Composite Roles in SAP
Composite Roles in SAP
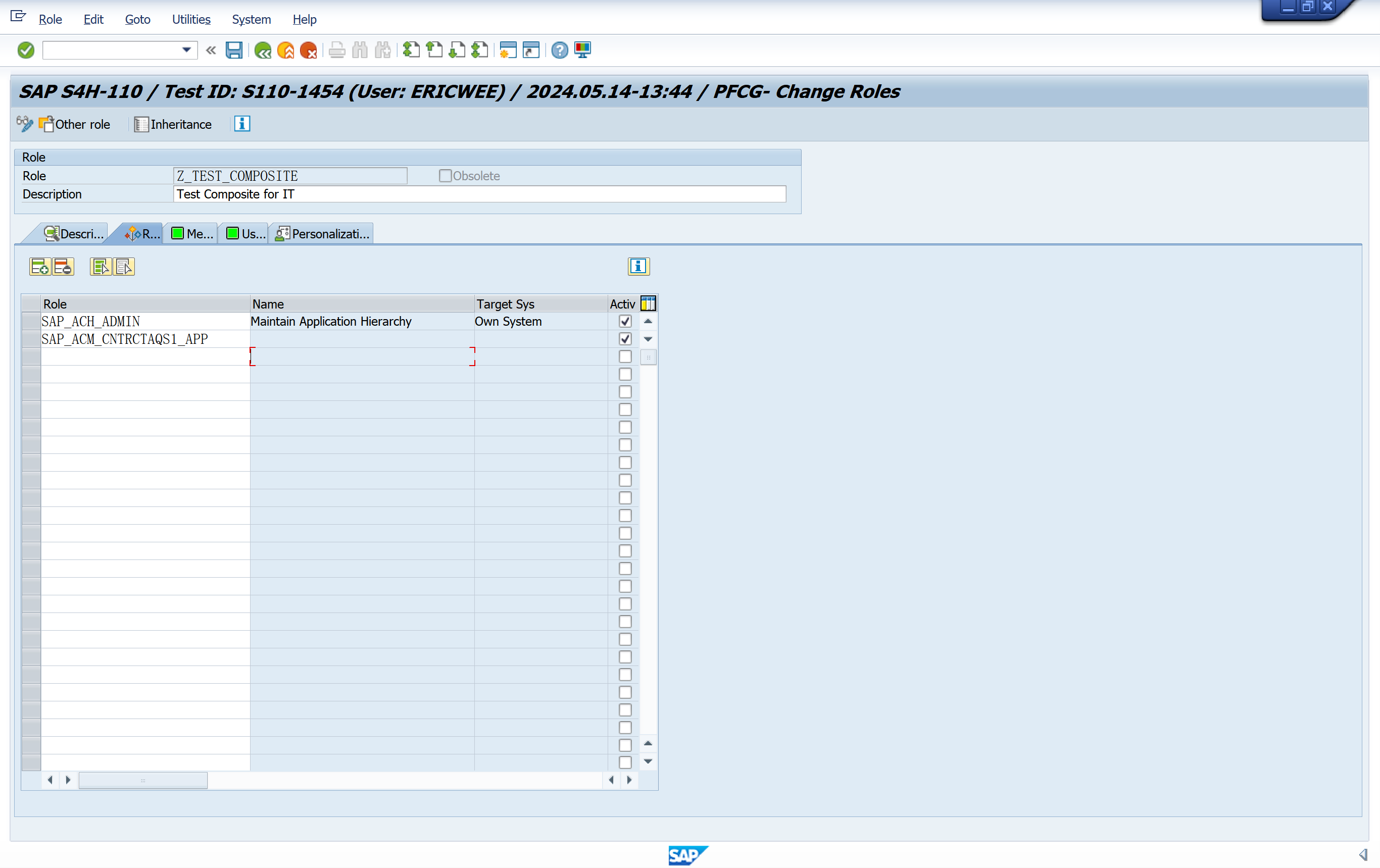
Composite Roles
- A composite role is a container with several different roles. For reasons of clarity, it does not make sense and is therefore not allowed to add composite roles to composite roles. Composite roles are also called roles.
- Composite roles do not contain authorization data. If you want to change the authorizations(that are represented by a composite role), you must maintain the data for each role of the composite role.
- It only groups the roles, but menus can be compressed
- Creating composite roles makes sense if some of your employees need authorizations from several roles. Instead of adding each user separately to each role required, you can set up a composite role and assign the users to that group.
- The users assigned to a composite role are automatically assigned to the corresponding (elementary) roles during comparison.
- Composite roles are identified by customer naming conventions only.
Single roles are mapped to tasks performed by users. Since a typical user performs multiple tasks, the total access for a user is represented through a composite role which includes the individual task roles.
Access is divided into transaction role (which contain transactions but no authorization object access) and value/controller roles (authorization objects but no transactions).
Complete access is represented through a composite role with the transaction and value roles.
The entire system landscape consists of aa number of separate SAP systems (like ECC, BW, SRM, CRM etc.) and users are administrated through a CUA connecting the individual systems.
A user getting role A in ECC will need the corresponding role B in BW and role C in CRM.
This can be achieved through a composite role created in the central system which links the individual roles in the different systems.


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号