常用算法的总结——链表
链表常用算法:快慢指针、利用HashMap、栈
如:
1 快慢指针
1) 输入链表头节点,奇数长度返回中点,偶数长度返回上中点
2) 输入链表头节点,奇数长度返回中点,偶数长度返回下中点
3) 输入链表头节点,奇数长度返回中点前一个,偶数长度返回上中点前一个
4) 输入链表头节点,奇数长度返回中点前一个,偶数长度返回下中点前一个
第一题代码如下,其他同理:
// head头 public static Node mi d0rUpMi dNode(Node head) { if (head == nu11|I head.next == nu11Il| head.next.next == nu1l) { return head;
} Node slow = head . next; Node fast = head. next . next; while (fast.next != nu11 && fast. next.next != nu11) { slow = slow. next; fast = fast. next. next;
} return slow;
}
2 给定一个单链表的头节点head,请判断该链表是否为回文结构。
1) 哈希表方法特别简单——利用栈
public static boolean isPalindrome1 (Node head) { Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<Node>( ); Node cur = head; while (cur != nu1l) { stack. push(cur); cur = cur. next; } while (head != nu1l) { if (head.value != stack. pop().value) { return false; } head = head. next; } return true; }
2) 改原链表的方法就需要注意边界了
3) 利用快慢指针的算法:先让快指针到终点,慢指针到中点,然后让指向中点的慢指针指向null,后半部分全部倒转,后面的指向前面的,最后由终点和起点开始往中间遍历,只要有一步不相等就返回false,最后由如果需要恢复则将其恢复成原样,代码如下(包含了最后恢复成原样的步骤):
public static boolean isPalindrome3(Node head) { if (head == null | head.next == null) { return true; } Node n1 = head; Node n2 = head; while (n2.next != null && n2.next.next != null) { // find mid node n1 = n1.next; // n1 -> mid n2 = n2.next.next; // n2 -> end } n2 = n1.next; // n2 -> right part first node n1.next = null; // mid.next -> null Node n3 = null; while (n2 != null) { // right part convert n3 = n2.next; // n3 -> save next node n2.next = n1; // next of right node convert n1 = n2;//n1move n2 = n3;//n2move } n3 = n1; // n3 -> save last node n2 = head;// n2 -> left first node . boolean res = true; while (n1 != null && n2 != null) { // check palindrome if (n1.value != n2. value) { res = false; break ; } n1 = n1.next; // left to mid n2 = n2.next; // right to mid } n1 = n3.next; n3.next = null; while (n1 != null) { // recover list n2 = n1. next; n1.next = n3; n3 = n1; n1 = n2; } return res; }
3
将单向链表按某值划分成左边小、中间相等、右边大的形式
方法:把链表放入数组里,在数组上做partition ,代码如下:
public static Node listPartition1(Node head, int pivot) { if (head == null) { return head; } Node cur = head; int i = 0; while (cur != null) { i++; cur = cur.next; } Node[] nodeArr = new Node[i]; i = 0; cur = head; for (i = 0; i != nodeArr.length; i++) { nodeArr[i] = cur; cur = cur.next; }
//将数组进行交换,大于pivot的放pivot左边,反之放右边 arrPartition(nodeArr, pivot); for (i = 1; i != nodeArr.length; i++) { nodeArr[i - 1].next = nodeArr[i]; } nodeArr[i - 1].next = null; return nodeArr[0]; } public static int[] arrPartition(int[] arr, int L, int R, int p) { int less = L - 1; int more = R + 1; while(L < more) { if(arr[L] < p) { swap(arr, ++less, L++); } else if (arr[L] > p) { swap(arr, --more, L); } else { L++; } } return new int[] { less + 1, more - 1 }; } public static void swap(int[] arr, int i, int j) { int temp = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = temp; }
4 利用HashMap
一种特殊的单链表节点类描述如下
class Node {
int value;
Node next;
Node rand;
Node(int val) { value = val;
}
rand指针是单链表节点结构中新增的指针,rand可 能指向链表中的任意一个节 点,也可能指向null。
给定一个由Node节点类型组成的无环单链表的头节点head,请实现一个函数完成这个链表的复制,并返回复制的新链表的头节点。
代码如下:
public static Node copyListWithRand1 (Node head) { HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<Node, Node>(); Node cur = head; while (cur != null) { map . put(cur, new Node( cur.value)); cur = cur.next; } cur = head; while (cur != null) { // cur 老 // map.get(cur) 新 map.get(cur).next = map. get(cur.next); map. get(cur).rand = map. get(cur.rand); cur = cur.next ; } return map . get(head); }
[进阶] 时间复杂度O(N),额外空间复杂度0(1)
方式2:保证时间复杂度的前提下,不使用大的空间
public static Node copyListWithRand2(Node head) { if (head == null) { return null; } Node cur = head; Node next = null; // copy node and link to every node // 1-> 2 //1->1'->2 while (cur != null) { // cur老 next = cur.next; cur.next = new Node(cur.value); cur.next.next = next; cur = next; } cur = head; Node curCopy = null; // set copy node rand 搞定rand结点 //1->1'->2->2' while (cur != null) { // cur老 // cur.next 新copy next = cur.next.next; curCopy = cur.next; curCopy.rand = cur.rand != null ? cur.rand.next : null; cur = next; } //返回结果的头结点要为head的下一个 Node res = head.next; cur = head; // split,搞定next结点 while (cur != null) { next = cur.next.next; curCopy = cur.next; cur.next = next; curCopy.next = next != null ? next.next : null; cur = next; } return res; }
5 相交链表
给定两个可能有环也可能无环的单链表,头节点head1和head2。请实现一个函数,如果两个链表相交,请返回相交的第一个节点。如果不相交,返回null
[要求]如果两个链表长度之和为N,时间复杂度请达到O(N),[进阶]额外空间复杂度请达到O(1)。
5.1 无环情况下解法:head1、end1为第一个链表的头结点、尾结点,head2、end2为第二个链表的头结点、尾结点,判断end1是否为end2,不是则直接返回null(两者必不相交);是的话,长链表先走长链表比短链表长的部分(如长链表为100,短链表为80,则长链表先走20步),然后同时走,他们一定会在第一个结点相遇,代码如下:
//如果两个链表都无环,返回第-一个相交节点,如果不想交,返回null public static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2) { if (head1 == null || head2 == null) { return null; } Node cur1 = head1; Node cur2 = head2; //n为差值 int n = 0; while (cur1.next != null) { n++; cur1 = cur1.next; } while (cur2.next != null) { n--; cur2 = cur2.next; } //此时cur1、cur2分别到达链表1、2的末尾, if (cur1 != cur2) { return null; } // n :链表1长度减去链表2长度的值 cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2; //谁长,谁的头变成cur1 cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1; //谁短,谁的头变成cur2 n = Math.abs(n); //先走差值的步骤 while (n != 0) { n--; cur1 = cur1.next; } //再同时一块走 while (cur1 != cur2) { cur1 = cur1.next; cur2 = cur2.next; } return cur1; }
5.2 有环的情况下解法
分析:①两条不想交的有环链表;②两条相交点为同一点;③相交点为不同点;三种情况图示如下:②其实和无环情况一样,只需要把cur1、cur2到达末尾改成到达公共结点即可
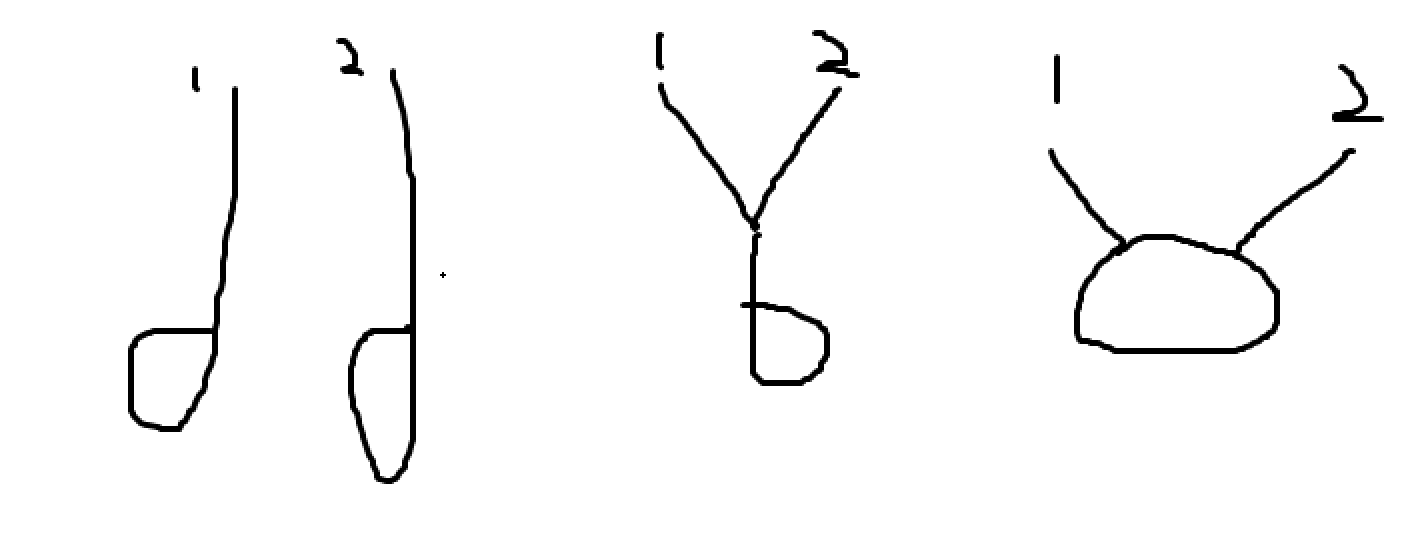
代码如下:
/** 两个有环链表, 返回第一个相交节点,如果不想交返回null * @param head1 1的头 * @param loop1 1的入环 * @param head2 2的头 * @param loop2 2的入环 * @return 返回相交结点,情况③的话有两个,返回任意一个即可 */ public static Node bothLoop(Node head1, Node loop1, Node head2, Node loop2) { Node cur1 = null; Node cur2 = null; //这部分的代码其实和无环的类似,只不过把while循环的终止条件改成到达入环的结点 if (loop1 == loop2) {//说明相交点在环外,为情况② cur1 = head1; cur2 = head2; int n = 0; while (cur1 != loop1) { n++; cur1 = cur1.next; } while (cur2 != loop2) { n--; cur2 = cur2.next; } cur1 = n > 0 ? head1 : head2; cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1; n = Math.abs(n); while (n != 0) { n--; cur1 = cur1.next; } while (cur1 != cur2) { cur1 = cur1.next; cur2 = cur2.next; return cur1; } } else {//情况①和情况③ cur1 = loop1.next; //开始从入环结点处开始遍历这个环, // 如果找到另外一个入环结点,则为情况③,返回任意一个入环结点即可 while (cur1 != loop1) { if (cur1 == loop2) { return loop1; } cur1 = cur1.next; } //如果没找到,则说明为情况①,返回null return null; } }
5.3 汇总有环和无环情况
总的方法如下:
public static Node getIntersectNode(Node head1, Node head2) { if (head1 == null|| head2 == null) { return null; } //getLoopNode()为获取入环结点的方法 Node loop1 = getLoopNode (head1); Node loop2 = getLoopNode (head2); //如果两个链表的入环结点都为空,则说明二者都为无环链表 if (loop1 == null && loop2 == null) { return noLoop( head1, head2); } //如果两个链表的入环结点都不为空,则说明二者都为有环链表 if (loop1 != null && loop2 != null) { return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, loop2); } //其他情况都不可能相交 return null; }
5.4 里面的获取入环结点的方法如下(其实这也是一道简单的面试题,代码省略了):
链表是否有环,有则找到入环结点,没有则返回null
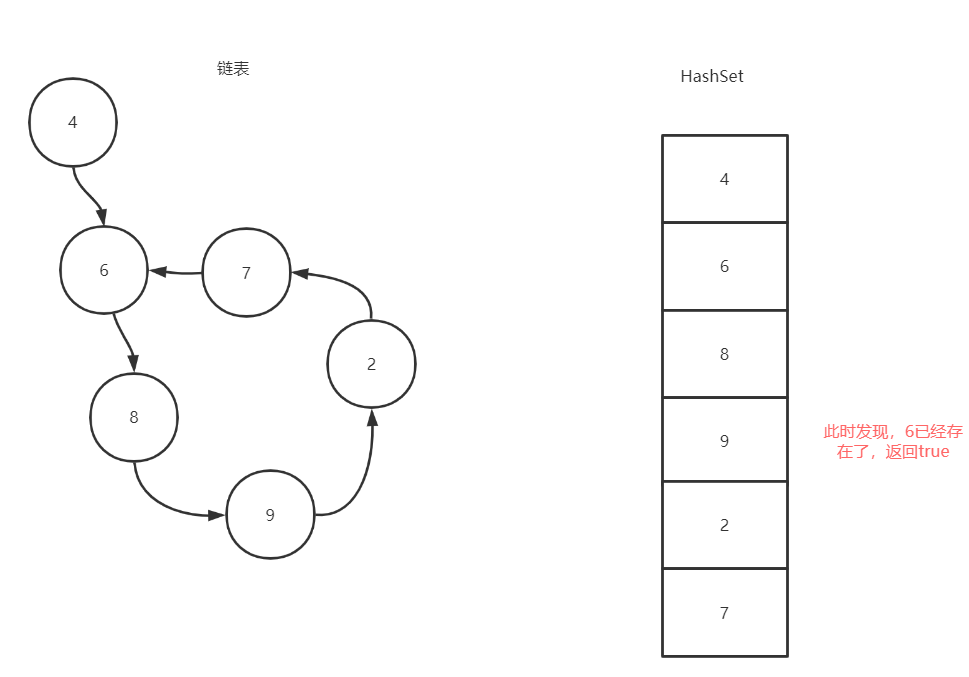
解法一:HashSet
利用HashSet的唯一性,遍历链表,不存在则放入,存在则说明有环,没有环一定会返回null,图示如下:
解法二:快慢指针
慢指针走一步,快指针走两步,那么一定会在某个点相遇,此时让快指针回到开头,变成一次走一步,两者同时出发(此时慢指针在相遇的点),两个慢指针就必然会在入环的点相遇
6 删除链表结点
能不能不给单链表的头节点,只给想要删除的节点,就能做到在链表上把这个点删掉?
抖机灵的做法:给出要删除的结点,把该节点的next赋值给该节点,然后让该节点跨过下一个结点,让next指针指向下下一个节点
其实这样本质上并没有把自己删除掉,除此之外,尾巴结点删除不掉
其实这样是不行的,只能给出头结点才能解决。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号