SAP GRC Rule Set
SAP GRC Rule Set
Rules are ceated in ARA based on the "risks" you define.
Rules are logical constructions composed of a circumstance or condition, and the appropriate response to that condition.
This is commonly represented as an IF-Then statement.
IF
Employee X can Create a Vendor &
Employee X can Authorize Pay vendor
Then
Employee X has been granted High Risk Conflicting Roles
This is an example of a SOD risk.
The core engine of SAP ARA contains a rules library that maintains the risks for SOD conflicts.
This liabray will contain conflicting transactions, grouped into functions, including the object and activity settings and runs to 1000s of records.
For each identified risk the rules need to be configured so that the risk is properly recorded, in essence this means the removal of false positives.
False positives are identified when at the object level potential risk is not realized e.g. the action is to read only.
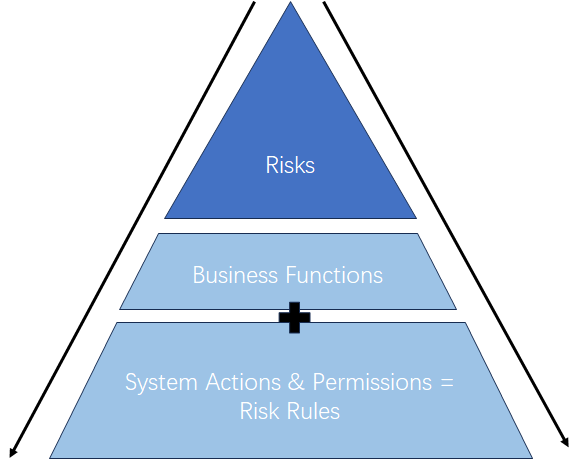
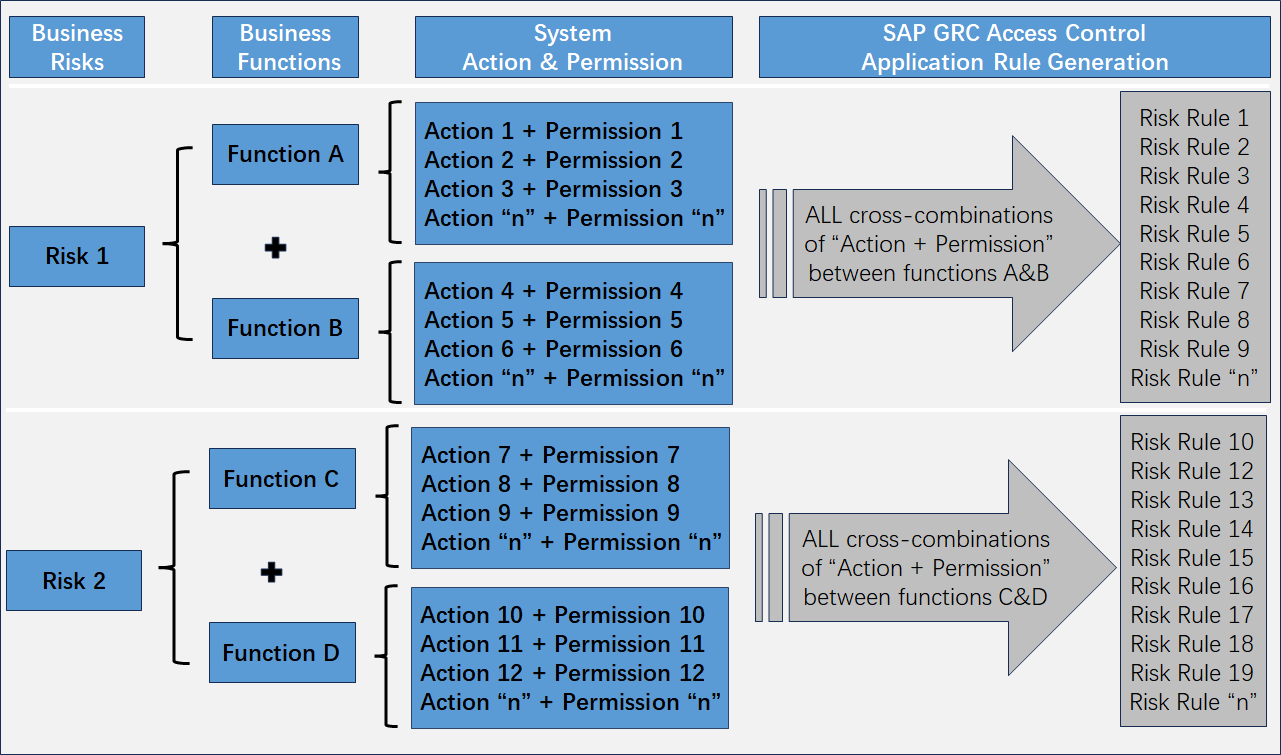
Building rule sets
- Set up functions (groups of activities that users perform to carry out their role) by mapping transaction activities.
- Map two or more functions together to define a risk
- SAP ARA ceates rules based on the risks which are used for risk analysis reporting and alert monitoring.
- Business process can also be defined and mapped to risks for ease of reporting e.g. Finance Accounting.
- Multiple rule sets can also be set up to act as reporting filters, version control and other uses.
Building rule sets can be complex an time consuming. Typically three distinct roles and skills are involved.
Internal Controls Expert
Provides information on SOD risks, criticality and represents business (process) owners in decisions to mitigate or remove risks.
SAP Functional Expert
Provides expertise on the business process configuration in SAP, knowledge Expert on objects and activity values. Helps to set the configuration data for the rule set library. It helps to identify false positives.
SAP ARA Expert
Provides knowledge on rules setting in SAP ARA performing mass upload changes and risk analysis.
Once the rule set has been defined and implemented risk analysis can be performed to identify the SOD conflict and cirtical transaction risks in the staging and production system.
Risk analysis can be performed at the user or role level. Risk analysis and remediation is most efficient when a structured authorizations concept is implemented that maps roles to job and people. In these circumstance remedial efforts correct risks for large groups of users.
Risk Analysis can be performed:
- During the project lifecycle before users are allowed in the production system.
- Before each change request for role maintenance is deployed to production.
- Before provisioning exceptional roles to individual users
- To execute periodic security controls


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号