Central User Administration - CUA
Central User Administration - CUA
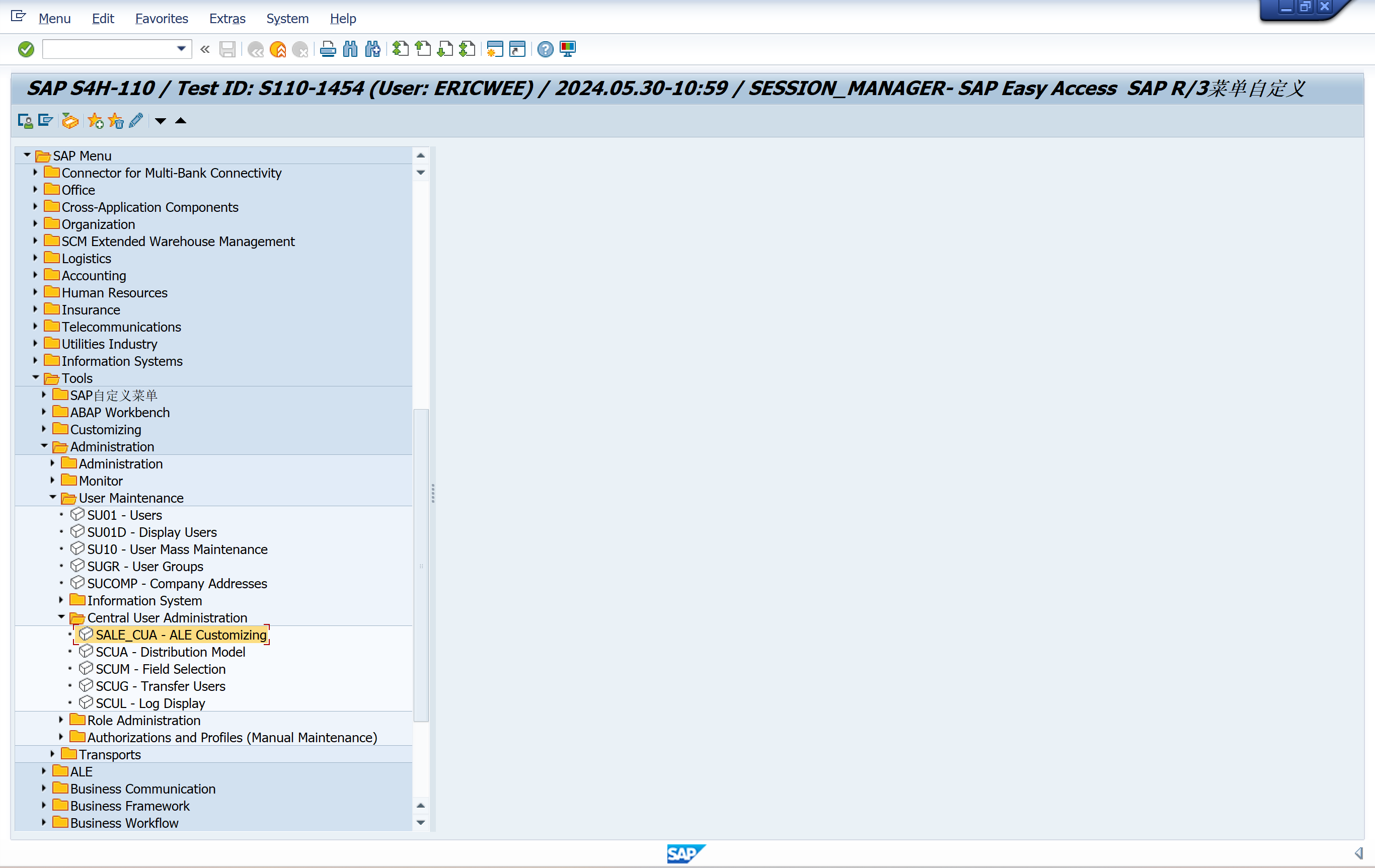
SALE_CUA - ALE Customizing
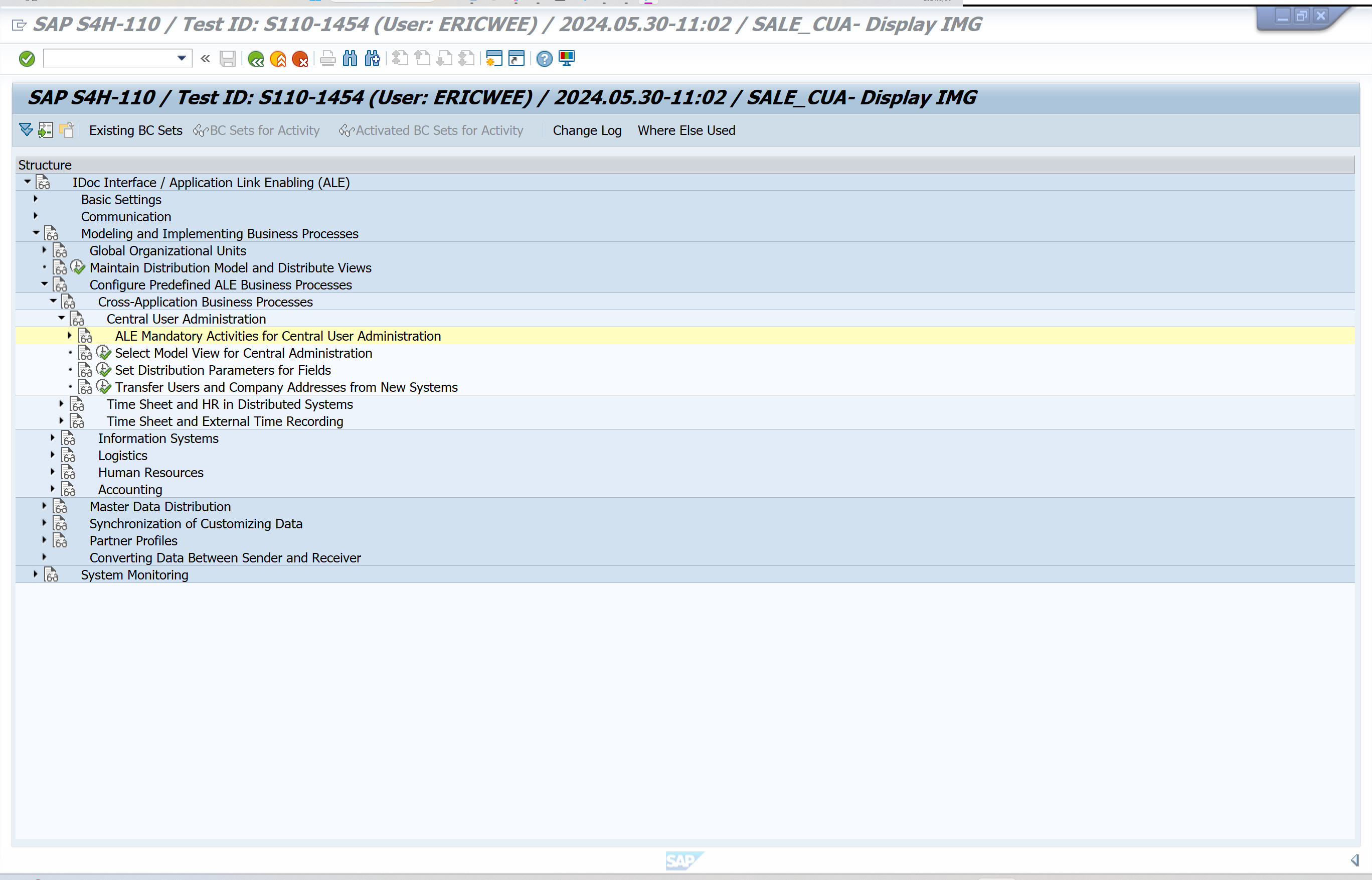
ALE Mandatory Activities for Central User Administration
Carry out all the mandatory actvities in this Implementation Guide. (see Additional information -> Activity importance).
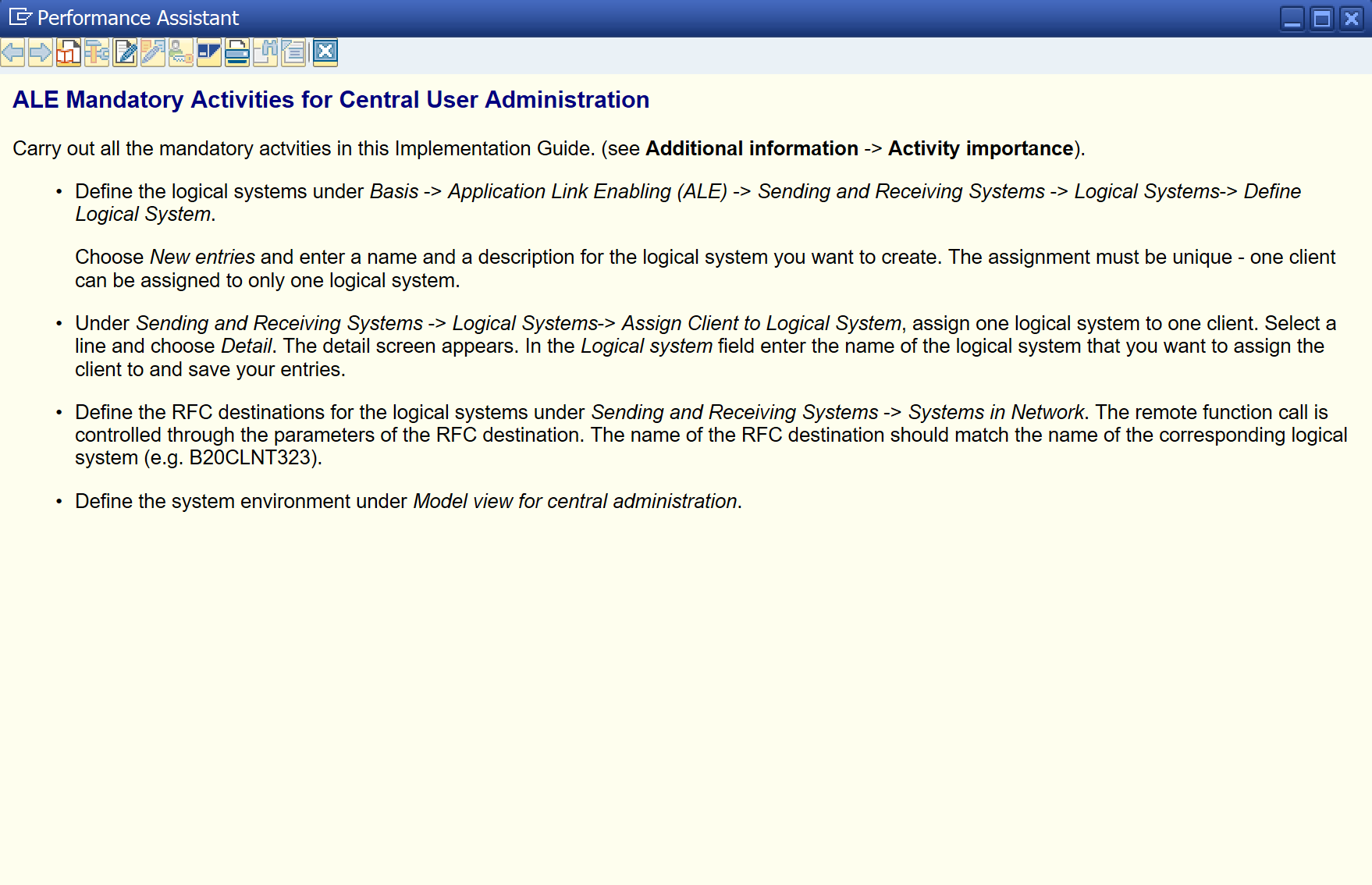
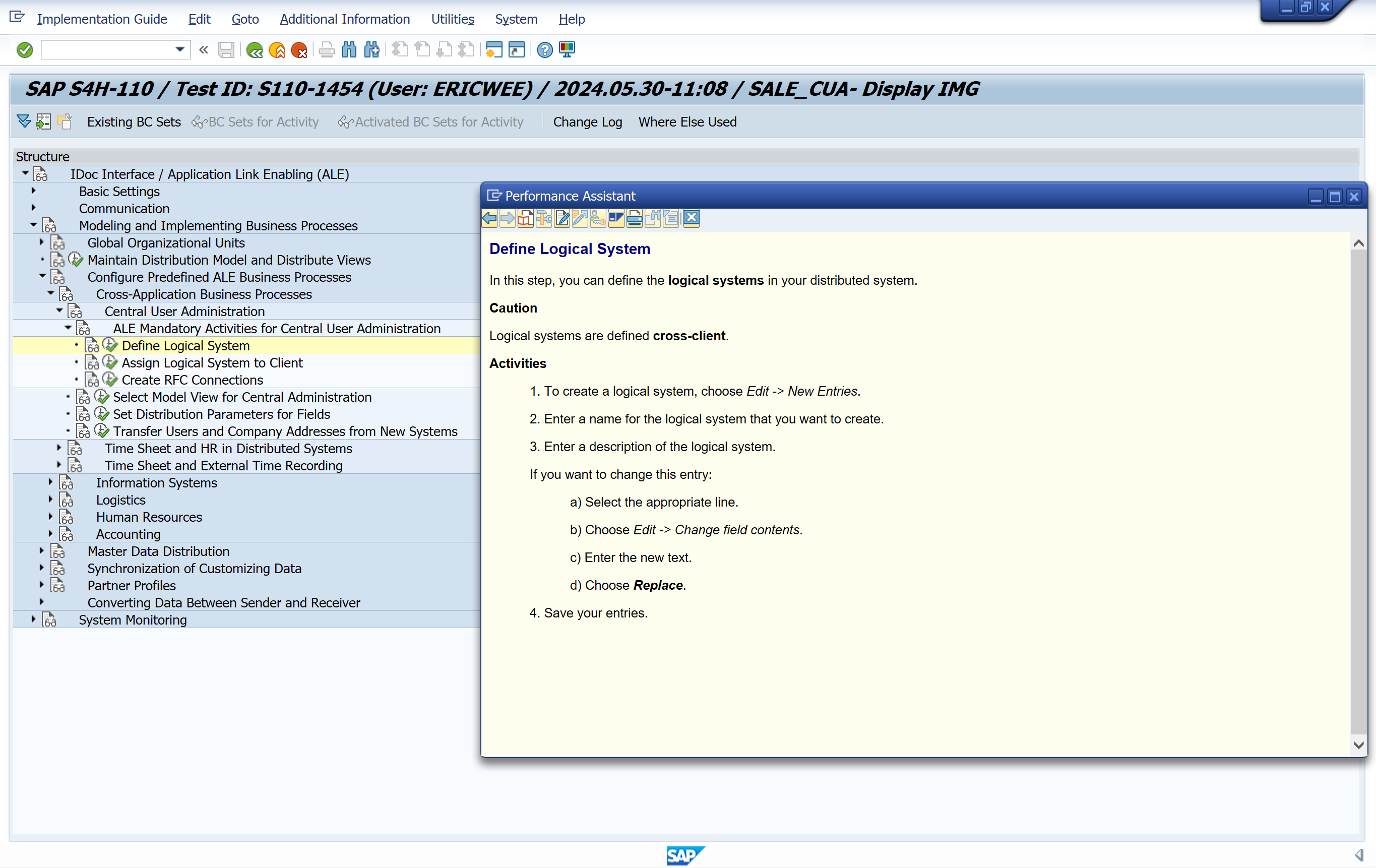
- Define the logical systems under Basis -> Application Link Enabling (ALE) -> Sending and Receiving Systems -> Logical Systems-> Define Logical System.
Choose New entries and enter a name and a description for the logical system you want to create. The assignment must be unique - one client can be assigned to only one logical system.
-
Under Sending and Receiving Systems -> Logical Systems-> Assign Client to Logical System, assign one logical system to one client. Select a line and choose Detail. The detail screen appears. In the Logical system field enter the name of the logical system that you want to assign the client to and save your entries.
-
Define the RFC destinations for the logical systems under Sending and Receiving Systems -> Systems in Network. The remote function call is controlled through the parameters of the RFC destination. The name of the RFC destination should match the name of the corresponding logical system (e.g. B20CLNT323).
-
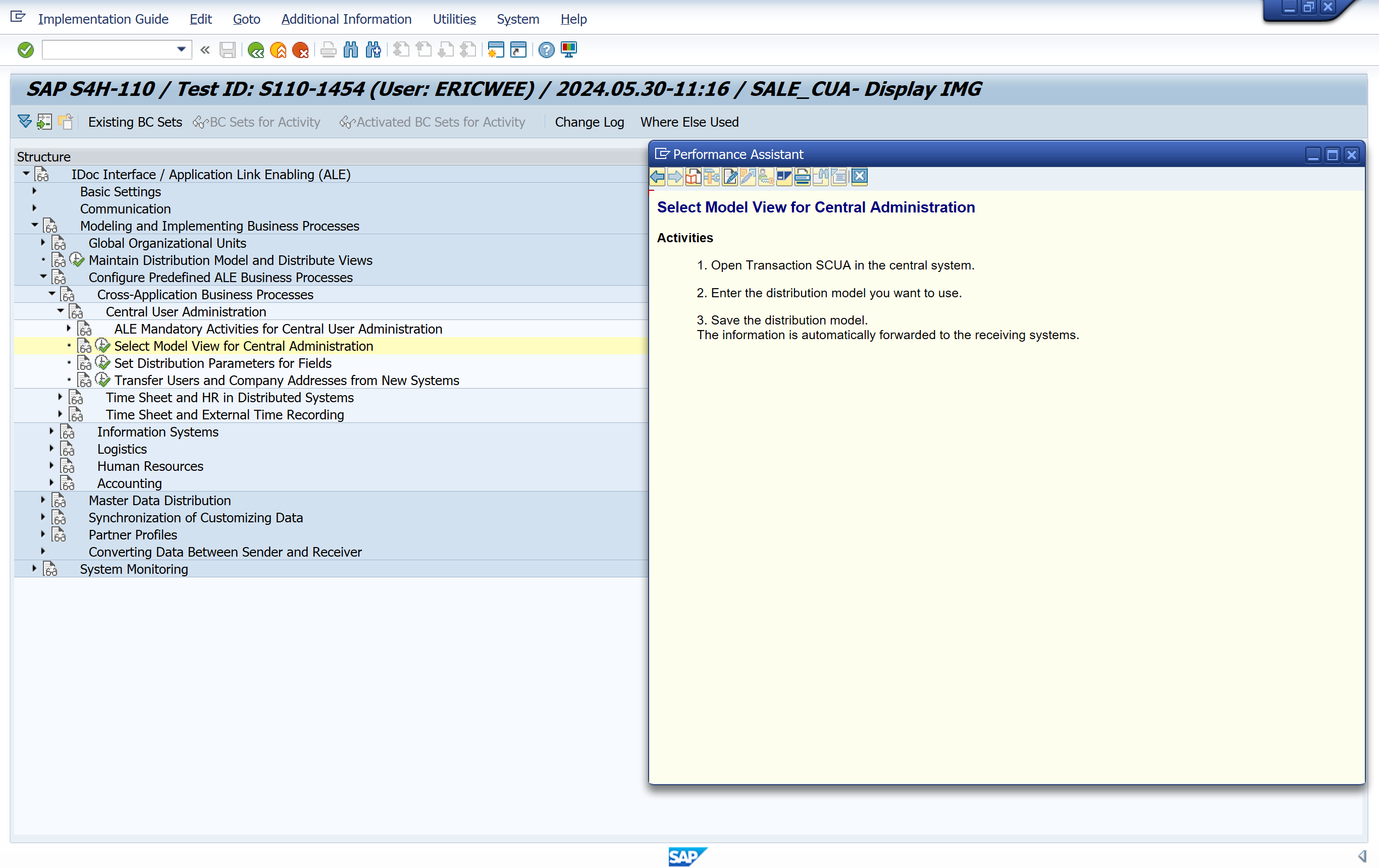
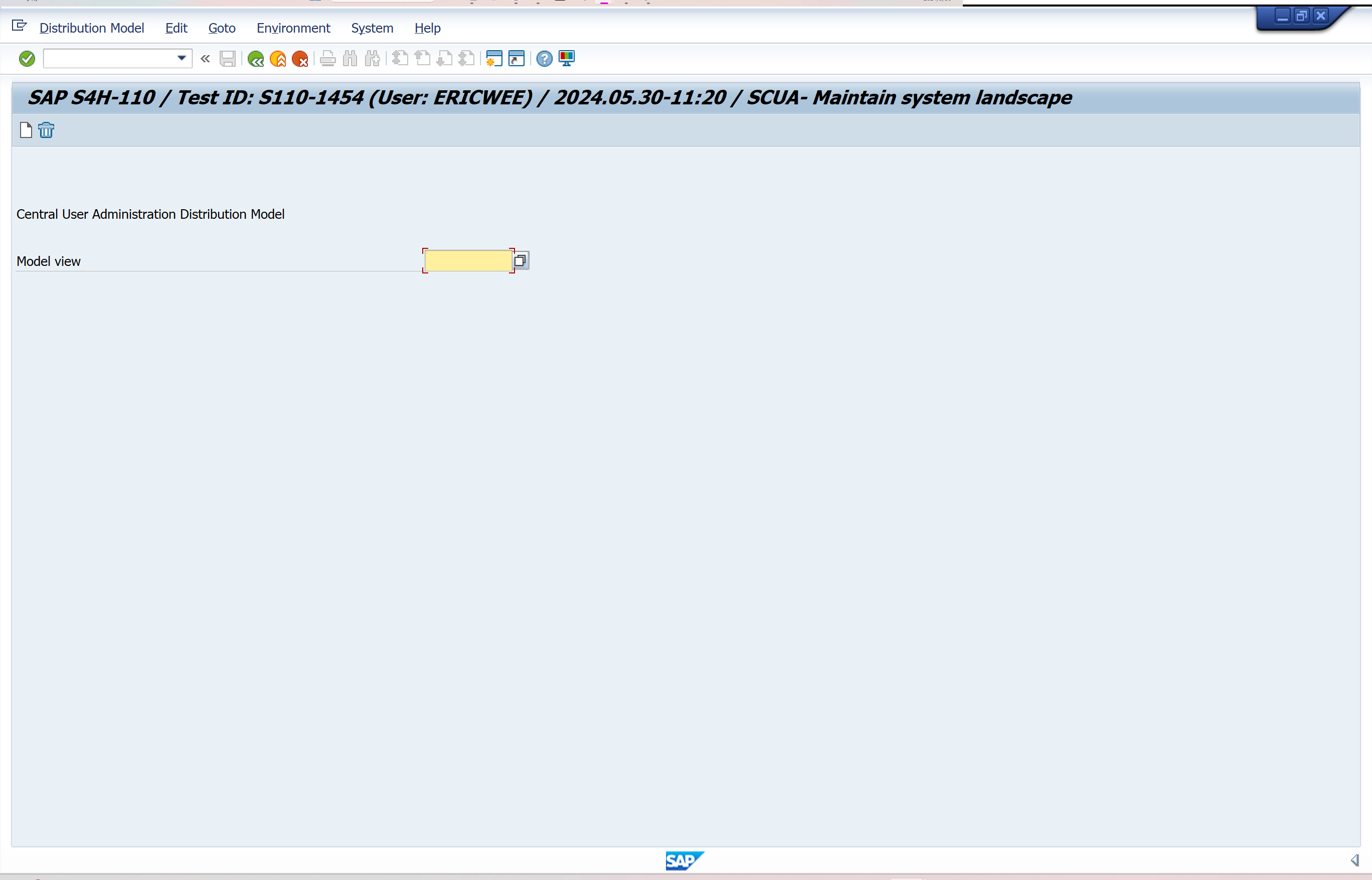
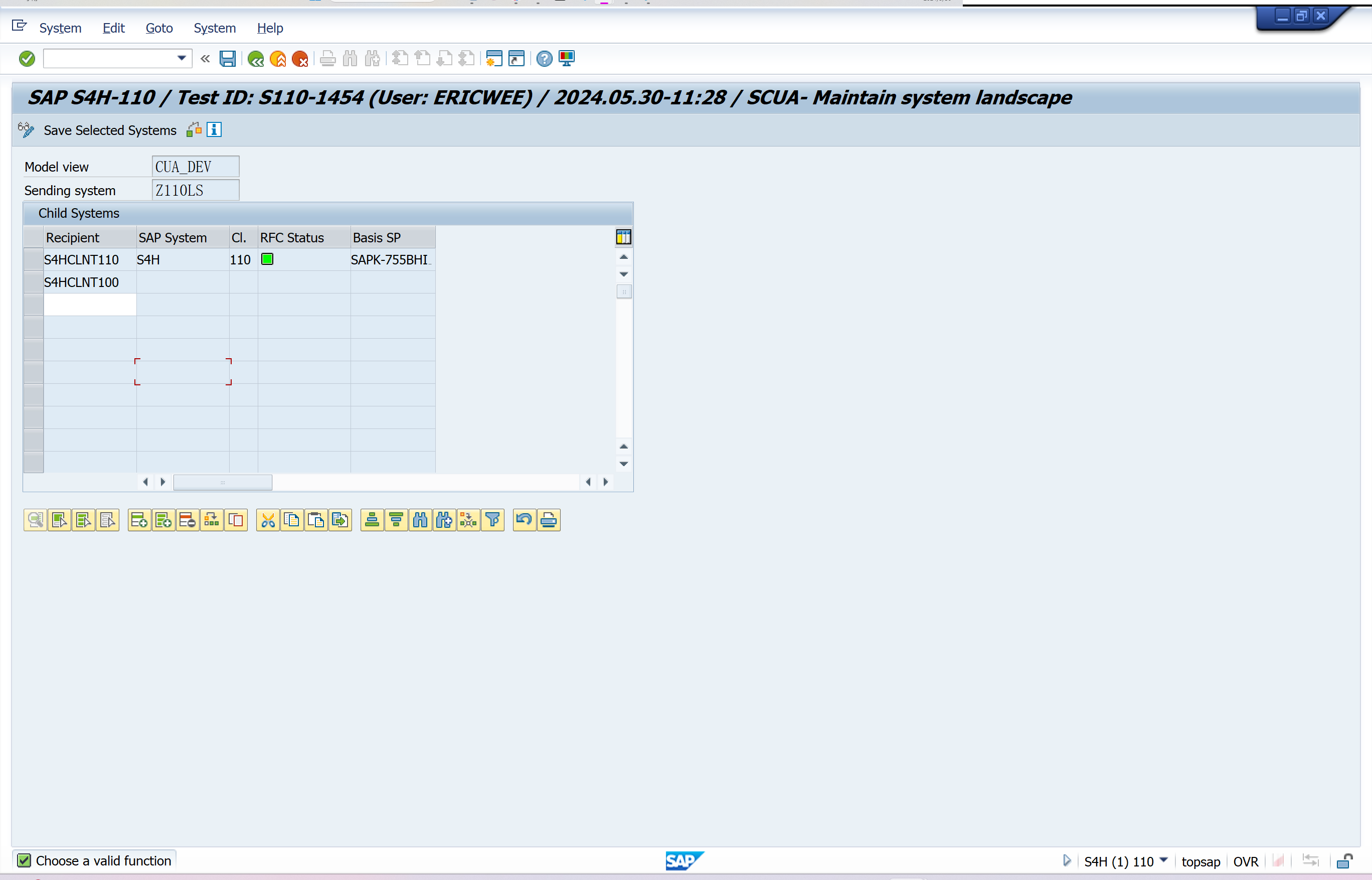
Define the system environment under Model view for central administration.
Define Logical System
Assign Logical System to Client
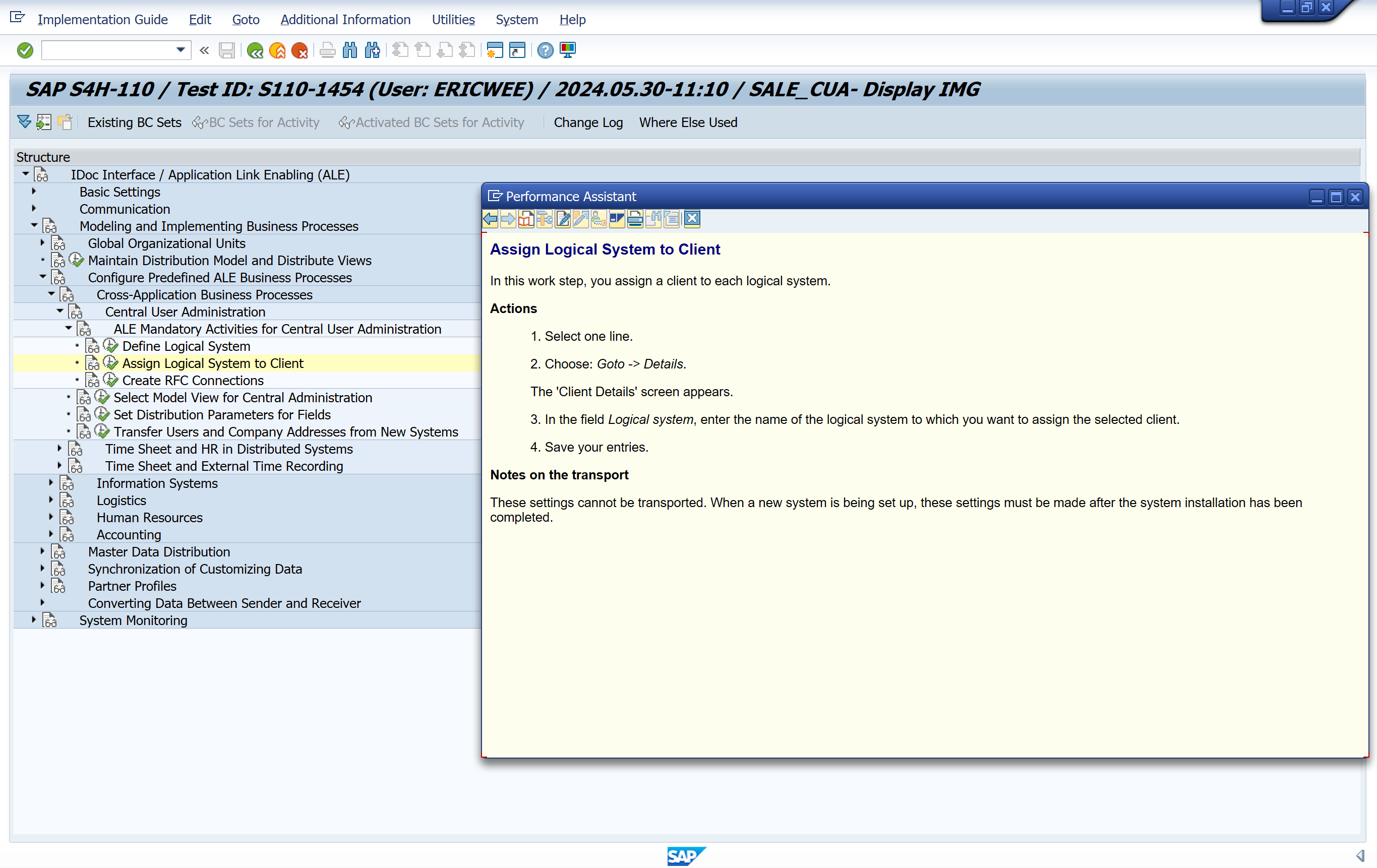
Create RFC Connections
In this section, you define the technical parameters for the RFC destinations.
The Remote Function Call (RFC) is controlled by the RFC destination parameters.
To create an RFC port, the RFC destinations must be assigned.
The name of the RFC destination should be the same as the logical system name.
The following types of RFC destinations can be assigned:
-
R/2 connections
-
SAP connections
-
Internal connections
-
Logical destinations
-
CMC connections
-
SNA/CPI-C connections
-
TCP/IP connections
-
ABAP driver connections
Example
- For an SAP connection, enter the following parameters:
-
- Name of RFC destination: S11BSP001
-
- Connection type: 3 (for SAP connection)
-
- Target system: bspserver01
-
- System number: ,11
-
- User in target system: CPIC
-
- Password, language and target client.
Standard settings
No RFC destinations are assigned in the standard system.
Activities
-
Select one of the types (for example, SAP connections) and choose Edit -> create;
-
Enter the parameters required for that type.
-
For an SAP connection, these are, for example, the name of the RFC destination, the name of the partner system, logon parameters (see example).
Processing RFCs With Errors
Since RFC destinations are usually registered in the QOUT Scheduler when you use ALE, it is usually no longer necessary to schedule the program RSARFCEX in a background job for the collective processing of RFCs with errors. We also recommend that you do not do this. The QOUT Scheduler now repeats the execution of RFCs with errors automatically (See transaction SMQ1. For detailed documentation about the QOUT Scheduler, see the SAP Library under qRFC (Queued Remote Function Call)).
In some cases, for example, if there are many RFCs with errors, and they cannot be executed again with the QOUT Scheduler, you can start the report RSARFCEX manually.
Practise handling errors in remote function calls before the function is used productively.
Further notes
The 'SAP*' user cannot be used for remote function calls on the target system.
For connecting to R/2 Systems:
-
Use an R/2 destination to read the users with passwords. The actual communication uses CPI-C.
-
Select 'Unencrypted password'
Notes on the transport
The maintenance of the RFC destination is not a part of the automatic Change and Transport System. Therefore the setting has to be made manually on all systems.
Select Model View for Central Administration
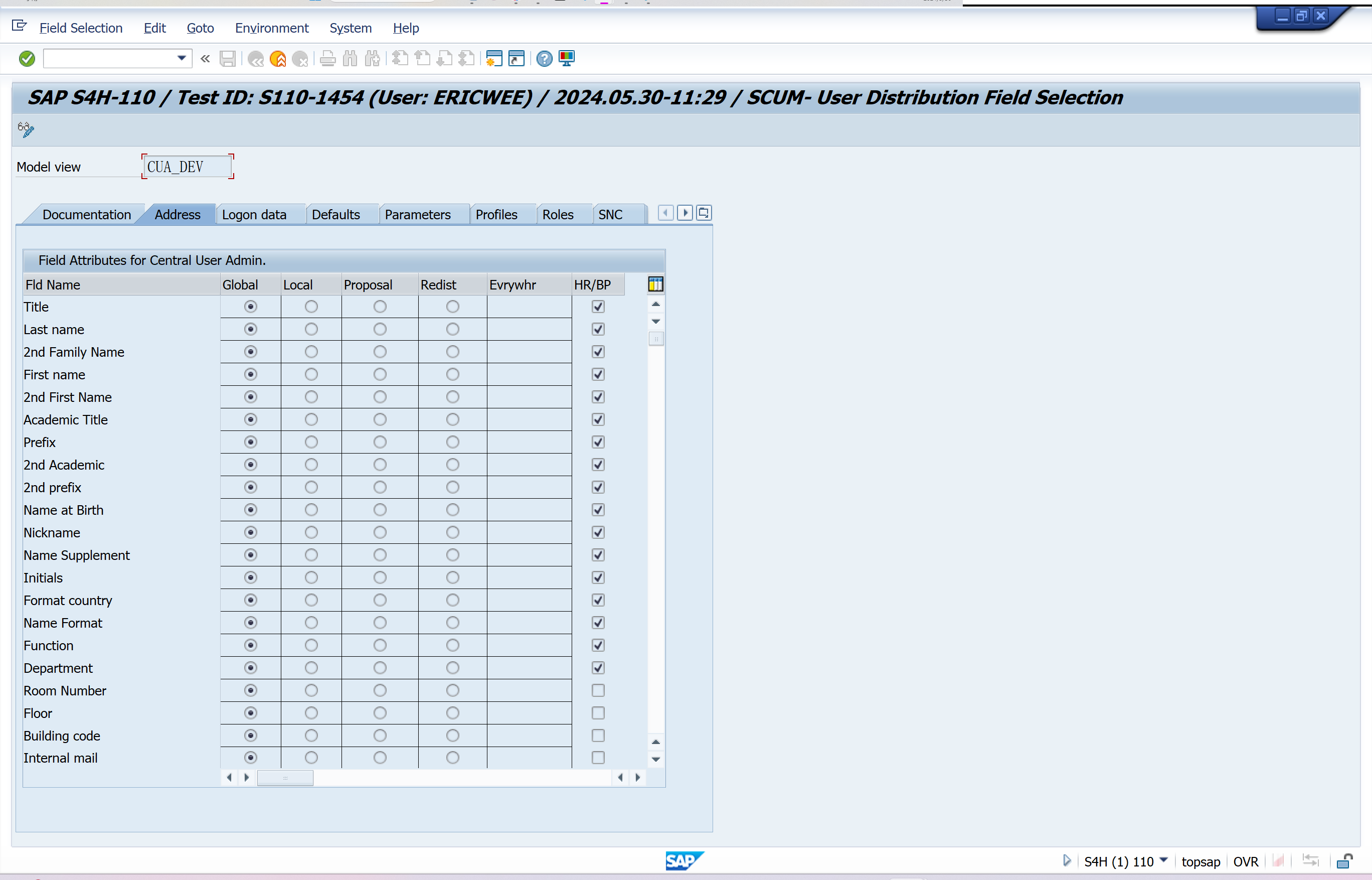
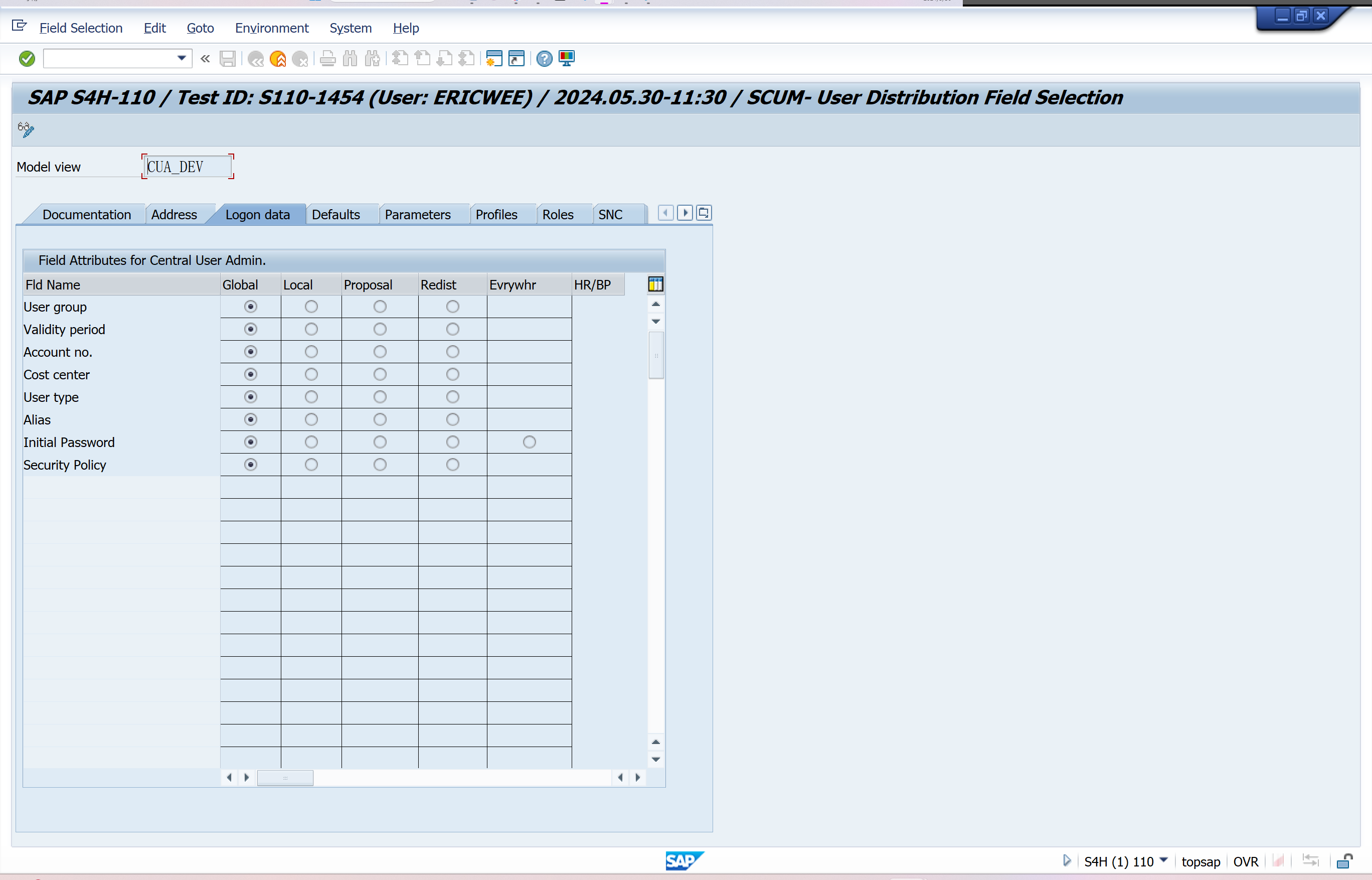
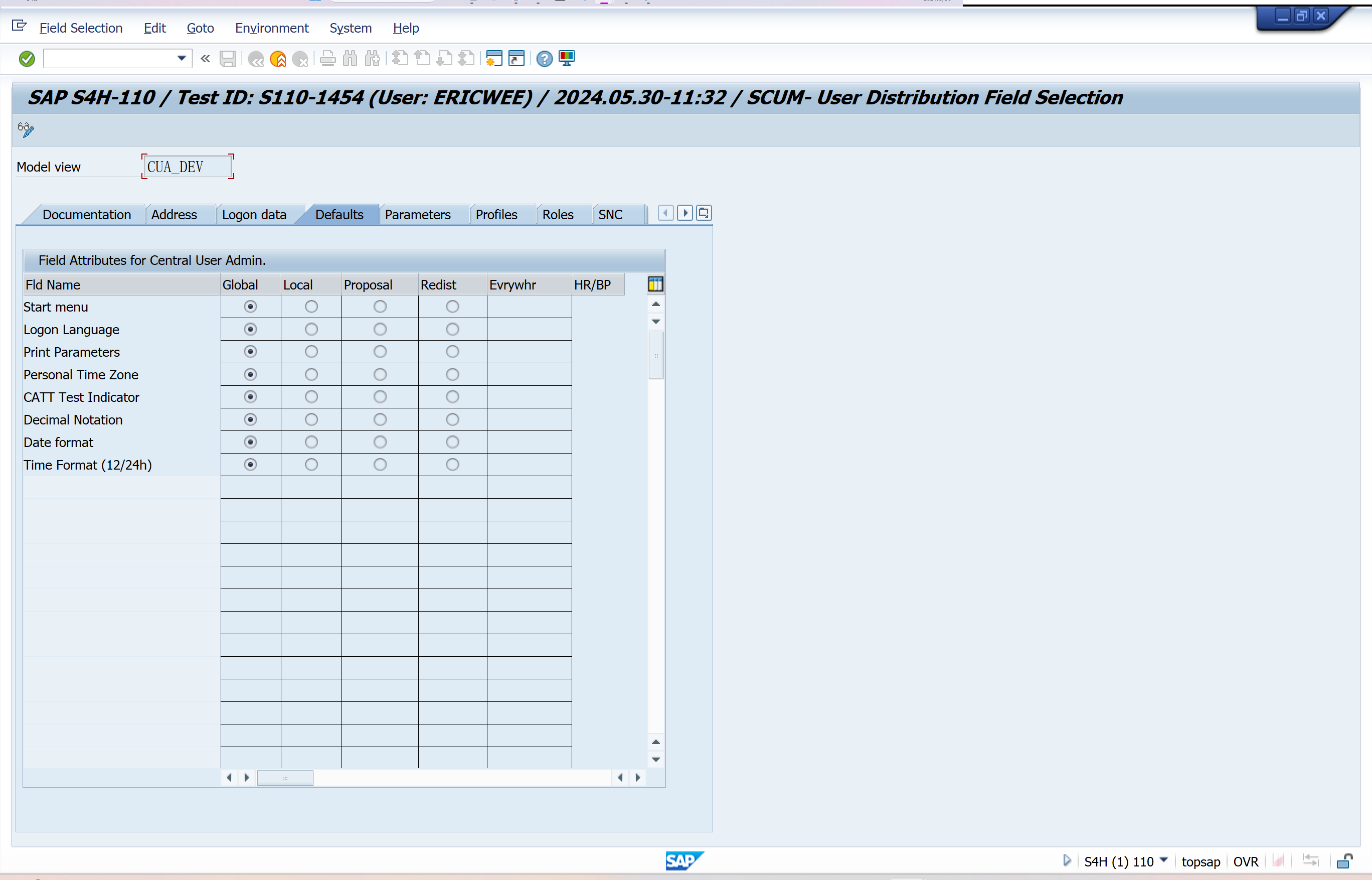
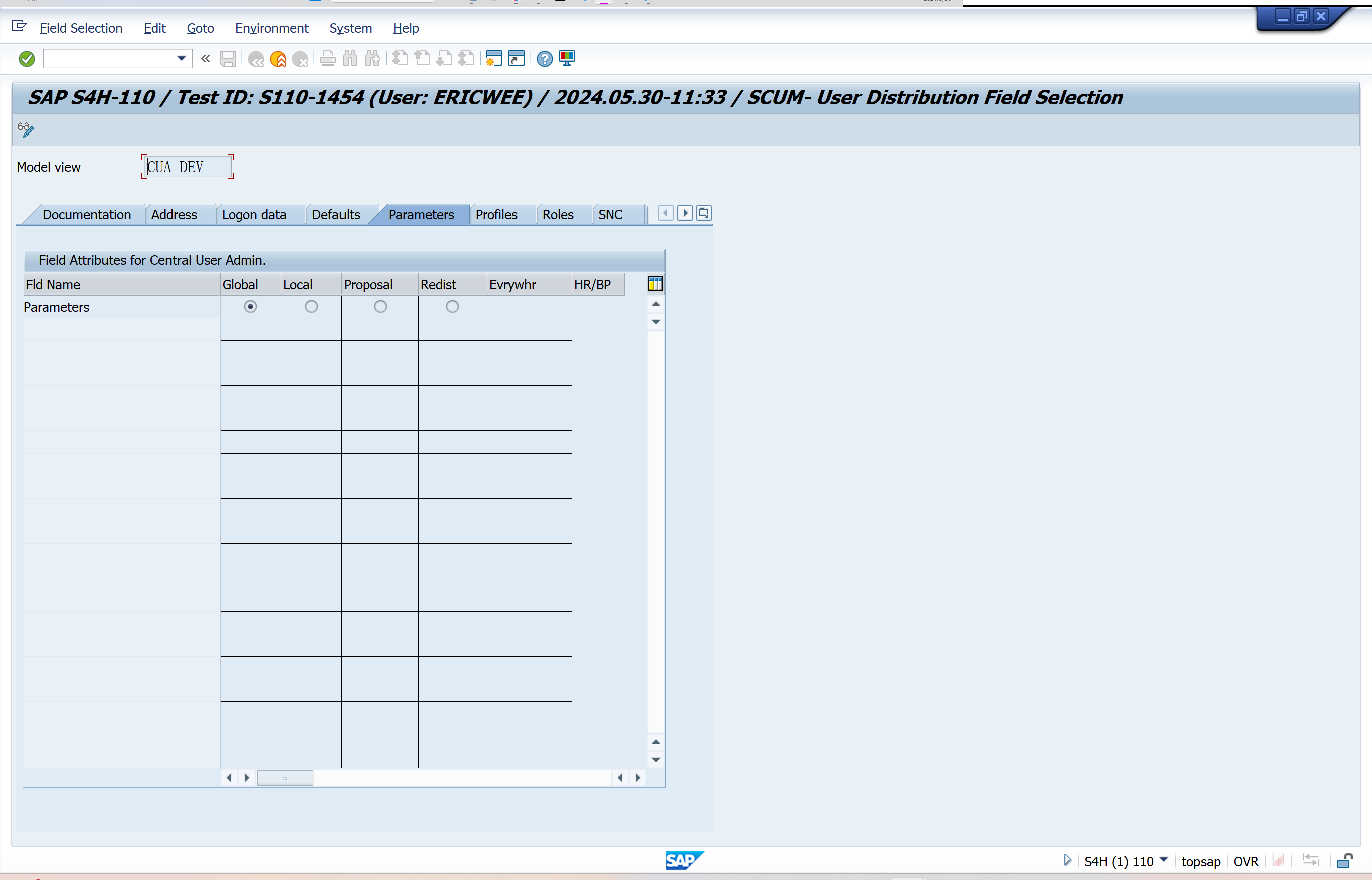
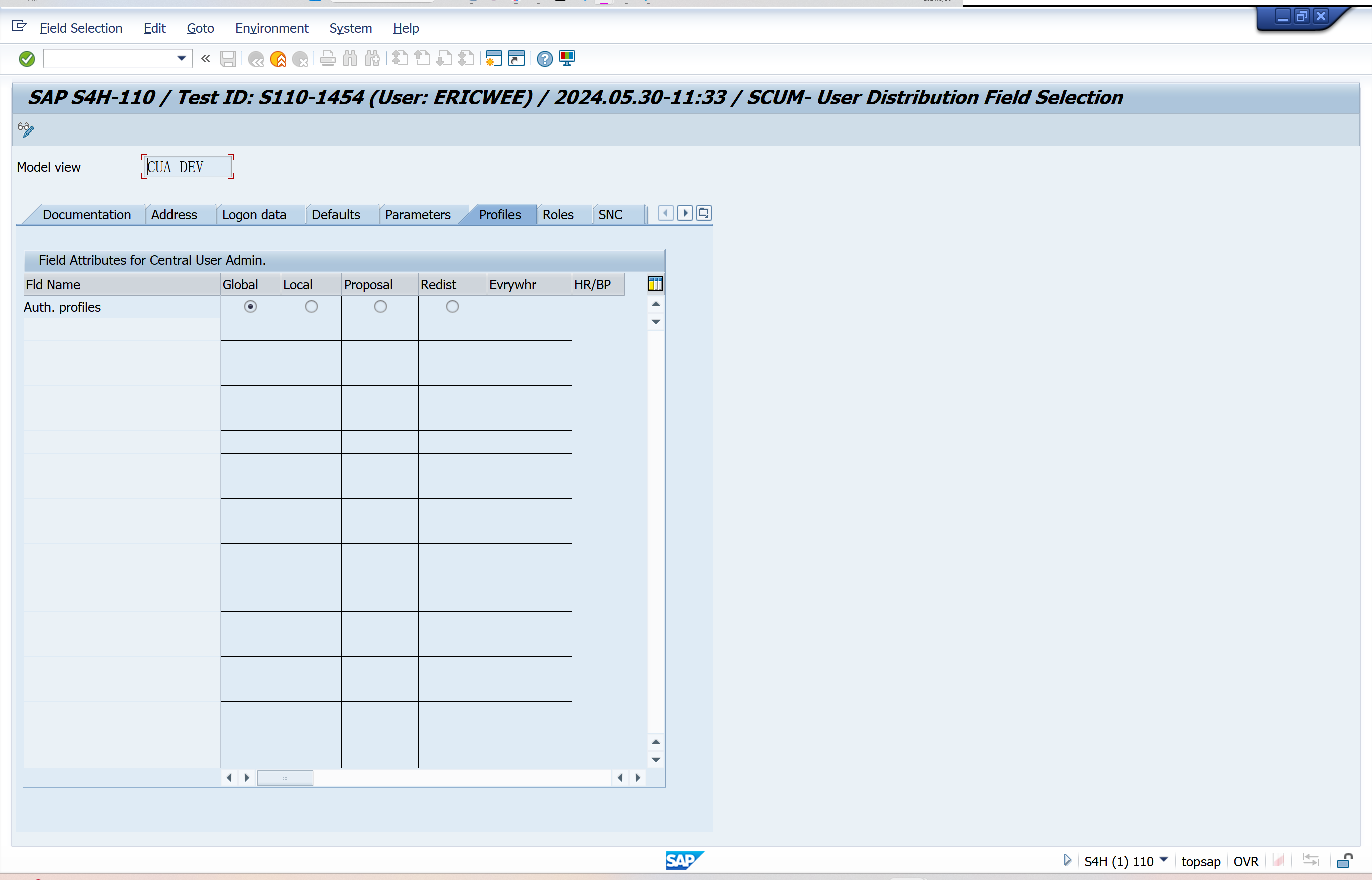
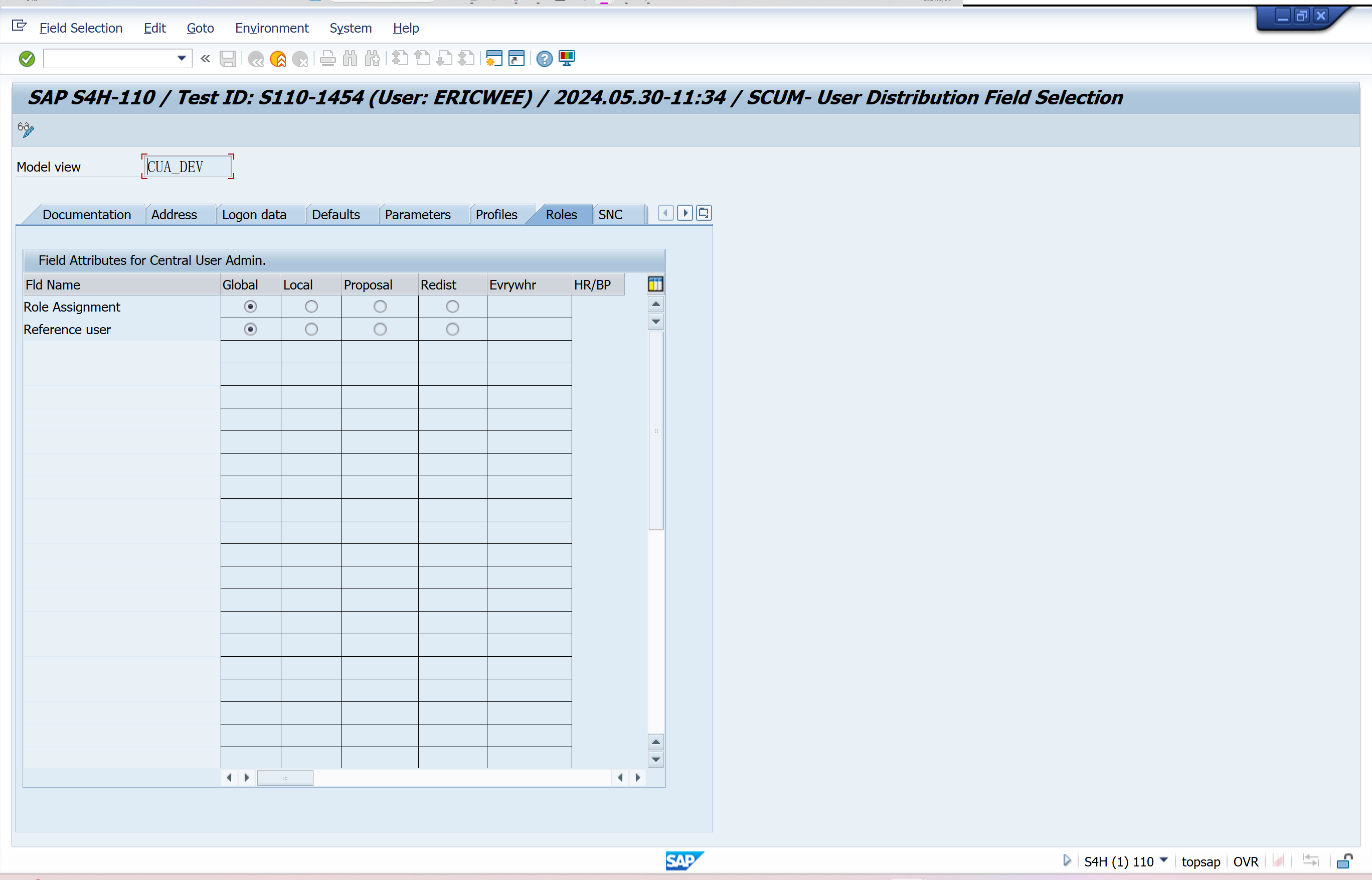
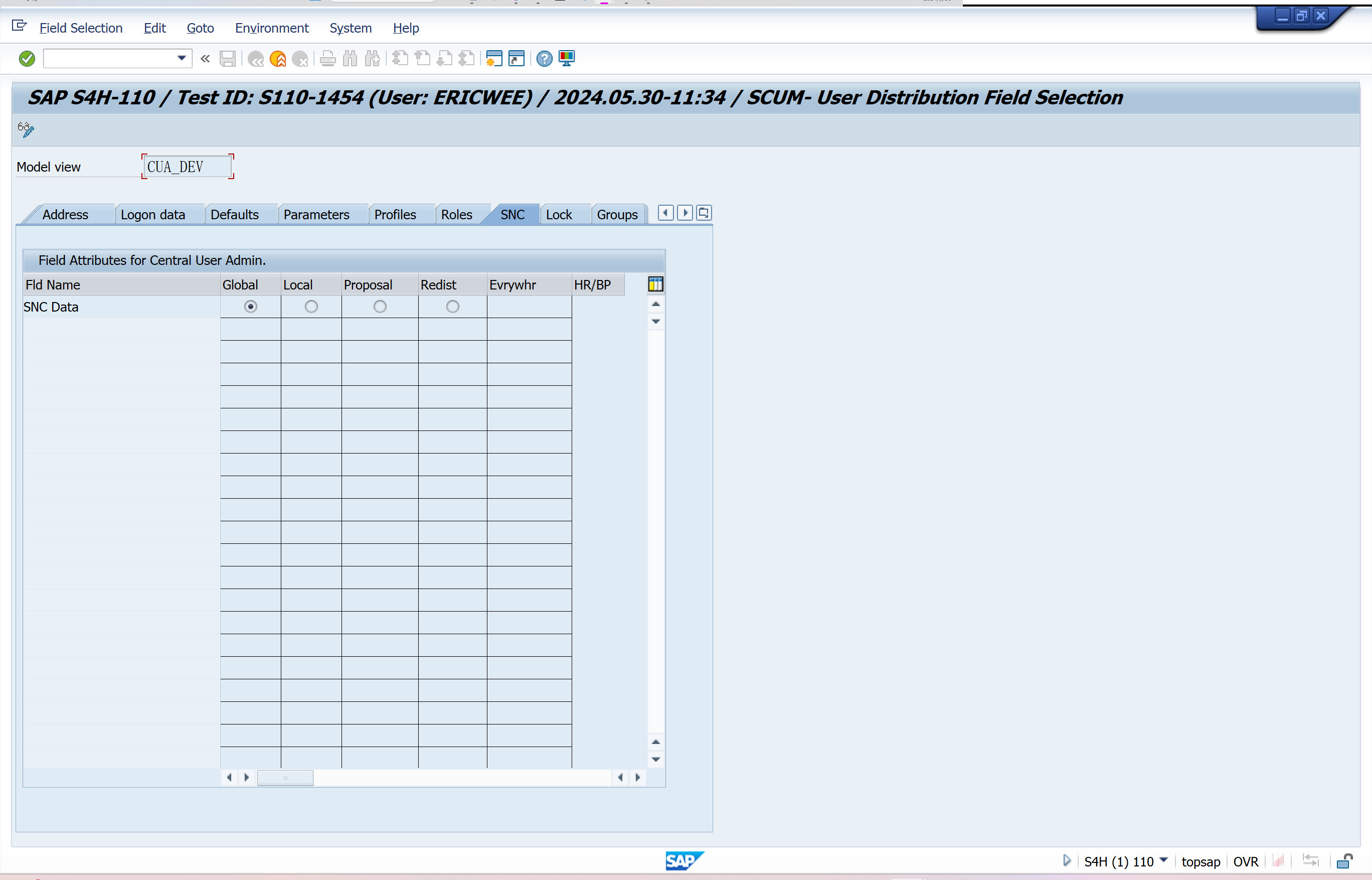
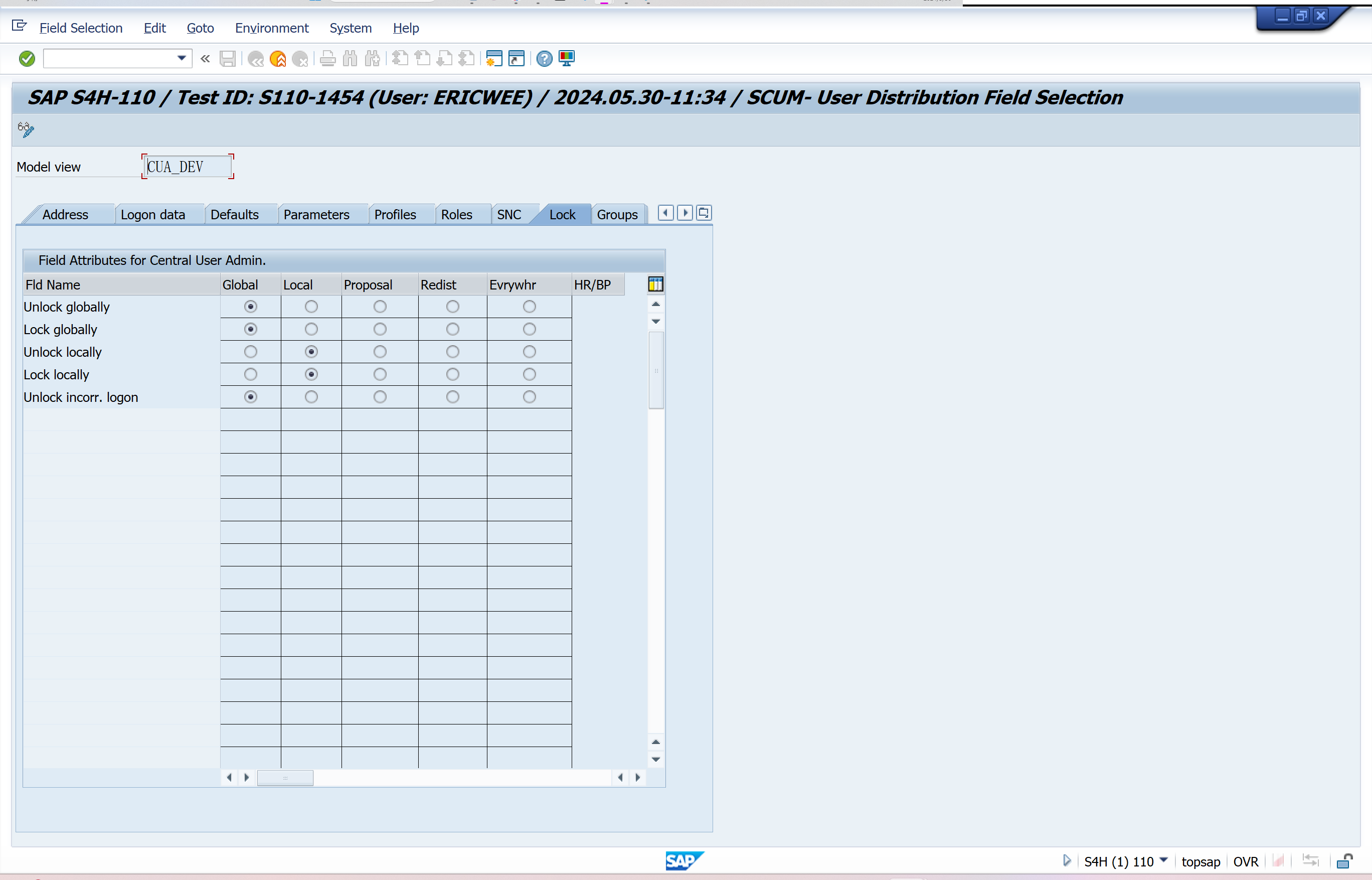
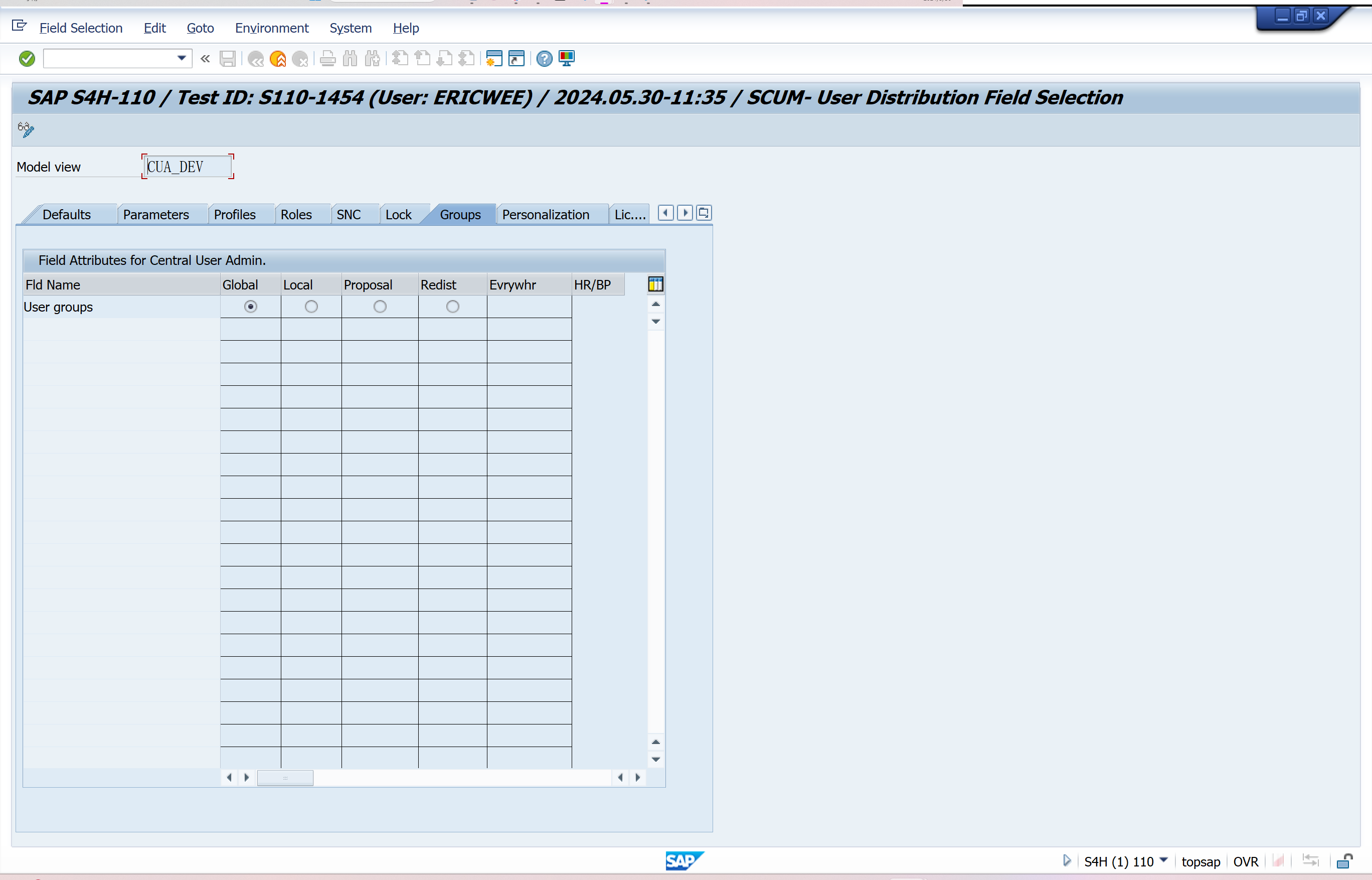
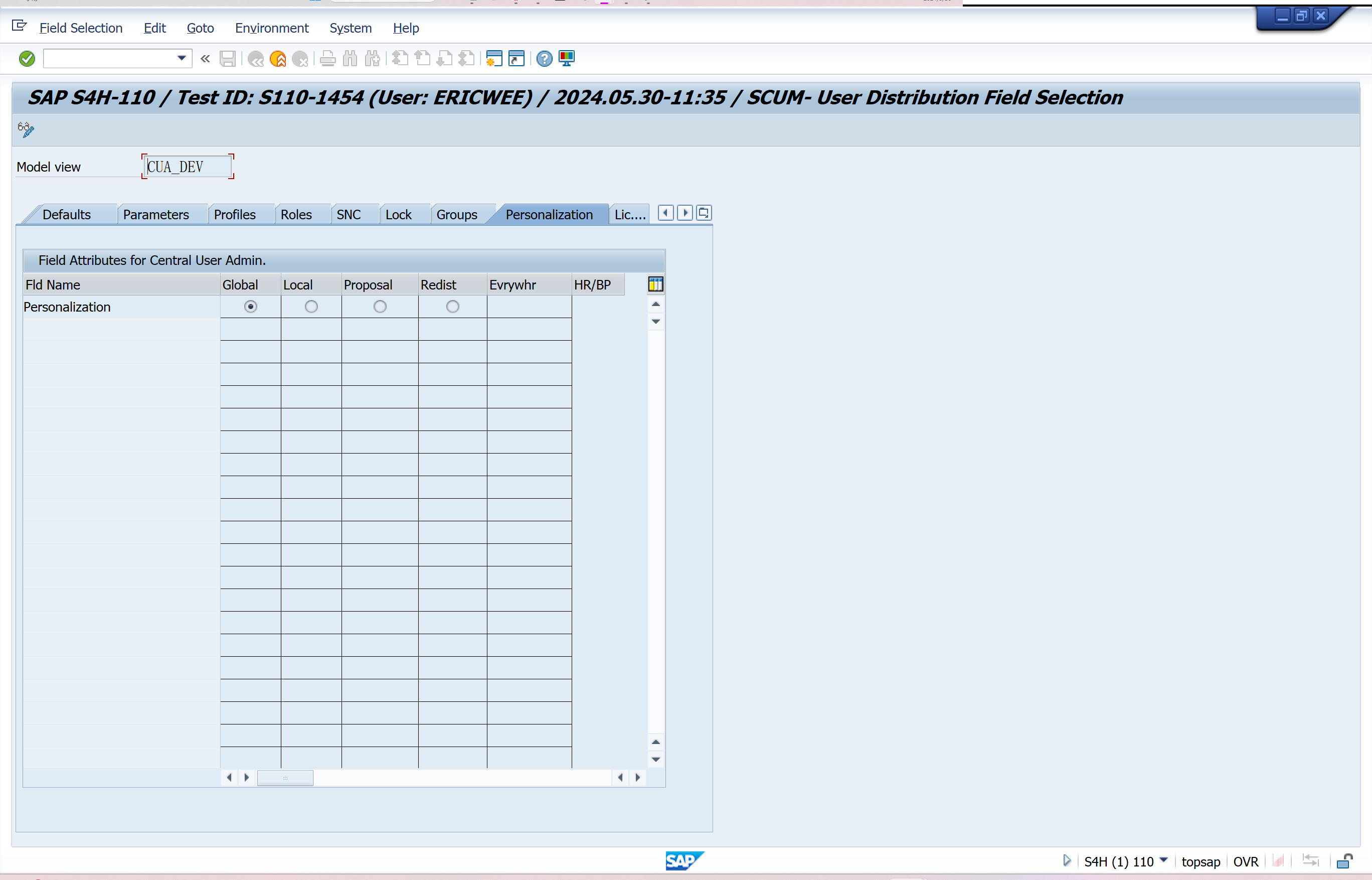
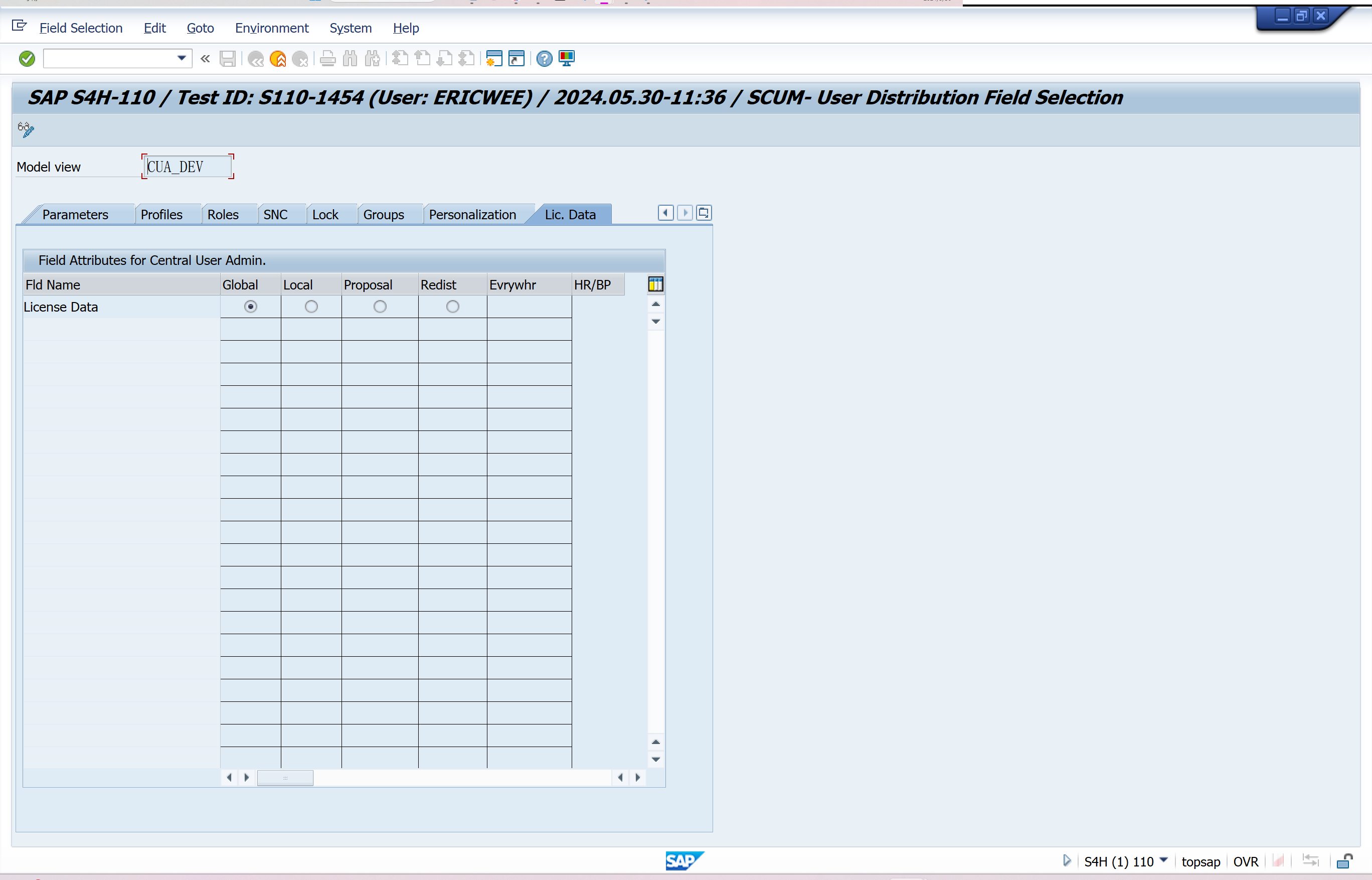
Set Distribution Parameters for Fields
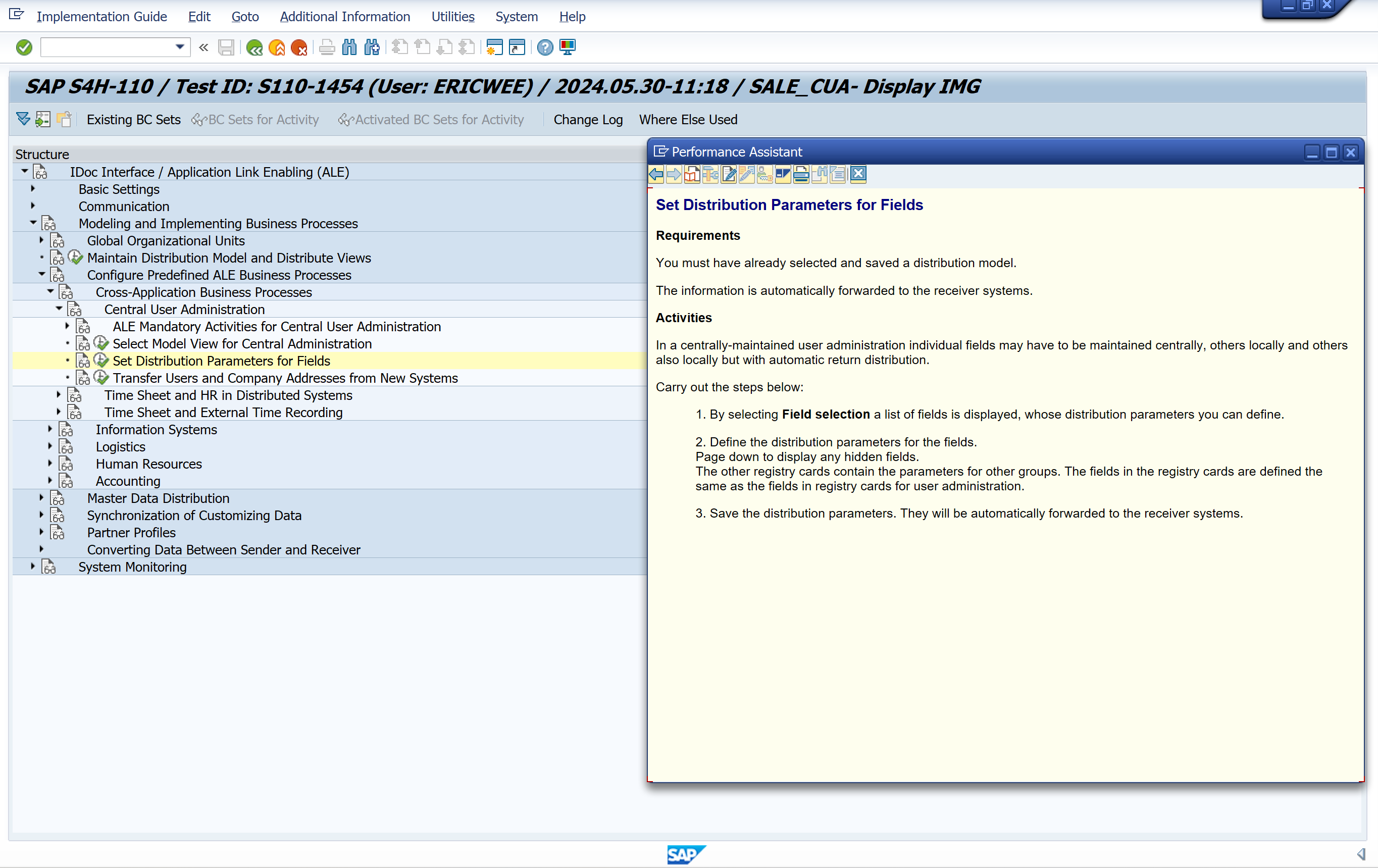
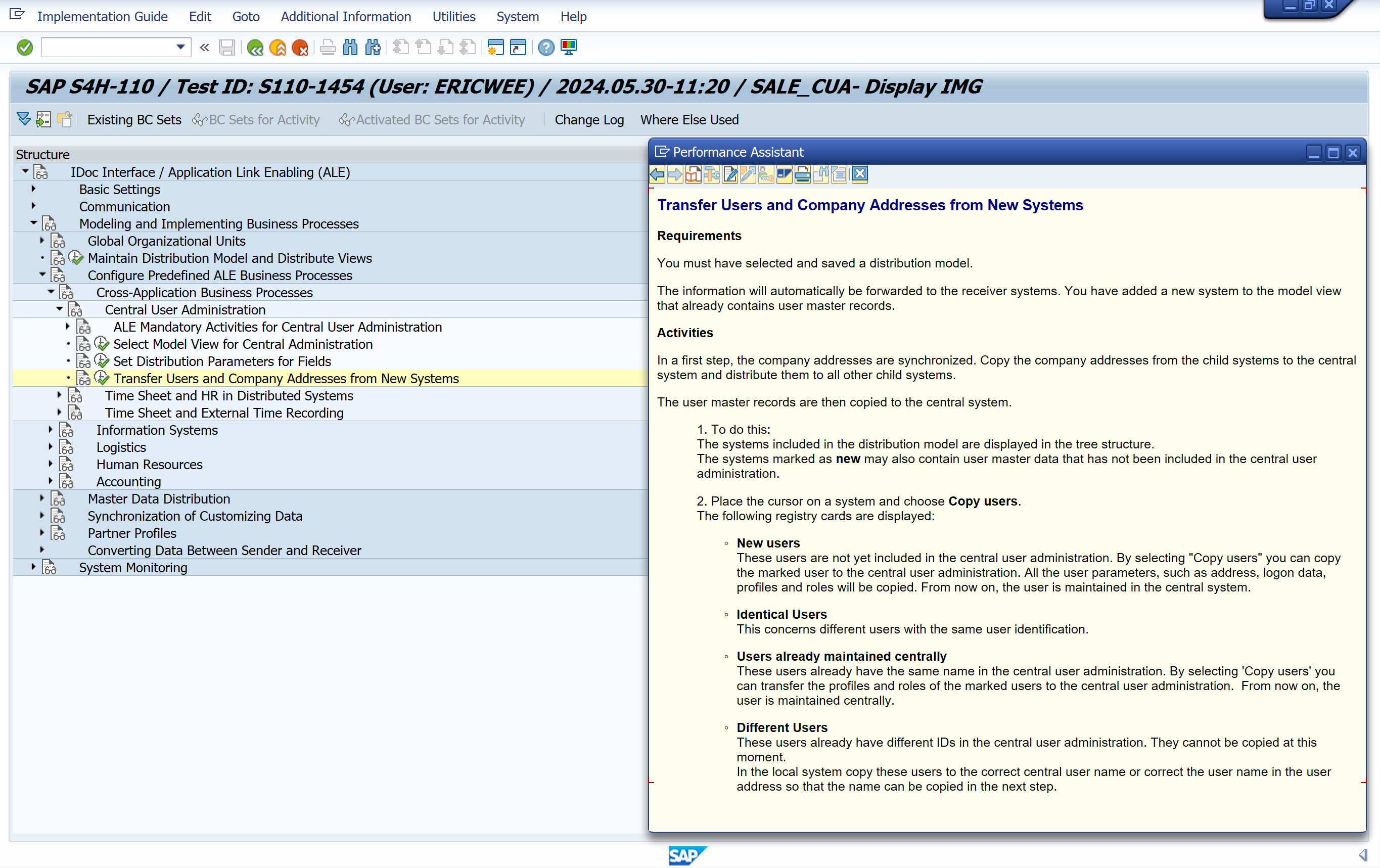
Transfer Users and Company Addresses from New Systems
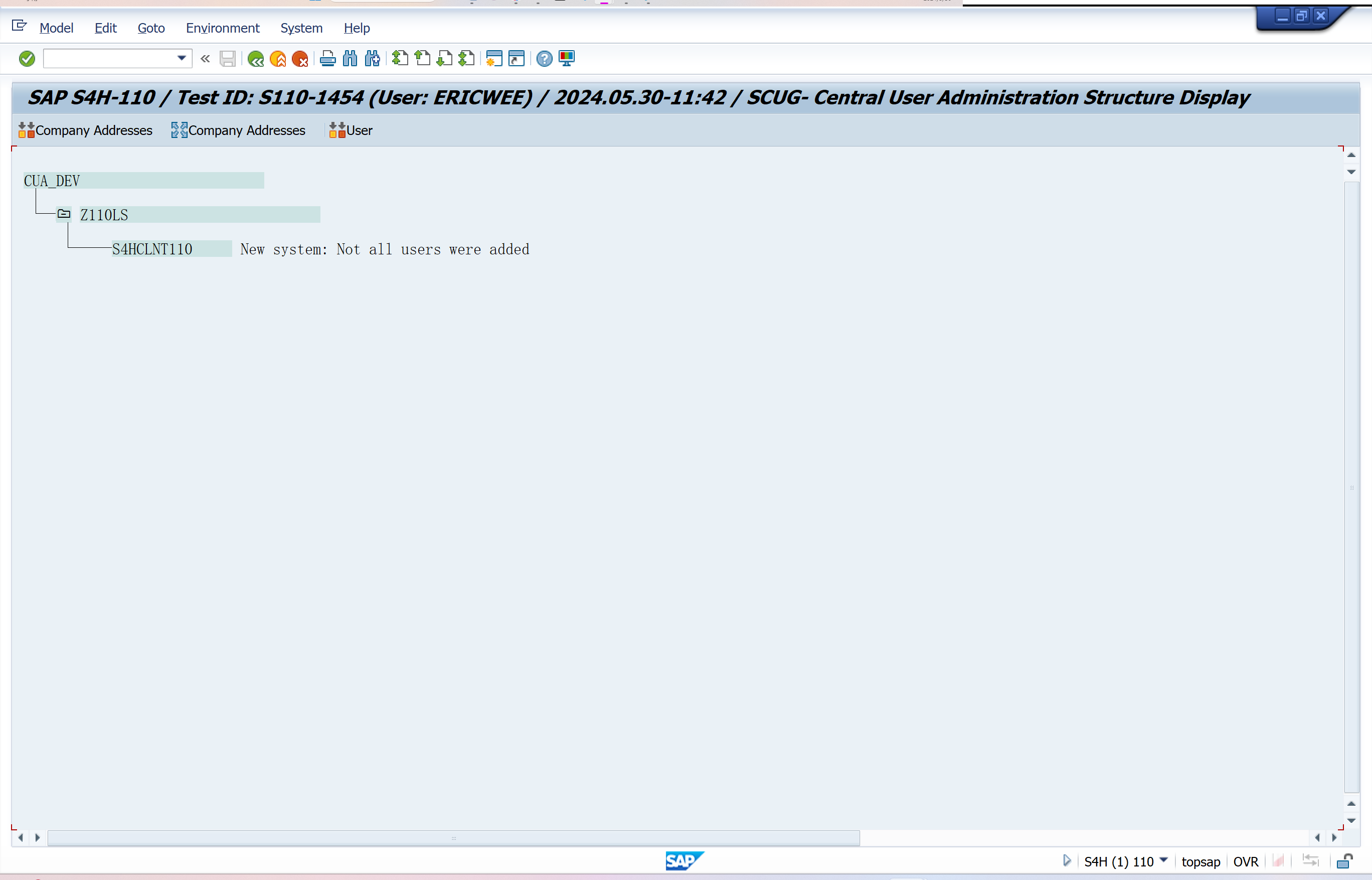
SCUG-Central User Administration
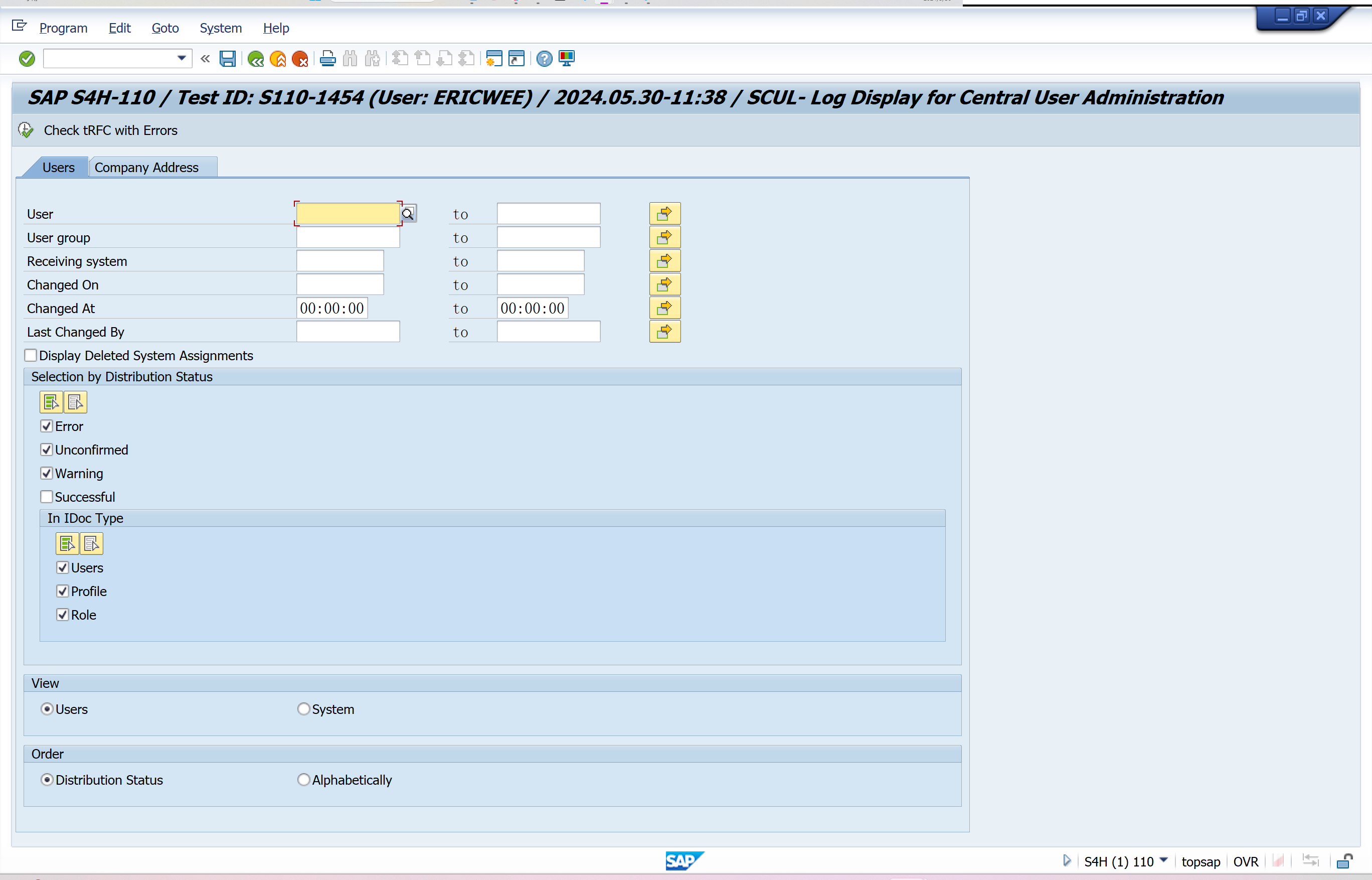
Log Display


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号