C/C++细碎知识点
1.引入头文件
共性
#include<> 与 #include" "区别?
前者常用来包含系统提供的头文件,编译器会到保存系统标准头文件的位置查找头文件;后者常用于包含程序员自己编写的头文件,用这种格式时,编译器先查找当前目录是否有指定名称的头文件,然后从标准头目录中进行查找。
防卫式声明,C,C++用法一样。
加不加.h
经常会看到#include<iostream> 和 #include<iostream.h>。这两种方式都有人使用
iostream和iostream.h是不同的文件,他们的实现代码也不一样。后缀为.h的头文件在C++标准中已经明确提出不再支持了,早些C语言为了实现将标准库功能定义在全局空间里,声明放在带.h的头文件里面。C++标准为了和C语言区分开,也为了正确使用命名空间,规定头文件不再使用后缀.h。因此,当使用<iostream.h>时,相当于在C中调用库函数,使用的是全局命名空间,也就是早期C++实现方法。换句话说,iostream是iostream.h的升级版,大部分的头文件都有一个不带.h的扩展名的文件与之相对应。不过有个特例,<string>并非是<string.h>的升级版。
C++向下兼容C,因此C标准库自然也在支持之中。
旧式C header files带有.h,目前仍可以使用。例如 #include<stdio.h>。特别注意:旧式headers里面的组件不在std中。
新式C header files不带有.h,例如#include<cstdio>
2.开启IDE对C++11的支持
以目前微软最新IDE为例,如下代码可以输出当前C++所采用的标准。在不做任何额外配置的前提下,输出始终为 199711,这说明visual studio仍采用C++98标准。
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { cout << __cplusplus << endl; return 0; }
若支持C++11 或者 更新标准需做如下配置
/std (Specify Language Standard Version)
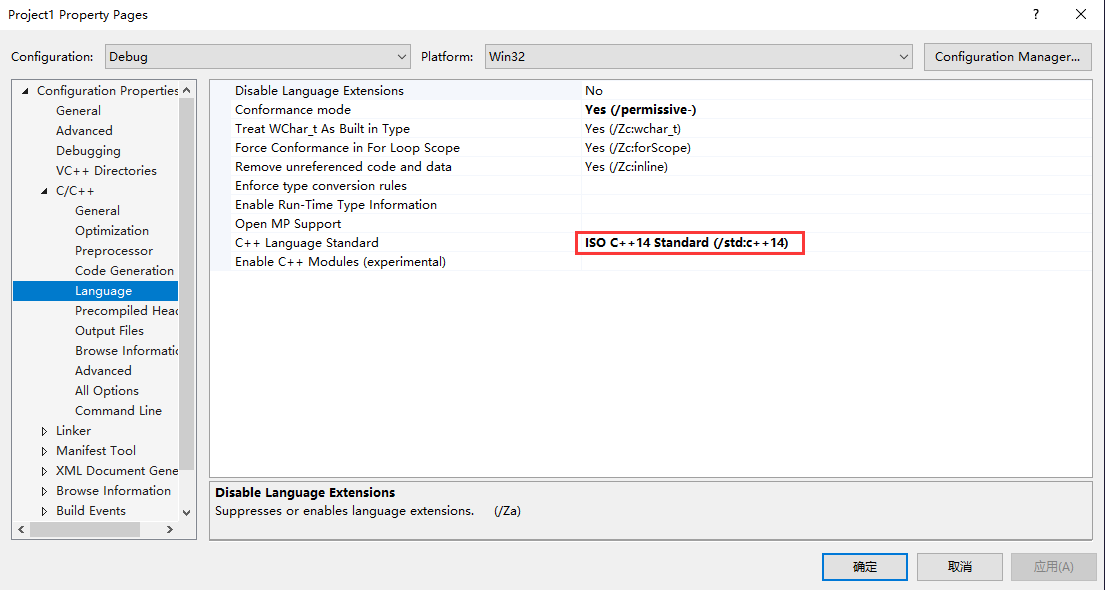
/Zc:__cplusplus (Enable updated __cplusplus macro)
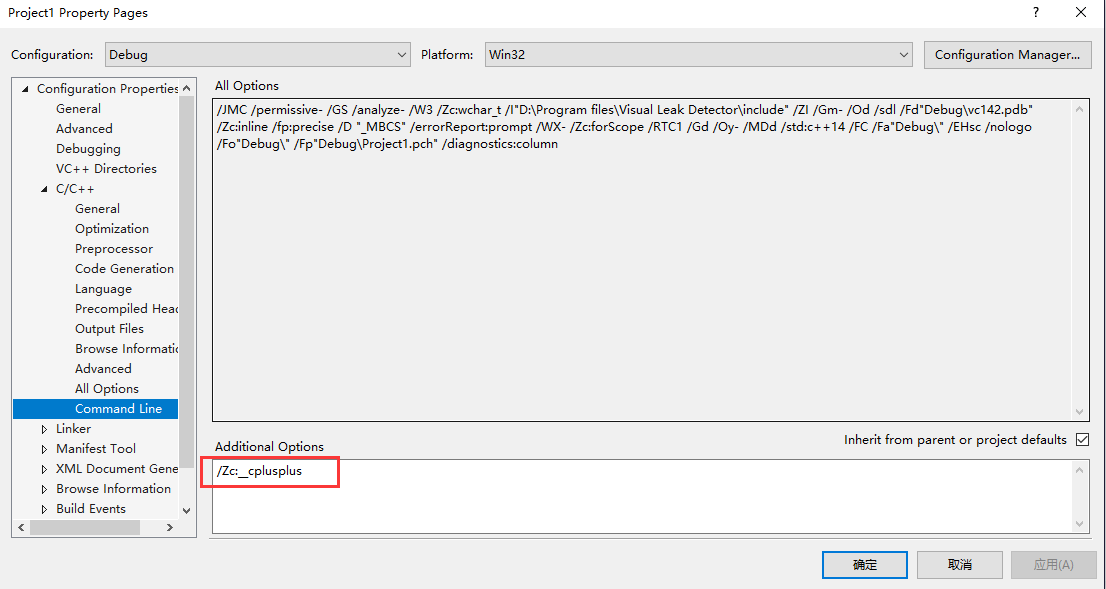
此时在执行代码输出 201402
3.多使用<algorithm>提供的函数
C代码中我们查找一个collection(collection是C++ STL中的叫法,对应C里面的数组概念)里面满足指定条件元素个数,或者把满足制定条件的元素找出来。基本上处理这样的问题都是使用遍历(for, while, do while)。C++提供了更好的方式,使用<algorithm>中提供的库函数。
#include <iostream> // std::cout #include <algorithm> // std::count #include <vector> // std::vector bool IsEven(int i) { return ((i % 2) == 0); } int main() { // counting elements in array: int myints[] = { 10,20,30,30,20,10,10,20 }; // 8 elements int mycount = std::count(myints, myints + 8, 10); std::cout << "10 appears " << mycount << " times.\n"; // counting elements in container: std::vector<int> myvector(myints, myints + 8); mycount = std::count(begin(myvector),end(myvector),20); std::cout << "20 appears " << mycount << " times.\n"; //int evens = std::count_if(begin(myvector), end(myvector), [](auto elem) {return elem % 2 == 0; }); int evens = std::count_if(myvector.begin(), myvector.end(), IsEven); std::cout << "total have odd number is " << evens << std::endl; bool allof_even, noneof_even, anyof_even; allof_even = (evens == myvector.size());//可以不使用all_of函数 noneof_even = (evens == 0); anyof_even = (evens > 0); allof_even = std::all_of(begin(myvector), end(myvector), [](auto elem) {return elem % 2 == 0; }); noneof_even = std::all_of(begin(myvector), end(myvector), [](auto elem) {return elem % 2 != 0; }); anyof_even = std::all_of(begin(myvector), end(myvector), [](auto elem) {return elem % 2 == 0; }); return 0; }
几点需要注意:
begin 、 end等方法可以使用member functions,也可以是free functions。对于STL中实现的collections类型,都默认提供了begin、end等member function的实现。此时调用free fuction内部也是调用具体collection的member function实现。对于自定义的类型,你需要自己实现begin,end等free function。
count_if里面第三个参数,可以使用函数指针,也可使用lambda表达式。推荐使用lamda表达式。
实例代码列举了count,count_if,all_of,any_of,none_of等函数的使用。除此之外,还有find、 find_if、 find_if_not、 find_first_of、 find_end、 search、 search_n、 adjacent_find等函数。
4.不要自己重复造轮子
C里面,我们需要自己手撸各种排序代码,冒泡,选择,归并,快速等等。很多时间浪费在扣边界上,而且写的算法效率还不高。C++ <algorithm>为我们提供了现成的排序算法,你可以不必了解其具体实现,会用即可。
sort和stable_sort
- sort是快速排序实现,因此是不稳定的;stable_sort是归并排序实现,因此是稳定的;
- 对于相等的元素sort可能改变顺序,stable_sort保证排序后相等的元素次序不变;
- 如果提供了比较函数,sort不要求比较函数的参数被限定为const,而stable_sort则要求参数被限定为const,否则编译不能通过。
判断是否有序
查找最大最小值
无序collection,需要遍历每个元素。查找最大值使用max_element(),查找最小值使用min_element(),查找符合特定条件的值使用find()
有序collention查找最大最小值无需遍历整个collention,首位元素即可。查找特定值的元素使用upper_bound()或者lower_bound()
随机数
有两种方式可以生成 [first, last) 范围的随机数,shuffle 和 random_shuffle。两者区别参考:shuffle vs random_shuffle in C++
局部排序
partial_sort,is_sorted_until,partial_sort_copy
5.void main (), int main () 和int main (int argc, char *argv[])
What is the difference among void main (), int main () and int main (int argc, char *argv[])?
void main(void) 旧式C的做法
int main() 标准C的做法
int main(int argc, char * argv[]) 适用于你需要想main传参数的情形,eg: console程序
6.指针和引用
C语言中,为了帮助我们理解程序运行过程中内存开辟释放过程,常常使用内存四区模型来辅助理解。内存四区模型下面我们指定指针是占据栈空间的,X86下是4B,X64下是8B
那么C++下面的引用到底占不占内存呢?更确切的说占不占栈内存呢?
答案是不确定,参考
国外有人将引用是否占据内存分为2中情况,不确定说的对不对
If the passed variable is located in memory, then a reference to that variable is usually a pointer, which could be kept in register or stored in memory. If the passed variable is located in a register due to compiler optimization, then a reference to that variable will use the same register.
理解引用内存占据情况,不能简单使用sizeof来求解,参考
以我使用的IDE Visual Studio 2019为例,其对引用的实现就是采用的指针
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class A { public: double& a; }; int main() { cout << "sizeof(A)= " <<sizeof(A) << endl; // this will print out 4 cout << "sizeof(double*)= " << sizeof(double*) << endl; cout << "sizeof(double)= " << sizeof(double) << endl; return 0; }
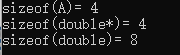 如果不是指针的话,那么sizeof(A)应该是8,但实际上是4
如果不是指针的话,那么sizeof(A)应该是8,但实际上是4
7.不要再使用NULL
C语言中NULL往往被定义成0,这在某些情况下会使人困惑
void f(int); void f(void*); f(0); //调用f(int) f(NULL)//调用f(int),如果NULL被定义成0 f(nullptr);//调用f(void*)
C++下你应该使用nullptr,nullptr用于表示一个指针(pointer)指向所谓的no value(此时拥有一个不确定值)。nullptr是一个新关键字,他可以被转换成各种pointer类型,但不会被转换为任何整数类型。它拥有类型std::nullptr_t,定义于<cstddef>。
8.explicit
explicit是C++下面一个关键字,用途很少,注意就是用在构造函数上。其功能是禁止编译器“自作聪明”帮我们实现类型转换。
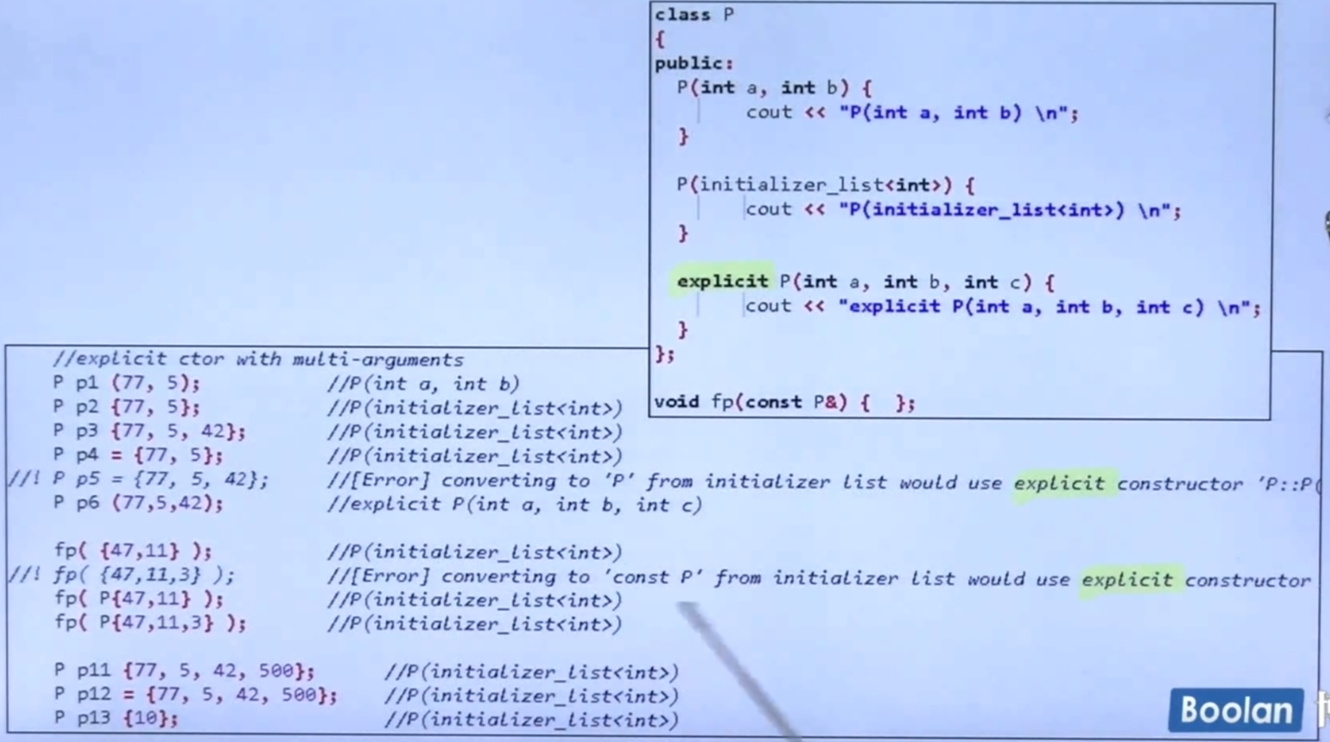
explicit for ctors taking one argument
在C++ 11标准确定之前,explicit关键字只支持接收一个参数的ctor(如果ctor接收2个参数,但是有一个参数有默认参数,那么仍满足explicit使用场景。大于等于2个参数的场景同理)。

上图左侧未加explicit的ctor有个专门术语: non-explicit one argument constructor
C++ 11 以前只有non-explicit one argument constructor才可以做类型转换
explicit for ctors taking one argument
C++ 11取消了只有non-explicit one argument constructor才可以做类型转换的限制。
9.C++如何识别class
识别类的过程未必与你代码书写过程一致。
①先识别类这个类型
②识别数据成员,无论public、protected还是private
③识别成员函数,改写成员函数
我们知道,在C里面必须先定义后使用(有点废话),注意C的要求很严,是把定义放在最前面。
那像下面这种代码,岂不是会报错。因为fun1函数里面使用的变量a,fun1定义在变量a之前,会不会报未定义错误呢? 并不会 原因见C++如何识别类

class Test { public: void fun1() { std::cout << a << std::endl; } void fun2(); private: int a; int b; }; Test test;
11.C语言原生不支持bool
C++中,bool作为一个关键字是语言原生支持的。而C语言却不是这样,在C99之前,是没有bool这个关键字的。C99中对bool的定义也是通过宏实现的。C99引入了一个头文件<stdbool.h>,这里面定义了一个宏就是bool。同时我们熟知的true,false也是在这个头文件中定义的。为了使用bool类型,如下做法从最好到最坏依次是:
Option 1 (C99)
#include <stdbool.h>
Option 2
typedef enum { false, true } bool;
Option 3
typedef int bool; enum { false, true };
Option 4
typedef int bool; #define true 1 #define false 0
10.左值 右值 右值引用
左值:是一个有名字,有固定地址的表达式
右值:是一个和运算相匹配的临时对象,这个临时对象在其所对应的语句执行完毕后就销毁了. 所以无法从语法层面上直接访问.





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号