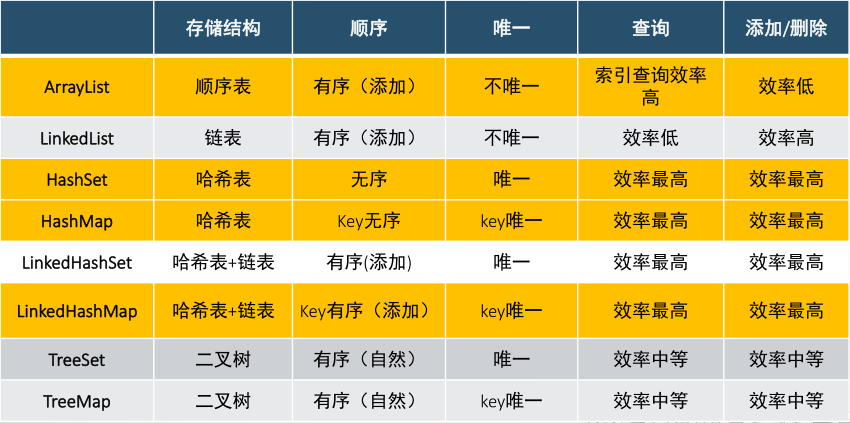
容器
集合架构
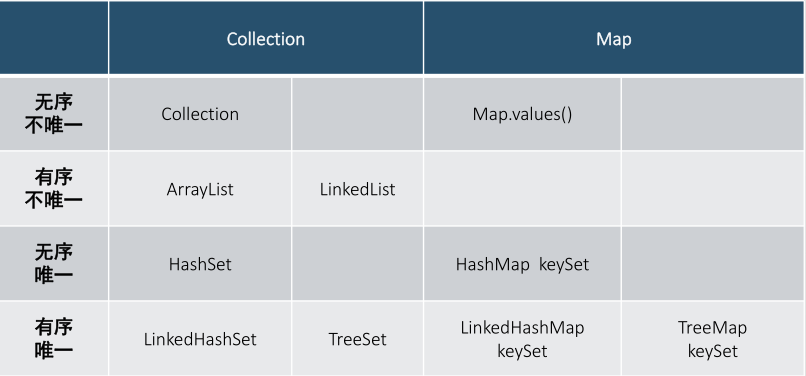
• Collection 接口存储一组不唯一,无序的对象
• List 接口存储一组不唯一,有序(索引顺序)的对象
• Set 接口存储一组唯一,无序的对象
• Map接口存储一组键值对象,提供key到value的映射
• Key 唯一 无序
• value 不唯一 无序
List
• List
• 特点:有序 不唯一(可重复)
• ArrayList(线程不安全,效率高) 线性表中的顺序表
• 在内存中分配连续的空间,实现了长度可变的数组
• 优点:遍历元素和随机访问元素的效率比较高
• 缺点:添加和删除需大量移动元素效率低,按照内容查询效率低,
• LinkedList (线程不安全,效率高)线性表中双向链表
• 采用双向链表存储方式。
• 缺点:遍历和随机访问元素效率低下
• 优点:插入、删除元素效率比较高(但是前提也是必须先低效率查询才可。如果插入删除发生在头尾可以减少查询次数)
• Vector (线程安全,效率底)和ArrayList一样(唯一区就是一个线程安全,一个线程不安全)

1 public class MyArrayList /*implements List*/ { 2 3 private Object[] elementData; 4 private int size; 5 6 7 public int size(){ 8 return size; 9 } 10 11 public boolean isEmpty(){ 12 return size==0; 13 } 14 15 public MyArrayList(){ 16 this(10); 17 } 18 19 public MyArrayList(int initialCapacity){ 20 if(initialCapacity<0){ 21 try { 22 throw new Exception(); 23 } catch (Exception e) { 24 e.printStackTrace(); 25 } 26 } 27 elementData = new Object[initialCapacity]; 28 } 29 30 public void add(Object obj){ 31 if(size==elementData.length){ 32 Object[] newArray = new Object[size*2+1]; 33 System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, newArray, 0, elementData.length); 34 elementData = newArray; 35 } 36 elementData[size++]=obj; 37 } 38 39 public Object get(int index){ 40 rangeCheck(index); 41 42 return elementData[index]; 43 } 44 45 public void remove(int index){ 46 rangeCheck(index); 47 int numMoved = size - index - 1; 48 if (numMoved > 0){ 49 System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, 50 numMoved); 51 } 52 elementData[--size] = null; 53 } 54 55 public void remove(Object obj){ 56 for(int i=0;i<size;i++){ 57 if(get(i).equals(obj)){ 58 remove(i); 59 } 60 } 61 } 62 63 public Object set(int index,Object obj){ 64 rangeCheck(index); 65 66 Object oldValue = elementData[index]; 67 elementData[index] = obj; 68 return oldValue; 69 } 70 71 public void add(int index,Object obj){ 72 rangeCheck(index); 73 74 ensureCapacity(); 75 76 System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1, 77 size - index); 78 elementData[index] = obj; 79 size++; 80 } 81 82 private void ensureCapacity(){ 83 if(size==elementData.length){ 84 Object[] newArray = new Object[size*2+1]; 85 System.arraycopy(elementData, 0, newArray, 0, elementData.length); 86 elementData = newArray; 87 } 88 } 89 90 91 private void rangeCheck(int index){ 92 if(index<0||index>=size){ 93 try { 94 throw new Exception(); 95 } catch (Exception e) { 96 e.printStackTrace(); 97 } 98 } 99 } 100 101 102 public static void main(String[] args) { 103 MyArrayList list = new MyArrayList(3); 104 list.add("333"); 105 list.add("444"); 106 list.add("5"); 107 list.add("344433"); 108 list.add("333"); 109 list.add("333"); 110 System.out.println(list.size()); 111 list.remove("444"); 112 System.out.println(list.size()); 113 } 114 115 }

1 public class Node { 2 private Node previous; 3 private Object obj; 4 private Node next; 5 6 public Node() { 7 } 8 9 public Node(Node previous, Object obj, Node next) { 10 super(); 11 this.previous = previous; 12 this.obj = obj; 13 this.next = next; 14 } 15 16 public Node getPrevious() { 17 return previous; 18 } 19 20 public void setPrevious(Node previous) { 21 this.previous = previous; 22 } 23 24 public Object getObj() { 25 return obj; 26 } 27 28 public void setObj(Object obj) { 29 this.obj = obj; 30 } 31 32 public Node getNext() { 33 return next; 34 } 35 36 public void setNext(Node next) { 37 this.next = next; 38 } 39 } 40 41 42 private void rangeCheck(int index){ 43 if(index<0||index>=size){ 44 try { 45 throw new Exception(); 46 } catch (Exception e) { 47 e.printStackTrace(); 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 52 public Object get(int index){ //2 53 rangeCheck(index); 54 // 0 1 2 3 4 55 Node temp = node(index); 56 if(temp!=null){ 57 return temp.getObj(); 58 } 59 return null; 60 } 61 62 public Node node(int index){ 63 Node temp = null; 64 if(first!=null){ 65 if (index < (size >> 1)) {// size >> 1 == size/2 66 temp = first; 67 for(int i=0;i<index;i++){ 68 temp = temp.getNext(); 69 } 70 }else{ 71 temp = last; 72 for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--){ 73 temp = temp.getPrevious(); 74 } 75 } 76 77 } 78 // LinkedList l; 79 return temp; 80 } 81 82 83 public void remove(int index){ 84 Node temp = node(index); 85 86 if(temp!=null){ 87 Node up = temp.getPrevious(); 88 Node down = temp.getNext(); 89 up.setNext(down); 90 down.setPrevious(up); 91 size--; 92 } 93 94 } 95 96 public void add(int index,Object obj){ 97 Node temp = node(index); 98 99 Node newNode = new Node(); 100 newNode.setObj(obj); 101 102 if(temp!=null){ 103 Node up = temp.getPrevious(); 104 up.setNext(newNode); 105 newNode.setPrevious(up); 106 107 newNode.setNext(temp); 108 temp.setPrevious(newNode); 109 110 size++; 111 } 112 } 113 114 115 116 117 118 public static void main(String[] args) { 119 MyLinkedList list = new MyLinkedList(); 120 list.add("aaa"); 121 list.add("bbb"); 122 // list.add(1,"BBBB"); 123 list.add("ccc"); 124 list.add("ddd"); 125 list.add("eee"); 126 // list.remove(1); 127 System.out.println(list.get(3)); 128 } 129 130 131 }
Set
• Set
• 特点:无序 唯一(不重复)
• HashSet(底层是HashMap)
• 采用HashMap哈希表存储结构(神奇的结构)
• 优点:添加速度快 查询速度快 删除速度快
• 缺点:无序
• LinkedHashSet
• 采用哈希表存储结构,同时使用链表维护次序
• 有序(添加顺序)
• TreeSet
• 采用二叉树(红黑树)的存储结构
• 优点:有序 查询速度比List快(按照内容查询)
• 缺点:查询速度没有HashSet快
• Set常用方法
• Set相对Collection没有增加任何方法
• Set的遍历方法
• for-each
• Iterator迭代器
• 无法使用for进行遍历(因为无序,所以没有get(i))
• HashSet、HashMap或Hashtable中对象唯一性判断
• 重写(一般使用idea生成重写代码即可)其hashCode()和equals()方法
• Java中规定,两个内容相等的对象,应该具有相等的hashCode,反之,hashCode相同,内容不一定相同
- 比较对象是先在数组中找到hashCode对应的那个链表,然后在遍历链表执行equals,所以两个内容相等的对象,应该具有相等的hashCode,hashCode相同,内容不一定相同
• TreeSet中指明排序依据
• 实现Comparable接口
• 创建实现Compator接口的类。

1 public class MyHashSet { 2 3 HashMap map; 4 private static final Object PRESENT = new Object(); 5 6 public MyHashSet(){ 7 map = new HashMap(); 8 } 9 10 public int size(){ 11 return map.size(); 12 } 13 14 public void add(Object o){ 15 map.put(o, PRESENT); 16 } 17 18 public static void main(String[] args) { 19 MyHashSet s = new MyHashSet(); 20 s.add("aaa"); 21 s.add(new String("aaa")); 22 System.out.println(s.size()); 23 } 24 25 }
Map
• Map(底层实现:数据+链表)
• 特点 key-value映射
• HashMap(线程不安全,效率高)Hashtable(线程安全,效率低,其他的和HashMap一样)
• Key无序 唯一 (Set)
• Value 无序 不唯一 (Collection)
• LinkedHashMap
• 有序的HashMap 速度快
• TreeMap
• 有序 速度没有hash快
• 问题:Set和Map有关系吗?
• 采用了相同的数据结构,只用于map的key存储数据,就是Set

1 /** 2 * 1. 提高查询的效率 3 * 2. Map底层:数组 + 链表 4 */ 5 public class MyMap { 6 7 LinkedList[] arr = new LinkedList[9]; //Map的底层结构就是:数组+链表! 8 int size; 9 10 public void put(Object key,Object value){ 11 MyEntry e = new MyEntry(key,value); 12 // 每个对象在内存中都有一个地址,hashCode是根据对象的内存地址生成的序列码 13 int hash = key.hashCode(); 14 hash = hash<0?-hash:hash; 15 16 int a = hash%arr.length; 17 if(arr[a]==null){ 18 LinkedList list = new LinkedList(); 19 arr[a] = list; 20 list.add(e); 21 }else{ 22 LinkedList list = arr[a]; 23 for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){ 24 MyEntry e2 = (MyEntry) list.get(i); 25 if(e2.key.equals(key)){ 26 e2.value = value; //键值重复直接覆盖! 27 return; 28 } 29 } 30 31 arr[a].add(e); 32 } 33 //a:1000-->1 b:10000-->13 34 } 35 36 public Object get(Object key){ 37 int a = key.hashCode()%arr.length; 38 if(arr[a]!=null){ 39 LinkedList list = arr[a]; 40 for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){ 41 MyEntry e = (MyEntry) list.get(i); 42 if(e.key.equals(key)){ 43 return e.value; 44 } 45 } 46 } 47 48 return null; 49 } 50 51 public static void main(String[] args) { 52 MyMap m = new MyMap(); 53 m.put("高琪", new Wife("杨幂")); 54 m.put("高琪", new Wife("李四")); 55 Wife w = (Wife) m.get("高琪"); 56 System.out.println(w.name); 57 } 58 59 } 60 61 class MyEntry { 62 Object key; 63 Object value; 64 65 public MyEntry(Object key, Object value) { 66 super(); 67 this.key = key; 68 this.value = value; 69 } 70 }
Iterator
• 所有集合类均未提供相应的遍历方法,而是把把遍历交给迭代器完成。迭代器为集合而生,专门实现集合遍历
• Iterator是迭代器设计模式的具体实现
• Iterator方法
• boolean hasNext(): 判断是否存在另一个可访问的元素
• Object next(): 返回要访问的下一个元素
• void remove(): 删除上次访问返回的对象。
• 问题:可以使用Iterator遍历的本质是什么
• 实现Iterable接口
• For-each循环
• 增强的for循环,遍历array 或 Collection的时候相当简便
• 无需获得集合和数组长度,无需使用索引访问元素,无需循环条件
• 遍历集合时底层调用Iterator完成操作
• For-each缺陷:
• 数组:
• 不能方便的访问下标值
• 不要在for-each中尝试对变量赋值,只是一个临时变量
• 集合:
• 与使用Iterator相比,不能方便的删除集合中的内容
• For-each总结:
• 除了简单遍历并读出其中的内容外,不建议使用增强for
• ListIterator和Iterator的关系
• public interface ListIterator<E> extends Iterator<E>
• 都可以遍历List
• ListIterator和Iterator的区别
• 使用范围不同
• Iterator可以应用于更多的集合,Set、List和这些集合的子类型。
• 而ListIterator只能用于List及其子类型。
• 遍历顺序不同
• Iterator只能顺序向后遍历; ListIterator还可以逆序向前遍历
• Iterator可以在遍历的过程中remove();ListIterator可以在遍历的过程中remove()、add()、set()
• ListIterator可以定位当前的索引位置,nextIndex()和previousIndex()可以实现。Iterator没有此功能。
泛型
• 起因:
• JDK1.4以前类型不明确:
• 装入集合的类型都被当作Object对待,从而失去自己的实际类型。
• 从集合中取出时往往需要转型,效率低,容易产生错误(转型的类型可能不是你存入的类型)。
• 解决办法:
• 泛型,在定义集合的时候同时定义集合中对象的类型
• 好处:
• 增强程序的可读性和安全性,在编译的时候就进行了类型检查
注意(数组没有泛型):
泛型类: 修饰词 Class 类名<字母> {}
• 在接口中泛型字母只能使用在方法中,不能用于全局常量
• 泛型只能使用引用类型,不能使用基本数据类型
• 泛型只能访问对象信息,不能修改对象信息(因为泛型的类型没有定)
• 泛型声明时不能使用在静态属性和静态方法上(泛型是在使用的时候确定类型,静态属性,静态方法等是在编译的时候确定类型)
• 泛型使用字母的含义
T Type 表示类型
K V分别表示键值中的Key Value
E 代表Element
? 不确定类型
泛型方法:修饰词 static <字母> 方法名(字母){}
排序容器
1. TreeSet : 确保元素实体可以排序
注意:TreeSet在添加数据时排序,添加完成后,更改TreeSet中元素的数据不会更改原来的顺序,在使用过程中不要修改数据,否则可能重复,如果要达到不能修改数据的要求,则在元素的属性上加final
1)Set接口对比:
HashSet不可以排序,存放在HashSet中的元素必须重写hashCode和equals方法
TreeSet不需要重写hashCode和equals方法,因为在排序的过程中无非就是正数、负数、零,当等于零的时候就表示相等,就可以去重了
2)确保元素可以排序,实现java.lang.Comparable,重写compareTo
new TreeSet();
3)提供元素比较器(排序业务类)实现java.util.Comparator,重写compare
new TreeSet(Comparator<? super E> comparator);

1 public class Person { 2 private final String name;//名称 3 private final int handsome;//帅气指数 4 5 public Person() { 6 name =null; 7 handsome =0; 8 } 9 10 public Person(String name, int handsome) { 11 super(); 12 this.name = name; 13 this.handsome = handsome; 14 } 15 16 public String getName() { 17 return name; 18 } 19 20 public int getHandsome() { 21 return handsome; 22 } 23 24 @Override 25 public String toString() { 26 return "姓名:"+this.name+",帅气指数:"+this.handsome+"\n"; 27 } 28 } 29 30 /** 31 * 提供了 解耦的方式:业务排序类 32 * @author Administrator 33 * 34 */ 35 public class TreeSetDemo { 36 37 /** 38 * @param args 39 */ 40 public static void main(String[] args) { 41 Person p1 =new Person("您",100); 42 Person p2 =new Person("刘德华",1000); 43 Person p3 =new Person("梁朝伟",1200); 44 Person p4 =new Person("老裴",50); 45 46 //依次存放到TreeSet容器中,使用排序的业务类(匿名内部类) 47 TreeSet<Person> persons =new TreeSet<Person>( 48 new java.util.Comparator<Person>(){ 49 50 @Override 51 public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) { 52 return -(o1.getHandsome()-o2.getHandsome()); 53 } 54 55 } 56 ); 57 persons.add(p1); 58 //TreeSet 在添加数据时排序 59 persons.add(p2); 60 persons.add(p3); 61 persons.add(p4); 62 63 System.out.println(persons); 64 65 /* 66 //改变数据 67 p4.setHandsome(100); 68 p4.setName("您"); 69 */ 70 //p4 与p1 内容重复 71 System.out.println(persons); 72 } 73 } 74 75 76 public class Worker implements java.lang.Comparable<Worker> { 77 //工种 78 private String type; 79 //工资 80 private double salary; 81 public Worker() { 82 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 83 } 84 85 86 public Worker(String type, double salary) { 87 super(); 88 this.type = type; 89 this.salary = salary; 90 } 91 92 93 public String getType() { 94 return type; 95 } 96 public void setType(String type) { 97 this.type = type; 98 } 99 public double getSalary() { 100 return salary; 101 } 102 public void setSalary(double salary) { 103 this.salary = salary; 104 } 105 106 /** 107 * 按工资升序 108 */ 109 @Override 110 public int compareTo(Worker o) { 111 return this.salary>o.salary?1:( this.salary==o.salary?0:-1); 112 } 113 114 @Override 115 public String toString() { 116 return "工种:"+this.type+",工资:"+this.salary+"\n"; 117 } 118 119 } 120 121 /** 122 * 实体类实现Comparable 接口的应用 123 * @author Administrator 124 * 125 */ 126 public class TreeSetDemo2 { 127 128 /** 129 * @param args 130 */ 131 public static void main(String[] args) { 132 Worker w1 =new Worker("垃圾回收员",12000); 133 Worker w2 =new Worker("农民工",8000); 134 Worker w3 =new Worker("程序猿",5000); 135 136 TreeSet<Worker> employees =new TreeSet<Worker>(); 137 employees.add(w1); 138 employees.add(w2); 139 employees.add(w3); 140 System.out.println(employees); 141 142 } 143 144 }
2. TreeMap : 确保key可以排序或者提供比较器
1)确保key可以排序,实现java.lang.Comparable,重写compareTo
new TreeMap();
2)提供key比较器(排序业务类)实现java.util.Comparator,重写compare
new TreeMap(Comparator<? super E> comparator);

1 public class Person { 2 private final String name;//名称 3 private final int handsome;//帅气指数 4 5 public Person() { 6 name =null; 7 handsome =0; 8 } 9 10 public Person(String name, int handsome) { 11 super(); 12 this.name = name; 13 this.handsome = handsome; 14 } 15 16 public String getName() { 17 return name; 18 } 19 20 public int getHandsome() { 21 return handsome; 22 } 23 24 @Override 25 public String toString() { 26 return "姓名:"+this.name+",帅气指数:"+this.handsome+"\n"; 27 } 28 29 } 30 31 /** 32 * 提供了 解耦的方式:业务排序类 33 * @author Administrator 34 * 35 */ 36 public class TreeMapDemo { 37 38 /** 39 * @param args 40 */ 41 public static void main(String[] args) { 42 Person p1 =new Person("您",100); 43 Person p2 =new Person("刘德华",1000); 44 Person p3 =new Person("梁朝伟",1200); 45 Person p4 =new Person("老裴",50); 46 47 TreeMap<Person,String> map =new TreeMap<Person,String>(new java.util.Comparator<Person>(){ 48 49 @Override 50 public int compare(Person o1, Person o2) { 51 return -(o1.getHandsome()-o2.getHandsome()); 52 } 53 54 } ); 55 map.put(p1, "bjsxt"); 56 map.put(p2, "bjsxt"); 57 map.put(p3, "bjsxt"); 58 map.put(p4, "bjsxt"); 59 60 //查看键 61 Set<Person> persons =map.keySet(); 62 System.out.println(persons); 63 } 64 } 65 66 public class Worker implements java.lang.Comparable<Worker> { 67 //工种 68 private String type; 69 //工资 70 private double salary; 71 public Worker() { 72 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 73 } 74 75 76 public Worker(String type, double salary) { 77 super(); 78 this.type = type; 79 this.salary = salary; 80 } 81 82 83 public String getType() { 84 return type; 85 } 86 public void setType(String type) { 87 this.type = type; 88 } 89 public double getSalary() { 90 return salary; 91 } 92 public void setSalary(double salary) { 93 this.salary = salary; 94 } 95 96 /** 97 * 按工资升序 98 */ 99 @Override 100 public int compareTo(Worker o) { 101 return this.salary>o.salary?1:( this.salary==o.salary?0:-1); 102 } 103 104 @Override 105 public String toString() { 106 return "工种:"+this.type+",工资:"+this.salary+"\n"; 107 } 108 109 } 110 111 /** 112 * 实体类实现Comparable 接口的应用 113 * @author Administrator 114 * 115 */ 116 public class TreeMapDemo02 { 117 118 /** 119 * @param args 120 */ 121 public static void main(String[] args) { 122 Worker w1 =new Worker("垃圾回收员",12000); 123 Worker w2 =new Worker("农民工",8000); 124 Worker w3 =new Worker("程序猿",5000); 125 126 TreeMap<Worker,String > employees =new TreeMap<Worker,String >(); 127 employees.put(w1,"bjsxt"); 128 employees.put(w2,"bjsxt"); 129 employees.put(w3,"bjsxt"); 130 System.out.println(employees.keySet()); 131 } 132 133 }
java.util接口 Queue<E>
public interface Queue<E>extends Collection<E>
Queue:单向
队列通常 FIFO(先进先出)
优先级队列和堆栈LIFO(后进先出)
| 抛出异常 | 返回特殊值 | |
| 插入 | add(e) |
offer(e) |
| 移除 | remove() |
poll() |
| 检查 | element() |
peek() |
Deque:双向(两端访问)
deque 是“double ended queue(双端队列)”的缩写,是一种具有队列和栈的性质的数据结构,双端队列中的元素可以从两端弹出,其限定插入和删除操作在表的两端进行。
此接口扩展了Queue接口,在将双端队列用作队列时,将得到FIFO行为
可用作LIFO堆栈
| 第一个元素(头部) | 最后一个元素(尾部) | |||
| 抛出异常 | 特殊值 | 抛出异常 | 特殊值 | |
| 插入 | addFirst(e) |
offerFirst(e) |
addLast(e) |
offerLast(e) |
| 移除 | removeFirst() |
pollFirst() |
removeLast() |
pollLast() |
| 检查 | getFirst() |
peekFirst() |
getLast() |
peekLast() |
Enumeration
枚举Enumeration(线程安全的)作用和Iterator类似,都是输出数据(这个接口比较古老,被Iterator取代)
方法:hasMoreElements() nextElement()
Vector的elements()返回的就是Enumeration

1 /** 2 * Enumeration 的使用 3 * 1、判断 hasMoreElements() 4 * 2、获取 nextElement() 5 * 6 * Vector 的 elements()方法 7 * 8 * 9 * @author Administrator 10 * 11 */ 12 public class Demo01 { 13 14 /** 15 * @param args 16 */ 17 public static void main(String[] args) { 18 Vector<String> vector =new Vector<String>(); 19 vector.add("javase"); 20 vector.add("html"); 21 vector.add("oracle"); 22 23 //遍历该Vector 24 Enumeration<String> en =vector.elements(); 25 while(en.hasMoreElements()){ 26 System.out.println(en.nextElement()); 27 } 28 } 29 }
Enumeration的子类StringTokenizer等同于String split() 字符串分割,但是不支持正则表达式StringTokenizer(String str, String delim)

1 /** 2 * Enumeration 子类 3 * StringTokenizer:String split() 字符串分割 4 * 不支持正则表达式 5 * 6 * StringTokenizer(String str, String delim) 7 8 * @author Administrator 9 * 10 */ 11 public class Demo02 { 12 13 /** 14 * @param args 15 */ 16 public static void main(String[] args) { 17 String emailStr="bjq@163.com;bjq@qq.com;bjq@sohu.com"; 18 StringTokenizer token =new StringTokenizer(emailStr,";"); 19 //遍历获取 20 while(token.hasMoreElements()){ 21 System.out.println(token.nextElement()); 22 } 23 } 24 25 }
其它集合类
WeakHashMap
键为弱引用,回收键后自动删除key-value对象
IdentityHashMap
键只以地址去重,而不是比较hashCode与equals
注意:键是常量池中的字符串
EnumMap
键必须为枚举的值
构造器:public EnumMap (指定枚举类class对象)

1 /** 2 * WeakHashMap 键为弱类型,gc运行立即回收 3 * @author Administrator 4 * 5 */ 6 public class WeakHashMapDemo { 7 8 /** 9 * @param args 10 */ 11 public static void main(String[] args) { 12 WeakHashMap<String,String> map =new WeakHashMap<String,String>(); 13 //测试数据 14 //常量池对象,不会回收 15 map.put("abc", "a"); 16 map.put("d", "test"); 17 //gc运行 已被回收 18 map.put(new String("bjsxt"), "c"); 19 map.put(new String("dsf"), "d"); 20 21 //通知回收 22 System.gc(); 23 System.runFinalization(); 24 25 System.out.println(map.size()); 26 } 27 28 } 29 30 /** 31 * IdentityHashMap 键比较地址去重 32 * @author Administrator 33 * 34 */ 35 public class IdentityHashMapDemo { 36 37 /** 38 * @param args 39 */ 40 public static void main(String[] args) { 41 IdentityHashMap<String ,String> map =new IdentityHashMap<String,String>(); 42 //常量池中的"a" 43 map.put("a", "a1"); 44 map.put("a", "a2"); 45 System.out.println(map.size()); 46 map.put(new String("a"), "a3"); 47 map.put(new String("a"), "a4"); 48 System.out.println(map.size()); 49 50 } 51 52 } 53 54 /** 55 * EnumMap要求键为枚举 56 * @author Administrator 57 * 58 */ 59 public class EnumMapDemo { 60 61 /** 62 * @param args 63 */ 64 public static void main(String[] args) { 65 EnumMap<Season,String> map =new EnumMap<Season,String>(Season.class); 66 //存放值 67 map.put(Season.SPRING, "春困"); 68 map.put(Season.SUMMER, "夏无力"); 69 map.put(Season.AUTUMN, "秋乏"); 70 map.put(Season.WINTER, "冬眠"); 71 72 System.out.println(map.size()); 73 74 } 75 76 } 77 //季节 78 enum Season{ 79 SPRING,SUMMER,AUTUMN,WINTER 80 }
Collections
• 专门用来操作集合的工具类
• 构造方法私有,禁止创建对象
• 提供一系列静态方法实现对各种集合的操作
• 具体操作:搜索、复制、排序、线程安全化等
• 常用方法
• Collections.addAll(list, "aaa","bbb","ccc","ccc");
• int index = Collections.binarySearch(list, "ccc");
• Collections.copy(list2, list);
• Collections.fill(list3, "888");
• String max = Collections.max(list4);
• String min = Collections.min(list4);
• Collections.reverse(list4);
• List list5 = Collections.synchronizedList(list4);
• 同步控制:多线程并发访问集合的线程安全
1. 常用容器ArrayList、HashSet、HashMap等都是线程不安全的
2. Collection提供了synchronizedXxx()方法,将指定容器包装成同步
synchronizedList()
synchronizedSet()
synchronizedMap()

1 /** 2 * 使用Collections管理同步 容器 3 * synchronizedList() 4 synchronizedSet() 5 synchronizedMap() 6 7 * @author Administrator 8 * 9 */ 10 public class Demo01 { 11 12 /** 13 * @param args 14 */ 15 public static void main(String[] args) { 16 List<String> list =new ArrayList<String>(); 17 list.add("a"); 18 list.add("b"); 19 //list可以同步 20 List<String> synList =Collections.synchronizedList(list); 21 System.out.println("线程安全的list制作完毕"); 22 } 23 24 }
• 不可变设置:只读访问,Collection提供了三种方法
1. emptyXxx() 空的不可变集合
2. singletonXxx() 一个元素不可变的集合
3. unmodifiableXxx() 不可变容器

1 /** 2 * 只读设置 3 * 1、emptyXxx() 空的不可变的集合 4 * emptyList() 5 * emptyMap() 6 * emptySet() 7 * 2、singletonXxx() 一个元素不可变的集合 8 * singleton(T o) 9 * singletonList(T o) 10 * singletonMap(K key, V value) 11 * 12 * 3、unmodifiableXxx() 不可变容器 13 * unmodifiableList(List<? extends T> list) 14 * unmodifiableSet(Set<? extends T> s) 15 * unmodifiableMap(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m) 16 * @author Administrator 17 * 18 */ 19 public class Demo02 { 20 21 /** 22 * @param args 23 */ 24 public static void main(String[] args) { 25 Map<String,String> map =new HashMap<String,String>(); 26 27 map.put("test", "test"); 28 map.put("bjsxt", "bjsxt"); 29 30 //只读控制 31 Map<String,String> map2 =Collections.unmodifiableMap(map); 32 //map2.put("a", "a"); //不能操作 33 System.out.println(map2.size()); 34 35 //一个元素的容器测试 36 List<String> list =Collections.singletonList(new String()); 37 list.add("test"); 38 //list.add("bjsxt"); //只能包含一个元素的容器 39 } 40 41 public static Set<String> oper(Set<String> set){ 42 if(null==set){ 43 return Collections.EMPTY_SET; //外部获取避免NullPointerException 44 } 45 //操作 46 return set; 47 } 48 49 }
旧的集合类
• Vector
• 实现原理和ArrayList相同,功能相同,都是长度可变的数组结构,很多情况下可以互用
• 两者的主要区别如下
• Vector是早期JDK接口,ArrayList是替代Vector的新接口
• Vector线程安全,效率低下;ArrayList重速度轻安全,线程非安全
• 长度需增长时,Vector默认增长一倍,ArrayList增长50%
• Hashtable类
• 实现原理和HashMap相同,功能相同,底层都是哈希表结构,查询速度快,很多情况下可互用
• 两者的主要区别如下
• Hashtable是早期JDK提供的接口,HashMap是新版JDK提供的接口
• Hashtable继承Dictionary类,HashMap继承AbstractMap类
• Hashtable线程安全,HashMap线程非安全
• Hashtable键值都不允许null值,HashMap键允许一个null值,值允许有多个null值
• 子类Properties
作用:读写资源配置文件
要求键和值只能为字符串
方法:
setProperty(String key, String value)
getProperty(String key)
getProperty(String key, String defaultValue)
load(InputStream inStream)
store(OutputStream out, String comments)
store(Writer writer, String comments)
storeToXML(OutputStream os, String comment)// 字符集默认UTF-8
storeToXML(OutputStream os, String comment, String encoding)
类路径加载文件
1)类.class.getResourceAsStream("/com/others/pro/db.properties")
2)Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("com/others/pro/db.properties")

1 /** 2 * 使用Properties 输出到文件 3 * 资源配置文件: 4 * 5 * 1、.properties 6 * store(OutputStream out, String comments) 7 store(Writer writer, String comments) 8 2、.xml 9 storeToXML(OutputStream os, String comment) :UTF-8字符集 10 storeToXML(OutputStream os, String comment, String encoding) 11 12 13 * @author Administrator 14 * 15 */ 16 public class Demo01{ 17 18 /** 19 * @param args 20 * @throws IOException 21 * @throws FileNotFoundException 22 */ 23 public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException { 24 //创建对象 25 Properties pro =new Properties(); 26 //存储 27 pro.setProperty("driver", "oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver"); 28 pro.setProperty("url", "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl"); 29 pro.setProperty("user", "scott"); 30 pro.setProperty("pwd", "tiger"); 31 32 //存储到e:/others 绝对路径 盘符: 33 //pro.store(new FileOutputStream(new File("e:/others/db.properties")), "db配置"); 34 //pro.storeToXML(new FileOutputStream(new File("e:/others/db.xml")), "db配置"); 35 //使用相对路径 当前的工程 36 // pro.store(new FileOutputStream(new File("db.properties")), "db配置"); 37 // pro.store(new FileOutputStream(new File("src/db.properties")), "db配置"); 38 pro.store(new FileOutputStream(new File("src/com/bjsxt/others/pro/db.properties")), "db配置"); 39 } 40 41 } 42 43 44 /** 45 * 使用Properties读取配置文件 46 * 资源配置文件: 47 * 使用相对与绝对路径读取 48 * load(InputStream inStream) 49 load(Reader reader) 50 loadFromXML(InputStream in) 51 * @author Administrator 52 * 53 */ 54 public class Demo02 { 55 56 /** 57 * @param args 58 * @throws IOException 59 * @throws FileNotFoundException 60 */ 61 public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException, IOException { 62 Properties pro=new Properties(); 63 //读取 绝对路径 64 //pro.load(new FileReader("e:/others/db.properties")); 65 //读取 相对路径 66 pro.load(new FileReader("src/com/others/pro/db.properties")); 67 System.out.println(pro.getProperty("user", "uuu")); 68 } 69 } 70 71 /** 72 * 使用类相对路径读取配置文件 73 * bin 74 * @author Administrator 75 * 76 */ 77 public class Demo03 { 78 79 /** 80 * @param args 81 * @throws IOException 82 */ 83 public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { 84 Properties pro =new Properties(); 85 //类相对路径的 / bin 86 //pro.load(Demo04.class.getResourceAsStream("/com/others/pro/db.properties")); 87 //"" bin 88 pro.load(Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader() 89 .getResourceAsStream("com/others/pro/db.properties")); 90 System.out.println(pro.getProperty("user", "uuu")); 91 } 92 93 }
新的线程同步集合类
• 早期集合类Vector、Hashtable:线程安全的
• 是怎么保证线程安排的,使用synchronized修饰方法
• 为了提高性能,使用ArrayList、HashMap替换,线程不安全,但是性能好。使用ArrayList、
HashMap,需要线程安全怎么办呢?
• 使用Collections.synchronizedList(list);Collections.synchronizedMap(m);解决
• 底层使用synchronized代码块锁
• 虽然也是锁住了所有的代码,但是锁在方法里边,比锁在方法外边性能可以理解为稍有提高吧。毕竟进方法本身就要分配资源的
• 在大量并发情况下如何提高集合的效率和安全呢?
• 提供了新的线程同步集合类,位于java.util.concurrent包下,使用Lock锁
• ConcurrentHashMap、CopyOnWriteArrayList 、CopyOnWriteArraySet:
• 注意不是CopyOnWriteHashSet
集合总结
• 集合和数组的比较
• 数组不是面向对象的,存在明显的缺陷,集合完全弥补了数组的一些缺点,比数组更灵活更实用,可大大提高软件的开发效率而且不同的集合框架类可适用于不同场合。具体如下:
• 1 : 数组容量固定且无法动态改变,集合类容量动态改变。
• 2:数组能存放基本数据类型和引用数据类型的数据,而集合类中只能放引用数据类型的数据。
• 3:数组无法判断其中实际存有多少元素,length只告诉了array容量;集合可以判断实际存有多少元素,而对总的容量不关心
• 4:集合有多种数据结构(顺序表、链表、哈希表、树等)、多种特征(是否有序,是否唯一)、不同适用场合(查询快,便于删除、有序),不像数组仅采用顺序表方式
• 5:集合以类的形式存在,具有封装、继承、多态等类的特性,通过简单的方法和属性调用即可实现各种复杂操作,大大提高软件的开发效率。
• ArrayList和LinkedList 的联系和区别
• 联系:
• 都实现了List接口
• 有序 不唯一(可重复)
• ArrayList
• 在内存中分配连续的空间,实现了长度可变的数组
• 优点:遍历元素和随机访问元素的效率比较高
• 缺点:添加和删除需大量移动元素效率低,按照内容查询效率低,
• LinkedList
• 采用链表存储方式。
• 缺点:遍历和随机访问元素效率低下
• 优点:插入、删除元素效率比较高(但是前提也是必须先低效率查询才可。如果插入删除发生在头尾可以减少查询次数)
• Vector和ArrayList的联系和区别
• 实现原理相同,功能相同,都是长度可变的数组结构,很多情况下可以互用
• 两者的主要区别如下
• Vector是早期JDK接口,ArrayList是替代Vector的新接口
• Vector线程安全,效率低下;ArrayList重速度轻安全,线程非安全
• 长度需增长时,Vector默认增长一倍,ArrayList增长50%
• HashMap和Hashtable的联系和区别
• 实现原理相同,功能相同,底层都是哈希表结构,查询速度快,在很多情况下可以互用
• 两者的主要区别如下
• Hashtable是早期JDK提供的接口,HashMap是新版JDK提供的接口
• Hashtable继承Dictionary类,HashMap继承AbstractMap类
• Hashtable线程安全,HashMap线程非安全
• Hashtable键值都不允许null值,HashMap键允许一个null值,值允许有多个null值
• Collection和Collections的区别
• Collection是Java提供的集合接口,存储一组不唯一,无序的对象。它有两个子接口List和Set。
• Java中还有一个Collections类,专门用来操作集合类 ,它提供一系列静态方法实现对各种集合的搜索、排序、线程安全化等操作。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号