typeof的使用技巧
typeof 对于基本类型,除了 null 都可以显示正确的类型
<template>
<section class="p-10">
<el-button type="danger" @click="get()">点击</el-button>
</section>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
get() {
console.log(typeof '666'); // string
console.log(typeof 66); // number
console.log(typeof true); // boolean
console.log(Symbol()); // Symbol()
console.log(typeof undefined); // undefined
console.log(typeof b); // undefined (没有声明,但是还是会显示undefined)
}
}
};
</script>

typeof 对于对象,除了函数都会显示 object
<template>
<section class="p-10">
<el-button type="danger" @click="get()">点击</el-button>
</section>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
get() {
console.log(typeof {key: 1}); // object
console.log(typeof null); // object
console.log(typeof []); // object
console.log(typeof function () { // function
});
}
}
};
</script>
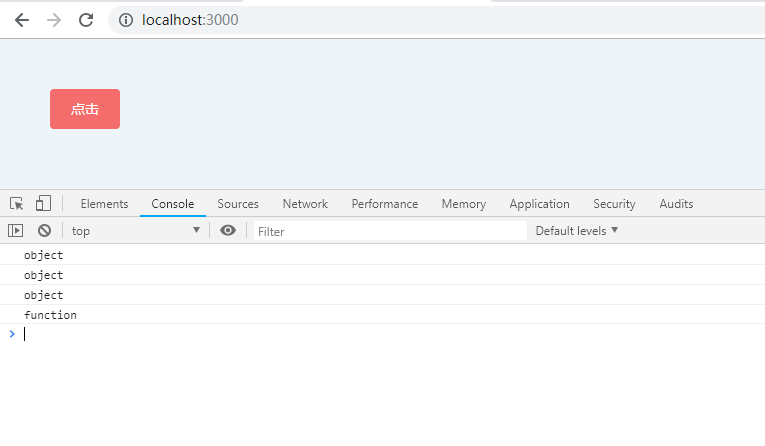
对于 null 来说,虽然它是基本类型,但是会显示 object ,这是一个存在很久了的 Bug
PS:为什么会出现这种情况呢?因为在 JS 的最初版本中,使用的是 32 位系统,为了性能考虑使用低位存储了变量的类型信息,000 开头代表是对象,然而 null 表示为全零,所以将它错误的判断为 object 。虽然现在的内部类型判断代码已经改变了,但是对于这个 Bug 却是一直流传下来。
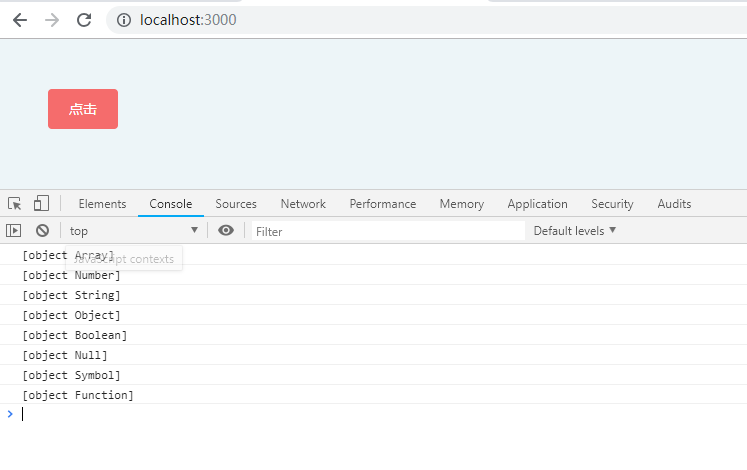
如果我们想获得一个变量的正确类型,可以通过 Object.prototype.toString.call(xx) 。这样我们就可以获得类似 [object Type] 的字符串。
<template>
<section class="p-10">
<el-button type="danger" @click="get()">点击</el-button>
</section>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
get() {
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call([1]));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(1));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call('1'));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call({}));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(true));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(null));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(Symbol()));
console.log(Object.prototype.toString.call(function () {
}));
}
}
};
</script>
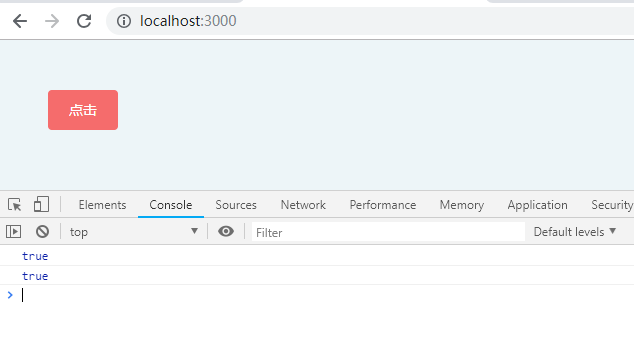
判断Array的的时候,我们可以使用 instanceof 来判断,但是这里还要区别 object
<template>
<section class="p-10">
<el-button type="danger" @click="get()">点击</el-button>
</section>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
get() {
let a = [1,2];
console.log(a instanceof Array);
console.log(a instanceof Object);
}
}
};
</script>
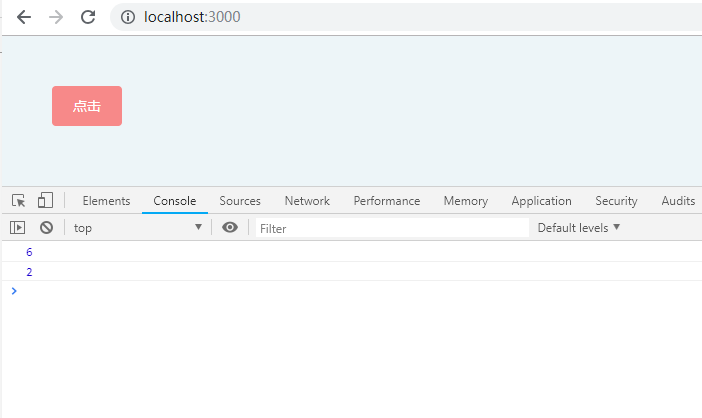
判断undefined的时候,有时候我们需要留意一下,undefined 不是保留字,能够在低版本浏览器被赋值,这样判断就会出错
<template>
<section class="p-10">
<el-button type="danger" @click="get()">点击</el-button>
</section>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
get() {
let a;
if (a === undefined) {
console.log(6);
}
let undefined = 2;
console.log(undefined);
if (a === undefined) {
console.log(66);
}
}
}
};
</script>
所以可以用下面的方式来判断,并且代码量更少,因为 void 后面随便跟上一个组成表达式,返回就是 undefined
<template>
<section class="p-10">
<el-button type="danger" @click="get()">点击</el-button>
</section>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
get() {
let a;
if (a === void 0) {
console.log(66);
}
}
}
};
</script>

嗯,就酱~
https://www.cnblogs.com/chuhui/archive/2018/12/03/10060071.html



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号