C++提高编程 4 STL -内建函数对象
4.3.1 内建函数对象意义
概念:STL内建了一些函数对象
分类:
1、算术仿函数;
2、关系仿函数;
3、逻辑仿函数;
用法:这些仿函数所产生的对象,用法和一般函数完全相同
使用内建函数对象,需要引入头文件#include<functional>
4.3.2 算术仿函数

#include<iostream> using namespace std; #include<functional> //内建函数头文件 //内建函数对象 算术仿函数 //negate 一元仿函数 取反仿函数 //plus 二元仿函数 加 减 乘 除 取模 //negate 取反仿函数 一元 void test1() { negate<int>n; n(50); cout << n(50) << endl; //-50 } //plus 加法 二元 void test2() { //减(minus)乘(multiplies)除(divides) 取模(modulus)用法和加法一样 plus<int>p; //定义一个int就够了,因为肯定是int+int 不会是int+float cout << p(10, 20) << endl; //30 } int main() { test1(); test2(); system("pause"); return 0; }
4.3.3 关系仿函数

#include<iostream> using namespace std; #include<vector> #include<algorithm> //标准算法头文件 #include<functional> //内建函数头文件 //内建函数对象 关系仿函数 //大于 greater class MyCompare { public: bool operator()(int v1,int v2) { return v1 > v2; } }; void test1() { vector<int>v; v.push_back(10); v.push_back(30); v.push_back(20); v.push_back(50); v.push_back(40); for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; //10 30 20 50 40 } cout << endl; //降序 //sort默认为升序,sort(v.begin(), v.end());想要降序得自己写个谓词 //way1 //sort(v.begin(), v.end(), MyCompare()); //way2 sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>()); for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; //50 40 30 20 10 } cout << endl; } int main() { test1(); system("pause"); return 0; }
总结:关系仿函数最常用的就是大于greater<>
4.3.4 逻辑仿函数
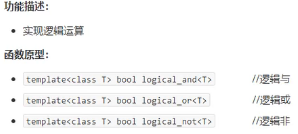
#include<iostream> using namespace std; #include<vector> #include<algorithm> //标准算法头文件 #include<functional> //内建函数头文件 //内建函数对象 逻辑仿函数 //非 logical_not void test1() { vector<bool>v; v.push_back(true); v.push_back(false); v.push_back(true); v.push_back(false); for (vector<bool>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; //1 0 1 0 } cout << endl; //利用逻辑非 将容器v取反搬运到v2中 vector<bool>v2; v2.resize(v.size()); //将v2容量初始化为v的大小 transform(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin(), logical_not<bool>()); for (vector<bool>::iterator it = v2.begin(); it != v2.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; //0 1 0 1 } cout << endl; } int main() { test1(); system("pause"); return 0; }






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号