OS第1次实验报告:熟悉使用Linux命令和剖析ps命令
- 姓名:吴永锋
- 学号:201821121051
- 班级:计算1812
1. 实验环境介绍
给出实验环境:
- 操作系统:Window10(版本:18363.657)
- 平台:Cygwin
用户名:wuyongfeng
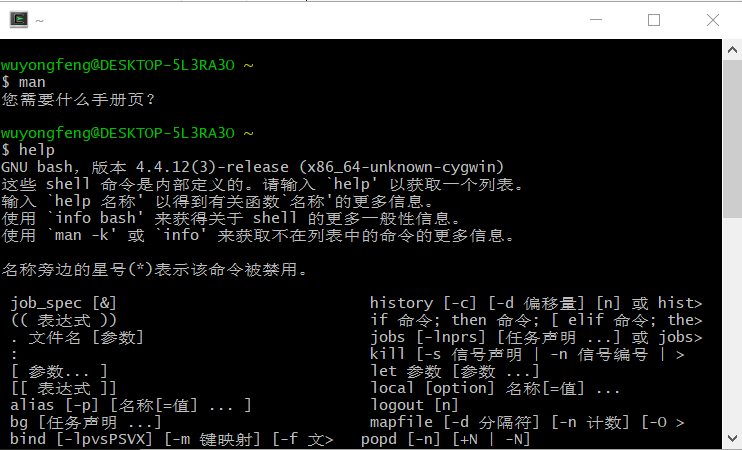
2. 常用命令使用
3. 剖析ps命令
(1)运行man ps:
SYNOPSIS ps [-AaCcEefhjlMmrSTvwXx] [-O fmt | -o fmt] [-G gid[,gid...]] [-g grp[,grp...]] [-u uid[,uid...]] [-p pid[,pid...]] [-t tty[,tty...]] [-U user[,user...]] ps [-L]
−a Write information for all processes associated with termi‐ nals. Implementations may omit session leaders from this list. −A Write information for all processes. −d Write information for all processes, except session leaders. −e Write information for all processes. (Equivalent to −A.) −f Generate a full listing. (See the STDOUT section for the contents of a full listing.) −g grouplist Write information for processes whose session leaders are given in grouplist. The application shall ensure that the grouplist is a single argument in the form of a <blank> or <comma>-separated list. −G grouplist Write information for processes whose real group ID numbers are given in grouplist. The application shall ensure that the grouplist is a single argument in the form of a <blank> or <comma>-separated list. −l Generate a long listing. (See STDOUT for the contents of a long listing.) −n namelist Specify the name of an alternative system namelist file in place of the default. The name of the default file and the format of a namelist file are unspecified. −o format Write information according to the format specification given in format. This is fully described in the STDOUT section. Multiple −o options can be specified; the format specifica‐ tion shall be interpreted as the <space>-separated concate‐ nation of all the format option-arguments. −p proclist Write information for processes whose process ID numbers are given in proclist. The application shall ensure that the proclist is a single argument in the form of a <blank> or <comma>-separated list. −t termlist Write information for processes associated with terminals given in termlist. The application shall ensure that the termlist is a single argument in the form of a <blank> or <comma>-separated list. Terminal identifiers shall be given in an implementation-defined format. On XSI-conformant sys‐ tems, they shall be given in one of two forms: the device's filename (for example, tty04) or, if the device's filename starts with tty, just the identifier following the characters tty (for example, "04"). −u userlist Write information for processes whose user ID numbers or lo‐ gin names are given in userlist. The application shall en‐ sure that the userlist is a single argument in the form of a <blank> or <comma>-separated list. In the listing, the nu‐ merical user ID shall be written unless the −f option is used, in which case the login name shall be written. −U userlist Write information for processes whose real user ID numbers or login names are given in userlist. The application shall ensure that the userlist is a single argument in the form of a <blank> or <comma>-separated list. With the exception of −f, −l, −n namelist, and −o format, all of the options shown are used to select processes. If any are specified, the default list shall be ignored and ps shall select the processes repre‐ sented by the inclusive OR of all the selection-criteria options.
(2)运行并解释ps命令参数
$ ps PID PPID PGID WINPID TTY UID STIME COMMAND 1812 1803 1812 4040 pty0 197609 14:49:01 /usr/bin/ps 1803 1802 1803 13280 pty0 197609 14:38:17 /usr/bin/bash 1802 1 1802 2128 ? 197609 14:38:17 /usr/bin/mintty
$ ps -ef UID PID PPID TTY STIME COMMAND wuyongfe 1803 1802 pty0 14:38:17 /usr/bin/bash wuyongfe 1802 1 ? 14:38:17 /usr/bin/mintty wuyongfe 1813 1803 pty0 14:51:49 /usr/bin/ps
解释ps -ef命令中参数的含义:
-e:将所有信息写入进程;
-f:生成完整的列表。
解释返回结果每个字段的含义:
UID:用户ID
PID:进程ID
PPID:父进程ID
PGID:进程组ID
TTY:终端的次要装置号码
STIME:进程开始时间
COMMAND:所执行的指令
$ ps aux PID PPID PGID WINPID TTY UID STIME COMMAND 1803 1802 1803 13280 pty0 197609 14:38:17 /usr/bin/bash 1802 1 1802 2128 ? 197609 14:38:17 /usr/bin/mintty 1814 1803 1814 25204 pty0 197609 14:55:50 /usr/bin/ps
解释ps aux命令中参数的含义:
a:为终端相关的所有进程写入信息
u:以用户为主的格式来显示程序状况
x:显示所有程序,不以终端机来区分
4. 通过该实验产生新的疑问及解答
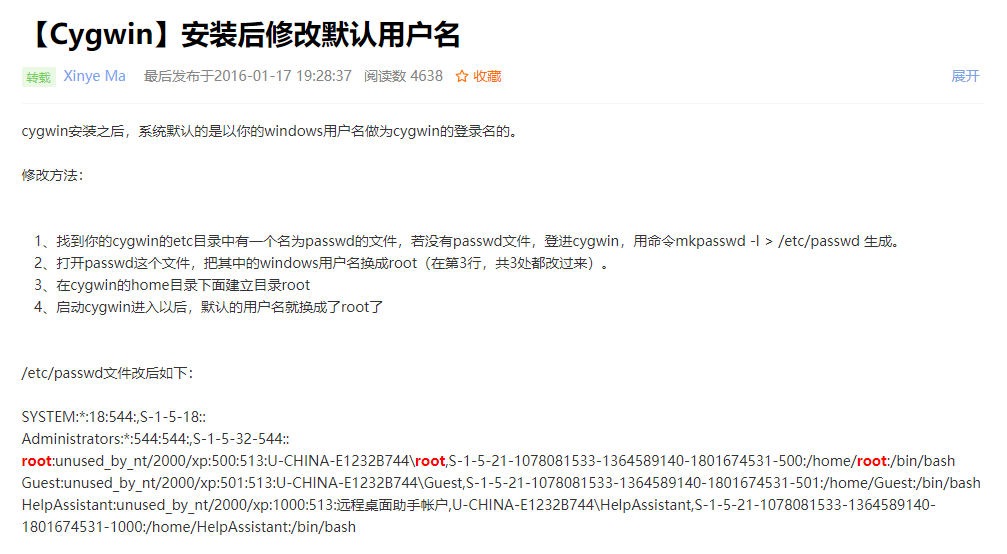
(1)如何修改用户名为自己名字的拼音
(2)执行命令man ps后出现如下界面:
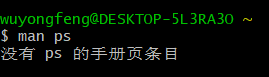
将man-pages-posix-2013-a文件解压后,文件夹重命名为man,替换掉原来C:\cygwin64\usr\share下的man文件。


