结构体
C 结构体
C 数组允许定义可存储相同类型数据项的变量,结构是 C 编程中另一种用户自定义的可用的数据类型,它允许您存储不同类型的数据项。
结构用于表示一条记录,假设您想要跟踪图书馆中书本的动态,您可能需要跟踪每本书的下列属性:
- Title
- Author
- Subject
- Book ID
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
// 结构体,相当于Java中的Class
struct Books
{
// Books的属性
char title[ 50 ];
char author[ 50 ];
char subject[ 100 ];
int bookId;
};
int main()
{
// 声明结构体
struct Books Book1;
struct Books Book2;
/* 定义结构体 */
// Book1
strcpy(Book1.title, "C Programming");
strcpy(Book1.author, "Nuha Ali");
strcpy(Book1.subject, "C Programming Tutorial");
Book1.bookId = 6379;
// Book2
strcpy(Book2.title, "Telecom Billing");
strcpy(Book2.author, "Zara Ali");
strcpy(Book2.subject, "Telecom Billing Tutorial");
Book2.bookId = 6380;
// 输出Book1和Book2的信息
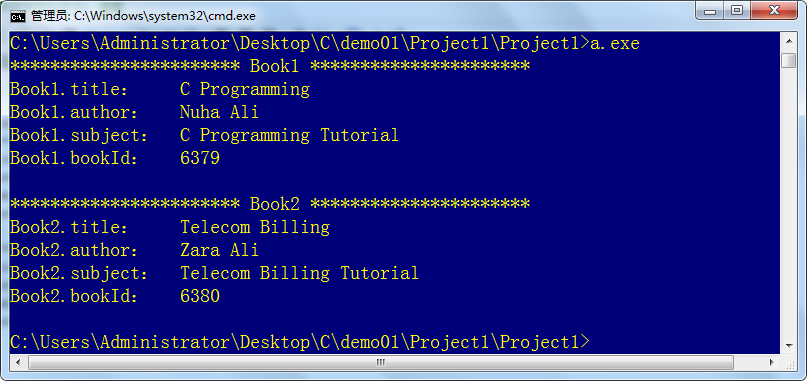
printf("*********************** Book1 **********************\n");
printf("Book1.title:\t %s \n", Book1.title);
printf("Book1.author:\t %s \n", Book1.author);
printf("Book1.subject:\t %s \n", Book1.subject);
printf("Book1.bookId:\t %d \n\n", Book1.bookId);
printf("*********************** Book2 **********************\n");
printf("Book2.title:\t %s \n", Book2.title);
printf("Book2.author:\t %s \n", Book2.author);
printf("Book2.subject:\t %s \n", Book2.subject);
printf("Book2.bookId:\t %d \n", Book2.bookId);
// 结束main函数
return 0;
}
结构作为函数参数
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
// 结构体,相当于Java中的Class
struct Books
{
// Books的属性
char title[ 50 ];
char author[ 50 ];
char subject[ 100 ];
int bookId;
};
// 函数声明:结构体入参
void printBook(struct Books book);
int main()
{
// 声明结构体
struct Books Book1;
struct Books Book2;
/* 定义结构体 */
// Book1
strcpy(Book1.title, "C Programming");
strcpy(Book1.author, "Nuha Ali");
strcpy(Book1.subject, "C Programming Tutorial");
Book1.bookId = 6379;
// Book2
strcpy(Book2.title, "Telecom Billing");
strcpy(Book2.author, "Zara Ali");
strcpy(Book2.subject, "Telecom Billing Tutorial");
Book2.bookId = 6380;
// 输出Book1和Book2的信息
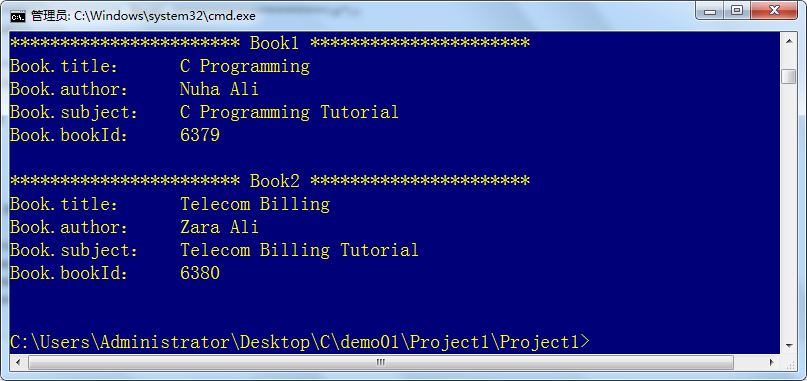
printf("*********************** Book1 **********************\n");
printBook(Book1);
printf("*********************** Book2 **********************\n");
printBook(Book2);
// 结束main函数
return 0;
}
// 函数定义
void printBook(struct Books book)
{
printf("Book.title:\t %s \n", book.title);
printf("Book.author:\t %s \n", book.author);
printf("Book.subject:\t %s \n", book.subject);
printf("Book.bookId:\t %d \n\n", book.bookId);
}

指向结构的指针
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
// 结构体,相当于Java中的Class
struct Books
{
// Books的属性
char title[ 50 ];
char author[ 50 ];
char subject[ 100 ];
int bookId;
};
// 函数声明:结构体指针形式入参
void printBook(struct Books *book);
int main()
{
// 声明结构体
struct Books Book1;
struct Books Book2;
/* 定义结构体 */
// Book1
strcpy(Book1.title, "C Programming");
strcpy(Book1.author, "Nuha Ali");
strcpy(Book1.subject, "C Programming Tutorial");
Book1.bookId = 6379;
// Book2
strcpy(Book2.title, "Telecom Billing");
strcpy(Book2.author, "Zara Ali");
strcpy(Book2.subject, "Telecom Billing Tutorial");
Book2.bookId = 6380;
// 输出Book1和Book2的信息
printf("*********************** Book1 **********************\n");
printBook(&Book1);
printf("*********************** Book2 **********************\n");
printBook(&Book2);
// 结束main函数
return 0;
}
// 函数定义
void printBook(struct Books *book)
{
printf("Book.title:\t %s \n", book->title);
printf("Book.author:\t %s \n", book->author);
printf("Book.subject:\t %s \n", book->subject);
printf("Book.bookId:\t %d \n\n", book->bookId);
}







 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号