Python笔记
本文摘自<<Python编程从入门到实践>>,为个人总结文档
第一部分 基础知识
第一章 起步
无
第二章 变量和简单数据类型
2.1 变量
-变量命名规则:
- 以字母、数字和下划线命名,不能以数字开头(不允许使用$符)
- python建议变量以小写字母加下划线命名(非驼峰命名方式),变量命名规则应简短又具有描述性
2.2 数据类型
-字符串
- python中以引号(包括单引号或双引号)包含的一系列字符称之为字符串,如:
"Hello world"
'Hello world'
这种灵活性可以在字符串中包含双引号或单引号,如:
'Tom told lily,"Python is my favorite language"'
"One of Python's strength is its diverse and supportive community" #python的强大原因之一是它的多样性及支持社区
- 字符串方法:
修改字符串大小写:
title() #单词首字母大写,其它部分小写
upper() lower()
字符串拼接:+
使用制表符或换行符来添加空白:\t \n
删除空白:lstrip() rstrip() strip()
1 #2-3 2 name1 = "Gric" 3 print("Hello "+name1+",would you like to learn some Python today?") 4 #2-4 5 name2 = "Jimmy" 6 print("Upper name:"+name2.upper()) 7 print("Lower name:"+name2.lower()) 8 print("First Character Upper name:"+name2.title()) 9 #2-5 10 name3="Alber Einstein" 11 print(name3+' once said,"A person who never made a mistake never tried anything new."') 12 #2-6 13 famous_person=name3 14 message=famous_person+' once said,"A person who never made a mistake never tried anything new."' 15 print(message) 16 #2-7 17 name4=" Elic " 18 print("LStrip name:"+name4.lstrip()+"\tRStrip name:"+name4.rstrip()+"\nStrip name:"+name4.strip())
-数字
- 整数
在python中,可对整数执行加(+)、减(-)、乘(*)、除(/)运算,Python还支持运算次序
注意:在python2中,整数相除结果为整数,小数位被截断,若要保留小数位,至少将除数或被除数之一设置为浮点数
python以**代表幂运算,如2**3 #结果为8
- 浮点数
- 使用函数str()避免类型错误
在python中,字符串后面的数字不能默认为字符串,使用函数str()将其转换为字符串
注:可通过int()、long()、float()等函数将字符串转换为数字
-注释 #
-python之禅
关键字:import this
第三章 列表简介
3.1 列表是什么
- 列表由一系列按特定顺序排列的元素组成
- 列表名建议由复数组成(如letters)
- 列表由方括号([])组成,并用逗号隔开其中的元素,如:
bicycles=['trek','cannondale','redline','specialized']
3.2 添加、删除、修改列表
-访问列表元素
#index=0,1,2...
#index可以为负数(从-1开始),用于访问倒数第n个元素,如-2返回倒数第二个列表元素,-3返回倒数第三个列表元素
list_name[index]
1 #3-2 2 names=['huayongli','huangxiaoyan','hetao','fanhongtao','hujinlin','shixiang'] 3 for name in names: 4 print("Hello "+name+",nice to meet you") 5 #3-3 6 vehicles=['Honda motocyle','Audi car','Fenghuang bycycles'] 7 print("\nI would like to own a "+vehicles[0])
-修改、添加和删除元素
- 修改:list_name[index]=new_value
- 添加:
list_name.append(value) #在列表末尾添加
list_name.insert(index,value) #在列表中插入元素,index可为负数,表示在倒数某元素前插入新元素
- 删除:
del list_name[index]
list_name.pop() #弹出栈顶元素(即删除末尾元素)
list_name.pop(index) #弹出指定位置元素
list_name.remove(value) #删除某值,只能删除列表中的第一个指定值 #列表长度len(list_name)
1 def invitation_message(names): 2 for name in names: 3 print(name.title()+",今天晚上到我家做客"); 4 #3-4 5 guest_names=['朱守斌','沈康','傅相存'] 6 invitation_message(guest_names) 7 #3-5 8 print("\n") 9 print(guest_names[1]+"今晚没有空") 10 guest_names[1]="仁波" 11 invitation_message(guest_names) 12 #3-6 13 print("\n我有一个更大的餐桌,所以我想邀请更多的客人") 14 guest_names.insert(0,"崔强") 15 guest_names.insert(int(len(guest_names)/2),"傅磊") 16 guest_names.append("傅勇") 17 invitation_message(guest_names) 18 #3-7 19 print("\n我的餐桌今晚不能按时送达") 20 while len(guest_names)>2: 21 guest_name = guest_names.pop() 22 print(guest_name+",非常抱歉,由于我的餐桌今晚不能按时送达,没办法请您来家里做客了,我们改日再约吧。再次致歉!") 23 print("\n") 24 for guest_name in guest_names: 25 print(guest_name+",我的餐桌不能按时送达,但是您仍在受邀之列,请按时参加!") 26 while len(guest_names)>0: 27 guest_names.pop() 28 print("") 29 if len(guest_names)==0: 30 print("受邀嘉宾名单被清空") 31 else: 32 print("受邀嘉宾名单未清空")
3.3 组织列表
-使用sort()对列表进行永久性排序 list_name.sort([reverse=True])
-使用sorted()对列表进行临时排序 sorted(list_name,[reverse=True])
-使用reverse()倒着打印列表 list_name.reverse() #reverse()方法永久性地修改列表元素的排列顺序
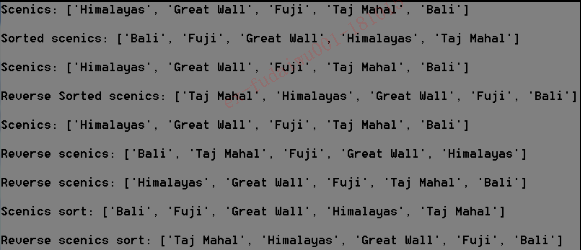
1 #3-8 2 scenics=['Himalayas','Great Wall','Fuji','Taj Mahal','Bali'] 3 print("Scenics: "+str(scenics)) 4 print("\nSorted scenics: "+str(sorted(scenics))) 5 print("\nScenics: "+str(scenics)) 6 print("\nReverse Sorted scenics: "+str(sorted(scenics,reverse=True))) 7 print("\nScenics: "+str(scenics)) 8 scenics.reverse() 9 print("\nReverse scenics: "+str(scenics)) 10 scenics.reverse() 11 print("\nReverse scenics: "+str(scenics)) 12 scenics.sort() 13 print("\nScenics sort: "+str(scenics)) 14 scenics.sort(reverse=True) 15 print("\nReverse scenics sort: "+str(scenics))
运行结果:
第四章 操作列表
4.1 遍历列表
for list_name in list_names:
loop operation #循环内操作
out loop operation #循环结束后的系列操作
4.2 缩进
python通过缩进来判断程序的结构
4.3 创建数值列表
-函数range() #range:范围
range(start,end[,step]) #取[start,end)之间的数值,step为可选参数,用于设置步长
1 #打印1-10之间的奇数 2 for value in range(1,11,2): 3 print(value,end=" ")
运行结果:
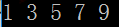
-函数list()与函数range()
函数list()与range()结合可生成数字列表
print(list(range(1,5))) #[1,2,3,4]
1 eg.生成数字1-10的平方值 2 3 squares=[] 4 for i in range(1,11): 5 squares.append(i**2) 6 print(squares)
测试结果:
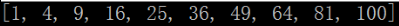
-对数字列表进行简单的统计
max(list_name) #统计最大值
min(list_name) #统计最小值
sum(list_name) #统计列表和
-列表解析
列表解析将for循环和创建新元素的代码合并成一行
# 生成数字1-10的平方值 squares=[i**2 for i in range(1,11)] print(squares)
测试结果:

4.4 使用列表的一部分
-切片
#注意:以下m、n的值均可以为负值
list_name(m:n) #输出list列表中[m,n)之间的值
list(m:) #输出list列表中[m,end]之间的值,
list(:n) #输出list列表中[start,n]之间的值
-复制列表
new_list=list_name[:]
-元组
不可改变的列表被称为元组,形式上用圆括号括起来而非方括号,如
(1,2,3,4,5)
第五章 if语句
-if语句模型
#elif与else均可以省略
#Python只执行if-elif-else结构中的一个代码块,它依次检查条件测试,直到遇到通过了的条件测试,执行后面的语句。执行完成后,将跳过结构中余下的测试,执行紧跟在结构后面的代码
#如果只执行一个代码块,就使用if-elif-else结构;如果要运行多个代码块,就使用一系列独立的if语句
if conditional_test_1:
do sth...
elif conditional_test_2:
do sth...
elif conditional_test_n:
do sth...
else:
do sth...
-逻辑表达式
- Python中检查是否相等时区分大小写 #使用函数lower()解决该问题,函数lower()不会改变变量的大小写
- 检查多个条件使用and与or
- 检查列表中是否(不)包含某个值使用(not)in
-if语句与列表
if list_names #列表中元素不为空时为true
-Python建议,在诸如==、>=和<=等比较运算符两边各添加一个空格
第六章 字典
6.2 使用字典
字典是一系列键-值对,与键相关联的值可以是数字、字符串、列表乃至字典。字典格式如下:
{"key1":"value1","key2":"value2",...,"keyn":"valuen"}
-字典添加键-值对
dictionary_name[key]=value
-访问字典中的值
dictionary_name[key]
-删除键-值对
del dictionary_name[key] #删除的键-值对永久消失
6.3遍历字典
#遍历key-value值
for key,value in dictionary_name.items() #key、value可以是任意值
#遍历key值
for key in dictionary_name.keys() #key值的遍历顺序随机
按顺序遍历字典中的key值
for key in sorted(dictionary_name.keys())
#遍历value值
for value in dictionary_name.values()
去除重复项
for value in set(dictionary_name.values())
6.4 嵌套
字典、列表可以相互嵌套或自嵌套
1 试一试 2 3 #6-1 4 friend = { 5 "first_name":"shen", 6 "last_name":"kang", 7 "age":30, 8 "city":"hangzhou" 9 } 10 print("My friend's first name is: "+friend["first_name"].title()) 11 print("My friend's last name is: "+friend["last_name"].title()) 12 print("My friend's age is: "+str(friend["age"]).title()) 13 print("My friend's living city is: "+friend["city"].title()) 14 15 #6-2 16 lucky_number = { 17 "zhushoubin":18, 18 "fuxiangcun":23, 19 "shenkang":6, 20 "yangrongling":8, 21 "qiyandi":1 22 } 23 print("\nzhushoubin like the number: "+str(lucky_number["zhushoubin"])) 24 print("fuxiangcun like the number: "+str(lucky_number["fuxiangcun"])) 25 print("shenkang like the number: "+str(lucky_number["shenkang"])) 26 print("yangrongling like the number: "+str(lucky_number["yangrongling"])) 27 print("qiyandi like the number: "+str(lucky_number["qiyandi"])) 28 29 #6-3 30 dictionary = { 31 "print" : "打印", 32 "and" : "逻辑与", 33 "or" : "逻辑或", 34 "**" : "幂运算", 35 "+" : "加法运算" 36 } 37 print("\nprint:\n\t"+dictionary["print"]) 38 print("and:\n\t"+dictionary["and"]) 39 print("or:\n\t"+dictionary["or"]) 40 print("**:\n\t"+dictionary["**"]) 41 print("+:\n\t"+dictionary["+"]) 42 43 #6-4 44 print("") 45 for key,mean in dictionary.items(): 46 print(key+":\n\t"+mean) 47 48 #6-5 49 river_countries={ 50 "Nile":"Egypt", 51 "Changjiang":"China", 52 "Missouri":"America" 53 } 54 print("") 55 for river,country in river_countries.items(): 56 print("The "+river+" runs through "+country) 57 58 print("\nRiver:") 59 for river in river_countries.keys(): 60 print(river," ") 61 62 print("\nCountry:") 63 for country in river_countries.values(): 64 print(country," ") 65 66 67 68 #6-6 69 print("") 70 members=["fuxiangcun","sunmiaomiao","zhubin","qiyanru","qiyandi"] 71 for member in members: 72 for person in lucky_number.keys(): 73 if member == person: 74 print(person.title()+",thank you for your participation in the survey") 75 flag=False 76 break 77 if member != person: 78 print(member.title()+",would you like participation in the survey ") 79 80 #6-7 81 friend2 = { 82 "first_name":"yu", 83 "last_name":"zhongmin", 84 "age":27, 85 "city":"xuancheng" 86 } 87 88 friend3 = { 89 "first_name":"xu", 90 "last_name":"dan", 91 "age":33, 92 "city":"xiaoxian" 93 } 94 95 friends = [friend1,friend2,friend3] 96 97 for friend in friends: 98 friend_info(friend) 99 100 #6-9 101 favourite_places_dictionary={ 102 "yuzhongmin":["yunnan","dali","beijing"], 103 "fuxiangcun":["shanghai","sanya",""], 104 "zhushoubin":["japan","america"] 105 } 106 107 for person,favourite_places in favourite_places_dictionary.items(): 108 print("\n"+person.title()+" like places: ",end="") 109 for favourite_place in favourite_places: 110 print(favourite_place.title(),end=" ") 111 112 #6-11 113 cities={ 114 "Beijing":{ 115 "country":"China", 116 "population":21730000, 117 "fact":"the capital of China" 118 }, 119 "Paris":{ 120 "country":"France", 121 "population":11000000, 122 "fact":"romatic capital" 123 }, 124 "New York":{ 125 "country":"America", 126 "pupulation":8510000, 127 "fact":"disire city" 128 } 129 } 130 print("") 131 for city,describes in cities.items(): 132 print(city+":") 133 for describe,value in describes.items(): 134 print(" "+describe+": "+str(value))
第七章 用户输入和while循环
7.1 input函数
#python2.7中使用raw_input()输入
#python2中也有input()函数,它将用户的输入解读为代码并尝试运行它们
- message=input("description")
- input输入均为字符串,可用int()函数转换为数字
7.2 while循环
- break continue
- for循环与while循环遍历列表
for循环与while循环都可以遍历列表,但是for循环中不应修改列表,否则将导致Python难以跟踪其中的元素。要在遍历列表的同时对其进行修改,可以使用while循环
- while循环与列表、字典结合
while list_name: #循环不断运行,直到列表为空
while value in list_name: #循环不断进行过,判断value是否在list_name中
1 #7-1 2 car=input("What car would you want to lease?\n") 3 print("Let me see if I can find you a "+car) 4 5 #7-2 6 people_number=input("\nHow many people are here,please!\n") 7 if int(people_number)>8: 8 print("I'm very sorry,we have not table!") 9 else: 10 print("Yeah,we hava a table,welcome!") 11 12 #7-3 13 number=input("\nPlease input a number\n") 14 if int(number)%10 == 0: 15 print(number+"是10的整数倍") 16 else: 17 print(number+"不是10的整数倍") 18 19 #7-4 20 21 message = "\nWhat ingredients do you want to add in pizza?\ 22 +\nYou can input 'q' to end the program\n" 23 while True: 24 ingredient=input(message) 25 if ingredient != 'q': 26 print("Ok,we will add "+ingredient+" in your pizza") 27 else: 28 break 29 30 #7-5 31 32 message="\nHow old are your?"\ 33 +"\nYour can enter 'q' to end the progress!\n" 34 age = input(message) 35 while age != "q": 36 if age.isdigit(): 37 if int(age) > 12: 38 print("The ticket is 12 dollars") 39 elif int(age) > 3 and int(age) <= 12: 40 print("The ticket is 10 dollars") 41 elif int(age) <= 3 and int(age) > 0: 42 print("Baby are free") 43 else: 44 print("Print wrong!") 45 else: 46 print("Print wrong!") 47 if age != 'q': 48 age = input(message) 49 50 #7-8 51 sandwich_orders=["hardark","jeokea","pastrami","oswere","pastrami","opds","pastrami"] 52 finished_sandwich=[] 53 while sandwich_orders: 54 sandwich = sandwich_orders.pop() 55 print("I made your "+sandwich+" sandwich") 56 finished_sandwich.append(sandwich) 57 print("\nI have made these sandwich:") 58 for sandwich in finished_sandwich: 59 print(sandwich,end=" ") 60 61 #7-9 62 print("\n") 63 while "pastrami" in finished_sandwich: 64 finished_sandwich.remove("pastrami") 65 for sandwich in finished_sandwich: 66 print(sandwich,end=" ")
第八章 函数
8.1 函数编写指南
- 应给函数指定描述性名称,且只在其中使用小写字母和下划线
- 每个函数都应包含简要阐述其功能的注释,该注释应紧跟在函数定义后面,并采用文档字符串格式
def function_name():
"""
annotation
...
"""
function_body...
- 给形参指定默认值时,等号两边不要有空格
def function_name(parameter_0,parameter_1='default value')
- 定义函数时,如果形参很多,长度过长,可在函数定义中输入左括号按回车键,并在下一行按2次Tab键,从而将形参列表和只缩进一层的函数体区别开来
def function_name(
parameter_0,parameter_1,parameter_2,
parameter_3,...,parameter_n):
function body...
- 建议在相邻的函数之间使用两个空行将其隔开
8.2 定义函数
def function_name(parameter_name1,parameter_name2,...,parameter_namen): #参数可以为空
funciton_body
function_name(parameter_value1,parameter_value2,...,parameter_valuen) #调用函数体
8.3 参数类型
- 位置实参
- 关键字实参 传递给函数的名称-值对,可直接在实参中将名称和值关联起来
function_name(parameter_name1=parameter_value1,parameter_name2=parameter_value2,...,parameter_namen=parameter_valuen)
- 默认值 编写函数时,可给每个形参指定默认值。当显式的给指定默认值的形参提供实参时,Python将忽略这个形参的默认值
使用默认值时,在形参列表中必须先列出没有默认值的形参,再列出有默认值的形参
8.4 返回值
- 在函数中,可以使用return语句将值返回到调用函数的代码行
- 返回简单值
- 可使用默认值(空字符串)让实参变成可选的
def function_name(parameter_name1,parameter_name2,...,parameter_namen=''):
...
if parameter_namen: #Python将非空字符串解释为True
...
else:
...
...
- 返回字典、列表
- 禁止函数修改列表 使用列表实参的副本
"""
虽然向函数传递列表的副本可以保留原始列表的内容,但除非有充足的理由这样做,否则还是传递原始列表——避免函数花时间和内存创建副本,从而降低了效率,在处理大型列表时尤其如此
"""
function_name(function_value[:])
8.5 传递任意数量的参数
- 传递任意数量的实参
"""
形参名*parameter_name中的星号让Python创建一个名为parameter_name的空元祖,并将收到的所有值都封装到这个元组中
如果要让函数接受不同类型的实参,必须在函数定义中将接纳任意数量实参的形参放在最后
"""
def function_name(*parameter_name):
...
- 使用任意数量的关键字实参
def function_name(**parameter_name):
...
8.6 将函数存储在模块中
- 导入整个模块
import module_name [as alias]
module_name.function_name() #添加别名后可以使用 alias.function_name
- 导入特定的函数
from module_name import function_name [as alias]
fuction_name() #alias()
#导入模块中的多个函数
from module_name import function_name1,function_name2,...,function_namen
#导入模块中的所有函数
from module_name import *
1 #8-1 2 def display_message(): 3 print("I will learn Function in this lesson") 4 5 display_message() 6 7 #8-2 8 def favorite_book(title): 9 print("One of my favorite books is "+title) 10 11 favorite_book("Alice in wonderland") 12 13 #8-3 14 def make_shirt(size,word): 15 print("The T-shirt size is "+size+" and the word on the T-shirt is \""+word+"\"") 16 17 make_shirt("XXL","I love my motherland!") 18 19 #8-4 20 def make_shirt(size,word="I love Python"): 21 print("The T-shirt size is "+size+" and the word on the T-shirt is \""+word+"\"") 22 23 make_shirt("XXL") 24 make_shirt("XL") 25 make_shirt("M","I love Java") 26 27 #8-5 28 def describe_city(city,country="China"): 29 print(city+" is in "+country) 30 31 32 describe_city("Beijing") 33 describe_city("Shanghai") 34 describe_city("New York","America") 35 36 #8-6 37 def city_country(city,country): 38 return "\""+city+","+country+"\"" 39 40 print(city_country("Santiago","Chile")) 41 print(city_country("Tokyo","China")) 42 print(city_country("Beijing","China")) 43 44 #8-7 45 def make_album(singer,album_name): 46 album = {"singer":singer,"album_name":album_name} 47 return album 48 49 print(make_album("Join","看我72变")) 50 print(make_album("Jay Chou","依然范特西")) 51 print(make_album("Andy","Everyone is NO.1")) 52 53 #8-8 54 message = "\n请输入专辑的歌手和名称" 55 message += "\n您可以随时输入q键取消该操作" 56 while True: 57 print(message) 58 singer = input("请输入歌手名: ") 59 if singer == "q": 60 break 61 else: 62 album_name = input("请输入专辑名: ") 63 if album_name == "q": 64 break 65 else: 66 album={"singer":singer,"albume_name":album_name} 67 print(album) 68 69 #8-9 70 magacians=["大卫·科波菲尔","刘谦","傅琰东","刘世杰"] 71 72 def show_magicians(names): 73 for name in names: 74 print(name) 75 76 show_magicians(magacians) 77 78 #8-10 79 80 def make_great(names): 81 i = 0 82 while i < len(names): 83 names[i] = "著名的魔术师:"+names[i] 84 i += 1 85 86 make_great(magacians) 87 show_magicians(magacians) 88 89 #8-11 90 def make_great(names): 91 i = 0 92 great_magacians = [] 93 while names: 94 great_magacians.append("伟大的魔术师:" + names.pop()) 95 return great_magacians 96 97 show_magicians(make_great(magacians[:])) 98 show_magicians(magacians) 99 100 #8-12 101 def make_pizza(*toppings): 102 print("\nMake pizza for this toppings:") 103 for topping in toppings: 104 print("-"+topping) 105 106 make_pizza("Dried yeast") 107 make_pizza("Dried yeast","One egg","green pepper") 108 make_pizza("Carrot","Onion","Sausage") 109 110 #8-13 111 def build_profile(first_name,last_name,**introduction): 112 person={} 113 person["first_name"] = first_name 114 person["last_name"] = last_name 115 for key,value in introduction.items(): 116 person[key] = value 117 return person 118 119 myself = build_profile("Dave","Fu",hometown = "Anhui",Colledge="Huaibei normal university", 120 major = "Computer science and technology") 121 print(myself) 122 123 #8-14 124 def make_car(manufacturer,production_place,**introduction): 125 car = {} 126 car["manufacturer"] = manufacturer 127 car["production_place"] = production_place 128 for key,value in introduction.items(): 129 car[key] = value 130 return car 131 132 car1 = make_car("subaru","outback",color="blue",tow_package=True) 133 print(car1)
第九章 类
9.1 类编码风格
- 类名采用驼峰命名法——类名中的每个单词的首字母大写
- 每个类后面均应包含一个文档字符串
- 可使用空行来组织代码,但不要滥用。类中可使用一个空行来分隔方法,模块中可使用两个空行来分隔类
- 需要同时导入标准库中的模块和自定义模块时,先导入标准库中的模块,再隔一个空行导入自定义模块
9.2 类的创建和使用
1 class Dog(): 2 def __init__(self, name, age, color=''): 3 self.name = name 4 self.age = age 5 if color: 6 self.color = color 7 else: 8 self.color = "red" 9 10 def sit_down(self): 11 print(self.name + "is sitting down now!") 12 13 def roll_over(self): 14 print(self.name + "is roll over now!") 15 16 def desc(self): 17 print("My dog's name is "+self.name+", it's " +str(self.age)+" years old!, it's "+ self.color) 18 19 my_dog = Dog("Lighting",5) 20 my_dog.sit_down() 21 my_dog.roll_over() 22 my_dog.desc() 23 print(my_dog.name)
- Python中的类名首字母大写,类定义中的括号是空的(Python2中,括号中为object)
- 类中的函数称为方法,包括Python默认方法与普通方法(或自定义方法)
- __init__()为Python中的默认方法,每次创建实例时都会默认调用该方法。该方法中,开头和末尾均有2个下划线
- __init__()中的形参self必不可少,且必须位于其它参数的前面。self默认指向实例本身的引用,让实例能够访问类中属性和方法。每个与类相关联的方法调用都自动传递实参self
- 以self为前缀的变量可供类中的所有方法使用,还可以通过类中的任何实例来访问这些变量。可通过实例访问的变量称为属性
9.3 使用类和实例
1 class Dog(): 2 def __init__(self, name): 3 self.name = name 4 self.age = 0 5 6 def update_age(self, age_update): 7 if age_update < self.age: 8 print("年龄不能减小") 9 else: 10 self.age += self.age 11 print("年龄:"+str(self.age)) 12 13 def increment_age(self, age_increment): 14 self.age += age_increment 15 print("年龄:"+str(self.age)) 16 17 def desc_age(self): 18 print(self.name + "的年龄为:"+str(self.age)) 19 20 my_dog = Dog("lighting") 21 my_dog.desc_age() 22 my_dog.increment_age(1) 23 my_dog.desc_age() 24 my_dog.update_age(0) 25 my_dog.desc_age() 26 my_dog.update_age(2) 27 my_dog.desc_age()
- 类中的每个属性都必须有初始值,某些情况下,可在__init__()方法中直接指定某属性的初始值,此时无需包含为它提供初始值的形参
- 修改属性的值
- 直接修改属性的值
- 通过方法修改属性的值
- 通过方法对属性的值进行递增
9.4 继承
1 示例: 2 class Car(): 3 def __init__(self, make, model, year): 4 self.make = make 5 self.model = model 6 self.year = year 7 #里程计读数 8 self.odometer_reading = 0 9 10 def get_descriptive_name(self): 11 print(self.model+" "+self.make+" "+str(self.year)+" "+str(self.odometer_reading)) 12 13 def read_odometer(self): 14 print("This car has "+str(self.odometer_reading)+" miles on it\n") 15 16 def update_odometer(self, mileage): 17 if mileage < self.odometer_reading: 18 print("You can't roll back the odometer!") 19 else: 20 self.odometer_reading = mileage 21 22 def increment_odometer(self, miles): 23 self.odometer_reading += miles 24 25 class EletricCar(Car): 26 def __init__(self, make, model, year, electric_quantity ): 27 super().__init__(make, model, year) 28 self.electric_quantity = electric_quantity 29 30 def get_descriptive_name(self): 31 print(self.model+" "+self.make+" "+str(self.year)+" "+str(self.odometer_reading)+" "+str(self.electric_quantity)+"% electric_quantity") 32 33 34 my_car = EletricCar("tesla", "model s", 2017, 100) 35 my_car.get_descriptive_name() 36 my_car.read_odometer()
- 一个类继承另一个类时,将自动获得另一个类的属性和方法;原有的类称为父类,继承的类称为子类
- 子类__init__()方法继承父类的__init__()方法: super().__init__()
- 创建子类时,父类必须包含在当前文件中,且位于子类前面
- 定义子类时,必须在括号中指定父类的名称
9.5 导入类
- 导入单个类 from module_name import class_name
- 导入多个类 from module_name import class_name1, class_name2, ...
- 导入模块中的所有类 from module_name import *
- 导入模块 import module_name
9.6 Python标准库
eg. from collections import OrderDict #导入有序字典
1 #9-1 2 class Restaurant(): 3 #餐款名称 烹饪类型 4 def __init__(self, restaurant_name, cuisine_type): 5 self.restaurant_name = restaurant_name 6 self.cuisine_type = cuisine_type 7 8 def describe_restaurant(self): 9 print("The restaurant's name is "+self.restaurant_name+" and the cuisine type is "+self.cuisine_type) 10 11 def open_restaurant(self): 12 print("The restaurant " +self.restaurant_name+" is opening now") 13 14 restaurant = Restaurant("重庆火锅","川菜") 15 print("The restaurant name is "+restaurant.restaurant_name) 16 print("The restaurant cuisine type is "+restaurant.cuisine_type) 17 restaurant.describe_restaurant() 18 restaurant.open_restaurant() 19 20 #9-2 21 restaurant1 = Restaurant("贡院蜀楼","川菜") 22 restaurant2 = Restaurant("皖南水乡","徽菜") 23 restaurant3 = Restaurant("忘湘园","湘菜") 24 restaurant1.describe_restaurant() 25 restaurant2.describe_restaurant() 26 restaurant3.describe_restaurant() 27 28 #9-3 29 class User(): 30 def __init__(self, first_name, last_name, sex, age, job): 31 self.first_name = first_name 32 self.last_name = last_name 33 self.sex = sex 34 self.age = age 35 self.job = job 36 37 def describe_user(self): 38 introduction = self.first_name+"·"+self.last_name 39 if self.sex == "m": 40 introduction =introduction + " is a man and he is "+str(self.age)+" years old, his job is "+self.job 41 else: 42 introduction =introduction + " is a woman and she is "+str(self.age)+" years old, her job is "+self.job 43 print(introduction) 44 45 user1 = User("守兵", "朱", "m", 31, "技术员") 46 user2 = User("相存", "傅", "w", 32, "预算员") 47 user1.describe_user() 48 user2.describe_user() 49 50 #9-4 51 class Restaurant(): 52 #餐款名称 烹饪类型 53 def __init__(self, restaurant_name, cuisine_type): 54 self.restaurant_name = restaurant_name 55 self.cuisine_type = cuisine_type 56 self.number_served = 0 57 58 def describe_restaurant(self): 59 print("The restaurant's name is "+self.restaurant_name+" and the cuisine type is "+self.cuisine_type) 60 61 def open_restaurant(self): 62 print("The restaurant " +self.restaurant_name+" is opening now") 63 64 def set_number_served(self, number_served): 65 if self.number_served > number_served: 66 print("服务人数不能减少") 67 else: 68 self.number_served = number_served 69 70 def increment_number_served(self, increment_number_served): 71 self.number_served += increment_number_served 72 73 restaurant = Restaurant("重庆火锅","川菜") 74 restaurant.set_number_served(10) 75 print("服务人数: "+str(restaurant.number_served)) 76 restaurant.increment_number_served(13) 77 78 #9-5 79 class User(): 80 def __init__(self, first_name, last_name, sex, age, job): 81 self.first_name = first_name 82 self.last_name = last_name 83 self.sex = sex 84 self.age = age 85 self.job = job 86 self.login_attempts = 0 87 88 def describe_user(self): 89 introduction = self.first_name+"·"+self.last_name 90 if self.sex == "m": 91 introduction =introduction + " is a man and he is "+str(self.age)+" years old, his job is "+self.job 92 else: 93 introduction =introduction + " is a woman and she is "+str(self.age)+" years old, her job is "+self.job 94 print(introduction) 95 96 def increment_login_attempts(self): 97 self.login_attempts += 1 98 99 def reset_login_attempts(self): 100 self.login_attempts = 0 101 102 103 user = User("守兵", "朱", "m", 31, "技术员") 104 user.increment_login_attempts() 105 user.increment_login_attempts() 106 print("登录次数:"+str(user.login_attempts)) 107 user.reset_login_attempts() 108 print("登录次数:"+str(user.login_attempts)) 109 110 #9-6 111 class Restaurant(): 112 #餐款名称 烹饪类型 113 def __init__(self, restaurant_name, cuisine_type): 114 self.restaurant_name = restaurant_name 115 self.cuisine_type = cuisine_type 116 self.number_served = 0 117 118 def describe_restaurant(self): 119 print("The restaurant's name is "+self.restaurant_name+" and the cuisine type is "+self.cuisine_type) 120 121 def open_restaurant(self): 122 print("The restaurant " +self.restaurant_name+" is opening now") 123 124 def set_number_served(self, number_served): 125 if self.number_served > number_served: 126 print("服务人数不能减少") 127 else: 128 self.number_served = number_served 129 130 def increment_number_served(self, increment_number_served): 131 self.number_served += increment_number_served 132 133 restaurant = Restaurant("重庆火锅","川菜") 134 restaurant.set_number_served(10) 135 print("服务人数: "+str(restaurant.number_served)) 136 restaurant.increment_number_served(13) 137 138 class IceCreamStand(Restaurant): 139 def __init__(self, restaurant_name, cuisine_type, flavors): 140 super().__init__(restaurant_name, cuisine_type) 141 self.flavors = flavors 142 143 def describe_flavors(self): 144 print("冰激凌口味:"+str(self.flavors)) 145 146 flavors = ['巧克力','奶油','抹茶','香草','香芋','咖啡','树莓','芒果','绿茶','朗姆','橘子'] 147 ice_cream_stand = IceCreamStand("冰激凌小店","冷饮",flavors) 148 ice_cream_stand.describe_flavors() 149 150 #9-7 151 class User(): 152 def __init__(self, first_name, last_name, sex, age, job): 153 self.first_name = first_name 154 self.last_name = last_name 155 self.sex = sex 156 self.age = age 157 self.job = job 158 self.login_attempts = 0 159 160 def describe_user(self): 161 introduction = self.first_name+"·"+self.last_name 162 if self.sex == "m": 163 introduction =introduction + " is a man and he is "+str(self.age)+" years old, his job is "+self.job 164 else: 165 introduction =introduction + " is a woman and she is "+str(self.age)+" years old, her job is "+self.job 166 print(introduction) 167 168 def increment_login_attempts(self): 169 self.login_attempts += 1 170 171 def reset_login_attempts(self): 172 self.login_attempts = 0 173 174 175 user = User("守兵", "朱", "m", 31, "技术员") 176 177 class Admin(User): 178 def __init__(self, first_name, last_name, sex, age, job, privileges): 179 super().__init__(first_name, last_name, sex, age, job) 180 self.privileges = privileges 181 182 def show_privileges(self): 183 print("管理员权限: "+str(self.privileges)) 184 185 privileges = ["can add post", "can delete post", "can ban user"] 186 admin = Admin("守兵", "朱", "m", 31, "技术员",privileges) 187 admin.show_privileges() 188 189 #9-8 190 class User(): 191 def __init__(self, first_name, last_name, sex, age, job): 192 self.first_name = first_name 193 self.last_name = last_name 194 self.sex = sex 195 self.age = age 196 self.job = job 197 self.login_attempts = 0 198 199 def describe_user(self): 200 introduction = self.first_name+"·"+self.last_name 201 if self.sex == "m": 202 introduction =introduction + " is a man and he is "+str(self.age)+" years old, his job is "+self.job 203 else: 204 introduction =introduction + " is a woman and she is "+str(self.age)+" years old, her job is "+self.job 205 print(introduction) 206 207 def increment_login_attempts(self): 208 self.login_attempts += 1 209 210 def reset_login_attempts(self): 211 self.login_attempts = 0 212 213 user = User("守兵", "朱", "m", 31, "技术员") 214 215 class Privilege(): 216 def __init__(self, privileges): 217 self.privileges = privileges 218 219 def show_privileges(self): 220 print("管理员权限: "+str(self.privileges)) 221 222 class Admin(User): 223 def __init__(self, first_name, last_name, sex, age, job, privileges): 224 super().__init__(first_name, last_name, sex, age, job) 225 self.privileges = privileges 226 227 privileges = Privilege(["can add post", "can delete post", "can ban user"]) 228 admin = Admin("守兵", "朱", "m", 31, "技术员",privileges) 229 admin.privileges.show_privileges()
第十章 文件和异常
10.1 读写文件
1 pi_digits.txt文件 2 3.1415926535 3 8979323846 4 2643383279 5 6 #读文件 7 file_name = "pi_digits.txt" 8 #在当前执行的文件所在的目录中查找指定的文件 9 with open(file_name) as file_object: 10 contents = file_object.read() 11 print(contents.rstrip()) #删除末尾的空白行 12 13 #(with代码块内)逐行读取 line可以是任意变量 14 with open(file_name) as file_object: 15 for line in file_object: 16 print(line.rstrip()) 17 18 with open(file_name) as file_object: 19 lines = file_object.readlines() 20 21 #(with代码块外)逐行读取 22 #处理文件内容 23 pi = "" 24 for line in lines: 25 pi += line.strip() 26 27 print("pi = "+pi) 28 print("pi精度: "+str(len(pi)-2)+"位") 29 30 #写文件 31 file_name = "test.txt" 32 ''' 33 文件读取模式: 34 -r: 只读 35 -w: 写 覆盖写,不可读 36 -a: 附加 添加写,不可读 37 -r+: 读写 可读可写 38 ''' 39 with open(file_name,"a") as file_object: 40 file_object.write("I love python 才怪!\n") 41 # contents = file_object.read() #报错 42 print(contents)
10.2 异常
python异常继承关系
BaseException
+-- SystemExit
+-- KeyboardInterrupt
+-- GeneratorExit
+-- Exception
+-- StopIteration
+-- StopAsyncIteration
+-- ArithmeticError
| +-- FloatingPointError
| +-- OverflowError
| +-- ZeroDivisionError
+-- AssertionError
+-- AttributeError
+-- BufferError
+-- EOFError
+-- ImportError
| +-- ModuleNotFoundError
+-- LookupError
| +-- IndexError
| +-- KeyError
+-- MemoryError
+-- NameError
| +-- UnboundLocalError
+-- OSError
| +-- BlockingIOError
| +-- ChildProcessError
| +-- ConnectionError
| | +-- BrokenPipeError
| | +-- ConnectionAbortedError
| | +-- ConnectionRefusedError
| | +-- ConnectionResetError
| +-- FileExistsError
| +-- FileNotFoundError
| +-- InterruptedError
| +-- IsADirectoryError
| +-- NotADirectoryError
| +-- PermissionError
| +-- ProcessLookupError
| +-- TimeoutError
+-- ReferenceError
+-- RuntimeError
| +-- NotImplementedError
| +-- RecursionError
+-- SyntaxError
| +-- IndentationError
| +-- TabError
+-- SystemError
+-- TypeError
+-- ValueError
| +-- UnicodeError
| +-- UnicodeDecodeError
| +-- UnicodeEncodeError
| +-- UnicodeTranslateError
+-- Warning
+-- DeprecationWarning
+-- PendingDeprecationWarning
+-- RuntimeWarning
+-- SyntaxWarning
+-- UserWarning
+-- FutureWarning
+-- ImportWarning
+-- UnicodeWarning
+-- BytesWarning
+-- ResourceWarning
1 #coding=gbk 2 #除法 3 print("输入2个数字,用于除法操作\n") 4 print("输入'q'以退出\n") 5 6 while True: 7 firstNum = input("\n输入第一个数字:") 8 if firstNum == 'q': 9 break 10 secondNum = input("\n请输入第二个数字:") 11 if secondNum == 'q': 12 break 13 try: 14 answer = int(firstNum)/int(secondNum) 15 # print("\n商:"+str(answer)) 16 except Exception: 17 # print("不能除以0") 18 pass 19 else: 20 print("\n商:"+str(answer))
获取不同的异常信息
--str(e):返回字符串类型,只给出异常信息,不包括异常信息的类型,如1/0的异常信息
'integer division or modulo by zero'
--repr(e):给出较全的异常信息,包括异常信息的类型,如1/0的异常信息
"ZeroDivisionError('integer division or modulo by zero',)"
--e.message:获得的信息同str(e)
--采用traceback模块:需要导入traceback模块,此时获取的信息最全,与python命令行运行程序出现错误信息一致。使用traceback.print_exc()打印异常信息到标准错误,就像没有获取一样,或者使用traceback.format_exc()将同样的输出获取为字符串。你可以向这些函数传递各种各样的参数来限制输出,或者重新打印到像文件类型的对象。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号