Tensorflow学习报告
张量
import tensorflow as tf
#创建常量
rank_0_tensor = tf.constant(4)
print(rank_0_tensor)
#创建一阶张量(向量)
rank_1_tensor = tf.constant([2.0, 3.0, 4.0])
print(rank_1_tensor)
#创建二阶张量(向量)
rank_2_tensor = tf.constant([[1, 2],
[3, 4],
[5, 6]], dtype=tf.float16)
print(rank_2_tensor)
#创建三阶张量(向量)
rank_3_tensor = tf.constant([
[[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8, 9]],
[[10, 11, 12, 13, 14],
[15, 16, 17, 18, 19]],
[[20, 21, 22, 23, 24],
[25, 26, 27, 28, 29]],])
print(rank_3_tensor)
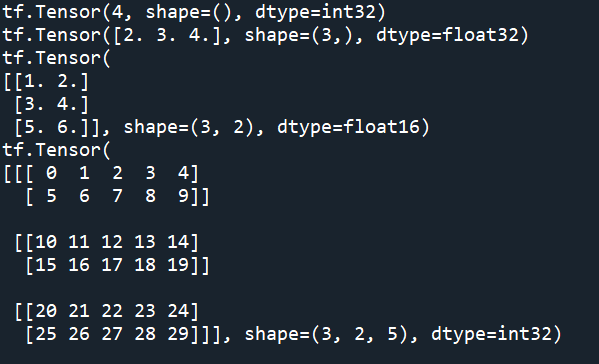
张亮运算
a = tf.constant([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) b = tf.constant([[1, 1], [1, 1]]) print(tf.add(a, b), "\n") #加法 print(tf.multiply(a, b), "\n") #逐元素乘法 print(tf.matmul(a, b), "\n") #矩阵乘法
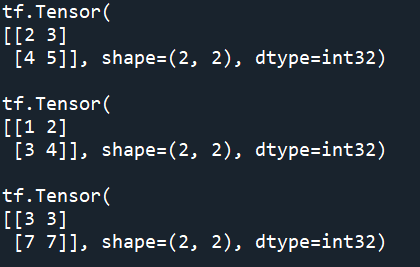
形状操作
tf.shape([[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]], [[3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4]]],name=None) #返回数据的shape tf.Tensor([2 2 3], shape=(3,), dtype=int32) tf.size([[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]], [[3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4]]], name=None) #返回数据的元素数量 tf.Tensor(12, shape=(), dtype=int32) tf.rank([[[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 2]], [[3, 3, 3], [4, 4, 4]]],name=None) #返回tensor的rank tf.Tensor(3, shape=(), dtype=int32)
低阶API实现线性回归
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt input_x=np.float32(np.linspace(-1,1,100))#在区间[-1,1)内产生100个数的等差数列,作为输入 input_y=2*input_x+np.random.randn(*input_x.shape)*0.3#y=2x+随机噪声 weight=tf.Variable(1.,dtype=tf.float32,name='weight') bias=tf.Variable(1.,dtype=tf.float32,name='bias') def model(x): #定义了线性模型y=weight*x+bias pred=tf.multiply(x, weight)+bias return pred step=0 opt=tf.optimizers.Adam(1e-1) #选择优化器,是一种梯度下降的方法 for x,y in zip(input_x,input_y): x=np.reshape(x,[1]) y=np.reshape(y,[1]) step=step+1 with tf.GradientTape()as tape: loss=tf.losses.MeanSquaredError()(model(x),y)#连续数据的预测,损失函数用MSE grads=tape.gradient(loss,[weight,bias])#计算梯度 opt.apply_gradients(zip(grads,[weight,bias]))#更新参数weight和bias print("Step:",step,"Traing Loss:",loss.numpy()) #用Matplotlib可视化原始数据和预测的模型 plt.plot(input_x,input_y,'ro',label='original data') plt.plot(input_x, model(input_x),label='predicted value') plt.plot(input_x,2*input_x,label='y=2x') plt.legend() plt.show() print(weight) print(bias)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号