Java中使用IO(输入输出)来读取和写入,读写设备上的数据、硬盘文件、内存、键盘......,根据数据的走向可分为输入流和输出流,这个走向是以内存为基准的,即往内存中读数据是输入流,从内存中往外写是输出流。
根据处理的数据类型可分为字节流和字符流
1.字节流可以处理所有数据类型的数据,在java中以Stream结尾
2.字符流处理文本数据,在java中以Reader和Writer结尾。
我们来看个IO流的详解图:
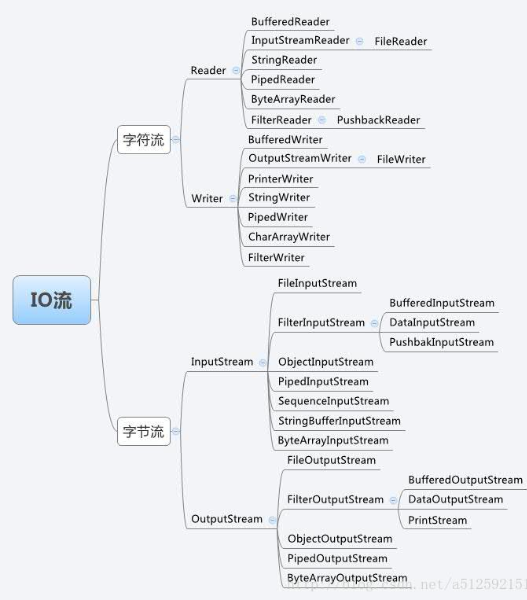
IO流的本质是对字节和字符的处理,那么我们平时也是用来处理文件的,就从文件处理开始接触这方面的知识。
1.文件操作(创建文件和文件夹,查看文件)
1 //创建一个文件路径 2 File file = new File("D:\\testData.txt"); 3 if(file.exists()){ 4 //得到文件路径 5 System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath()); 6 //得到文件大小 7 System.out.println("文件大小:"+file.length()); 8 } 9 //创建文件和创建文件夹 10 File file1 = new File("d:\\iotest.txt"); 11 if(!file1.exists()) 12 { 13 try { 14 file1.createNewFile(); 15 } catch (IOException e) { 16 // TODO Auto-generated catch block 17 e.printStackTrace(); 18 } 19 }else{ 20 System.out.println("文件已存在"); 21 } 22 //创建文件夹 23 File file2 = new File("d:\\testIO"); 24 if(file2.isDirectory()) 25 { 26 System.out.println("文件夹存在"); 27 }else{ 28 file2.mkdir(); 29 } 30 31 //列出一个文件夹下的所有文件 32 File f = new File("d:\\testIO"); 33 if(f.isDirectory()) 34 { 35 File lists[] = f.listFiles(); 36 for(int i=0;i<lists.length;i++) 37 { 38 System.out.println(lists[i].getName()); 39 } 40 }
常用字节流FileInputStream和FileOutputStream:
FileInputStream:
1 FileInputStream fis = null; 2 try { 3 fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\testData.txt"); 4 byte bytes[]=new byte[1024]; 5 int n=0; 6 while((n=fis.read(bytes))!= -1){ 7 String str = new String(bytes,0,n); 8 System.out.print(str); 9 } 10 } catch (Exception e) { 11 e.printStackTrace(); 12 } finally{ 13 try { 14 fis.close(); 15 } catch (IOException e) { 16 e.printStackTrace(); 17 } 18 }

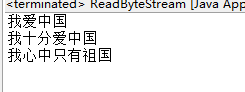
查看输出:
FileOutputStream:
1 FileOutputStream fos = null; 2 try { 3 fos = new FileOutputStream("D:\\testData.txt"); 4 String str = "报效国家,舍生忘死"; 5 byte bytes[] = str.getBytes(); 6 fos.write(bytes); 7 } catch (Exception e) { 8 e.printStackTrace(); 9 } finally { 10 try { 11 fos.close(); 12 } catch (Exception e2) { 13 e2.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 }
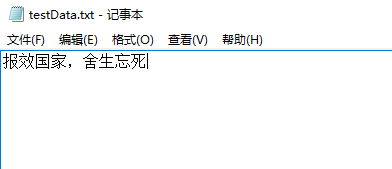
查看一下:
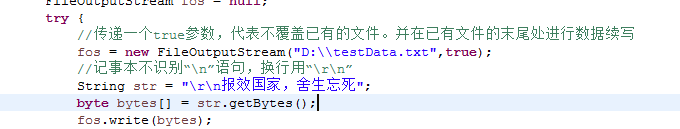
如果是续写文件,则可以加上参数
字符流FileReader和FileWriter:
1 //字符流 2 //文件写出 输入流 3 FileReader freader = null; 4 //写入到文件 输出流 5 FileWriter fwriter = null; 6 try { 7 //创建输入对象 8 freader = new FileReader("d:\\testData.txt"); 9 //创建输出对象 10 File f1 = new File("e:\\testData.txt"); 11 if(!f1.exists()){ 12 f1.createNewFile(); 13 } 14 fwriter = new FileWriter(f1); 15 16 //读入到内存 17 char chars[] = new char[1024]; 18 int n=0; 19 while((n=freader.read(chars))!= -1) 20 { 21 fwriter.write(chars); 22 //System.out.println(chars); 23 } 24 25 26 27 } catch (Exception e) { 28 e.printStackTrace(); 29 // TODO: handle exception 30 }finally{ 31 try{ 32 freader.close(); 33 fwriter.close(); 34 }catch(Exception e){ 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 } 37 } 38 39 40 41 //缓冲字符流 bufferedReader bufferedWriter 42 BufferedReader bfreader = null; 43 try { 44 FileReader freader = new FileReader("d:\\testData.txt"); 45 bfreader = new BufferedReader(freader); 46 //循环读取 47 String s =""; 48 while((s=bfreader.readLine())!= null) 49 { 50 System.out.println(s); 51 } 52 } catch (Exception e) { 53 // TODO: handle exception 54 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号