String
String
- 双引号括起来的字符串创建后,长度不能发生变化
- 双引号括起来的字符串是存在于方法区的字符串常量池中
- 垃圾回收器是不会释放常量的
- 基本类型存储的是值,引用类型存储的是地址
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//基本类型存储的是值
int a = 100;
int b = 100;
System.out.println(a==b);//true
char c = 'd';
char d = 'd';
System.out.println(c==d);//true
//引用类型存储的是地址值
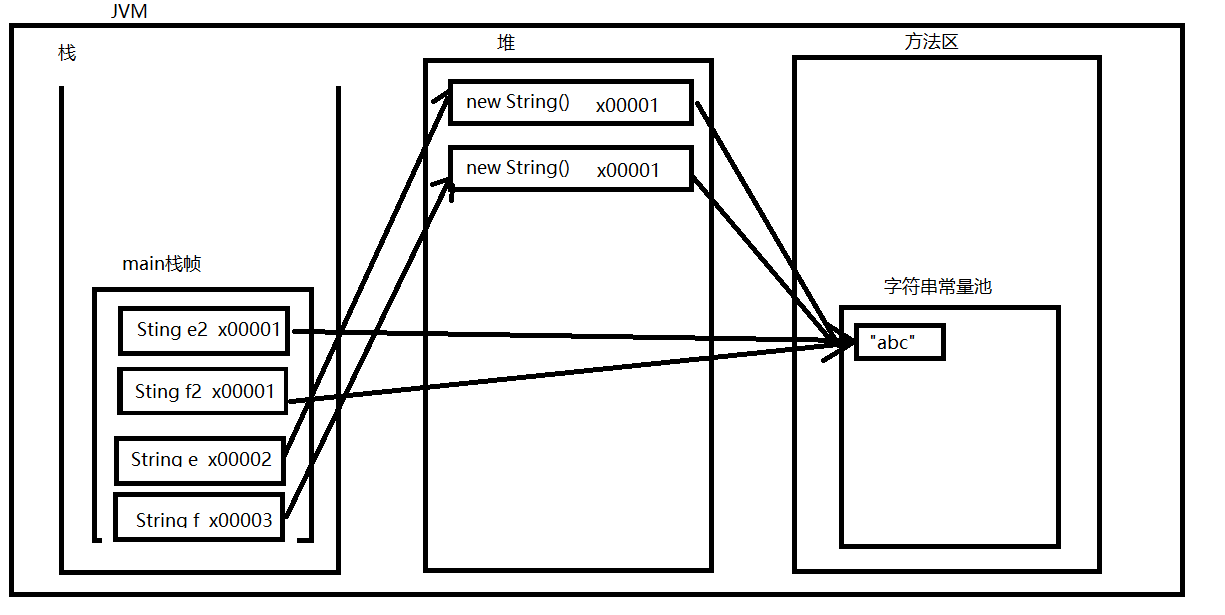
String e = new String("abc");
String f = new String("abc");
System.out.println(e==f);//false
String e2 = "abc";
String f2 = "abc";
System.out.println(e2==f2);//true
}
}
String的常用构造方法
//1. "abc"
String a1 = "abc";
//2. new String("abc")
String a2 = new String("abc");
//3.new String(byte[])
byte[] b1 = {97,98,99};
String a3 = new String(b1);
System.out.println(a3);//abc
//4.new String(byte[],索引位置,截取长度)
String a4 = new String(b1,1,2);
System.out.println(a4);//bc
//5.new String(char[])
char[] b2 = {'我','爱','学','习'};
String a5 = new String(b2);
System.out.println(a5);//我爱学习
//6.new String(char[],索引位置,截取长度)
String a6 = new String(b2,1,3);
System.out.println(a6);//爱学习
String 的常用方法
public class Demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
//String的底层结构是char[]数组
// String的常用方法
// 1.charAt(int i) 返回所在索引的字符,从0开始
String str = "afsdfsldk";
char c = str.charAt(5);
System.out.println(c); // s
// 2.length() 返回字符串的长度(包括空格)
int length = str.length();
System.out.println(length);// 9
// 3. isEmpty() 判断字符串长度是否为空,为null的话会报空指针异常
boolean empty = str.isEmpty();// false
System.out.println(empty);
String str2 = null;
try {
boolean empty1 = str2.isEmpty();//java.lang.NullPointerException
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("空指针异常");
}
// 4.compareTo(String s)从第一位开始比,如果一样,返回0,前大返回负数,前小返回正数
// 5.compareToIgnoreCase(String s)忽略大小写,其他跟compareTo()一致
int i = "abc".compareTo("abc");
int i2 = "bac".compareTo("abc");
int k = "abc".compareTo("cba");
int[] j = new int[3];
j[0] = i;
j[1] = i2;
j[2] = k;
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(j));
// 6.contains(String s)是否包含莫个字符串,返回boolean值
Boolean abc = str.contains("dd");
System.out.println(abc);
// 7.contentEquals(new StringBuffer()) 比较String类型的字符串和StringBuffer类型的字符串的内容是否一致
boolean d = str.contentEquals(new StringBuffer("afsdfsldk"));
System.out.println(d);
boolean flag = str.contentEquals(new StringBuilder("afsdfsldk"));
System.out.println(flag);
// 8.endsWith(String s)是否以某个字符串结尾
// startWith(String s)是否以某个字符串开始
// startWith(String s,int index)index处是否以某个字符串开始
boolean ldk = str.endsWith("ldk");
boolean afs = str.startsWith("afs");
boolean sdf = str.startsWith("sdf", 2);
System.out.println(ldk); //true
System.out.println(afs); //true
System.out.println(sdf); //true
// 9.equals(String s)和equalsIgnoreCase(String s)比较两字符串是否相等
boolean abc1 = "abc".equals("abc");
boolean aBc = "abc".equalsIgnoreCase("ABc");
System.out.println(abc1); //true
System.out.println(aBc); //true
// 10.getBytes() 返回byte数组
byte[] bytes = str.getBytes();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));// [97, 102, 115, 100, 102, 115, 108, 100, 107]
// 11.getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin) 将选中内容复制到dst数组中
// toCharArray() 返回一个字符串数组
int lenth = str.length();
char[] chars = new char[lenth];
str.getChars(0,lenth-2,chars,2);
char[] chars1 = str.toCharArray();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(chars1));// [a, f, s, d, f, s, l, d, k]
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(chars));// [ , , a, f, s, d, f, s, l]
// 12.indexOf(String s || int i || char c || int i,int i1) 返回字符串的所在索引
// lastIndexOf(String s || int i || char c || int i,int i1) 返回字符串的最后出现的索引
int i3 = "abc".indexOf(97);//0
System.out.println(i3);
int a = "abc".indexOf('a');
System.out.println(a); //0
int eds = "abcd".indexOf("eds");
System.out.println(eds); //-1
int cd = "abcd".indexOf("cd");
System.out.println(cd); //2
// indexOf(int i,int i1) 从i1处开始找,是否存在i对应的字符,有则返回它的索引,无则返回-1
int i1 = "abdcd".indexOf(97, 1);
int c1 = "abcde".indexOf('c', 2);
System.out.println(c1); //2
System.out.println(i1); //-1
int bc = "abcde".indexOf("bc", 2);
System.out.println(bc); //-1
int i4 = "abdabcabdaa".lastIndexOf(97);
System.out.println(i4);
/* 13. regionMatches((boolean ignoreCase), int toffset, String other, int ooffset, int len)
判断 两字符串分别从指定索引开始是否相等
*/
boolean fsd = "afsdfsdf".regionMatches(2, "fsd", 1, 2);
System.out.println(fsd);
/* 14.replace(String s,String s1) 将所有的s,替换成s1,如果s不存在,则不替换
replaceFirst(String s,String s1) 替换第一个出现的s
*/
String replace = "abcabcabc".replace("abcd", "cde");
String replace2 = "abcabcabc".replaceAll("abc", "cde");
String replace3 = "abcabcabc".replaceFirst("abc", "cde");
System.out.println(replace); //abcabcabc
System.out.println(replace2); //cdecdecde
System.out.println(replace3); //cdeabcabc
/*
15.split(String s,(int i)) 用出现的第i个s分割字符串,返回字符串数组
*/
String[] s = "dsf_sdf_sdfsd_df".split("_");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s)); //[dsf, sdf, sdfsd, df]
String[] s1 = "dsf_sdf_sdfsd_df".split("_", 2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s1));//[dsf, sdf_sdfsd_df]
/*
16. toUpperCase()转成大写
toLowerCase()转成小写
*/
String s2 = "abc".toUpperCase();//ABC
String s3 = "ABC".toLowerCase();//abc
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
// 17.trim()去除两边的的空格
String trim = " dfdsf fsdf ".trim();
System.out.println(trim);
/*18.println(Object obj)会调用String.valueOf(Object obj)方法
Static valueOf(Object obj) 会调用对象的toString()方法
所以,System.out.println(new Student());
等同于System.out.println(new Student().toString());*/
String s4 = String.valueOf(new Student());
System.out.println(s4); //我是Student的toString方法。。。
System.out.println(new Student()); //我是Student的toString方法。。。
System.out.println(new Student().toString()); //我是Student的toString方法。。。
String format = String.format("sd-fs-df", new String[]{"sdfdsf","sdfdsf","avasds"});
System.out.println(format);
}
}
class Student{
@Override
public String toString() { return "我是Student的toString方法。。。"; }
}
我成功因为我志在成功



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号