线程基础
- 一个进程可以有多个线程。
- 进程是资源分配的单位。
测试
测试0-callable的使用
public class T { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { /*//连接池调用Callable ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2); Future<Boolean> future = executorService.submit(new CallableTest()); System.out.println(future.get()); executorService.shutdown();*/ FutureTask<Boolean> futureTask = new FutureTask<Boolean>(new CallableTest()); new Thread(futureTask,"A").start(); new Thread(futureTask,"B").start();//测试Callable缓存:调用两次futureTask,观察输出几个“call” System.out.println(futureTask.get());//阻塞一分钟后,返回结果 } } class CallableTest implements Callable<Boolean> { @Override public Boolean call() throws Exception { System.out.println("call"); TimeUnit.MINUTES.sleep(1);//阻塞一分钟后,返回结果 return true; } }
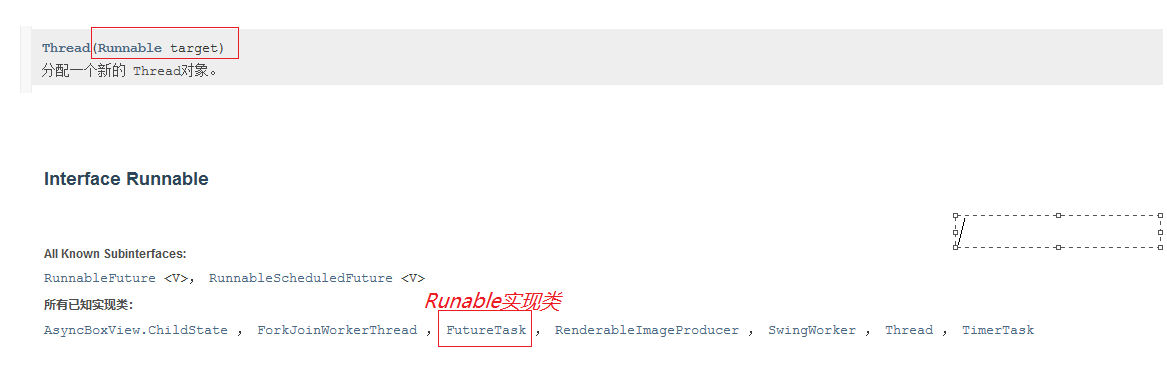
细节:
- 有缓存
- 返回结果可能会等待,会阻塞。可以使用异步通信来处理
测试1-线程常用方法
线程状态
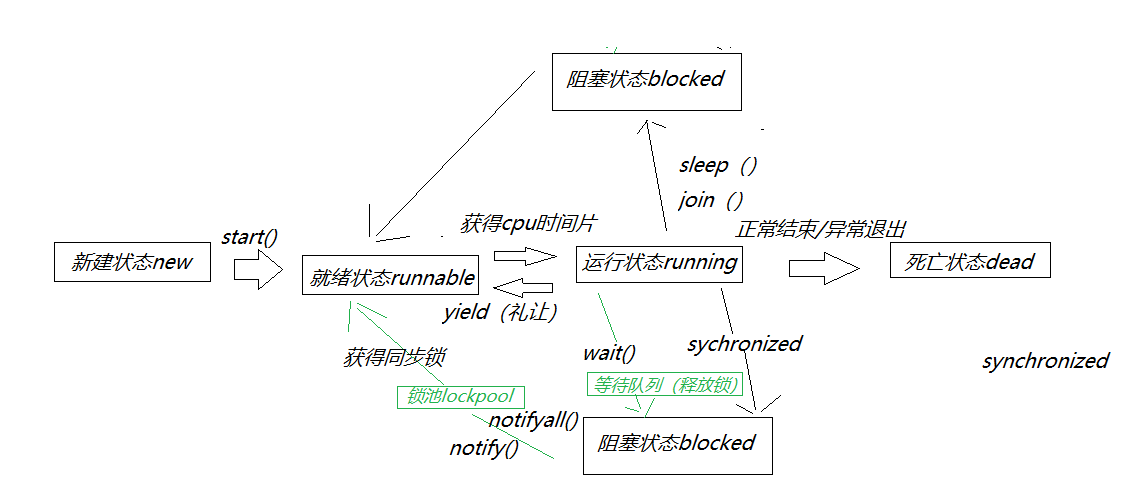
public class StateThreadTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException{ Thread thread = new Thread(()->{ for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } System.out.println("子线程结束了"); }); Thread.State state = thread.getState(); System.out.println("【新建状态】"+state);//new thread.start(); state = thread.getState(); System.out.println("【就绪状态】"+state);//runnable while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED){ Thread.sleep(1000); state = thread.getState(); System.out.println("【非终止状态】"+state); } } }
sleep()
sleep()让调用线程进入睡眠状态,让出执行机会给其他线程,等到休眠时间结束后,线程进入就绪状态和其他线程一起竞争cpu的执行时间。
因为sleep() 是static静态的方法,他不能改变对象的机锁,当一个synchronized块中调用了sleep() 方法,线程虽然进入休眠,但是对象的机锁没有被释放,其他线程依然无法访问这个对象。
因为一个类中的静态资源在类class被java虚拟机加载时就已经被初始化了,而非静态资源要在对象实例化的时候才会被初始化。sleep()方法是静态的,只依赖于类,不依赖于对象,而锁是对象锁,所以不能改变锁
sleep模拟网络延时,倒计时。
public class SleepThreadTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { // timedown(); Date startDate = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); while (true){ Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(startDate)); startDate = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());//更新时间 } } /** * 模拟倒计时 * @throws InterruptedException */ static void timedown() throws InterruptedException { int num = 10; while (true){ Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println(num--); if(num<=0) break; } } }
sleep() VS wait()
- 释放锁:wait 可以释放当前线程对 lock 对象锁的持有,而 sleep 则不会
- 使用场景:sleep 一般用于当前线程休眠,或者轮循暂停操作,wait 则多用于多线程之间的通信。
- 所属类:sleep 是 Thread 类的静态本地方法,wait 则是 Object 类的本地方法
- 使用限制:使用 sleep 方法可以让让当前线程休眠,时间一到当前线程继续往下执行,在任何地方都能使用。而使用 wait 方法则必须放在 synchronized 块里面。wait 还需要额外的方法 notify/ notifyAll 进行唤醒,它们同样需要放在 synchronized 块里面,且获取对象的锁。
- 线程切换:sleep 会让出 CPU 执行时间且强制上下文切换,而 wait 则不一定,wait 后可能还是有机会重新竞争到锁继续执行的。
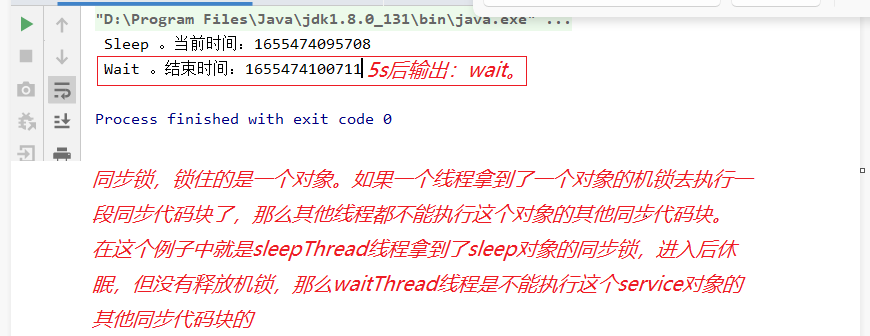
public class SleepThreadTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Sleep sleep = new Sleep(); Thread sleepThread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { sleep.sleep(); } }); sleepThread.start(); Thread waitThread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { sleep.mWait(); } }); waitThread.start(); } } class Sleep{ public void sleep(){ synchronized(this){ try{ System.out.println(" Sleep 。当前时间:"+System.currentTimeMillis()); Thread.sleep(5*1000); } catch(Exception e){ System.out.println(e); } } } public void mWait(){ synchronized(this){ System.out.println(" Wait 。结束时间:"+System.currentTimeMillis()); } } }
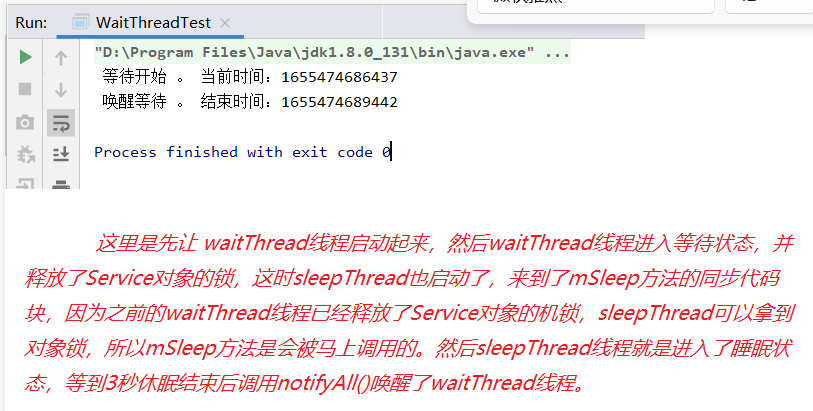
public class WaitThreadTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Wait wait = new Wait(); Thread waitThread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { wait.mWait(); } }); waitThread.start(); Thread sleepThread = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { wait.mSleep(); } }); sleepThread.start(); } } class Wait { public void mSleep() { try { Thread.sleep(3 * 1000); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(e); } synchronized (this) { this.notifyAll(); System.out.println(" 唤醒等待 。 结束时间:" + System.currentTimeMillis()); } } public void mWait() { synchronized (this) { try { System.out.println(" 等待开始 。 当前时间:" + System.currentTimeMillis()); this.wait(); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(e); } } } }
线程的优先级
public class PriorityThreadTest { public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"----"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); MyPriority myPriority = new MyPriority(); Thread t1 = new Thread(myPriority,"thread1"); Thread t2 = new Thread(myPriority,"thread2"); Thread t3 = new Thread(myPriority,"thread3"); Thread t4 = new Thread(myPriority,"thread4"); Thread t5= new Thread(myPriority,"thread5"); t1.setPriority(8); t1.start(); t2.setPriority(4); t2.start(); t3.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY); t3.start(); t4.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); t4.start(); t5.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY); t5.start(); } } class MyPriority implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"----"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority()); } }
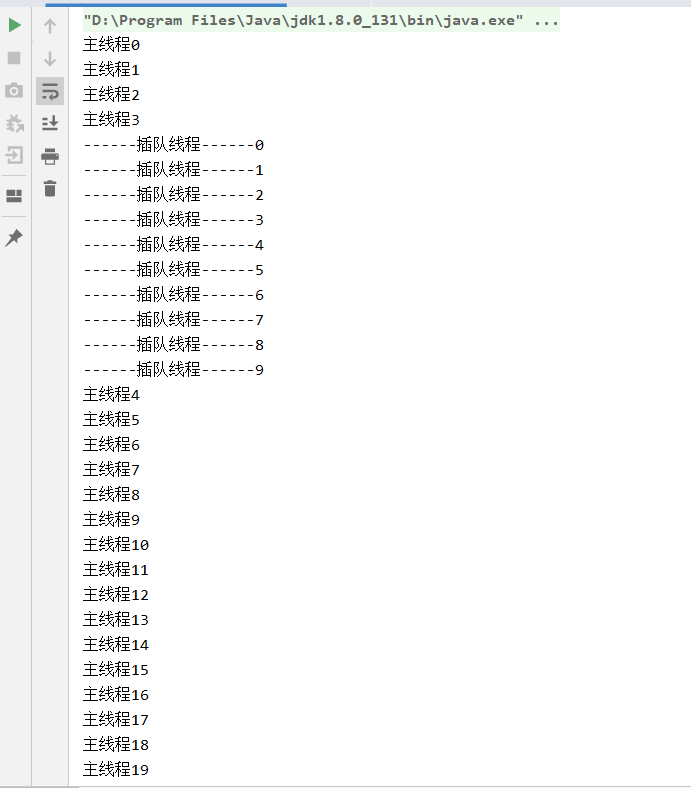
join()插队
- 等待插队线程结束后,再执行其他线程。
- 可以想象成插队
public class JoinThreadTest_ChaDui implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10 ; i++) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); System.out.println("------插队线程------"+i); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { JoinThreadTest_ChaDui joinThreadTest_chaDui = new JoinThreadTest_ChaDui(); Thread chaduiThread = new Thread(joinThreadTest_chaDui); chaduiThread.start(); for (int i = 0; i < 20 ; i++) { System.out.println("主线程"+i); if(i==3){ chaduiThread.join(); } } } }
stop()
- 推荐使用标志位
- 利用次数,不建议死循环
- jdk过时方法,不建议
public class StopThreadTest_UseFlag implements Runnable{ private boolean flag = true; @Override public void run() { int i=0; while (flag){ System.out.println("-------子线程运行----------"+i++); } } public boolean stop(){ this.flag = false; return flag; } public static void main(String[] args) { StopThreadTest_UseFlag sttu = new StopThreadTest_UseFlag(); new Thread(sttu).start();; for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) { System.out.println("main线程运行"+i); if(i==4){ sttu.stop(); } } } }
守护线程
- 虚拟机不用等待守护线程执行完毕
- 虚拟机必须确保用户线程执行完毕
- 用户线程:main
- 守护线程:gc、后台记录操作日志、监控内存
public class DaemonTest { public static void main(String[] args) { new Thread(new You()).start(); Thread godThread = new Thread(new God()); godThread.setDaemon(true); godThread.start(); } } class God implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { while(true){ System.out.println("上帝守护每一天"); } } } class You implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 365; i++) { System.out.println("开开心心每一天"+i); } } }

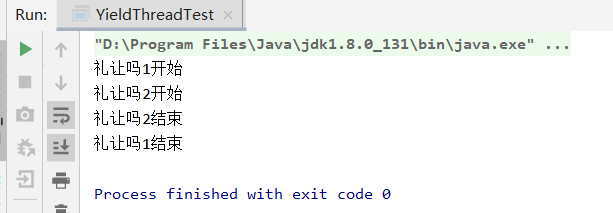
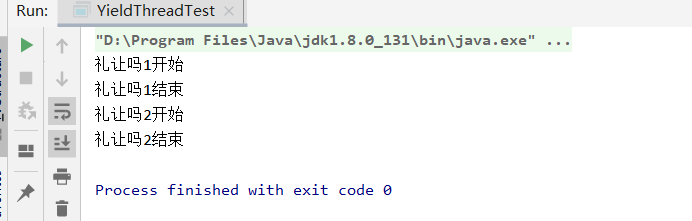
yield()
- 让当前正在执行的线程暂停,但不阻塞。
- 将线程从运行状态转为就绪状态
- 让cpu重新调度,礼让不一定成功,看cpu心情
public class YieldThreadTest { public static void main(String[] args) { YildThread yildThread = new YildThread(); new Thread(yildThread,"礼让吗1").start(); new Thread(yildThread,"礼让吗2").start(); } } class YildThread implements Runnable{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"开始"); Thread.yield(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"结束"); } }
测试...
模拟龟兔赛跑
/** * 模拟龟兔赛跑 */ public class RaceTest implements Runnable { private static String winner;//共享变量 @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i <= 1000 ; i++) { if(Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("兔子") && i/20==0){//模拟兔子睡了 try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } boolean winflag = gameOver(i); if(winflag){ break; } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"跑了"+i+"步"); } } /** * 是否跑到了终点 */ public boolean gameOver(int steps){ if(winner !=null){ return true; } if(steps == 1000){ winner = Thread.currentThread().getName(); System.out.println("************************赢家是"+winner); } return false; } public static void main(String[] args) { RaceTest raceTest = new RaceTest(); new Thread(raceTest,"兔子").start(); new Thread(raceTest,"tortoise").start(); } }
下载网络图片
package com.fh.thread.base.createThread; import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils; import java.io.*; import java.net.URL; import java.util.concurrent.*; public class CallableTest_DownloadPic implements Callable<Boolean> { String url; String name; public CallableTest_DownloadPic(String url,String name) { this.url = url; this.name = name; } @Override public Boolean call() throws Exception { DownloadPic downloadPic = new DownloadPic(); downloadPic.download(url,name); System.out.println("下载了文件:"+name); return true; } class DownloadPic{ void download(String url,String name){ try { FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url),new File(name)); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException { CallableTest_DownloadPic cdp1 = new CallableTest_DownloadPic("https://img0.baidu.com/it/u=3212253201,1261694971&fm=253&fmt=auto&app=120&f=PNG?w=488&h=594","src/main/resources/pic/1.png"); CallableTest_DownloadPic cdp2 = new CallableTest_DownloadPic("https://img0.baidu.com/it/u=3538204079,1027715215&fm=253&fmt=auto&app=138&f=PNG?w=500&h=249","src/main/resources/pic/2.png"); CallableTest_DownloadPic cdp3 = new CallableTest_DownloadPic("https://img2.baidu.com/it/u=1656231567,3874501242&fm=253&fmt=auto&app=120&f=JPEG?w=900&h=426","src/main/resources/pic/3.png"); ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3); Future<Boolean> future1 = executorService.submit(cdp1); Future<Boolean> future2 = executorService.submit(cdp2); Future<Boolean> future3 = executorService.submit(cdp3); boolean result1 = future1.get(); boolean result2 = future1.get(); boolean result3 = future1.get(); System.out.println(result1+"---"+result2+"---"+result3); executorService.shutdown(); } }
模拟买卖票
public class TicketTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Ticket ticket = new Ticket(); // 1. // new Thread(()->{ // ticket.sellTicket(); // },"小明").start(); // new Thread(()->{ // ticket.sellTicket(); // },"花花").start(); // new Thread(()->{ // ticket.sellTicket(); // },"JAY").start(); new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 60; i++) { ticket.sellTicket(); } }, "窗口1").start(); new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 60; i++) { ticket.sellTicket(); } }, "窗口2").start(); new Thread(() -> { for (int i = 0; i < 60; i++) { ticket.sellTicket(); } }, "窗口3").start(); } } class Ticket { int num = 10; public void sellTicket() { synchronized (this) { if (num > 0) { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖了" + num--); } } } // 1、 // public void sellTicket(){ // while (true){ // try { // Thread.sleep(1000); // } catch (InterruptedException e) { // // } // synchronized (this){ // if(num > 0){ // System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+num--); // }else break; // } // // } // } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号