力扣练习——20 接雨水 II
1.问题描述
给你一个 m x n 的矩阵,其中的值均为非负整数,代表二维高度图每个单元的高度,请计算图中形状最多能接多少体积的雨水。
示例:
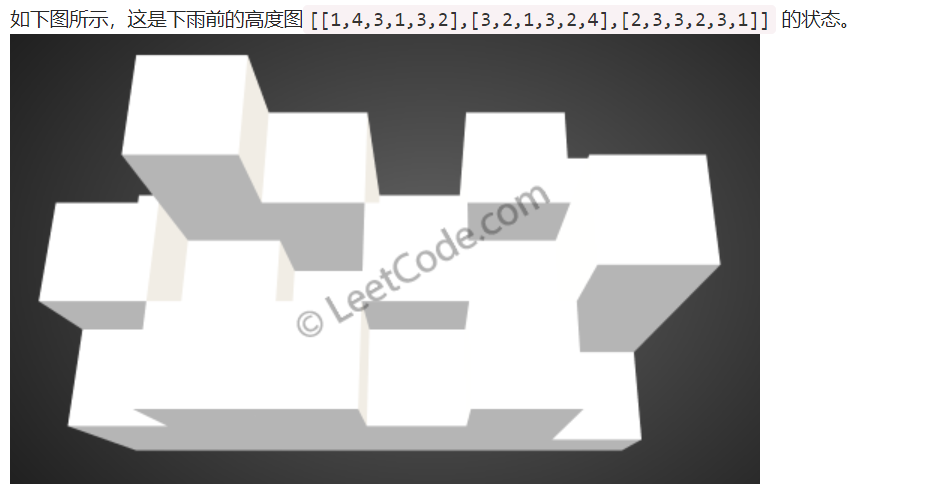
给出如下 3x6 的高度图:
[
[1,4,3,1,3,2],
[3,2,1,3,2,4],
[2,3,3,2,3,1]
]
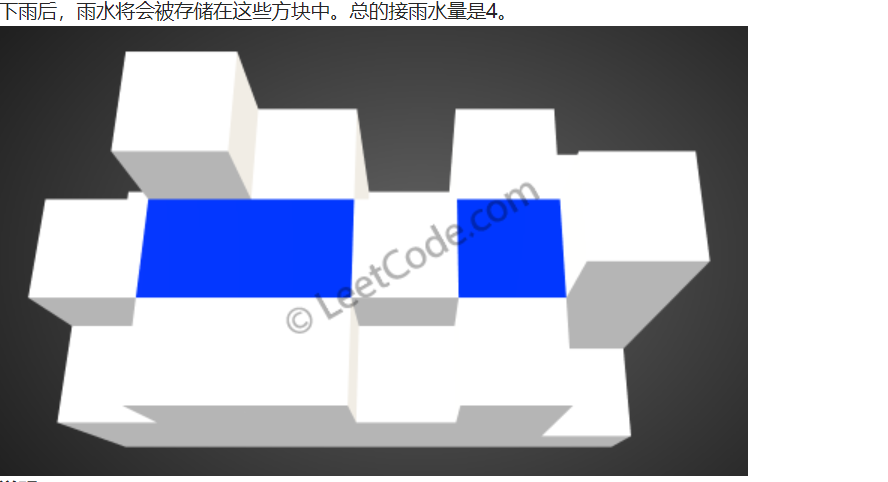
返回 4 。
说明:
-
1 <= m, n <= 110 -
0 <= heightMap[i][j] <= 20000
可使用以下代码,完成其中的trapRainWater函数,其中形参heightMap为上述的二维高度图,返回接到的雨水量。
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Solution {
public:
int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int> >& heightMap)
{
//填充本函数完成功能
}
};
int main()
{
int m, n,data;
vector<vector<int> > heights;
cin>>m>>n;
for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
{
vector<int> row;
for(int j=0; j<n; j++)
{
cin>>data;
row.push_back(data);
}
heights.push_back(row);
}
int res=Solution().trapRainWater(heights);
cout<<res<<endl;
return 0;
}
2.输入说明 :
首先输入高度图的行列数m和n
然后输入m行,每行n个非负整数,表示heightMap的元素值,以空格分隔。
-
1 <= m, n <= 110 -
0 <= heightMap[i][j] <= 20000
3.输出说明
输出一个整数,表示结果。
4.范例
输入
3 6
1 4 3 1 3 2
3 2 1 3 2 4
2 3 3 2 3 1
输出
4
5.代码
#include<iostream> #include<stack> #include<queue> #include<vector> using namespace std; class Solution { public: int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int> >& heightMap) { //木桶思想,参考题解https://leetcode.cn/problems/trapping-rain-water-ii/solution/jie-yu-shui-ii-by-leetcode-solution-vlj3/ //1.特殊情况 //heightMap.size()代表输入矩阵的行数,heightMap[0].size()代表列数;若最多只有两行或者两列,则都是四周最外层的方块,根本不可能接到雨水 if (heightMap.size() <= 2 || heightMap[0].size() <= 2) return 0; //2.定义 int m = heightMap.size();//行数 int n = heightMap[0].size();//列数 priority_queue<pair<int,int>, vector <pair<int,int>>, greater <pair<int,int>>>pq;//优先级队列 //3.访问标记初始化 //参考https://blog.csdn.net/BShanj/article/details/113817328 vector<vector<bool>> visited(m, vector<bool>(n, false)); //4.周边方块标记处理 for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { if (i == 0 || i == m - 1 || j == 0 || j == n - 1) { visited[i][j] = true; //最外层接水量water[i][j]=heightMap[i][j] pq.push({ heightMap[i][j],i*n + j });//这里second存储的是该方块在以列排序中的位置,相当于从第一类第一个元素开始,往后以S型串成串 } } } //5.处理中心部分 //假设方块的索引为 (i,j),方块的高度为heightMap[i][j],方块接水后的高度为water[i][j] //方块 (i,j)(i,j) 的接水后的高度为:water[i][j]=max(heightMap[i][j],min(water[i-1][j],water[i][j-1],water[i+1][j],water[i][j+1])) int res = 0; int direction[]={ -1,0,1,0,-1 };//左,上,右,下四个方位 while (!pq.empty())//非空时 { pair<int, int> cur = pq.top(); pq.pop(); //遍历这个方块四周的水位高度 for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) { int nx = cur.second / n + direction[k];//注意,这里cur.second/n代表的是原方块的横坐标 int ny = cur.second%n + direction[k + 1];//cur.second%n代表原方块的纵坐标 if (nx >= 0 && nx < m&&ny >= 0 && ny < n && !visited[nx][ny])//这里要保证nx,ny均在正常范围内 { //当前方块的高度比周围的方块要高,容器内水的高度取决于最外层高度最低的方块 if (heightMap[nx][ny] < cur.first)//cur.first就是当前出队列的那个方块的高度heightMap[i][j] res += cur.first - heightMap[nx][ny];//方块(i,j)实际接水量为water[i][j]-heightMap[i][j] visited[nx][ny] = true; pq.push({ max(heightMap[nx][ny], cur.first), nx * n + ny }); } } } return res; } }; int main() { int m, n, data; vector<vector<int> > heights; cin >> m >> n; for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { vector<int> row; for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { cin >> data; row.push_back(data); } heights.push_back(row); } int res = Solution().trapRainWater(heights); cout << res << endl; return 0; }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号