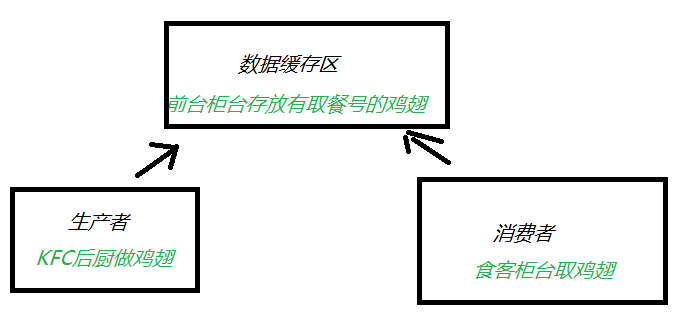
线程通信-生产者消费者模式
生产者消费者模式的两种实现方式
只有一个生产者和线程一个消费者线程的情况,这个时候使用if;
多个生产者和消费者线程的时候一定要使用while。
管程法
测试1-synchronized
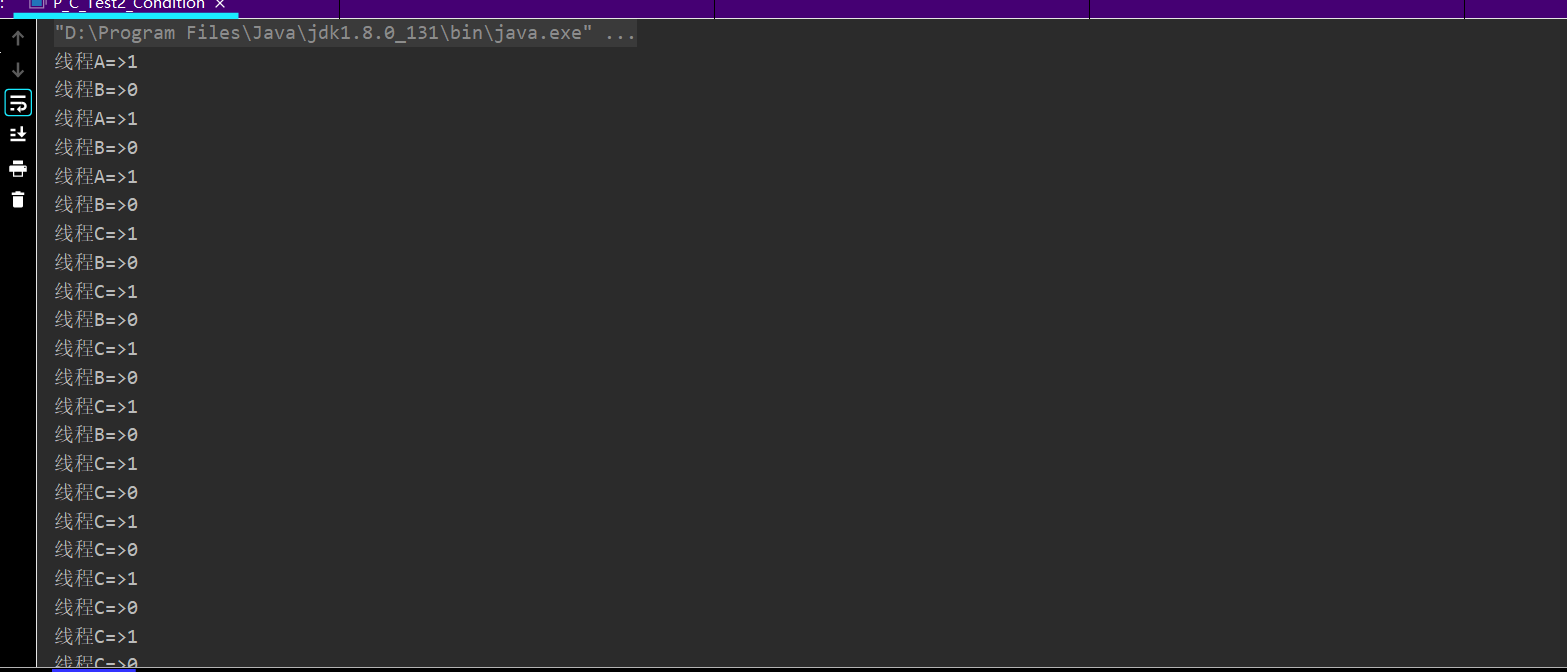
多生产者多消费者模式下,假设有两个生产者,第一个生产者获取数据的时候,发现 if(num!=0),便进入等待状态;因为第一个线程等待的时候会释放锁,所以第二个生产者可以进入并执行if(num!= 0) ,也发现num!=0,于是第二个线程也进入等待;而此时如果消费者消费了一个数据,便会唤醒两个生产者线程中的任意一个(假如唤醒了生产者1),执行num++,num=1并释放了锁;生产者2线程卡在被唤醒的地方,拿到生产者1释放的锁,继续执行操作,也会调用num++,num=2。所以出现了问题。
package com.fh.thread.p_c; public class P_C_Test2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Data data = new Data(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.increase(); } },"线程A").start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.decrease(); } },"线程B").start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.increase(); } },"线程C").start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.decrease(); } },"线程C").start(); } } /** * 循环判断等待生产 业务逻辑 通知 * 循环判断等待消费 业务逻辑 通知 */ class Data { private int num; public synchronized void increase() { try { while (num != 0) {//中断和虚假唤醒是可能的,并且该方法应该始终在循环中使用: this.wait(); } num++; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+ num); notifyAll(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } public synchronized void decrease() { try { while (num == 0) { this.wait(); } num--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+ num); notifyAll(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } }
测试1-Condition
public class P_C_Test2_Condition { public static void main(String[] args) { Data2 data = new Data2(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.increase(); } },"线程A").start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.decrease(); } },"线程B").start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.increase(); } },"线程C").start(); new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.decrease(); } },"线程C").start(); } } /** * 循环判断等待生产 业务逻辑 通知 * 循环判断等待消费 业务逻辑 通知 */ class Data2 { private int num; Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); public void increase() { try { lock.lock(); while (num != 0) {//中断和虚假唤醒是可能的,并且该方法应该始终在循环中使用: condition.await(); } num++; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+ num); condition.signalAll(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { }finally { lock.unlock(); } } public void decrease() { try { lock.lock(); while (num == 0) { condition.await(); } num--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"=>"+ num); condition.signalAll(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { }finally { lock.unlock(); } } }
测试1-Condition VS synchronized
Condition精准的通知和唤醒线程。
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition; import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock; import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock; public class P_C_Test3_Condition { public static void main(String[] args) { Data3 data = new Data3(); new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.printA(); } }, "A").start(); new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.printB(); } }, "B").start(); new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { data.printC(); } }, "C").start(); } } class Data3 { int num = 1; Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); Condition conditionA = lock.newCondition(); Condition conditionB = lock.newCondition(); Condition conditionC = lock.newCondition(); public void printA() { lock.lock(); try { if (num != 1) conditionA.await(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + num); num++; conditionB.signal(); } catch (Exception e) { } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public void printB() { lock.lock(); try { if (num != 2) conditionB.await(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + num); num++; conditionC.signal(); } catch (Exception e) { } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public void printC() { lock.lock(); try { if (num != 3) conditionC.await(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "=>" + num); num = 1; conditionA.signal(); } catch (Exception e) { } finally { lock.unlock(); } } }
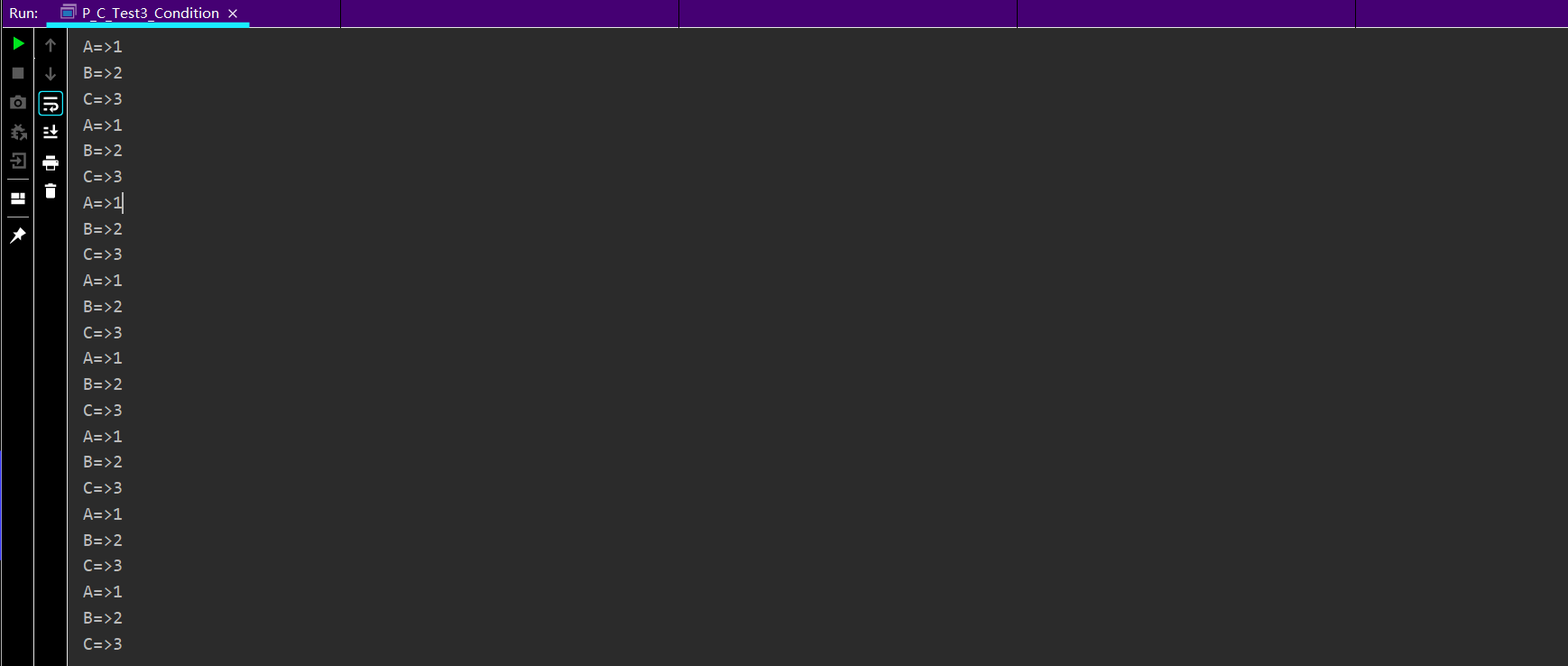
测试2
public class P_C_GuanChengFa { public static void main(String[] args) { SynContainer container = new SynContainer(); new Productor(container).start(); new Consumer(container).start(); } } //缓冲区 class SynContainer{ //需要容器大小 Chicken[] chickens = new Chicken[10]; //容器计数器 int count = 0; //生产者放入产品 public synchronized void push(Chicken chicken) throws InterruptedException { while(count == chickens.length){ this.wait(); } chickens[count] = chicken; ++count; //通知消费者 notifyAll(); } //消费者消费产品 public synchronized Chicken pop() throws InterruptedException{ while(count == 0){ this.wait(); } --count; Chicken chicken = chickens[count]; notifyAll(); return chicken; } } //生产者 class Productor extends Thread{ SynContainer container;//缓冲区 public Productor(SynContainer container) { this.container = container; } public void run() { try{ for(int i =1;i<=20;i++) { container.push(new Chicken(i)); System.out.println("生产有鸡"+ i +"只"); } }catch (Exception ex){ } } } //消费者 class Consumer extends Thread{ SynContainer container;//缓冲区 public Consumer(SynContainer container) { this.container = container; } public void run() { try{ for(int i =1;i<=20;i++) { System.out.println("********************消费了" + container.pop().id + "只鸡"); } }catch (Exception ex){ } } } //产品 class Chicken{ int id; public Chicken(int id) { this.id = id; } }

信号灯法
设置一个标志位,控制线程通信(红灯停、绿灯行)
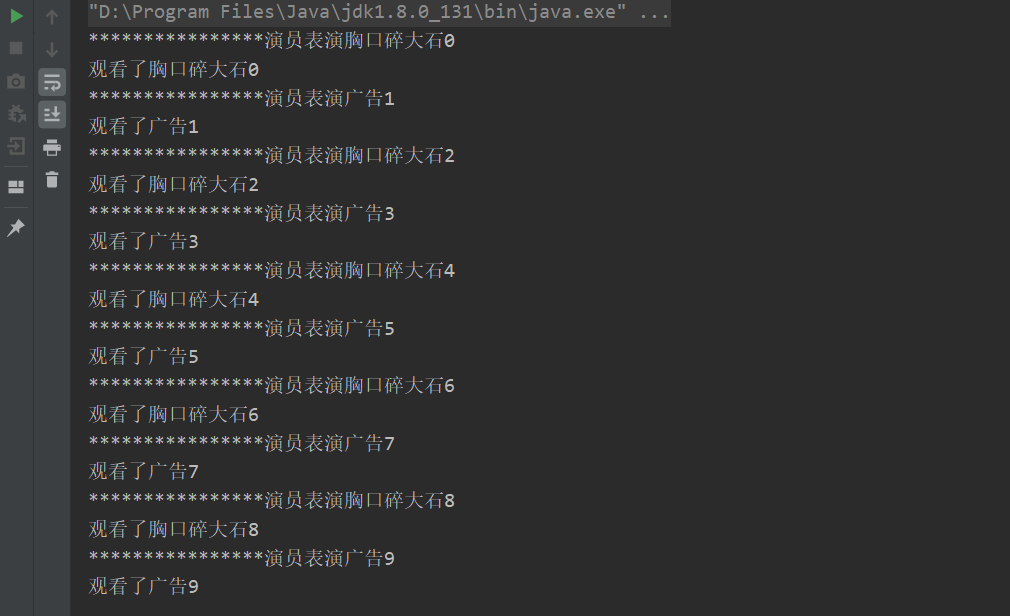
public class P_C_XinHaoDengUseFlag { public static void main(String[] args) { TV tv = new TV(); new Player(tv).start(); new Watcher(tv).start(); } } //生产者 演员 class Player extends Thread{ TV tv; public Player(TV tv) { this.tv = tv; } public void run() { for(int i = 0;i<10;i++) { if(i % 2 == 0) { this.tv.play("胸口碎大石"+i); }else { this.tv.play("广告"+i); } } } } //消费者 观众 class Watcher extends Thread{ TV tv; public Watcher(TV tv) { this.tv = tv; } public void run() { for(int i = 0;i<10;i++) { tv.watch(); } } } //产品 节目 class TV{ //演员表演 观众等待 //观众观看 演员等待 String voice;//表演的节目 boolean flag = true; //表演 public synchronized void play(String voice) { if(!flag) { try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } System.out.println("****************演员表演"+ voice); //通知观众观看 this.notifyAll();//通知唤醒 this.voice = voice; this.flag = !this.flag; } //观看 public synchronized void watch() { if(flag) { try { this.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } System.out.println("观看了"+ voice); this.notifyAll();//通知演员表演 this.flag = !this.flag; } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号