Flux,Redux,Vuex整理总结
Flux 要点
功能组成:
- View: 视图层
- Action(动作):视图层发出的消息(比如mouseClick)
- Dispatcher(派发器):用来接收Actions、执行回调函数
- Store(数据层):用来存放应用的状态,一旦发生变动,就提醒Views要更新页面
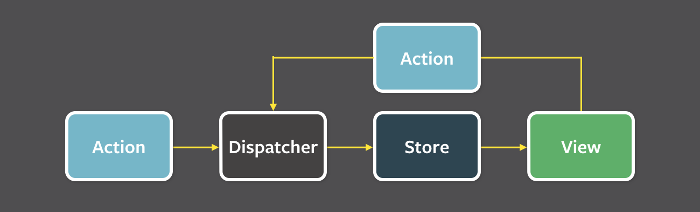
执行流程:
- 用户访问 View
- View 发出用户的 Action
- Dispatcher 收到 Action,要求 Store 进行相应的更新
- Store 更新后,发出一个"change"事件
- View 收到"change"事件后,更新页面
View:
- 确定相应的Store以及监听其变化来更新视图。
- 发起Action。
// Get binding store var ListStore = require('../stores/ListStore'); ..... // Subscribe store change event componentDidMount: function() { ListStore.addChangeListener(this._onChange); } ... // Pass action to Dispatcher createNewItem: function (event) { // There's a dispatcher instance in ButtonActions ButtonActions.addNewItem('new item'); }
Action:
- 每个Action都是一个对象,包含一个actionType属性(说明动作的类型)和一些其他属性(用来传递数据)
Dispatcher:
- 全局唯一。
- 逻辑简单,只用来派发action去相应的store。
- 通过 AppDispatcher.register() 来登记各种Action的回调函数。
// dispatcher/AppDispatcher.js 全局唯一 var Dispatcher = require('flux').Dispatcher; var ListStore = require('../stores/ListStore'); module.exports = new Dispatcher(); ..... //注册action回调函数 AppDispatcher.register(function (action) { switch(action.actionType) { case 'ADD_NEW_ITEM': ListStore.addNewItemHandler(action.text); ListStore.emitChange(); break; default: // no op } }) // actions/ButtonActions.js。dispatch方法只用来分发action var AppDispatcher = require('../dispatcher/AppDispatcher'); var ButtonActions = { addNewItem: function (text) { AppDispatcher.dispatch({ actionType: 'ADD_NEW_ITEM', text: text }); }, };
Store:
- 存放view中的数据。
- 发送change事件,通过view中定义的handler捕捉变化。
var EventEmitter = require('events').EventEmitter; var assign = require('object-assign'); var ListStore = assign({}, EventEmitter.prototype, { // data in View items: [], ....... emitChange: function () { this.emit('change'); }, addChangeListener: function(callback) { this.on('change', callback); } .... });
Redux 要点
Redux vs Flus: Redux = Reducer + Flux
功能组成:
- View
- Action
- Store
- Reducer
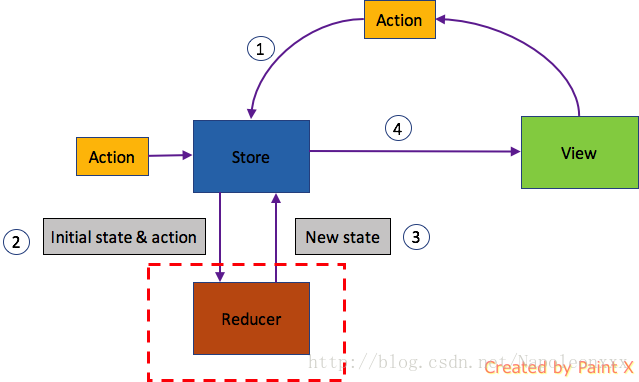
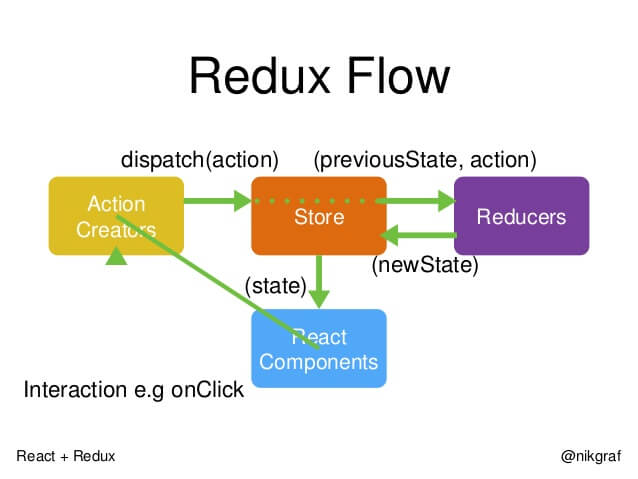
工作流程:
- 首先,用户发出 Action。
- 然后,Store 自动调用 Reducer,并且传入两个参数:当前 State 和收到的 Action。 Reducer 会返回新的 State 。
- State 一旦有变化,Store 就会调用监听函数。
- listener可以通过store.getState()得到当前状态。如果使用的是 React,这时可以触发重新渲染 View。
View:
- 通过全局唯一的store dispatch action 以及获取最新state
注: 通过对比flux的view 部分可以看出在Redux中,view不会关心具体的处理函数,只专注于收发就好。
Store:
- 全局唯一
- 包含整棵state树: state 和 view 是一一对应的关系
- Dispatcher功能已被整合进store:store.dispatch()
- state 一旦有变化,store 就会调用通过store.subscribe()注册的回调函数(一般是render)。
- Reducer的拆分就先不讲了。
const Counter = ({ value, onIncrement, onDecrement }) => (
<div>
<h1>{value}</h1>
<button onClick={onIncrement}>+</button>
<button onClick={onDecrement}>-</button>
</div>
);
const reducer = (state = 0, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'INCREMENT': return state + 1;
case 'DECREMENT': return state - 1;
default: return state;
}
};
const store = createStore(reducer);
const render = () => {
ReactDOM.render(
<Counter
value={store.getState()}
onIncrement={() => store.dispatch({type: 'INCREMENT'})}
onDecrement={() => store.dispatch({type: 'DECREMENT'})}
/>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
};
render();
store.subscribe(render);
Action:
- 普通对象,作用与Flux中相同
const action = { type: 'ADD_TODO', //必填字段 payload: 'Learn Redux' };
Reducer:
- reducer是current stae 和 action 为参数计算new state的纯函数。
- 纯函数无副作用:不能调用系统 I/O 的API,不能调用Date.now()或者Math.random()等不纯的方法,因为每次会得到不一样的结果 blabla…
const defaultState = 0; const reducer = (state = defaultState, action) => { switch (action.type) { case 'ADD': return state + action.payload; default: return state; } }; const state = reducer(1, { type: 'ADD', payload: 2 }); // Reducer 是纯函数,就可以保证同样的State,必定得到同样的 View。 // 但也正因为这一点,Reducer 函数里面不能改变 State,必须返回一个全新的对象,请参考下面的写法。 function reducer(state, action) { return Object.assign({}, state, { thingToChange }); // Or return { ...state, ...newState }; } // State 是一个数组 function reducer(state, action) { return [...state, newItem]; }
Vuex 要点
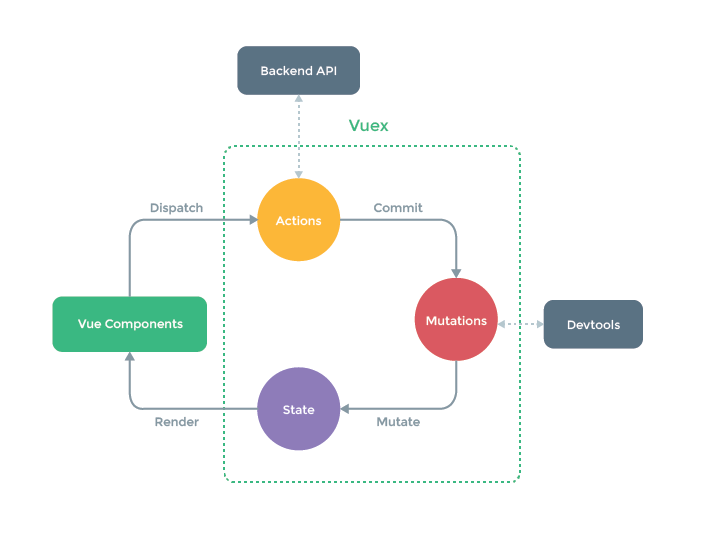
Redux vs Vuex:
- 使用mutation来替换redux中的reducer
- Vuex有自动渲染的功能,所以无需要专门监听state。(this.$store.getters.doneTodosCount)
- Vuex中的action是一个函数集合对象,用于async/sync commit mutaions. 和Redux或者Flux中的action只是简单对象有本质不同,只是叫了一个相同名字。
参考:
http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/01/flux.html
http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/09/redux_tutorial_part_one_basic_usages.html
https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/
https://blog.csdn.net/Napoleonxxx/article/details/79305575



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号