Redis Architecture&Source Code
redis 服务器本质上是一个事件驱动程序(redis处理两类事件:文件事件和时间事件)。
对于文件事件的处理,redis基于Reactor模式开发了文件事件处理器,首先介绍下Reactor模式是什么东西?
Reactor模式是网络编程模型的一种,是一种典型的事件驱动编程模型,其处理事件机制为:主程序将事件以及事件处理方法在Reactor上进行注册,如果对应事件发生,Reactor会主动调用事件注册的接口,即回调函数。分析到现在,我们可以知道,Reactor架构模式需要以下几个关键组件:
(1)事件源:linux通常为文件描述符。事件通常为I/O事件,由操作系统触发。对于redis来说,事件源为套接字描述符(文件描述符的一种)
(2)Reactor(反应器): 负责注册注销事件,运行事件循环,当有事件就绪后,调用注册事件的回调函数
(3)Event demultiplexer(事件多路分发机制):通常是由操作系统提供的I/O多路复用的机制,例如select, epoll. 程序首先将handler(事件源)以及对应的事件注册到event demultiplexer上;当有事件到达时,event demultiplexer就会发出通知,通知Reactor调用事件处理程序进行处理
(4)Event Handler(事件处理程序): 事件处理程序提供了一组接口,在Reactor相应的事件发生时调用,执行相应的事件处理,在事件注册过程中会将事件和对应的事件处理程序进行绑定
下面来分析下redis文件事件处理器的四个组成部分,它们分别是套接字, I/O多路复用程序,文件事件派发器,事件处理器:
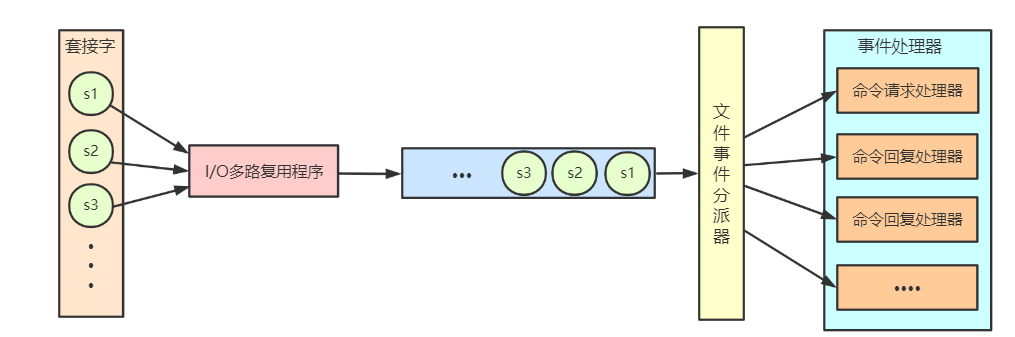
套接字就是事件源,每当一个套接字准备好执行连接应答(accept)、写入(write)、读取(read)、关闭(close)等操作时,就会相应产生一个文件事件;
I/O多路复用程序就是我们的Event demultiplexer, I/O多路复用器负责通过loop循环监听多个套接字,同时将一系列套接字按循序存储到一个队列中,由队列向文件事件分派器传送队列中套接字。这个队列中套接字是有序的,它会当一个套接字事件被处理完毕后,会立马向文件事件分配器传送下一个套接字。文件事件分配器接受队列中的套接字并根据套接字产生的事件类型,相应调用不同的事件处理器。相当于我们的Reactor,在redis中,队列中的事件类型在注册时候都已经绑定好了对应的事件处理函数。
源码阅读(source code version: redis-6.2.1):
(1)主事件循环:
void aeMain(aeEventLoop *eventLoop) { eventLoop->stop = 0; while (!eventLoop->stop) { aeProcessEvents(eventLoop, AE_ALL_EVENTS| AE_CALL_BEFORE_SLEEP| AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP); } }
eventLoop这个类型由接口aeCreateEventLoop创建,首先我们看下eventLoop的结构:
typedef struct aeEventLoop {
int maxfd; /* highest file descriptor currently registered */ 当前被注册的文件描述符的个数
int setsize; /* max number of file descriptors tracked */ 可跟踪的文件描述符大小
long long timeEventNextId;
aeFileEvent *events; /* Registered events */ 注册的可以被多路复用I/O函数触发的事件数组
aeFiredEvent *fired; /* Fired events */ 已经触发的事件数组
aeTimeEvent *timeEventHead; //事件链表事件,用于记录定时或者周期性的事件,由于redis实际上定时和周期性事件比较少,基本上只有一个周期性事件serverCron,所以链表存储是不会影响性能的
int stop;
void *apidata; /* This is used for polling API specific data */
aeBeforeSleepProc *beforesleep;
aeBeforeSleepProc *aftersleep;
int flags;
} aeEventLoop;
接下来介绍下提供的aeProcessEvents前(redis服务器初始化)会调用的API接口:
**** ae.c/aeCreateFileEvent函数:将给定套接字的给定事件mask放入到I/O多路复用程序的监听范围之内,并对事件和事件处理器进行关联:
int aeCreateFileEvent(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int fd(数组索引), int mask(事件类型),
aeFileProc *proc(事件处理器), void *clientData)
{
//多路复用程序监听的事件数最大值为setsize
if (fd >= eventLoop->setsize) {
errno = ERANGE;
return AE_ERR;
}
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[fd]; //这里有必要介绍下aeFileEvent这个事件结构,在创建eventLoop的时候,events数组中已经将事件的类型设置为AE_NONE(也就是空)
typedef struct aeFileEvent {
int mask; /* one of AE_(READABLE|WRITABLE|BARRIER) */
aeFileProc *rfileProc;
aeFileProc *wfileProc;
void *clientData;
} aeFileEvent;
if (aeApiAddEvent(eventLoop, fd, mask) == -1) //将给定套接字的给定事件mask放入到I/O多路复用程序的监听范围之内, 这里要注意像aeApiAddEvent这种函数其实是对系统 不同的I/O多路复用程序 (select\epoll等)做了一层统一接口封装。
return AE_ERR;
fe->mask |= mask;
// 对事件和事件处理器进行关联
if (mask & AE_READABLE) fe->rfileProc = proc;
if (mask & AE_WRITABLE) fe->wfileProc = proc;
fe->clientData = clientData;
if (fd > eventLoop->maxfd)
eventLoop->maxfd = fd; //更新当前被注册的文件描述符的个数
return AE_OK;
}
**** aeApiPoll,针对不同的I/O多路复用函数进行封装,以select封装为例:
static int aeApiPoll(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, struct timeval *tvp(超时时间)) {
aeApiState *state = eventLoop->apidata;
int retval, j, numevents = 0;
memcpy(&state->_rfds,&state->rfds,sizeof(fd_set));
memcpy(&state->_wfds,&state->wfds,sizeof(fd_set));
retval = select(eventLoop->maxfd+1,
&state->_rfds,&state->_wfds,NULL,tvp); //等待select函数返回套接字事件,等待超时时间为传入的tvp
if (retval > 0) {
// 遍历我们注册的事件,如果事件触发了,将事件加入到已经触发事件fired列表中
for (j = 0; j <= eventLoop->maxfd; j++) {
int mask = 0;
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[j];
if (fe->mask == AE_NONE) continue;
if (fe->mask & AE_READABLE && FD_ISSET(j,&state->_rfds))
mask |= AE_READABLE;
if (fe->mask & AE_WRITABLE && FD_ISSET(j,&state->_wfds))
mask |= AE_WRITABLE;
eventLoop->fired[numevents].fd = j;
eventLoop->fired[numevents].mask = mask;
numevents++;
}
}
return numevents; //返回本次触发的事件数量
}
还有一些其他的api函数暂时不一一介绍。下面再介绍ae.c/aeProcessEvent函数,也就是我们事件派发:
int aeProcessEvents(aeEventLoop *eventLoop, int flags)
{
int processed = 0, numevents;
/* Nothing to do? return ASAP */ 没有事件触发,直接返回
if (!(flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_FILE_EVENTS)) return 0;
if (eventLoop->maxfd != -1 ||
((flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS) && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))) {
int j;
struct timeval tv, *tvp;
long msUntilTimer = -1;
//找到最近的时间事件距离现在的时间间隔
if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS && !(flags & AE_DONT_WAIT))
msUntilTimer = msUntilEarliestTimer(eventLoop);
//如果时间间隔大于0,将其作为aeApiPoll接口调用的超时时间
if (msUntilTimer >= 0) {
tv.tv_sec = msUntilTimer / 1000;
tv.tv_usec = (msUntilTimer % 1000) * 1000;
tvp = &tv;
} else {
/* If we have to check for events but need to return
* ASAP because of AE_DONT_WAIT we need to set the timeout
* to zero */ 如果下一个时间事件的时间间隔小于0,代表时间事件已经过了,需要立即执行,这个时候调用aeApiPoll接口会立即返回,也就是不会在这个循环中执行文件事件
if (flags & AE_DONT_WAIT) {
tv.tv_sec = tv.tv_usec = 0;
tvp = &tv;
} else { // 如果没有时间事件,则会一直等待文件事件触发
/* Otherwise we can block */
tvp = NULL; /* wait forever */
}
}
if (eventLoop->flags & AE_DONT_WAIT) {
tv.tv_sec = tv.tv_usec = 0;
tvp = &tv;
}
if (eventLoop->beforesleep != NULL && flags & AE_CALL_BEFORE_SLEEP)
eventLoop->beforesleep(eventLoop);
/* Call the multiplexing API, will return only on timeout or when
* some event fires. */
numevents = aeApiPoll(eventLoop, tvp); //进入I/O多路复用程序中等待事件发生,超时事件设置为下一次时间事件的间隔,返回的值为在超时事件内触发的文件事件数量
/* After sleep callback. */
if (eventLoop->aftersleep != NULL && flags & AE_CALL_AFTER_SLEEP)
eventLoop->aftersleep(eventLoop);
//依次执行触发文件事件对应的处理函数
for (j = 0; j < numevents; j++) {
aeFileEvent *fe = &eventLoop->events[eventLoop->fired[j].fd];
int mask = eventLoop->fired[j].mask;
int fd = eventLoop->fired[j].fd;
int fired = 0; /* Number of events fired for current fd. */
int invert = fe->mask & AE_BARRIER;
if (!invert && fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) {
fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
fired++;
fe = &eventLoop->events[fd]; /* Refresh in case of resize. */
}
/* Fire the writable event. */
if (fe->mask & mask & AE_WRITABLE) {
if (!fired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc) {
fe->wfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
fired++;
}
}
/* If we have to invert the call, fire the readable event now
* after the writable one. */
if (invert) {
fe = &eventLoop->events[fd]; /* Refresh in case of resize. */
if ((fe->mask & mask & AE_READABLE) &&
(!fired || fe->wfileProc != fe->rfileProc))
{
fe->rfileProc(eventLoop,fd,fe->clientData,mask);
fired++;
}
}
processed++;
}
}
/* Check time events */
//处理需要处理的时间事件,周期性时间在处理完后会将下一次需要执行的时间事件加入到时间事件列表中
if (flags & AE_TIME_EVENTS)
processed += processTimeEvents(eventLoop);
return processed; /* return the number of processed file/time events */
}
redis 从客户端连接到操作指令处理流程
假设一个redis服务器正在运作,那么此时服务器的监听套接字(和redis服务端口绑定)的AE_READABLE事件应该处于监听状态,该事件对应的处理器为连接应答处理器(在redis服务器进行初始化的时候,程序会将连接应答处理器和服务器监听套接字的AE_READABLE事件进行关联,当客户端用sys/socket.h/connect函数连接服务器监听套接字时,套接字会产生AE_READABLE事件)。连接应答处理器会创建客户端套接字,然后将客户端套接字的AE_READABLE事件和命令请求处理器关联起来,当客户端向服务端发送请求的时候,套接字就会产生AE_READABLE事件,引发命令请求处理器执行,并执行相应的套接字读入操作,然后将命令传给相关的程序去执行。为了将执行命令产生的恢复传回给客户端,服务器将客户端套接字的AE_WRITABLE事件与命令回复处理器进行关联。当客户端尝试读取命令回复的时候,客户端套接字就会产生AE_WRITABLE事件,触发命令回复处理器执行,将命令回复写入客户端套接字后,服务器将解除客户端套接字的AE_WRITABLE事件与命令回复处理器关联。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号