单例模式
饿汉式
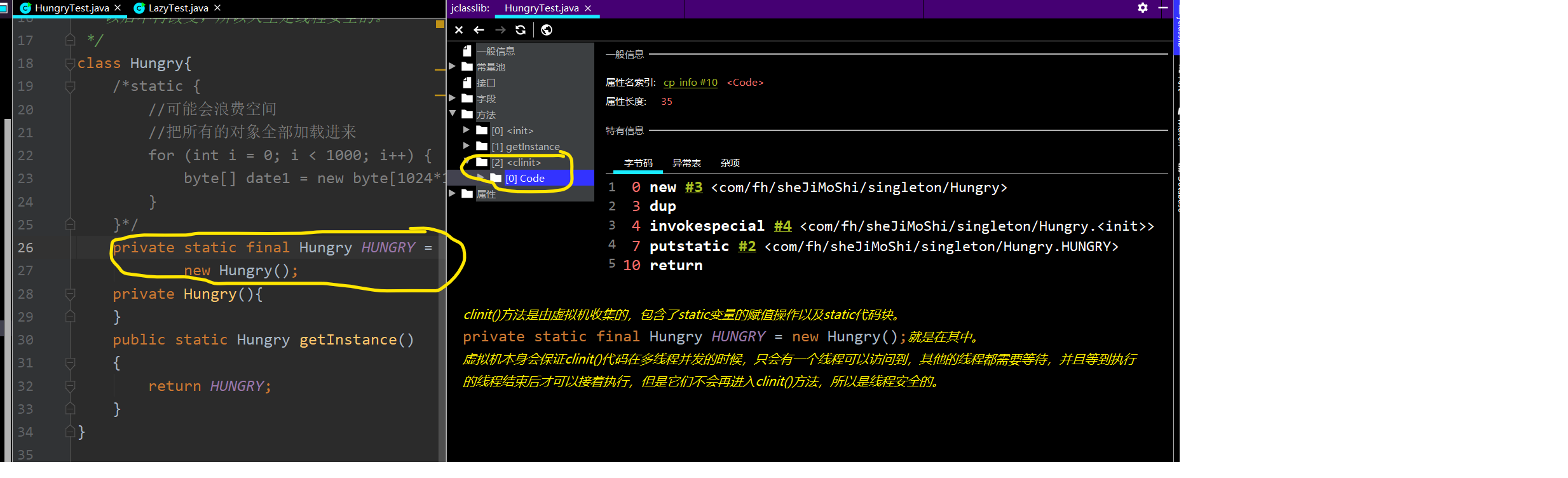
public class HungryTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { new Thread(()->{ System.out.println(Hungry.getInstance().hashCode()); }).start(); } } } /** * 饿汉式在类创建的同时就已经创建好一个静态的对象供系统使用, * 以后不再改变,所以天生是线程安全的。 */ class Hungry{ /*static { //可能会浪费空间 //把所有的对象全部加载进来 for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) { byte[] date1 = new byte[1024*1024]; } }*/ private static final Hungry HUNGRY= new Hungry(); private Hungry(){ } public static Hungry getInstance(){ return HUNGRY; } }
之所以是线程安全的,是因为JVM在类加载的过程,保证了不会初始化多个static对象。类的生命周期主要是:
加载-->验证-->准备-->解析-->初始化-->使用-->卸载
上面的代码,实际上类成员变量instance是在初始化阶段的时候完成初始化,所有的类变量以及static静态代码块,都是在一个叫clinit()的方法里面完成初始化。
懒汉式
import java.lang.reflect.*; public class LazyTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { safeEnum(); } /** * 反射破解使其不安全,破坏单例 * 一个懒汉式后的对象 * 一个利用反射获取对象 * 解决方式: * private Lazy() { * synchronized (Lazy.class) { * if (singleton != null) { * throw new RuntimeException("不要试图使用反射"); * } * } * } * Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException: 不要试图使用反射 */ private static void usnafeThreadUseReflection() throws Exception { Lazy instance = Lazy.getInstance(); System.out.println(instance); Constructor<Lazy> declaredConstructor = Lazy.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null); declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); Lazy lazy = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); System.out.println(lazy); } /** * 测试多线程下是安全的。 */ private static void testSingleton() { for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { new Thread(() -> { System.out.println(Lazy.getInstance().hashCode()); }).start(); } } /** * 反射破解使其不安全,破坏单例 * 两个利用反射获取对象 * private Lazy() { * synchronized (Lazy.class) { * if(flag == false){ * flag = true; * }else { * throw new RuntimeException("不要试图使用反射"); * } * } * } * * Caused by: java.lang.RuntimeException: 不要试图使用反射 */ private static void usnafeThreadUseReflection_twoObject2() throws Exception { Constructor<Lazy> declaredConstructor = Lazy.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null); declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); Lazy lazy = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); Lazy instance = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); System.out.println(lazy); System.out.println(instance); } /** * 反射破解使其不安全,破坏单例 * 两个利用反射获取对象 * private Lazy() { * synchronized (Lazy.class) { * if(flag == false){ * flag = true; * }else { * throw new RuntimeException("不要试图使用反射"); * } * } * } * com.fh.sheJiMoShi.singleton.Lazy@7ea987ac * com.fh.sheJiMoShi.singleton.Lazy@12a3a380 */ private static void usnafeThreadUseReflection_twoObject1() throws Exception { //通过反射破坏标志位qinjiang Field flag = Lazy.class.getDeclaredField("flag"); flag.setAccessible(true); Constructor<Lazy> declaredConstructor = Lazy.class.getDeclaredConstructor(null); declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); Lazy lazy = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); flag.set(lazy,false); Lazy instance = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); System.out.println(lazy); System.out.println(instance); } /** * 枚举是线程安全的单例 */ private static void safeEnum() throws Exception { /**枚举是线程安全的单列**/ // EnumSingle enumSingle1 = EnumSingle.INSTANCE; // EnumSingle enumSingle2 = EnumSingle.INSTANCE; // System.out.println(enumSingle1 == enumSingle2); /**枚举是线程安全的单列**/ /**java.lang.NoSuchMethodException: com.fh.sheJiMoShi.singleton.EnumSingle.<init>() */ Constructor<EnumSingle> declaredConstructor = EnumSingle.class.getDeclaredConstructor(); declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); EnumSingle enumSingle2 = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); System.out.println(enumSingle2); /**java.lang.NoSuchMethodException: com.fh.sheJiMoShi.singleton.EnumSingle.<init>() */ /**java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Cannot reflectively create enum objects jad反编译代码,构造函数用的是有参数的*/ // Constructor<EnumSingle> declaredConstructor = EnumSingle.class.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class); // declaredConstructor.setAccessible(true); // EnumSingle enumSingle2 = declaredConstructor.newInstance(); // System.out.println(enumSingle2); /**java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Cannot reflectively create enum objects jad反编译代码,构造函数用的是有参数的*/ } } class Lazy { private static volatile Lazy singleton = null; private static boolean flag = false;//标志位 private Lazy() { /*synchronized (Lazy.class) { if(flag == false){ flag = true; }else { throw new RuntimeException("不要试图使用反射"); } }*/ } public static Lazy getInstance() { if (singleton == null) { {//只有在空的时候才开始抢锁 synchronized (Lazy.class) { if (singleton == null) { singleton = new Lazy(); //1、分配内存空间 //2、执行构造函数,初始化对象 //3、把对象指向指向这个空间 } } } } return singleton; } } /** * 枚举是线程安全的 */ enum EnumSingle{ INSTANCE; }
静态内部类
/** * 静态内部类单例是线程安全的 */ class Holder { private Holder() { } public static Holder getInstance() { return InnerClass.HOLDER; } public static class InnerClass { private static final Holder HOLDER = new Holder(); } }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号