C++提高编程 4 STL -谓词
4.2 谓词
4.2.1 谓词概念
概念:
返回bool类型的仿函数称为谓词(Pred)
返回operator()接受一个参数,那么叫做一元谓词
返回operator()接受两个参数,那么叫做两元谓词
4.2.2 一元谓词
#include<iostream> using namespace std; #include<algorithm> #include<vector> //仿函数 返回值类型是bool数据类型,称为谓词 //一元谓词 class GreaterFive { public: bool operator()(int val) { return val > 5; } }; void test1() { vector<int>v; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { v.push_back(i); } //查找容器中有没有大于5的数字 //GreaterFive() 匿名对象 vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive()); if (it == v.end()) { cout << "未找到" << endl; } else { cout << "找到了" << endl; //不用再用for循环遍历了 因为此时的it已经是大于5的数字了 直接输出*it即可 //for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) //{ // cout << *it << endl; //} cout << *it << endl; } } int main() { test1(); system("pause"); return 0; }
4.2.2 二元谓词
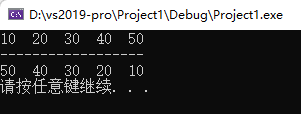
#include<iostream> using namespace std; #include<algorithm> #include<vector> //二元谓词 class myCompare { public: bool operator()(int val1, int val2) { return val1 > val2; } }; void test1() { vector<int>v; v.push_back(10); v.push_back(40); v.push_back(20); v.push_back(30); v.push_back(50); sort(v.begin(), v.end()); for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; // 10 20 30 40 50 } cout << endl; //使用函数对象 改变算法策略,变为排序规则为从大到小 sort(v.begin(), v.end(), myCompare()); cout << "------------------" << endl; for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++) { cout << *it << " "; // 50 40 30 20 10 } cout << endl; } int main() { test1(); system("pause"); return 0; }






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号