtracking(board))
return true;
board[i][j]='.';
}
}
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
bool isValid(int row,int col,char val,vector<vector<char>>&board)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
{ // 判断⾏⾥是否重复
if (board[row][i] == val||board[i][col]==val) {
return false;
}
}
int startRow = (row / 3) * 3;
int startCol = (col / 3) * 3;
for(int i =startRow;i<startRow+3;i++)
{
for(int j=startCol;j<startCol+3;j++)
{
if(board[i][j]==val)
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号